Chemistry : C7
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a hydrocarbon?
A covalent compound made up of only carbon and hydrogen atoms
What are alkanes, what are their bonds, how are they identified, what is their formula?
Alkanes
Single covalente bonds
Ends in -Ane
CnH2n + 2 =4 N for every carbon there are double hydrogens and 2 extra
What are alkenes, what are their bonds, how are they identified, what is their formula?
Alkenes
Joined by a double covalent bond
Ends in -ene
CnH2n = for every carbon there are double hydrogens
How are single bonds shown?
C - C
How are double bonds shown?
C = C
What are the first 4 alkanes?
Methane
Ethane
Propane
Butane
Pentane
Hexane (shape names from now on…)
What are the first 4 alkenes?
Ethene
Propene
Butene
Pentene
Hexene (shape names from now on..)
What is complete combustion?
Burning with a good supply of oxygen - burning to a blue flame
What us incomplete combustion?
Burning with a limited supply of oxygen. IT will burn at an orange flame.
What is the formula for combustion?
Hydrocarbon + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water
Define crude oil
Oil found in the ground formed from partially decayed plants and animals, under mud, millions of years ago.
It is a non-renewable fossil fuel.
What are the uses of crude oil?
diesel oil
Kerosene
Petroleum
Power stations
Polymers
Lubricants
Solvents
Detergents
What are the properties of smaller hydrocarbons?
more runny (less viscous)
Have lower boiling points
Very flammable
What are the properties of longer hydrocarbons?
less runny (more viscous)
Higher boiling points (due to more bonds)
Less flammable
Name each type of crude oil from smallest to longest hydrocarbon
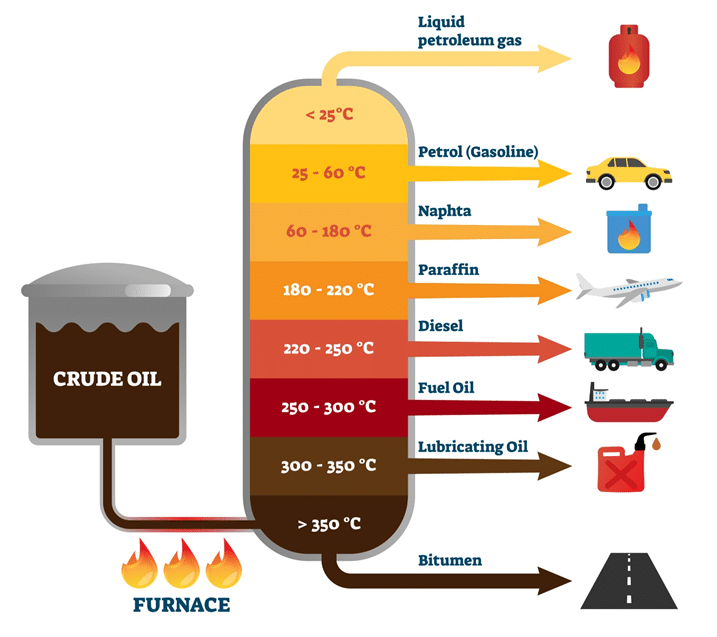
Define fractional distillation
Separates fractions which contain hydrocarbons of different lengths. This is because each fraction has a different boiling point
Define cracking
The breaking down of long hydrocarbon chains into smaller useful alkanes and alkenes, a thermal decomposition process
How does fractional distillation occur?
Crude oil is extracted from oil fields below the ground
It is heated in a fractionating tower
The liquid evaporates and the vapour condenses at different temperatures
The light fractions have lower boiling points and come out first
The fraction with the lowest boiling point exits the tower
The fraction with the lowest boiling point comes at the bottom of the tower
This process produces a range of useful oils and fuels
What is the formula for cracking?
Long chain alkane = shorter alkane + alkene
Make sure carbon atoms are equal
Define saturated and unsatured
Saturated = all single bonds = alkanes
Unsaturated = all double bonds = alkenes
How do you test for alkenes?
Place orange bromine water into an ‘alkene’ solution and if present the solution will turn colourless
What are the 2 types of cracking?
Catalyst cracking
Steam cracking
How do you carry out catalyst cracking?
Heat the molecule at a high temperature (400 degrees) until it vaporises
Combine the vapour with aluminum oxide catalyst (pass over it)
Hydrocarbons split into smaller useful alkanes molecules on the surface of the catalyst
How do you carry out steam cracking?
Heat the molecule at a high temperature (400 degrees) until it vaporises
Hydrocarbon vapor is mixed with steam and heated to a high temperature
The heating splits the bonds and the molecules split