Cardiovascular gross and histopathic lesions
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
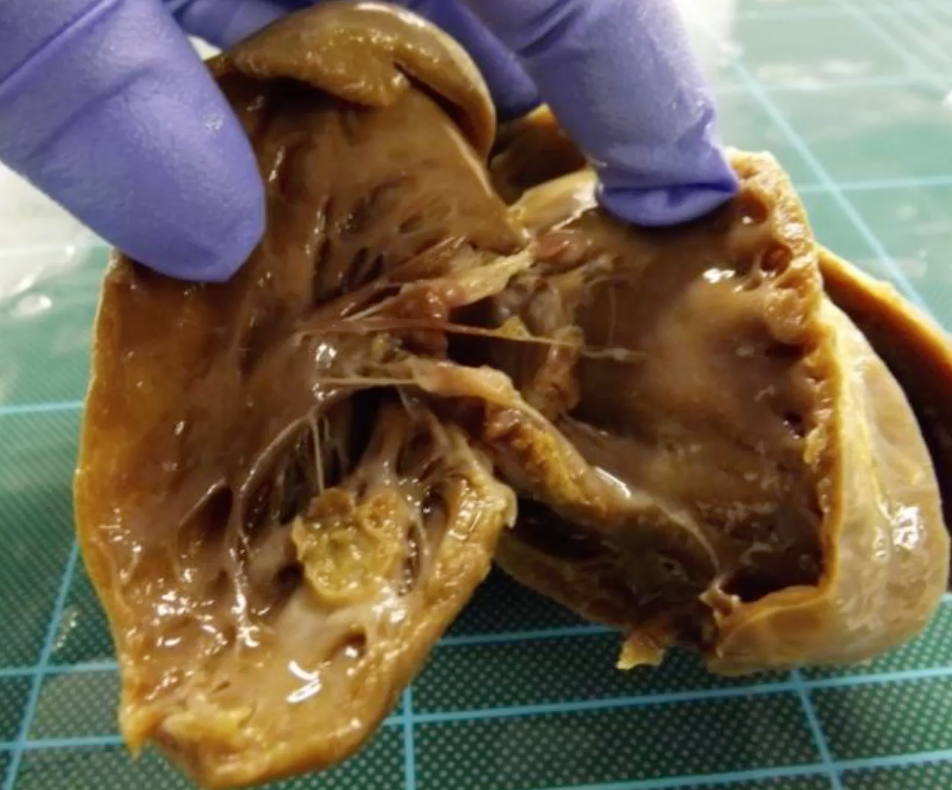
Pig with history of pyrexia and signs of generalised heart failure. Describe the gross lesion?
organ = heart
location = mural endocardium and valvular endocardium
distribution = multifocal to coalescing
size = 5mm to 1cm diameter
shape = circular nodule on mural endocardium, coalescing nodules on valve cusps
colour = nodules pale yellow / brown with some red mottled discolouration
consistency = soft-firm intermediate texture
what is the morphological diagnosis for this pig and what is the possible aetiology?
history - history of pyrexia and signs of heart failure
gross lesion - multifocal to coalescing pale yellow and red mottled nodules on mural and valvular endocardium, 0.5-1cm diameter, round shape and intermediate texture
morphological diagnosis = heart, moderate, acute to subacute, valvular and mural, suppurative and thrombotic vegetative endocarditis
aetiology = E. coli, Streptococcus spp.
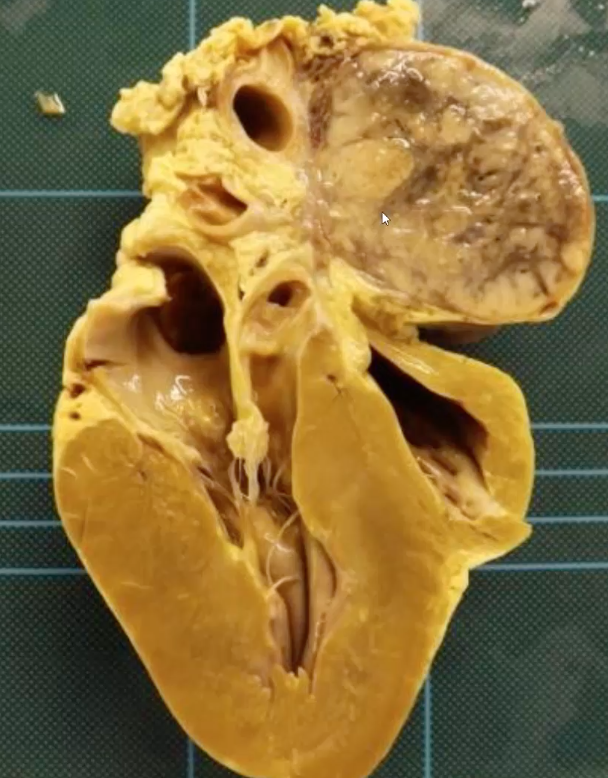
Boxer dog died after acute deterioration following chronic congestive heart failure. Describe the gross lesion
organ = heart
location = heart base
distribution = single focal lesion
size = 15 × 10 cm
shape = oval and well demarcated
colour = pale yellow/tan and black mottling
consistency = firm
also squashing of vessels due to tumour
what is the morphological diagnosis and origin of lesion?
history - acute deterioration following chronic congestive heart failure
gross lesion - 15×10cm oval and well demarcated, pale tan and black mottled, firm tumour at base of heart
morphological diagnosis = heart, chemodectoma
origin of lesion = chemoreceptors of the aortic / carotid bodies
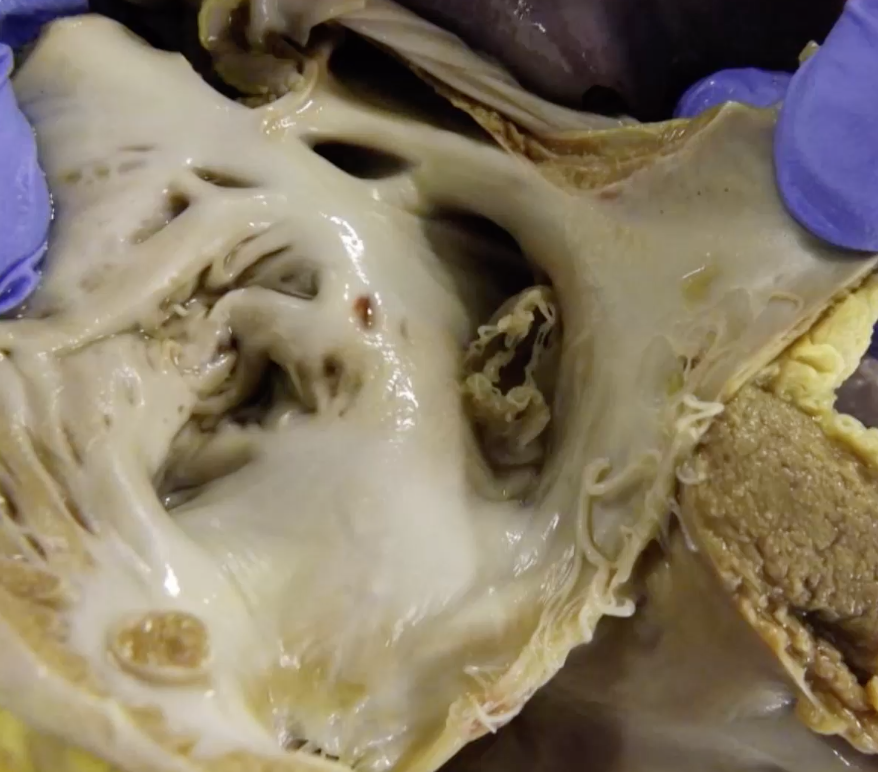
Foal died following signs of encephalopathy. Describe the gross lesion
organ = heart
location = interatrial septum
distribution = single focal lesion
size = 1-2cm diameter
shape = narrow band of tenuous membrane with feathered edge around periphery
—> patent foramen ovale
what is the morphological diagnosis?
history - few days old foal died following signs of encephalopathy
gross lesion - single focal lesion in interatrial septum, patent foramen ovale
morphological diagnosis - persistent foramen ovale
mixing of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood —> hypoxia —> ischaemic encephalopathy
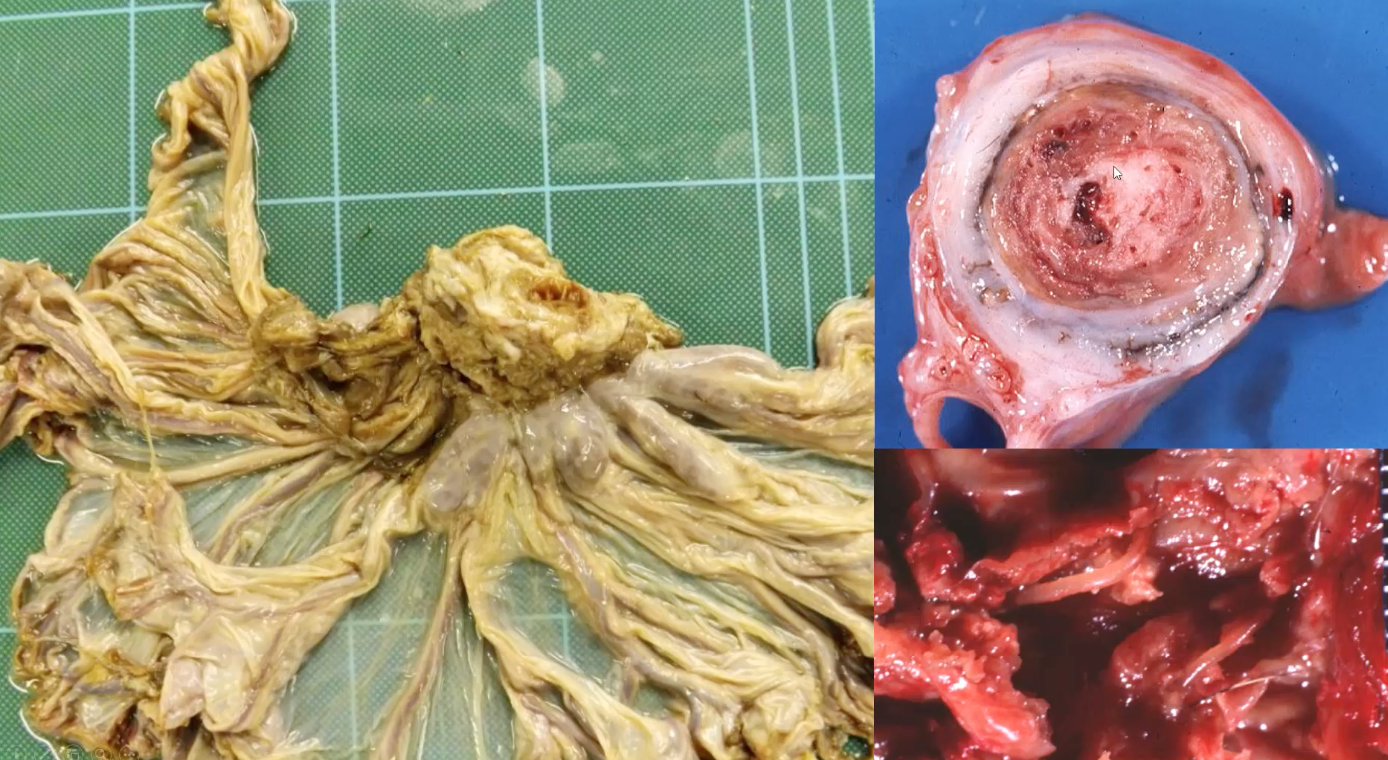
Horse in poor body condition, heavy worm burden throughout the GI tract. Describe the gross lesion
organ = mesenteric artery
location = arterial lumen
distribution = focal lesion (within the lesion there are multifocal larvae with few mm length)
shape = circular lesion filling lumen
colour = mottled white and red/pink with layering (likely thrombus) within the lumen, vessel wall has pale pink / white discolouration
consistency = firm
what is the morphological diagnosis and aetiology?
history - poor body condition horse, heavy worm burden in GI tract
gross lesion - white and red mottled thrombus occluding arterial lumen, within lumen there are multifocal larvae)
morphological diagnosis - mesenteric artery, chronic, severe, thrombosing and fibrosing, arteritis with intralesional nematode larvae
aetiology - Strongylus vulgaris larvae
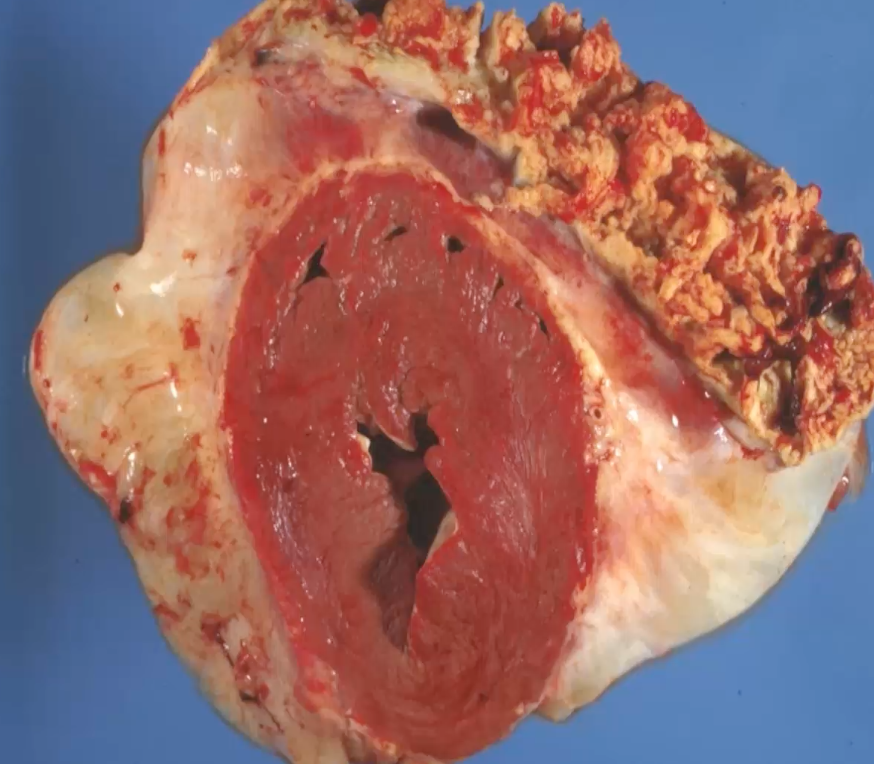
Cow exhibiting arched back, anxious expression, reluctance to move, groaning when forced sudden movements. Signs decreased in severity, but ongoing reduction in milk yield, food intake and faecal output. Muffled heart sounds and jugular pulses, brisket oedema developed. Describe this gross lesion
organ = heart (cross section)
location = epicardial surface
distribution = diffuse band of fibrous tissue enveloping epicardial surface, with focally extensive lesion at the top right
colour = band of fibrous tissue is white, focally extensive lesion is yellow and red mottled
shape = lesion at top right has small projections = fibrin
consistency = fibrous tissue is firm, while top right lesion is less firm and likely stringy and friable
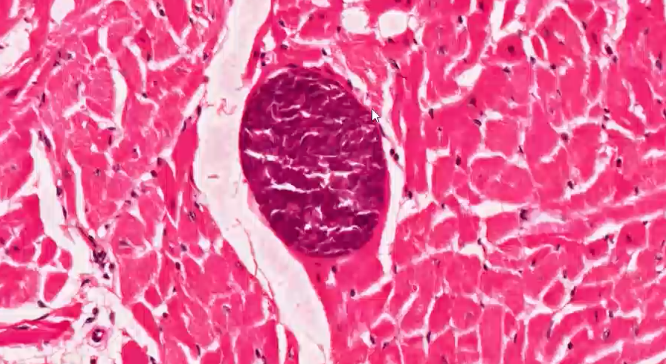
what is shown in this histology?
Sarcosystis (protozoa parasite) in myocardium - encyst themselves to protect themselves from immune system
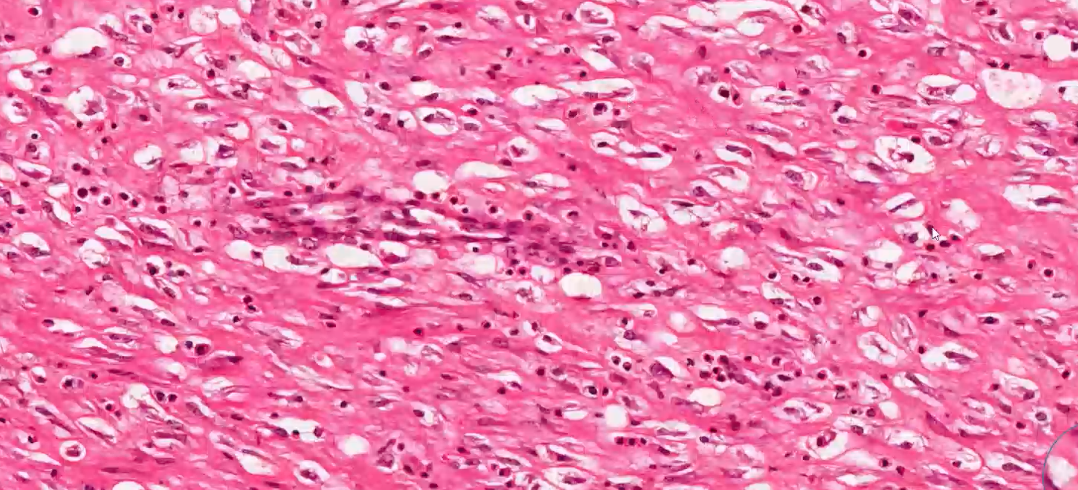
what can we see in this high power histology of epicardium?
fibroblasts = pink stand like cells
collagen = lots of pink dense material, lack of cells
—> fibrous tissue
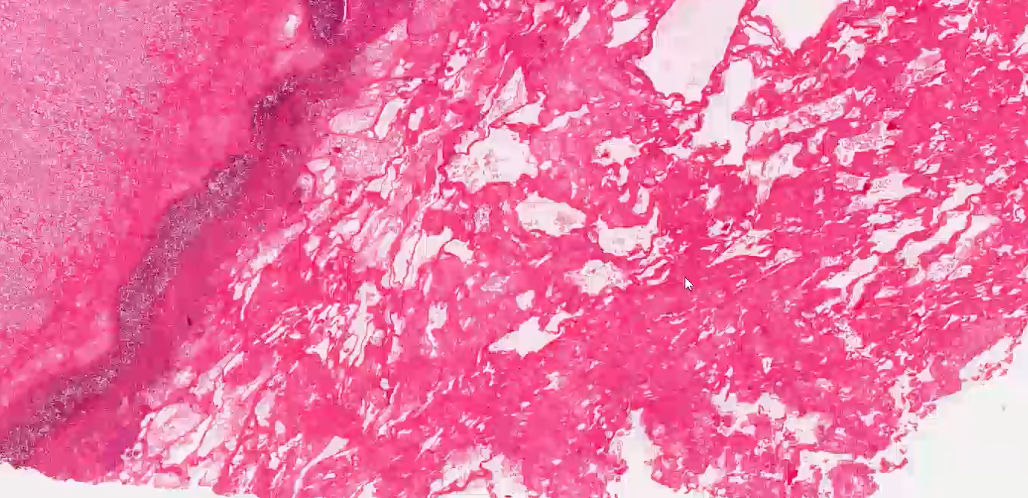
what can we see in this medium power histology?
pink, stringy / mesh-like material = fibrin
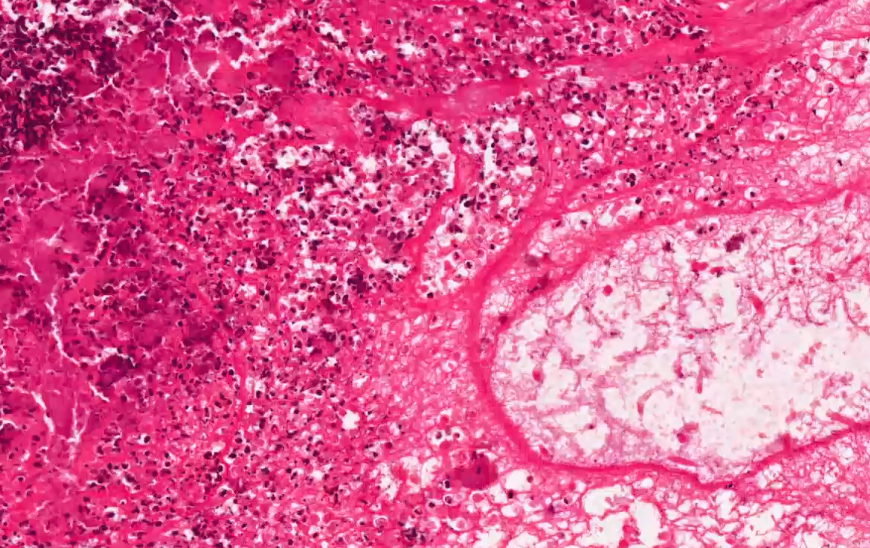
what inflammatory cells are these most likely to be within the fibrin?
degenerate neutrophils - can lose the segmentation of nucleus when involved in purulent inflammation
What is the morphological diagnosis and aetiology?
history - cow displaying signs such as arched back, reluctant to move, groaning with sudden movements. Severity of signs decreased but still reduction in milk yield, food intake and faecal output. Muffled heart sounds and jugular pulses, brisket oedema developed.
gross lesion - fibrous tissue enveloping epicardial surface, with mottled yellow and red lesion with fibrin
histology - fibroblasts and collagen in epicardium, protozoa cysts in myocardium, fibrinous tissue with degenerate neutrophils
morphological diagnosis - epicarditis, severe, chronic, fibrosing, with superficial fibrinous inflammation
aetiology - coccoid bacteria
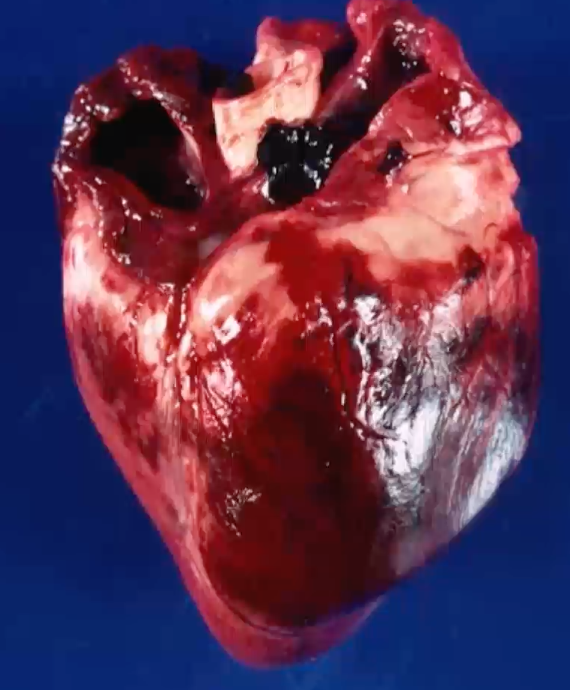
3 week old piglet with sudden death after a period of exercise. Describe the gross lesion
organ = heart
location = epicardial surface
distribution = multifocal to coalescing
size = 80% of epicardial surface affected
shape = irregular and poorly demarcated
colour = deep red discolouration —> haemorrhage
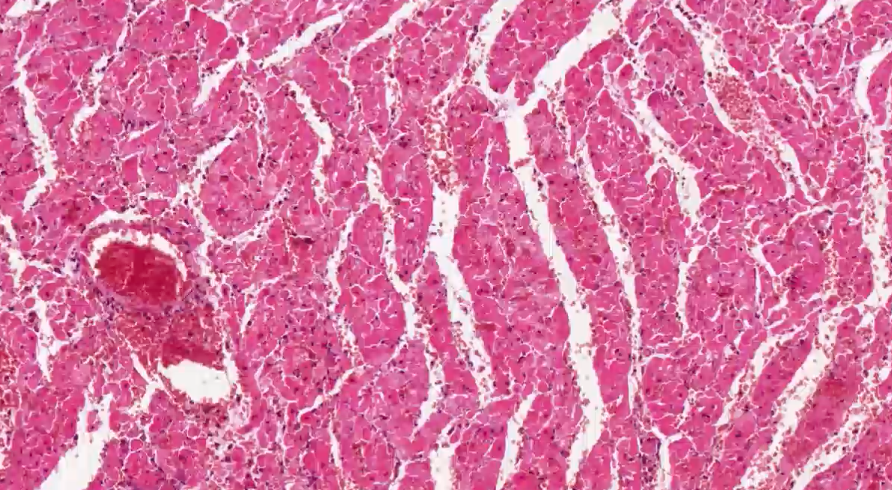
what can we see in this histology of myocardium?
vessels are congested
erythrocytes outside the vessels = extravascular —> haemorrhage
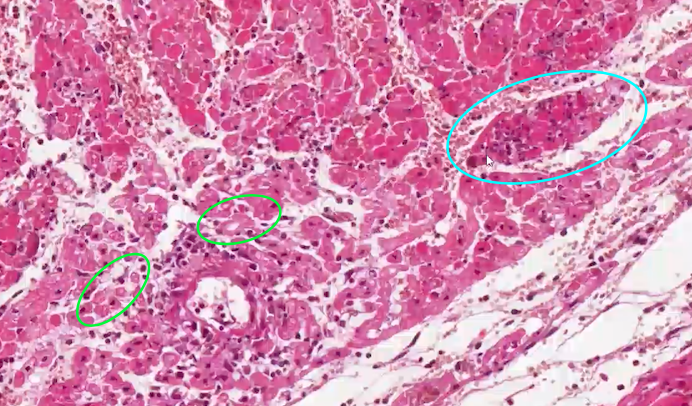
what can we see in this histology of heart?
green - degenerate cardiac myofibres (vacuolation of cytoplasm)
blue - inflammatory cells
—> necrosis
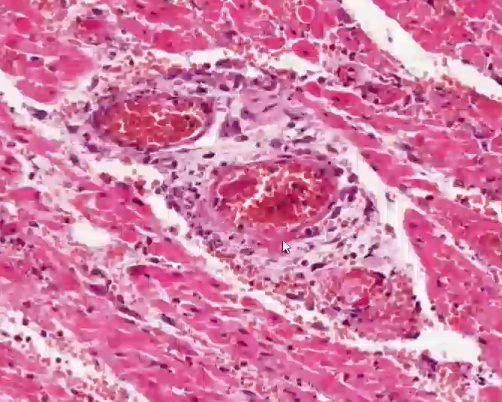
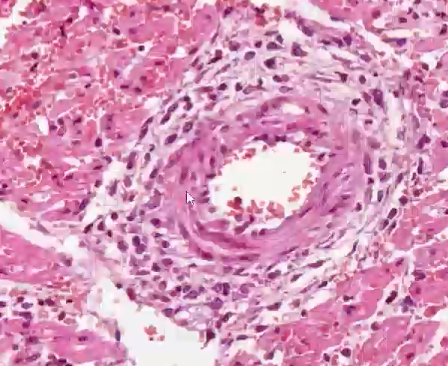
what is shown in this heart histology?
fibrinoid necrosis - vessel wall replaced with amorphous band of eosinophilic material
—> mulberry heart disease
what is the morphological diagnosis and aetiology?
history - piglet sudden death after exercise
gross lesion - multifocal to coalescing, poorly demarcated haemorrhage on 80% of epicardial surface
histology - multifocal necrotic myocytes, extravascular haemorrhage, multifocal fibrinoid necrosis of arteriolar wall
morphological diagnosis - necrotising myocarditis, acute, severe, diffuse, with multifocal acute haemorrhages, fibrinoid arterial necrosis and thrombosis
aetiology - mulberry heart disease due to vitamin E deficiency
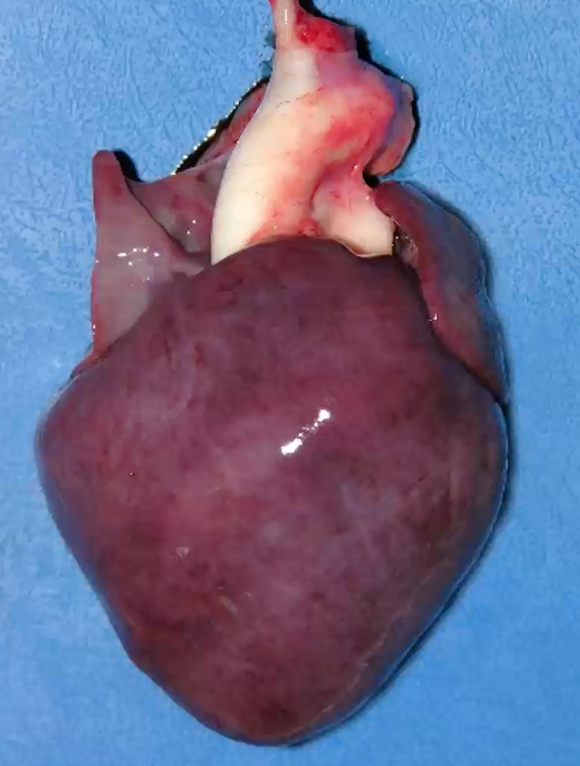
Dog showing neurological signs (seizures, depression) and lethargy with muscle weakness. Signs of bilateral heart failure (unproductive cough, exercise intolerance, mild ascites). Describe the gross lesion
organ = heart
location = epicardial surface
distribution = multifocal to coalescing
size = 80% of epicardial surface
shape = streaks, poorly demarcated
colour = pale grey discolouration (pallor)
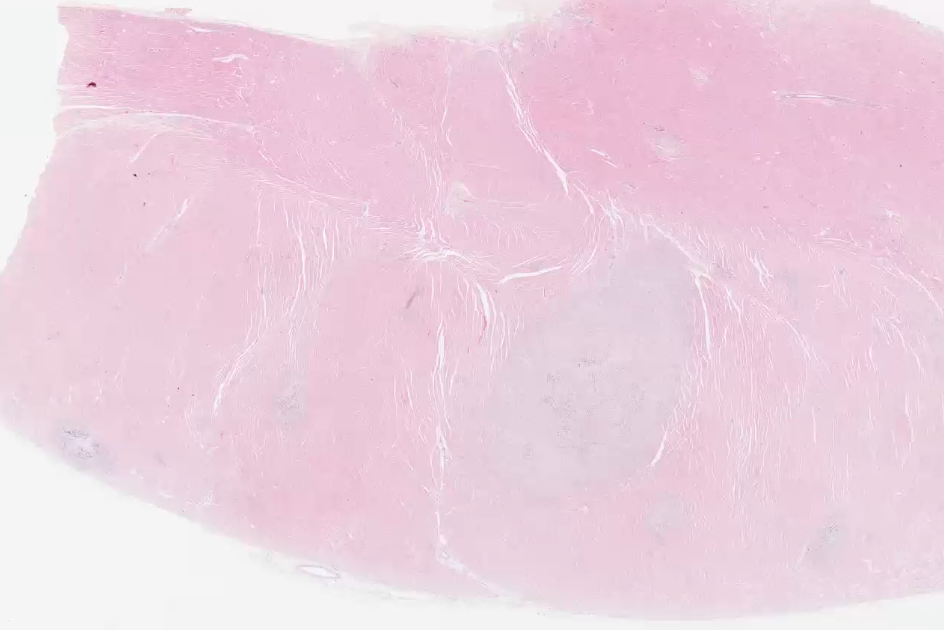
what can we see in this low power histology of the heart?
multifocal lesions - mainly in myocardium
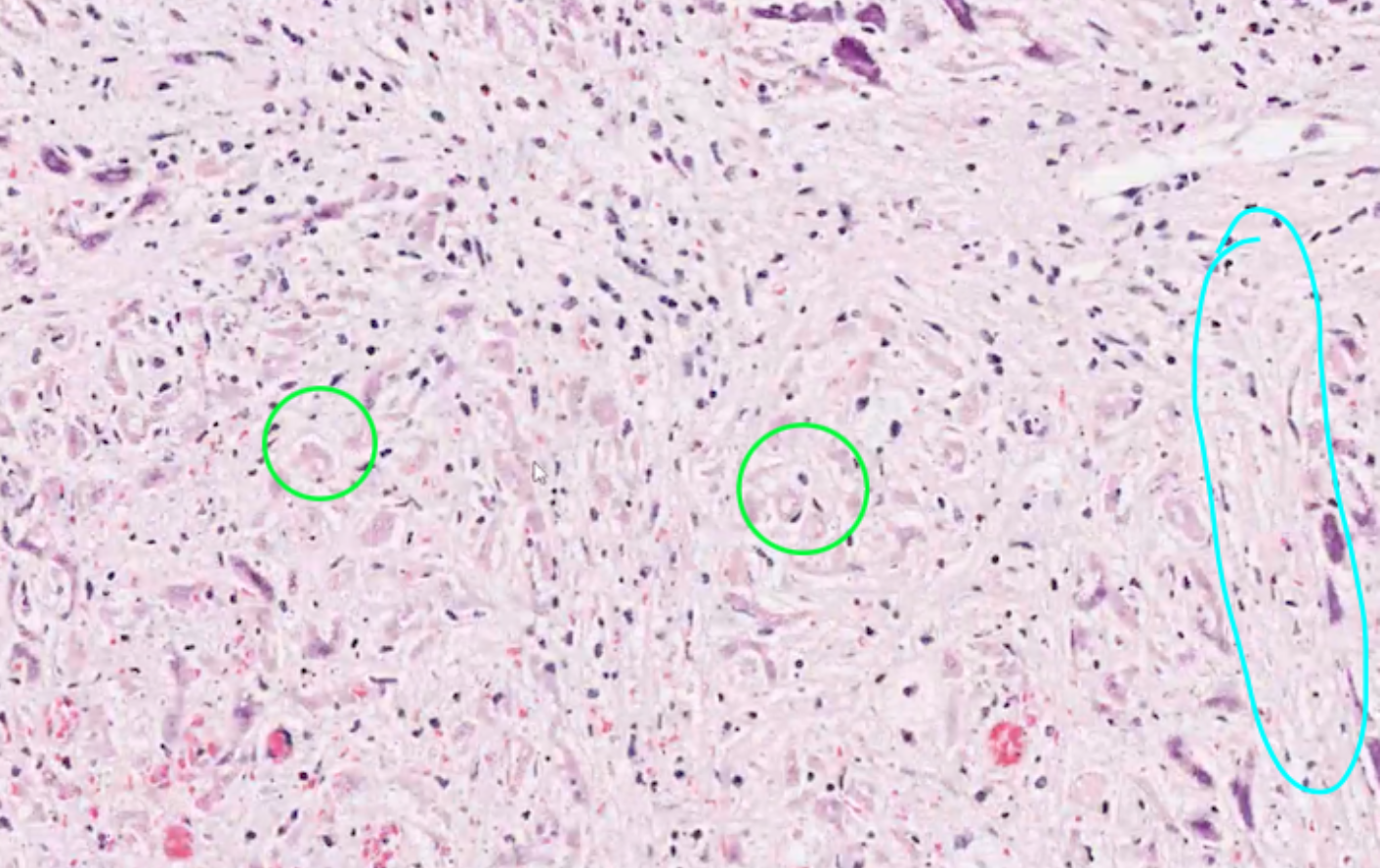
what can we see in this histology within the lesion?
green - a few degenerate cardiac myocytes - some vacuolation
most normal myocardium architecture is gone
blue - replacement with necrotic material
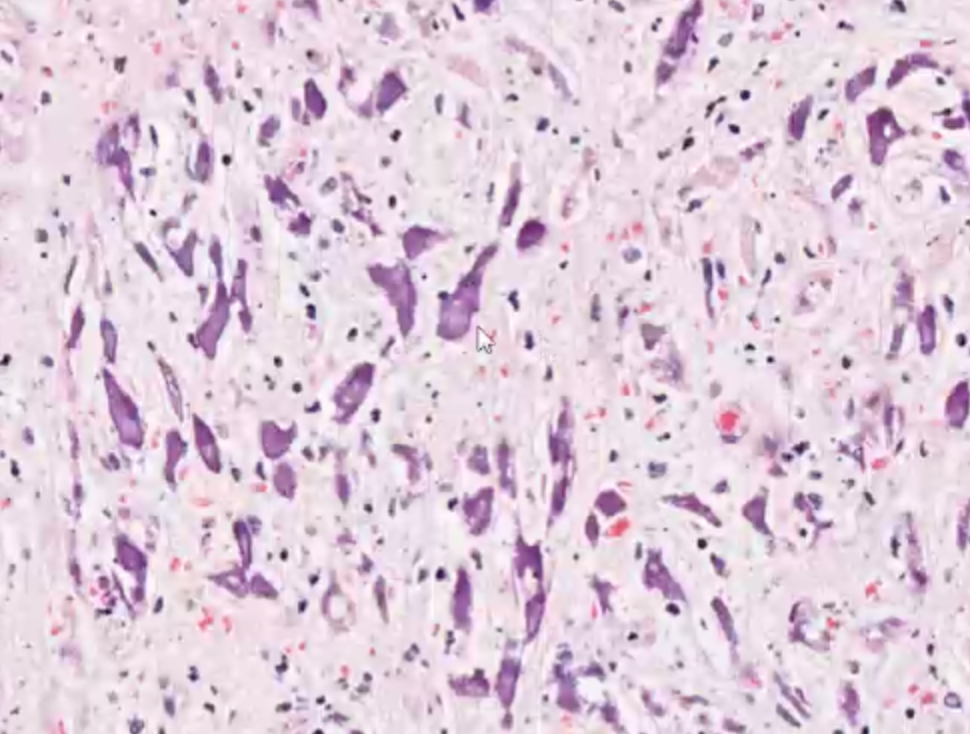
what does this histology of heart show?
mineralisation —> likely dystrophic calcification due to necrosis
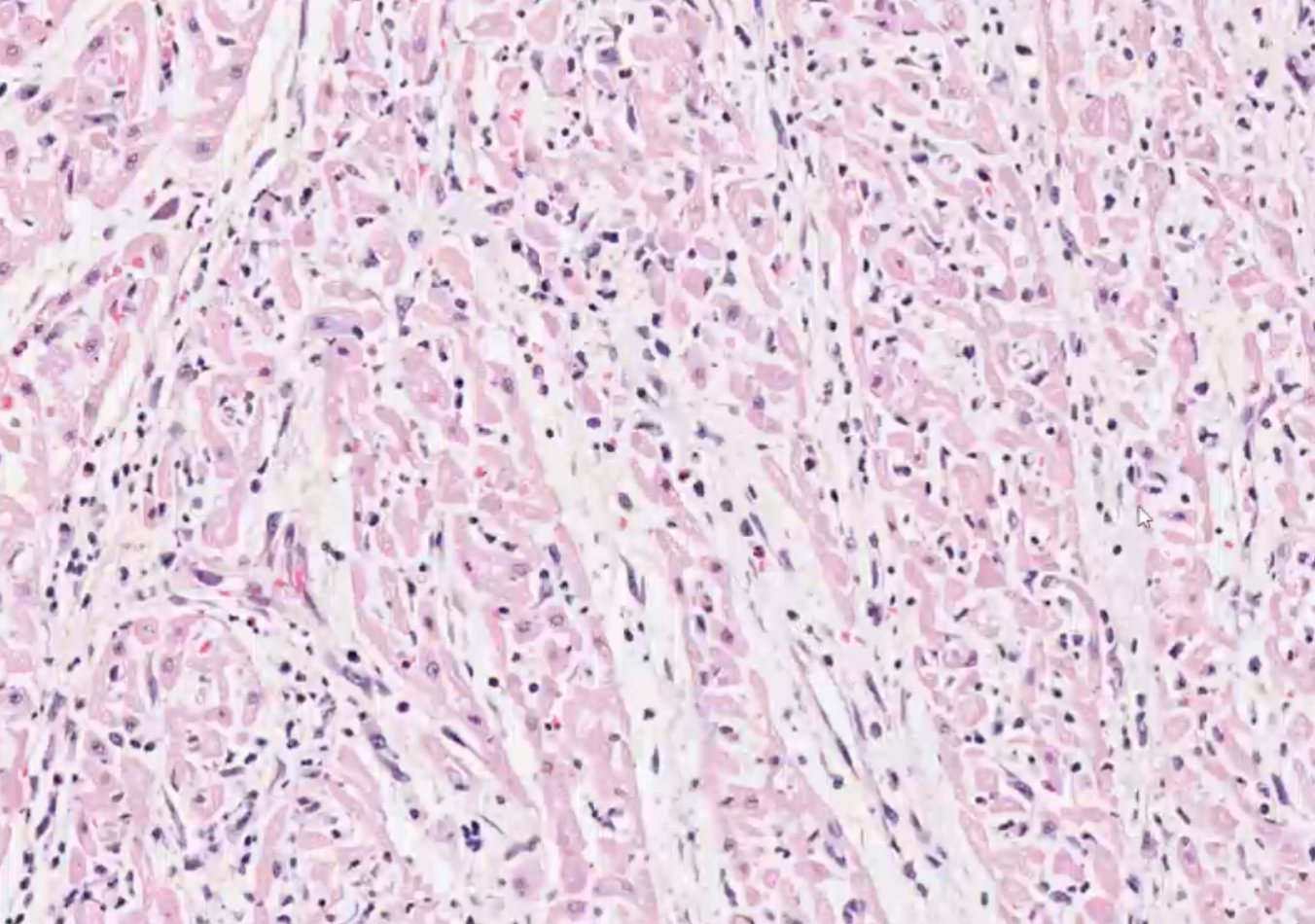
what can we see in this histology at the border between the normal myocardium and the lesion?
presence of inflammatory cells - mostly lymphocytes, plasma cells, and some neutrophils
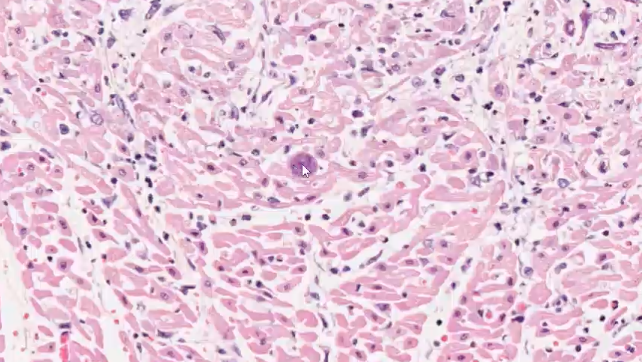
what does this histology show?
toxoplasma cyst - move through the myocardium, causing the multifocal lesions
what is the morphological diagnosis and aetiology?
history - dog with seizures, lethargy and muscle weakness. Also showing signs of heart failure (unproductive cough, mild ascites, exercise intolerance)
gross lesion - poorly demarcated, multifocal to coalescing, pale grey pallor affecting 80% of epicardial surface
histology - multifocal lesions, necrosis and inflammation, toxoplasma cysts
morphological diagnosis - multifocal acute to subacute, necrotising, myocarditis with mild to moderate mixed cellular infiltration, and parasite cysts
aetiology - toxoplasma gondii
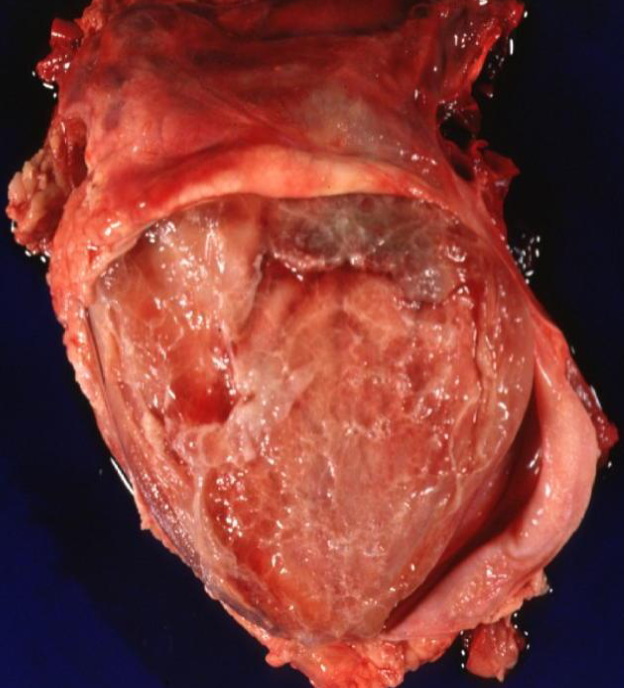
10 week old pig with signs of shallow respiration and unwillingness to move, discovered dead the next morning. Describe the gross lesion.
organ = heart
location = epicardium
distribution = diffuse
size = thin layer covering 100% of epicardium
colour = pale yellow with areas of reddening (haemorrhage)
consistency = sticky, with purulent exudate
what is the morphological diagnosis and aetiology?
history - pig with shallow breathing, unwillingness to move
gross lesion - thin layer of fibrin, pale yellow with areas of haemorrhage, diffusely covering epicardium, sticky consistency with purulent exudate
histology - band of fibrillary amorphous eosinophilic material, some fibroblasts, degenerate neutrophils, lymphocytes and plasma cells
morphological diagnosis - heart, fibrino-purulent epicarditis, moderate, subacute
possible aetiology - Haemophilus parasuis, streptococcus suis
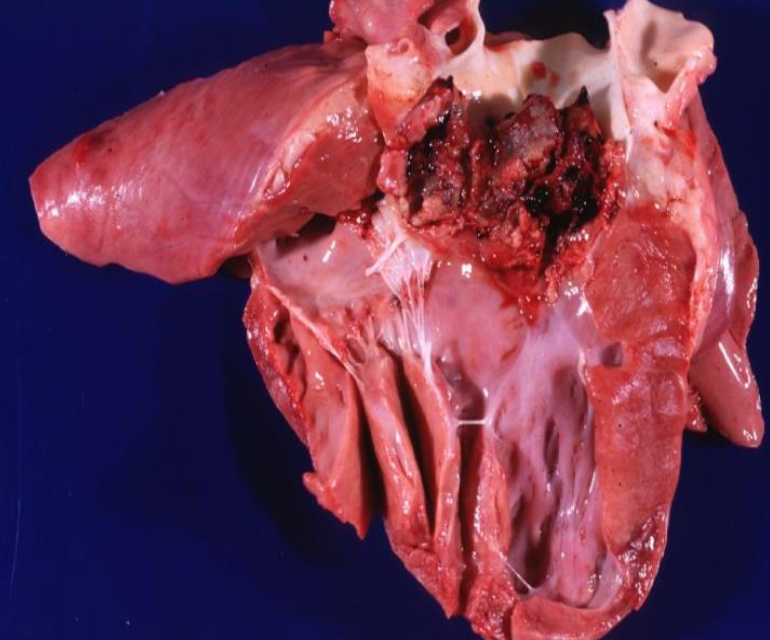
Pig with signs of dyspnoea and pyrexia, with lameness and neck pain. Describe the gross lesion.
organ = heart
location = aortic valve
distribution = multifocal to coalescing / focally aggregated
size = 3-5cm
shape = irregular, nodular and clusters
colour = dark red
consistency = firm to friable
what is the aetiology and morphological diagnosis?
history - pig with dyspnoea and pyrexia, lameness and neck pain
gross lesion - multifocal to coalescing, dark red, irregular and nodular lesion in the aortic valve, 3-5cm with a firm and friable consistency
histology - inflammatory cells (neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells) in the valve, thrombus, bacterial colonies
morphological diagnosis - endocarditis, valvular, subacute , severe, with bacteria
possible aetiologies - E. coli