Cellular Respiration: Key Concepts in Energy Production and Metabolism
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions
Reactions involving electron donors and acceptors.
Coenzymes
Molecules like NADH and FADH2 that assist enzymes in biochemical reactions.
Energy currency molecules
Molecules such as ATP and GTP that store and transfer energy in cells.
Oxidation
Removal, or loss, of an electron (OIL).
Reduction
Addition, or gain, of an electron (RIG).
Electron carriers
Molecules that transport electrons in redox reactions.
NADH
An electron carrier that undergoes oxidation and reduction reactions.
FADH2
An electron carrier that undergoes oxidation and reduction reactions.
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate
A molecule that releases energy when breaking down by removing phosphates.
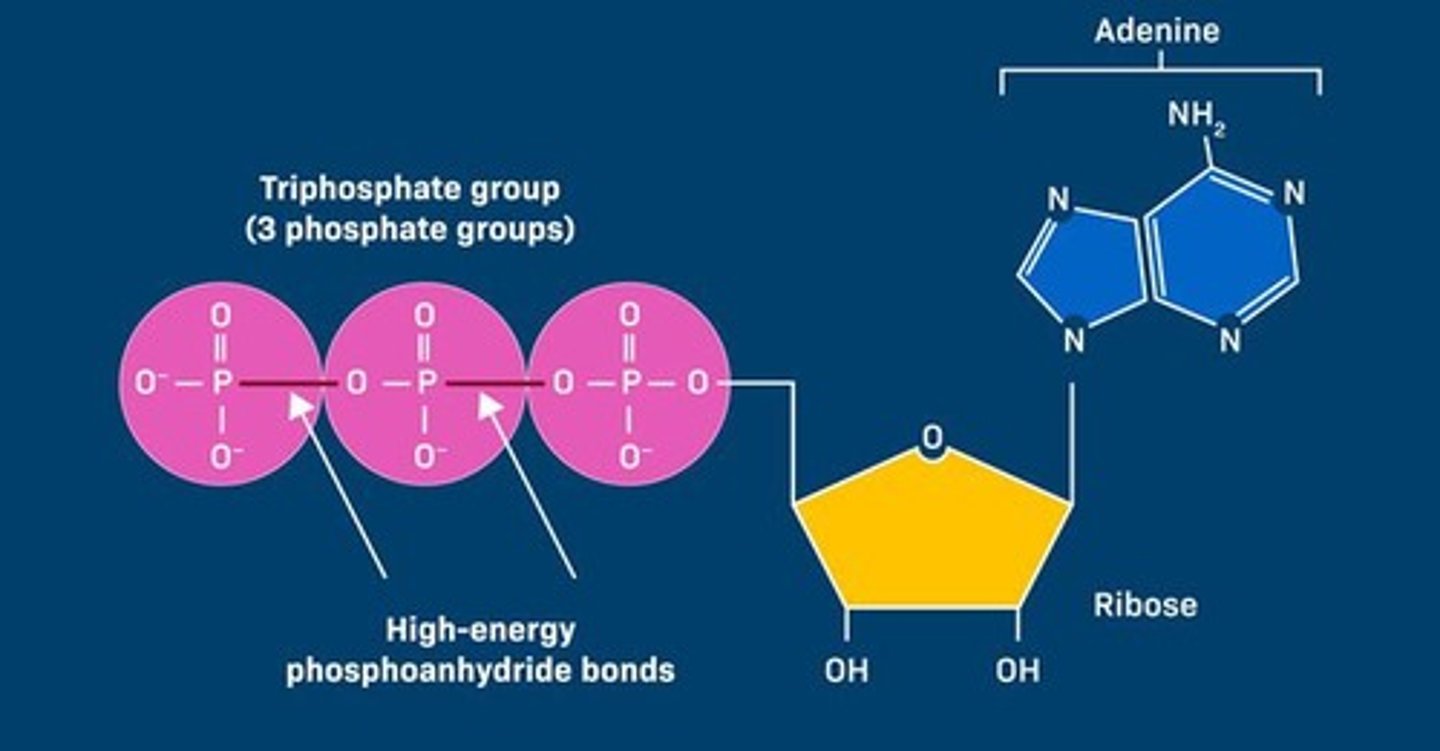
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Process where an enzyme catalyzes the addition of phosphate to ADP to form ATP.
Oxidative phosphorylation
An oxygen-requiring process that utilizes chemiosmosis to produce ATP in the mitochondria.
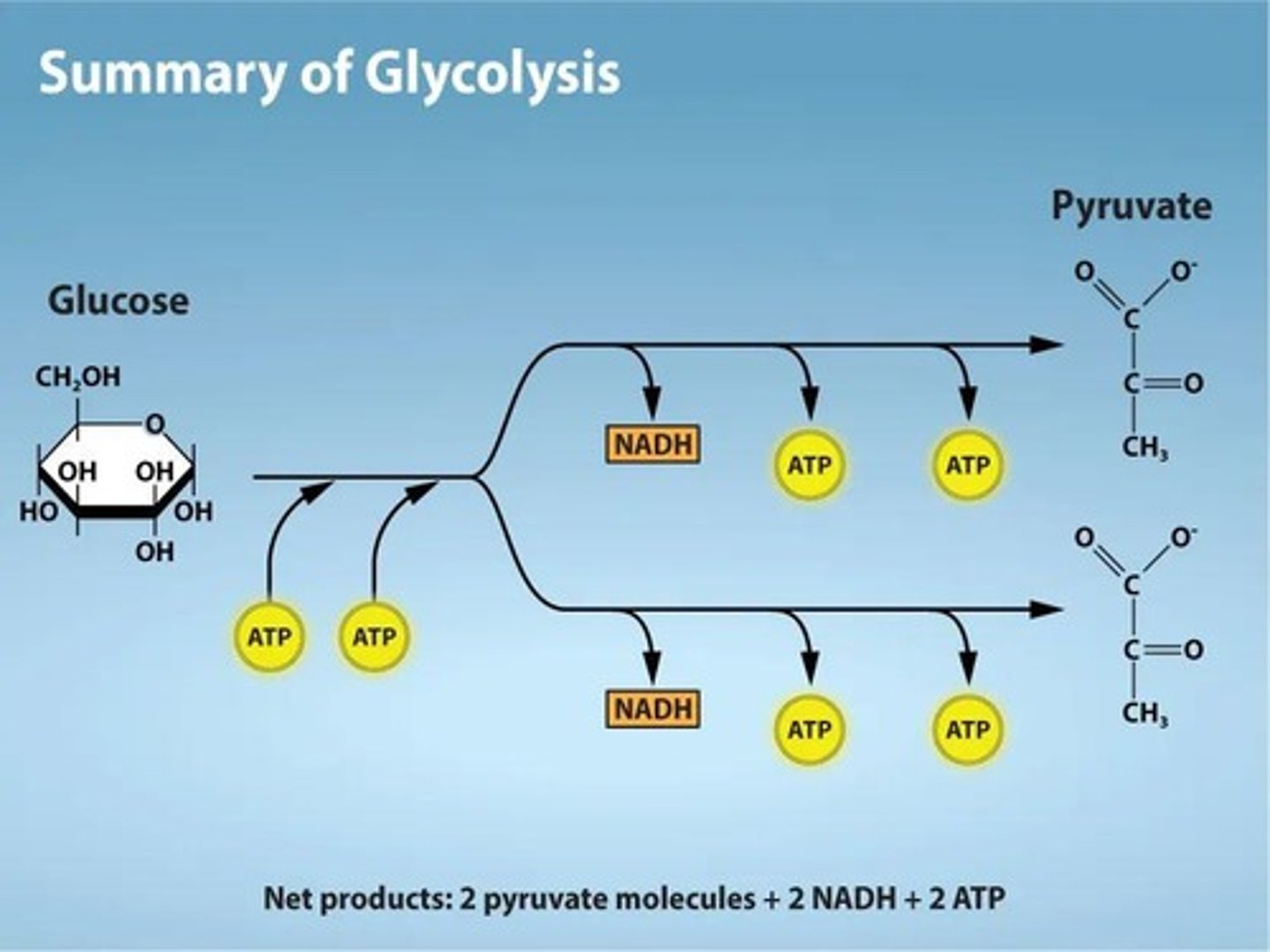
Glycolysis
The first stage of cellular respiration that occurs in the cytoplasm, producing 2 pyruvate, 2 NADH, and 2 ATP.
Anaerobic pathways
Pathways that break down pyruvate in the absence of oxygen, yielding low ATP.
Aerobic pathways
Pathways that break down pyruvate in the presence of oxygen, producing much more ATP.
Krebs cycle (TCA cycle)
A series of reactions that produce CO2, NADH, and FADH2 from Acetyl CoA.