Clinical Skills
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What are the 2 C’s to remember before ANY examination?
CLEAN and CONSENT
What does the CLEAN step entail before any examination?
Ensure hands are clean, gel hands before and after touching a patient and use gloves near bodily fluids
What does the CONSENT step entail before any examination?
ALWAYS get permission before touching a patient
What does the acronym STTSH mean?
See, touch, taste, smell, hear
How should you use a stethoscope?
Turn it on!
Use diaphragm (flat face) for most uses
Use bell for low frequencies
Used to auscultate respiratory and heart sounds
What is the name for a blood pressure monitor?
Sphygmomanometer
What is blood pressure?
Measure of the pressure that the circulating blood exerts against the arterial walls: cardiac output x peripheral vascular resistance
What is the examination sequence for a manual BP check?
rest patient for 5 minutes
Measure BP in both arms
Support arm comfortably at heart level and have no tight clothing constricting the upper arm
Apply cuff to upper arm
Palpate the brachial pulse or radial
inflate cuff until pulse is impalpable and inflate another 30mmHg
Slowly reduce pressure 2-3mmHgs until you hear the first Korotkoff sound and record toe reading - systolic
Continue to deflate until the sound disappears - record diastolic when sounds completely disappear
How many readings can you take of BP in one arm in 30 minutes?
2
How do you use a tympanic digital thermometer?
Do NOT touch the probe cover when putting on or discarding
Turn machine on
Check no discharges
Pull up pinna and take reading from external auditory meatus
What is a pulse?
Ejection of blood from the left ventricle into the systemic arterial circulation creates a pressure wave - travels faster than blood flow
What is the radial pulse?
At radial bone side of the wrist
What is the brachial artery?
Inner side of the biceps
Where is the carotid artery?
On the side of the neck between larynx and anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
Where is the femoral artery?
In the groin
Where is the posterior tibial artery?
Behind the inner ankle
Where is the dorsalis pedis artery?
Best felt in groove between 1st and 2nd metatarsals - can be absent or abnormally sited in 10% of subjects
What is a resting heart rate usually between?
60-90bpm
What is a bradycardia heart rate usually?
< 60bpm
What is a tachycardia bpm usually?
>100bpm
What can irregular rhythm of the heart be due to?
Ectopic beat or atrial fibrillation
What is a large pulse volume due to?
Reflection of large pulse pressure - physiological or pathological
What can a low pulse volume be due to?
Reduced stroke volume
What can be used to assess pulse character and volume?
Larger pulses - brachial, carotid, femoral
What is the character of the pulse?
Waveform or shape of arterial pulse
What does a pulse oximeter measure?
Arterial oxygen saturation by determining proportion of haemloglobin that is oxygenated
What is urinalysis used for?
Screening e.g., random for diabetes or for selective hypertensive patients, diagnosing UTIs, monitoring drug compliance e.g., rifampicin
What are the different markers for urinalysis?
Blood, Leukocytes, Nitrite, Specific gravity, glucose, protein, ketones and pH
What observations should you make when completing urinalysis?
Wear gloves, observe if fresh/warm, labelled, is it definitely urine, observe colour, cloudiness, blood and always discard in clinical bins
What does the presence of leukocytes mean in urinalysis?
infection or inflammation, usually in UTIs - normal result is negative
What does presence of nitrites mean in urinalysis?
Indicates bacterial infection and supports UTI diagnosis - should be negative
What does specific gravity mean in urinalysis?
Conc of solutes in urine and reflects hydration and kidney function - should be 1.005-1.030
What does a high specific gravity mean?
Dehydration, proteinuria, glycosuria
What does a low specific gravity?
Overhydration, impaired kidney concentrating ability
What does glucose in the urine inidcate?
Diabetes, can be pregnancy or kidney tubule disorders - usual result is negative
What does protein in the urine indicate?
Kidney damage, hypertension or diabetes - should be negative
What can ketones indicate in the urine?
Diabetes ketoacidosis - should be negative
What should the usual pH range be in urine?
4.5-8 - can be influenced by other factors
What is BMI a measure of?
An individuals height and weight to calculate if their weight is healthy
What does BMI take into consideration?
Variations in body shape and provides a healthy weight range
How do you calculate BMI?
Weight/Height x height
What equipment do you need to take someones blood glucose?
Gloves, glucose meter, test strips, single use lancet and cotton swab
How do you complete a capillary blood glucose measurement?
Introduce yourself, explain the procedure and obtain consent
Clean your hands and put on gloves
Clean patient’s fingertip and allow to dry
Insert the test strip into the glucose meter after checking it is in
datePrick the side of the patient’s finger with the lancet (no lower than
the nail bed) and gently massage to promote bleedingApply this drop of blood to the test strip until the meter confirms an
adequate sample has been receivedGive the patient the swab to stop the bleeding and safely dispose
of gloves, lancet and test stripClean your hands
What is a normal range for blood glucose?
4-5mmol/L when fasting, up to 7.8mmol/l 2 hours after eating
What does QRISK3 calculate?
Risk of an individual developing a heart attack or stroke over the next 10 years
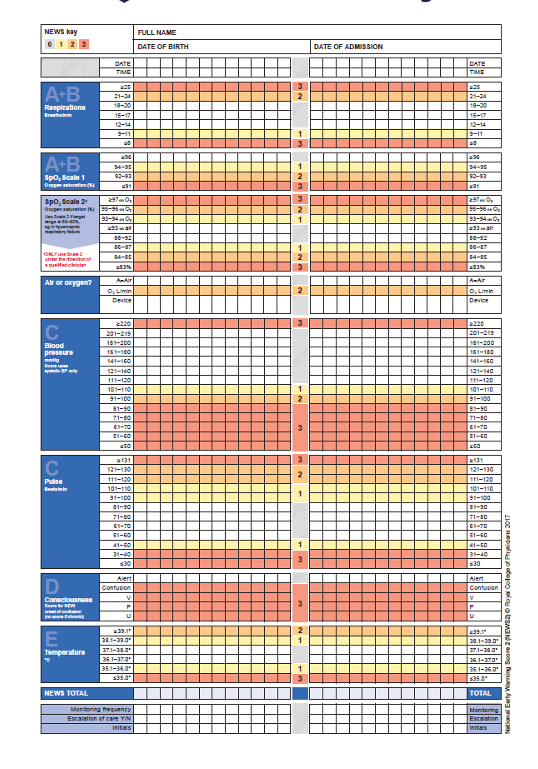
What does NEWS2 measure?
Detects deterioration in adults - better identifies patients likely to be septic, improved scoring for respiratory failure and recognises importance of new-onset delirium or confusion
What is an example sheet for NEWS2?