Nutrition & Growth
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What do organisms need carbon for?
Building macromolecules
What is an autotroph?
An organism that builds their own compounds from inorganic sources, they can take CO2 in from the environment
What is a hetertroph?
Organism that need to get their carbon from premade organic compounds and break it apart. Th
What do heterotrophs do in the carbon cycle?
They produce CO2 while doing cellular respiration using carbohydrates.
What do autotrophs do during the carbon cycle?
They produce carbohydrates during photosynthesis using CO2.
What is the 10% rule?
The idea that only 10% of energy is transferred from one level to the next.
Why are phototrophs important in ecological systems energy wise?
Because only 10% of energy transfers to each level, there has to be lots and lots of phototrophs so they can produce enough energy to travel up and support the ecosystem.
What is chemotroph?
An organism that gets its energy from breaking down covalent bounds between organic compounds and using the energy from breaking bonds for ATP synthesis.
What is a phototroph?
An organism that gets its energy from the sunlight fro ATP.
What is a photoheterotroph?
An organism that gets its energy from the sun and carbon from premade organic compounds.
What is a photoautotroph?
An organism that gets its energy from the sun and makes its own carbon from inorganic sources, sucking in CO2.
What is a chemoheterotroph?
An organism that gets its energy from breaking apart covalent bonds between compounds and its carbon from premade organic compounds.
What is a chemoautotroph?
An organism that gets its energy from breaking apart covalent bonds and makes its own organic compounds.
Why do organisms need Nitrogen?
They need nitrogen to build amino aids and nucleotides?
Why is nitrogen a growth-limiting factor?
It restricts growth of a population because without nitrogen nucleotides cannot be made to copy DNA and amino acids cannot be made for protein to be used when growing the cell length wise during binary fission.
What is nitrogren fixation?
The process of turning Nitrogen gas N2 into Ammonia NH3
What organisms do nitrogen fixation?
Some bacteria NO Eukarytoes
Why can’t all organism use oxygen?
They must have enzymes to detoxify many toxic forms of Oxygen.
What is an aerobe?
An organism that uses oxygen for metabolism.
What is an obligate aerobe?
An organism that needs oxygen for metabolism otherwise it dies.
What is a facultative anaerobe?
An organism that grows best in O2 but can survive without O2.
What is a microaerophilic?
An organism that can tolerate oxygen in small concentration <21%. It may or may not be required.
What is an anaerobe?
An oxygen that does not use oxygen fro metabolism?
What is an obligate anaerobe?
An organism that is killed by an aerobic environment, they do not have enzymes for oxygen.
What is a aerotolerant anaerobes?
An organism that has some enzymes to tolerate oxygen, they can survive in it.
Why is temperature important for organisms?
The temperature influences if their enzymes fold up correctly and helps keep their membrane lipids in tact and can break hydrogen bonds if too high.
What is a Psychrophile?
An organism that can tolerate temperatures up to 10 C. Algae, fungi, and bacteria
Where are psychrophiles founds?
Snow, Ice, and Cold Water
What is a Mesophile?
A mesophile is an organism that can survive temperatures up between 20C-40C. Normal flora and pathogens.
Where are mesophiles found?
Humans and animals
What is a thermophile?
An organism surviving temperature between 40C-80C.
Where are thermophiles found?
Compost piles and hot springs.
What are hyperthermophiles?
Organism that can survive temperatures above 80C. Mostly archaea and a few bacteria.
Where are hyperthermophiles found?
Hot springs
Why is pH important for organisms?
Change in pH affects the change in concentration between OH- and H+ atoms, this causes interference for H bonding in nucleic acids and protein folding.
What is a neutrophile?
An organism that can survive a pH near neutral 6.5-7.5
What is a acidophile?
An organism that grows best in acidic environments. Some even produce acids.A
What is an obligate acidophile?A
An organisms that requires an acidic environment.
What is an acid tolerant organism?
An organism that can tolerate an acidic environment but does not need one to grow.
What is an alkalinophile?
An organism that grown best in basic environments with an optimum pH of 11.5
How is a hypertonic solution used for preservation of food?
It pulls water out of microbes, killing their cells. Hy
What environment do most organism not live in?
Hypertonic
What is a Halophile?
An organism that grows best in hypertonic solution of up to 30%, they will explode if put in fresh water.
What is a facultative halophile?
Organism that do no require high salt concentrations but can tolerate them.
What is a barophile?
An organism that lives in very high pressure environments at the bottom of the sea.
What is a biofilm structure?
A structure made of many microbe species living together attached to a surface surrounded by a slime layer.
What is quorum sensing?
A change in physiology in response to the # of microbes present.
Why is a biofilm beneficial to microbes?
They can be protected from the environment and they can share resources to live together.
How is a biofilm made?
Microbes stick to a surface using their fimbrae.
They spit out chemicals
Once enough of the chemical is sensed they start to make the slime layer
Other organisms stick to it
What situation does the four specific growth phases work for?
Bacteria in a liquid medium
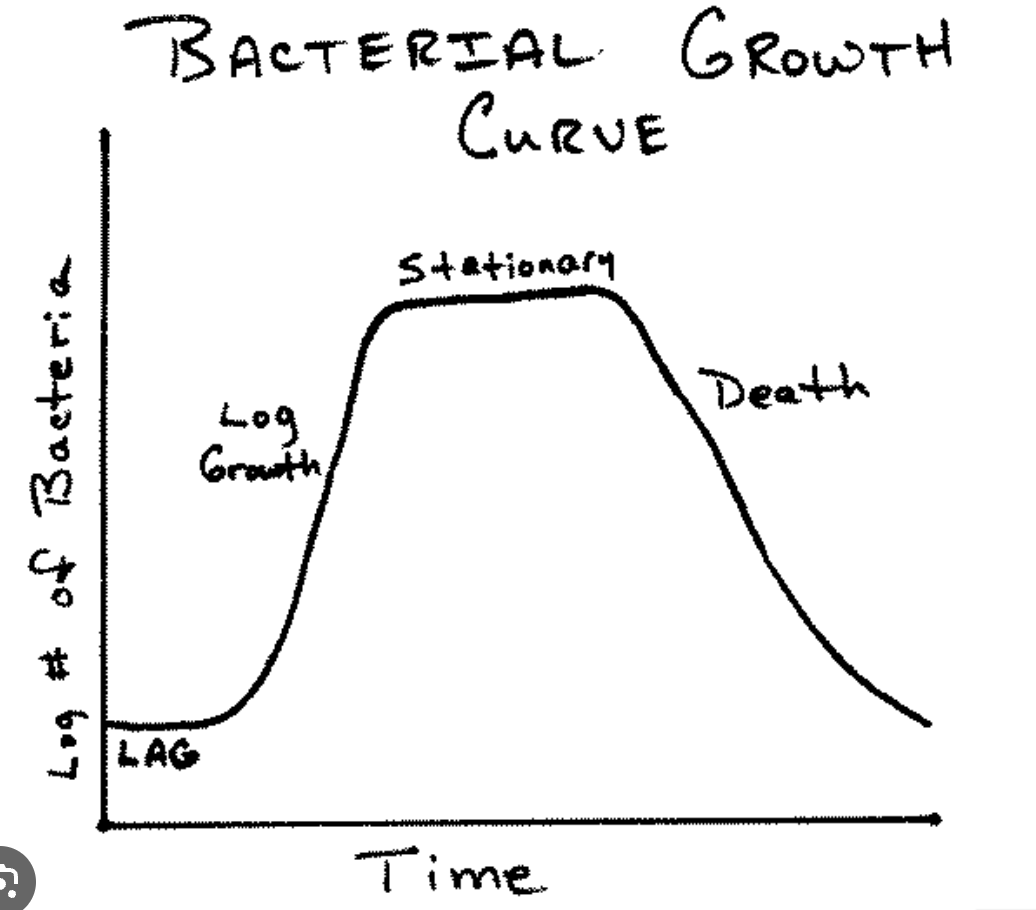
Explain the lag phase
cells just arrived
adjusting to the new environment
grwoth=death
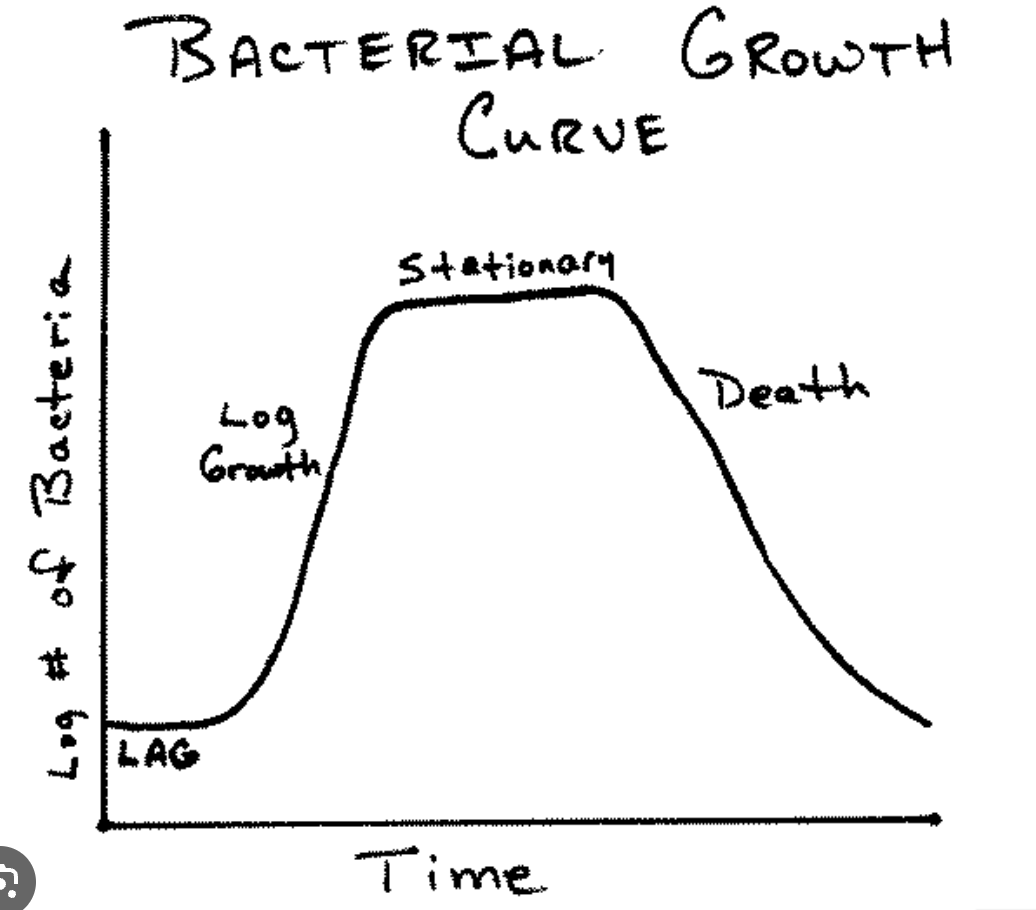
Explain the log phase.
where most binary fission occurs
best stage to use antibiotics
best stage for gram stain
growth>death
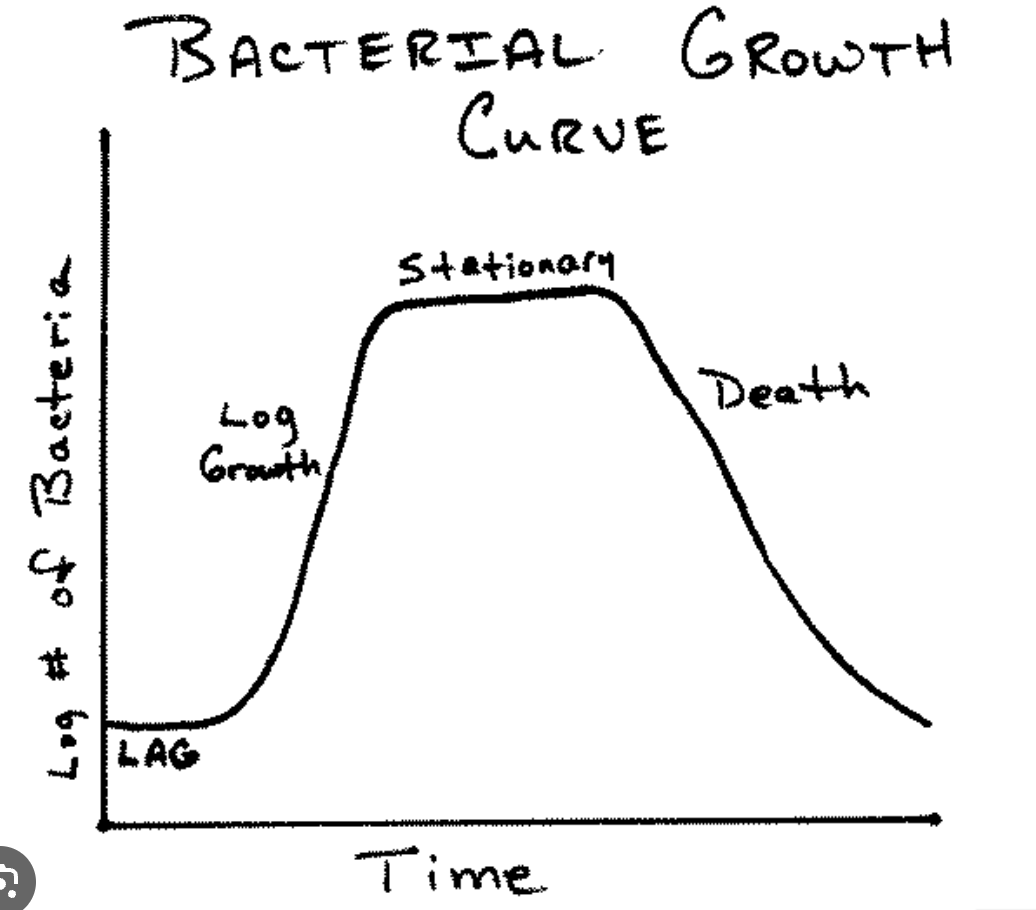
Explain the stationary phase
nutrients in the medium are at its critical level
growth=death
reached carrying capacity
mas number of organisms that can be supported by the environment
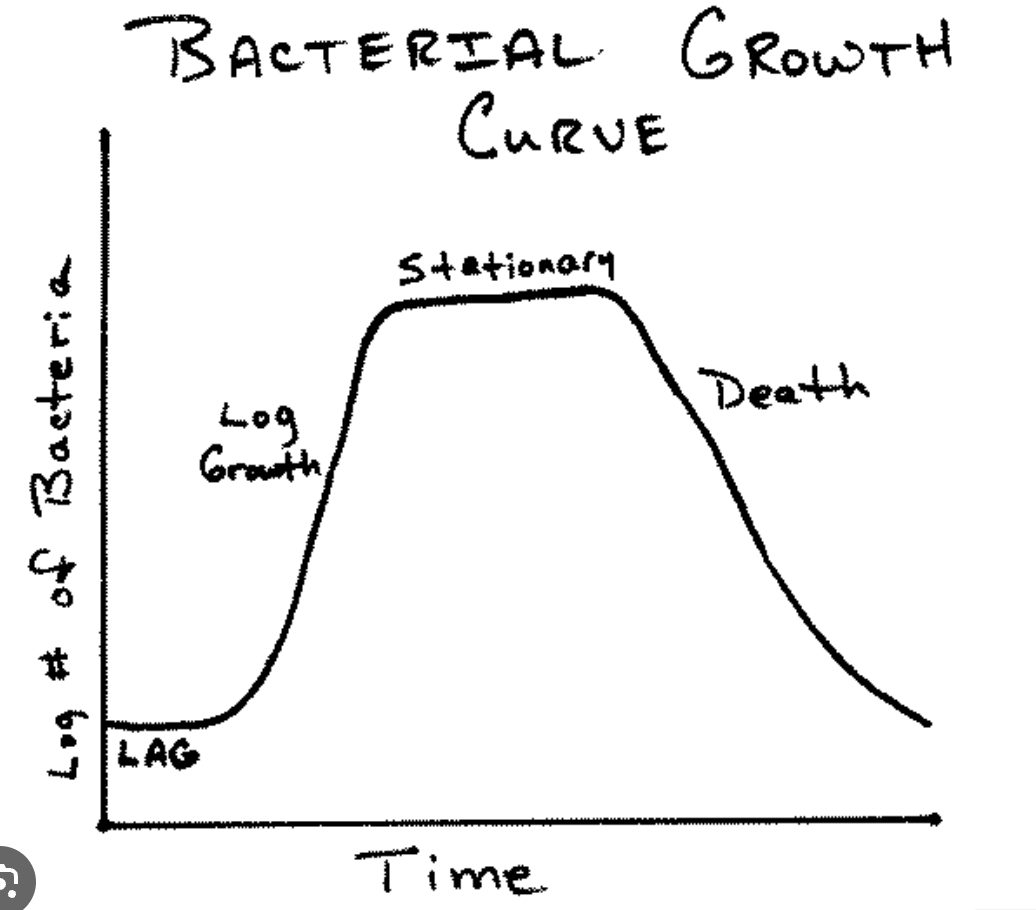
Describe the death phase
waste has accumulated and it is toxic
when plate needs to be restreaked
death>growth
What does generation time mean?
The time it takes divide from one generation to another
Why do bacteria grow exponentially?
They double every generation A gra
What is a growth curve?
A graph plotting the number of organism growing in a population over time, placed in a log scale to distinguish in early exponential growth and make graph a straight line.