AP Psychology Unit 5 (Learning)
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mrs. Weck 2025-26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Behavioral Perspective
The study of how observable behaviors are learned through interactions with the environment
Classical Conditioning
When a stimulus becomes associated with another stimulus that automatically triggers a response
If a dog hears a bell before getting food, it eventually salivates when it hears the bell even with no food
Acquisition
The early stage of learning when a response is first being linked to a new stimulus
When the dog starts to learn that the bell predicts food and begins salivating
Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS)
A stimulus that naturally & automatically triggers a response without any learning needed.
After a dog smells food (UCS), it starts to salivate (UR)
Unconditioned Response (UR)
A natural, automatic reaction to an unconditioned stimulus without any learning needed.
A dog starts to salivate (UR), when it smells food (UCS)
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
A former UCS that now triggers a learned response
A whistle (formerly a UCS) now makes a dog salivate (CR) because it associates the sound with food
Conditioned Response (CR)
A learned response that occurs when a CS is presented
A dog salivates (CR) after hearing a whistle (CS) because it associates the sound with food.
Extinction
The process by which a CR weakens & eventually disappears when the CS is repeatedly presented without the US
A dog stops salivating (CR) after hearing a whistle (CS) because food (US) stops being provided.
Spontaneous Recovery
The reappearance of a previously extinguished CR after a period of rest
A dog begins to salivate (CR) again after having no reaction to a whistle (CS) for a few weeks
Stimulus Discrimination
The ability to differentiate between similar stimuli and respond differently to them
A dog only salivates when hearing a referee whistle, not an Aztec death whistle
Stimulus Generalization
When a learned response occurs to similar stimuli, not just the CS
A dog salivates when hearing the sound of any whistle, not just a referee whistle (CS)
Higher-Order Conditioning
When a new, neutral stimulus becomes another CS by being paired with an already existing CS
After establishing a whistle as a CS, a red light is turned on along with the sound of the whistle during the dog’s feeding time. Now, when the dog sees red lights, it starts to salivate as well.
Counterconditioning
Changing a CR to something more desirable by pairing it with a different stimulus
A child who fears dogs is told to practice breathing techniques when around them. Over time the fear (CR) is replaced with a calmer response.
Taste Aversion
A strong dislike for a food that develops after getting sick from it
One-Trial Conditioning
Learning that happens after just one pairing of two things
A child gets bitten by a dog and now avoids being near them at all costs
Biological Preparedness
The theory that organisms are naturally predisposed to learn certain fears/associations quickly because they helped their ancestors
Habituation
Decreased response to a stimulus after repeated exposure
You stop noticing the loud city sounds after living in New York for a few months
Law of Effect
Behaviors followed by favorable outcomes are more likely to be repeated, while behaviors followed by unfavorable outcomes are less likely to be repeated
Operant Conditioning
A type of learning in which behaviors are strengthened or weakened by reinforcement or punishment
Positive Reinforcement
Increasing a behavior by adding something pleasant
Giving a kid a sticker for participating in class causing the kid to be more likely to participate again
Negative Reinforcement
Increasing behavior by removing something unpleasant after the behavior occurs
Buckling your seatbelt to make the annoying beeping stop causing a person to be more likely to buckle up
Positive Punishment
Decreasing a behavior by adding something unpleasant
A teacher gives extra homework to students who talk, making them less likely to talk during class again
Negative Punishment
Decreasing a behavior by removing something pleasurable
A teen loses phone privileges after missing curfew, making them less likely to break curfew again
Primary Reinforcers
Rewards that are naturally satisfying because they meet basic biological needs
using food, water, warmth, etc. as rewards to increase behaviors
Secondary Reinforcers
Rewards that are satisfying because they are linked to primary reinforcers or other desirable outcomes
Money (can be used to buy food)
Trophies (prove your skill to others)
Shaping
Gradually teaching a behavior by rewarding small steps that get closer & closer to a desired behavior
A coach praises a gymnast for first touching her toes, then for going lower, then for doing a full split as desired
Instinctive Drift
When animals go back to their natural instincts instead of learned behaviors through training
A dolphin who was taught to jump through hoops now misbehaves because it wants to hunt fish
Superstitious Behavior
When behaviors are repeated because a person thinks they cause a certain outcome, even when they don’t
Learned Helplessness
When when someone stops trying to change a situation because past failures taught them that no matter the effort, it won’t work
Continuous Reinforcement
Reinforcing a desired behavior every time it occurs
Partial Reinforcement
Reinforcing a behavior only some of the time it occurs (leads to slower extinction, but less consistent responding)
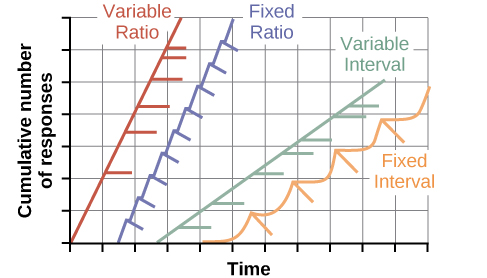
Fixed Ratio
A reinforcement schedule where a reward is given after a set number of responses
A game rewards players with a treasure chest after every 10 levels they complete
Variable Ratio
A reinforcement schedule where a reward is given after an unpredictable number of responses
Slot machines pay out after a random number of lever pulls which keeps gamblers playing because the next pull might be the winner
Variable Interval
A reinforcement schedule where a reward is given after unpredictable amounts of time
Social media likes (reward) come at random times, so a man keeps checking Instagram throughout the day
Fixed Interval
A reinforcement schedule where a reward is given after a set amount of time has passed
An office worker is paid every two weeks
Cognitive Maps
A mental representation of spatial layouts
A freshman asks for directions to the cafeteria, & a senior points them to the right location using their mental map of the school
Latent Learning
Learning that happens without any obvious reinforcement & only shows up later when needed
A freshman learns the layout of his school by merely walking to classes. Eventually, he needs to take a shortcut he has not used before and knows exactly where to go.
Insight Learning
A sudden realization to the solution of a problem (the answer just “clicks” without trial and error)
Vicarious Conditioning
Learning by observing the consequences of someone else, not through your own direct experience.
Social Learning Theory
People learn behaviors by observing & imitating other people
Scalloped Graph (Fixed Interval)
Post-reward pause: Decreased behavior after a reward is given because additional responses are not rewarded with immediate reinforcement
Increasing response rate: Behavior increases as reinforcement gets closer until a reward is given
ex: A person works slowly after payday (PRP), but works harder as the next paycheck approaches (IRR)