Lymphatics I
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
intracellular fluid (ICF)
abt 2/3 of the total body fluids
extracellular fluid (ECF)
a third of total body fludis
blood (plasma) and interstitial (tissue) fluid
provides the nutrients cells need
interacts with ICF across the plasma membrane
body fluid distribution
hydrostatic and osmotic forces control the movement of fluid between the tissue spaces and the capillaries, affecting blood volume
urine formation and water intake (drinking) also affect blood volume
total volume of intracellular and extracellular fluid is normally maintained constant by a balance between water loss and water gain
hydrostatic pressure (HP)
pressure exerted by blood within capillaries or by tissue fluids
capillary hydrostatic pressure is ~34mmHg (arterial end) and ~14mmHg (venous end)—causes fluid to filter out of the capillaries into the tissues
tissue hydrostatic pressure varies, low, ~1mmHg~opposes filtration out of capillaries
net hydrostatic pressure
= capillary HP - tissue HP
favors the movement of fluid out of the capillaries
capillary filtration
glucose, comparably sized organic molecules, inorganic salts, and ions are filtered along with water through the capillary pores into the tissue fluid
larger molecules like plasma proteins retained in the capillaries
plasma protein concentration (6 to 8 g/100 mL) is therefore higher than interstitial fluid protein concentration (2 g/100 mL)
colloid osmotic pressure
pressure exerted by proteins dissolved in a fluid
draws fluid in
plasma colloid osmotic pressure (20mmHg) greater than tissue fluid colloid osmotic pressure (~0mmHg) due to greater concentration of proteins in the plasma as compared to tissue fluid
oncotic pressure
the difference between plasma colloid osmotic pressure and tissue fluid colloid osmotic pressure
oncotic pressure = 20mmHg
favors the movement of fluid into the capillaries
starling forces
opposing forces of hydrostatic pressure and oncotic pressure that predicts movement of fluid across capillary membranes
fluid movement factors
(HPc - HPt) - (OPc - OPt)n
net hydrostatic pressure
(HPc - HPt)
(OPc - OPt)
net oncotic pressure
HPc
hydrostatic pressure in capillary
HPt
Hydrostatic pressure of tissue fluid
OPc
Colloid osmotic pressure of blood plasma
OPt
Colloid osmotic pressure of tissue fluid
distribution of fluid across capillary walls
favor movement of fluid out of the capillaries at the arteriole end (positive value) and into the capillaries at the venule end (negative value)
only 85-90% of fluid filtrate returs to capillaries at venule end
10-15% remains in the tissue spaces and re-enters venous system via lymphatic vessels
oedema
excessive accumulations of tissue fluids
oedema causes
high arterial blood pressure
venous obstruction
leakage of plasma proteins into interstitial space
decreased plasma protein concentration
obstruction of lymphatic drainage
the lymphatic system
network of organs and vein-like vessels that recover fluid lost from the circulatory system
the lymphatic system functions
return fluid to the bloodstream
immune defense
fat transport
return fluid to the bloodstream
returns ~3L of protein containing fluid from the interstitial fluid to the blood
immune defense
inspect it for disease agents and active immune responses
macrophages filter lymph, and b & t lymphocytes provide immunity
fat transport
transport fat and fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) from GI to blood
the lymphatic system fluid recovery
fluid continually filters from the blood capillaries into the tissue spaces
blood capillaries reabsorb 85%
15% (2-4L/day) of the water and about half of the plasma proteins enter the lymphatic system and then are returned to the blood
helps restore the fluid balance
primary lymphatic organs
where lymphocytes are formed and mature
provides an environment for stem cells to dicide and mature into B- and T-cells
primary lymphatic organ examples
bone marrow
thymus
secondary lymphatic organs
the tissues are arranged as a series of filters monitoring the contents of the extracellular fluids
i.e. lymph, tissue fluid, and blood
where lymphocytes are activated
secondary lymphatic organ examples
spleen
lymphnodes
tonsils
peyer’s patches
mucosa associated lymphoid tissue
largest lymphoid organ
spleen
MALT
mucosa associated lymphoid tissue
lymph
refers to the fluid that enters the lymph cappilaries from the interstitial fluid
similar in composition to blood plasma with less protein and more fat
looks clear or faintly opalescent
the excess water and solutes that filter out of the capillary are picked up by the lymph vessels and returned to the circulation
lymphatics (lymphatic vessels)
structure is similar to veins but thinner, with numerous valves and associated with lymph nodes
extensively located, and normally arrange in 2 sets—one deep and one superficial
they normally carry lymph through lymph nodes and to larger lymphatic ducts
afferent vessels go into into a lymph node, and efferent vessels go OUT of lymph nodes
NO lymph vessels in the CNS, bone marrow, bone, and cornea
lymphatic trunks
structured like veins
collect lymph from lymphatic and deliver it to the large lymphatic ducts, which are structured like large veins carrying lymph into the subclavian veins
right lymphatic duct
1.25cm long
junction of the right jugular vein and the right subclavian vein
drains the upper right limb, the right side of the head, neck, and thorax
thoracic duct
38-45cm long
extends from L2 to the left subclavian vein
lies in the midline of the thorax, near the aorta
begins as a dilation called the cisterna chylii
drains lymph from the rest of the body
lymphoid cells
lymphocytes
macrophages
dendritic cells
reticular cells
lymphocytes
arise in red bone marrow then migrate to other tissues to become immunocompetent
B lymphocytes
T lymphocytes
B lymphocytes
produce antibody secreting plasma cells
T lymphocytes
fight antigens directly and regulate the immune response
macrophages
phagocytose antigens and help to activate T cells
dendritic cells
antigen presenting cells found in mucosal membranes and in the skin
reticular cells
connective tissue cells that produce reticular fibers for the stroma that support other lymphoid cells in lymphoid tissue
lymphoid tissue
made of reticular fibers (stroma) and lymphoid cells (macrophages, lymphocytes)
diffuse lymphoid tissue
lymphoid follicles
places where lymphoid nodules can be found: lymph nodes, peyer’s patches, appendix
diffuse lymphoid tissue
small areas of un-encapsulated tissue found in most organs and in lamina propia of mucous membranes
lymphoid follicles
like diffuse tissue, but has a greater density of fibres
swollen glands
swollen cervical nodes
may have tenderness or pain
response to bacterial or viral infection, rarely due to cancer
sentinel node
the first few lymph nodes to which cancer spreads
in sentinel node biopsy, a tracer material is used to help the surgeon find the sentinel nodes during surgery
the sentinel nodes are removed and tested in a lab
if the sentinel nodes are free of cancer, then cancer probably hasn’t spread
lymphatic obstruction
lymphedema
myxedema
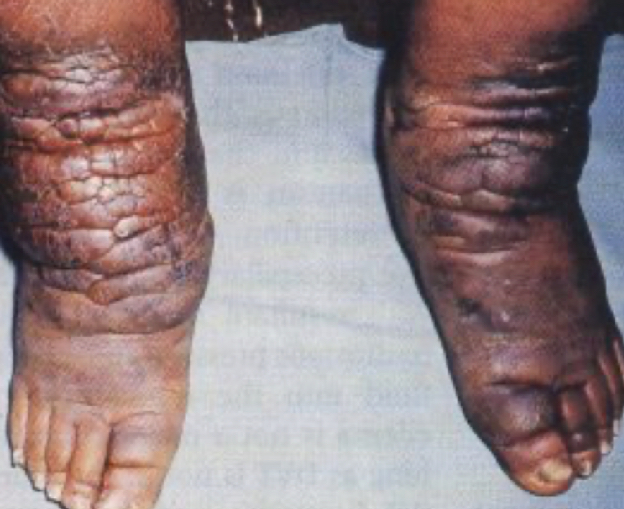
filariasis
lymphedema
swelling due to build-up of lymph fluid in the body
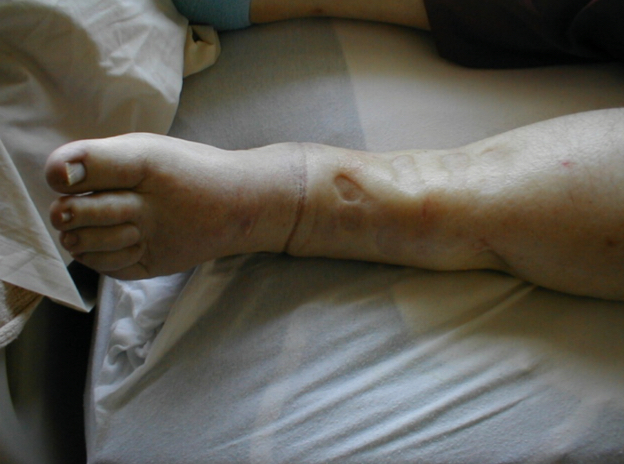
myxdema
hypothyroidism that leads to swelling and pretibial skin changes

filariasis
a parasitic disease caused by microscopic, thread-like worms