Aerobic Gram-negative Cocci: Neisseria & Moraxella catarrhalis
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Neisseria traits
-GNC in pairs
-inhabit mucous membranes
-nonmotile, non-spore
-capnophilic (likes CO2!), grows best in moist conditions 35-37C
-oxidase =pos
-catalase = pos
N. gonorrhoeae is always ___ and humans are ___.
clinically significant; only host
N. gonorrhoeae infn
-how does it present in males vs females?
other forms?
males: symptomatic urethritis
-painful urination, discharge from urethra, swollen testicles
females: cervicitis (most asympt)
-abdominal pain, but mostly unaware → can cause purulent discharge
rectal & throat/pharygeal gonorrhoea → most asympt
N. gonorrhoeae clinical complications
ascending infns (10-20% females)
-acute PID (pelvic inflam disease) → affect child birth
-Salpingitis (fallopian tubes)
-Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome - perihepatitis
epidymitis, prostatitis in males
bacteremia, arthritis (joint fluid **remember Susan!), endocarditis, meningitis
opthalmia neonatorum (crusty baby eyes)
N. gonorrhoeae virulence factors
pili - adhere to host cells, impede phagocytosis
protein II - helps invasion
IgA protease - deactivates IgA at mucosal surfaces
LPS - stimulates inflam response → lysis of PMns and epi’s
plasmids: Abx-R
N. gonorrhoeae specimen collection
-dacron or rayon swab (calcium alginate and cotton swabs may inhibit)
-avoid oil-based lubricants, cold water for vaginal specula
-max recovery via inoculating media at bed side
if not possible → transport systems: JEMBEC, Gono-pak, Transgrow
acceptable specimens for N. gonorrhoeae
genital
male - urethra
adult female - endocervix
prepubertal female - vagina or urethra
orophargyngeal
anal
disseminated: blood, skin lesions, joint fluid (Susan!)
transgrow bottle
MTM medium, CO2, inoc at RT, inoc in upright position
selective media for N. gonorrhoeae
Thayer Martin
Modified TM
Martin Lewis
New York City
what is the role of each Abx?
TM: vancomycin, colistin, nystatin
MTM: same ^ + trimethoprim sulfa
Martin Lewis: same as MTM, except anisomycin instead of nystatin
NYC: vancomycin, colistin, amphotericin B, trimethoprim sulfa + etc → supports genital mycoplasma & ureaplasma
vancomycin → inhibits G+
colistin → inhibits GNR
nystatin, anisomycin, amph B: antifungals (yeast in genital)
trimethoprim sulfa: inhibits swarming in Proteus (can still grow)
Why do candle jars work for N. gonorrhoeae?
burns O2 in jar → makes capnophilic conditions
N. gonorrhoeae morph
small, translucent, gray, convex, smooth or irregular margin
may be mucoid, sticky

5 things for presumptive ID of N. gonorrhoeae
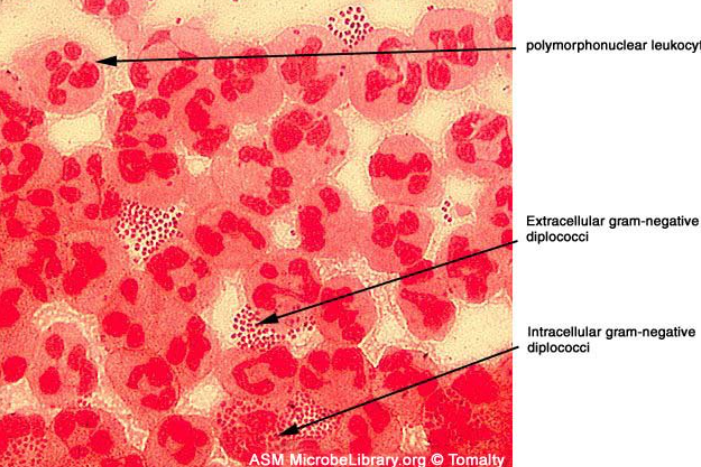
G- intracellular cocci in pairs
genital site (adults only)
grows on GC selective agar
oxidase +
superoxol +
oxidase test
tests for cytochrome oxidase → breaks down tetra(or di)methyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrocholride → indophenol blue
reagent = tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (Kovacs reagent)
on filter paper in petri dish, 1 drop of Kovacs reagent → wooden stick of colony (better if from non-choc media)
pos = dark purple
neg = no color change
superoxol test
used for N. gonorrhoeae ID
same as catalase
reagent = 30% hydrogen peroxide
pos = vigorous rapid bubbles
neg = weak or no bubbles
confirming N. gonorrhoeae ID (once growth on GC selective media)
carbohydrate utilization, immunologic (coagglutination & direct fluorescent antibody test), enzymatic, multitest ID systems (Vitek - uses sugar-utilization & enzyme rxns)
carbohydrate utilization tests for N. gonorrhoeae
only uses glucose
pos = yellow from phenol red pH indicator
neg = red
N. gonorrhoeae recovered from children must be confirmed by at least 2 methods of different principles →
nucleic acid hybridization, immunological, carbohydrate utilization
for legal cases → only culture acceptable, no PCR, too risky for a false +
Neisseria meningitidis epidemiology
humans only host
transmitted by respiratory droplets, colonizes upper respiratory mucosa
asymptomatic carriage common: 8-20% general popn
N. meningitidis cause epidemic & endemic meningitis
90% cases caused by serogroups __
A, B, C, Y; Group B is worldwide cause of bacterial meningtis
N. meningitidis clinical significance
transient bacteremia, or rapidly fatal disease
2nd leading cause of community-acquired meningitis after S. pneumo
meningocephalitis, meningitis w/ or w/o meningococcemia, …
N. meningitidis clin manif
classic: headache, fever, confusion, nuchal rigidity
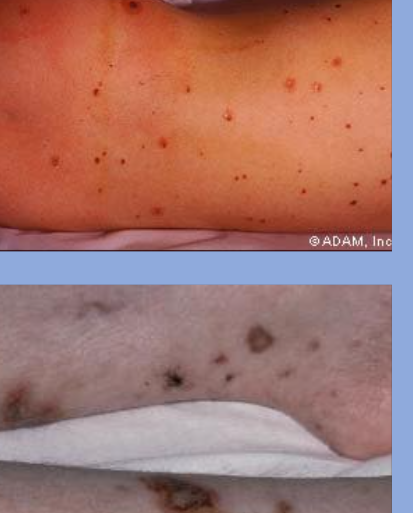
meningococcemia (petechiae - red spots)
necrotic skin lesions
fulminant shock
DIC - disseminated intravascular coagulation
Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome → attack adrenal glands
N. meningitidis virulence factors
polysacc capsule - antiphagocytic
endotoxin = LPS
pili = adhere to mucosal cells of nasopharynx
IgA protease
plasmids
(protein II only one missing - in N. gono)
N. meningitidis acceptable specimens
body fluids: CSF, blood, synovial fluids, pleural fluid, aspirates of petechiae
nasopharyngeal swab for detecting colonization
biopsies
genital, anus, eyes
N. meningitidis risk of lab transmitted infns
need BSC 2, avoid aerosols (beware of this in urine cx!!)
N. meningitidis media
SBA, CHOC, supportive broth medium, other selective media if applicable
incubate 5-10% CO2, moist, 36-37C, at least 72h
N. meningitidis is a ____ in pairs.
col morph?
intracellular GNC
gray, may impart diffuse green color to agar

N. meningitidis is + for which carbohydrates?
glucose & maltose
Which sp of Neisseria is weak sometimes a + glucose reaction?
N. cinerea → may misID as N. gonorrhoeae (they rhyme)
normal oropharyngeal & genital flora
assoc’d w/bacteremia, conjunctivitis, nosocomial pneumoniae & proctitis

other Neisseria ssp
found where?
inhabit mucosal membrane of oral cavity; sometimes genital tract
low virulence, DON’T grow on GC selective media, most grow on nutrient agar, usually susceptible to colisitin
Moraxella catarrhalis
found where
opportunistic pathogen when?
normal upper respiratory flora
otitis media, sinusitis, pneumonia
septicemia, meningitis, endocarditis, conjunctivitis; for infants, immunocomp, COPD pts
Moraxella catarrhalis is an ____ in pairs
col morph
intracellular GNC
col: whiter, more raised than Neisseria; may be pink on choc, may be hockey puck (scoots on agar)
M. catarrhalis ID
carbohydrate utilization?
DNase test
assachrolytic → doesn’t use any sugar
Dnase = pos
Beta-lactamase = pos
butyrate esterase = pos
DNase test
if DNA is depolymerized, toluidine blue turns from blue to rose color → for ID of M. catarrhalis
streak & incubate 35C overnight
pos = rose color
neg = blue
M. catarrhalis enzyme test
butyrate esterase +
uses disk of indoxyl butyrate