Art Exam Studyguide
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Shape
Element of Art: two-dimensional enclosed area that is defined by lines, colors, or textures. Shapes can be geometric (squares, circles, triangles) or organic (free-form, natural shapes).
Line
Element of Art: a moving point through space, and is used to create shapes, forms, and texture. Artists use a wide variety of lines, such as horizontal, vertical, and diagonal, as well as straight, curved, and zigzag, to define edges and suggest movement.
Value
Element of Art: the lightness or darkness of a color, which helps create depth and contrast in art.
Color
Element of Art: the property of an object that is produced by the way it reflects or emits light. It consists of three main elements: hue (the color name), value (lightness or darkness), and intensity (brightness or dullness)
Texture
Element of Art: The look or feel of a surface, existing as actual which you can physically touch (like rough bark or smooth metal), or implied (visual). Created through techniques like line, shading, and paint application. It adds realism, emotion, and depth, making objects seem soft, hard, bumpy, or shiny
Form
Element of Art: the three-dimensional quality of an object, defined by its volume and shape, often created through the use of light and shadow in art.
Space
Element of Art: the area around, between, and within objects in a composition. It can be positive (space taken up by objects) or negative (the space around and between them). You can use the negative and positive space to measure the object and get an accurate replica drawing of it.
Balance
Principle of Design: the principle of arranging visual elements (like shapes, colors, textures) to create a sense of stability, where visual weight is distributed evenly to guide the viewer's eye
Contrast
Principle of Design: the use of differing elements (such as light and dark colors, diverse textures, or varying shapes) in a composition to create visual interest and focus. Contrast helps to highlight important areas and place emphasis on specific elements, enhancing the overall composition.
Line
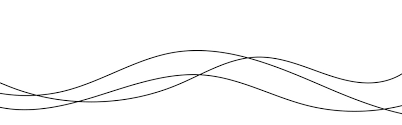
Drawing Technique: create shapes, forms, and texture. Artists employ various types of lines, such as horizontal, vertical, diagonal, straight, curved, and zigzag, to define edges,

Accent Line
Drawing Technique: varied line weight (thickness/darkness) to create depth, emphasis, and form in a drawing

Contour Line
Drawing Technique: defines an object's edges and surface ridges, creating the illusion of 3D form on a 2D surface by following the contours of the subject, capturing its shape and volume.

Hatch Line
Drawing Technique: parallel lines to create tonal, shading, or texture effects, with varying density and direction indicating light, shadow, depth, or material
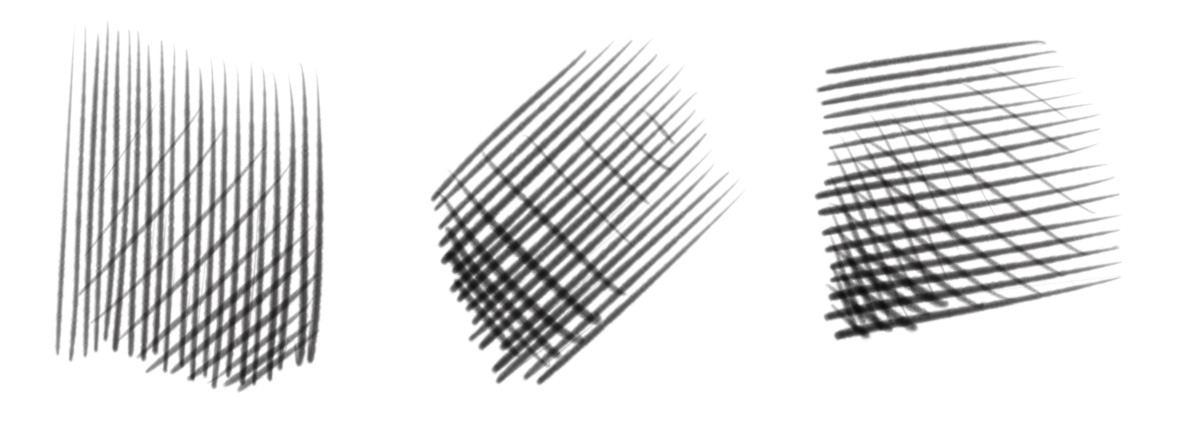
Crosshatch
Drawing Technique: layering intersecting lines to create textures, shading, and depth by varying line direction, density, and overlap.
Scumble

Drawing Technique: a method of applying color or tone by using circular or random, overlapping strokes to create a soft, textured effect.
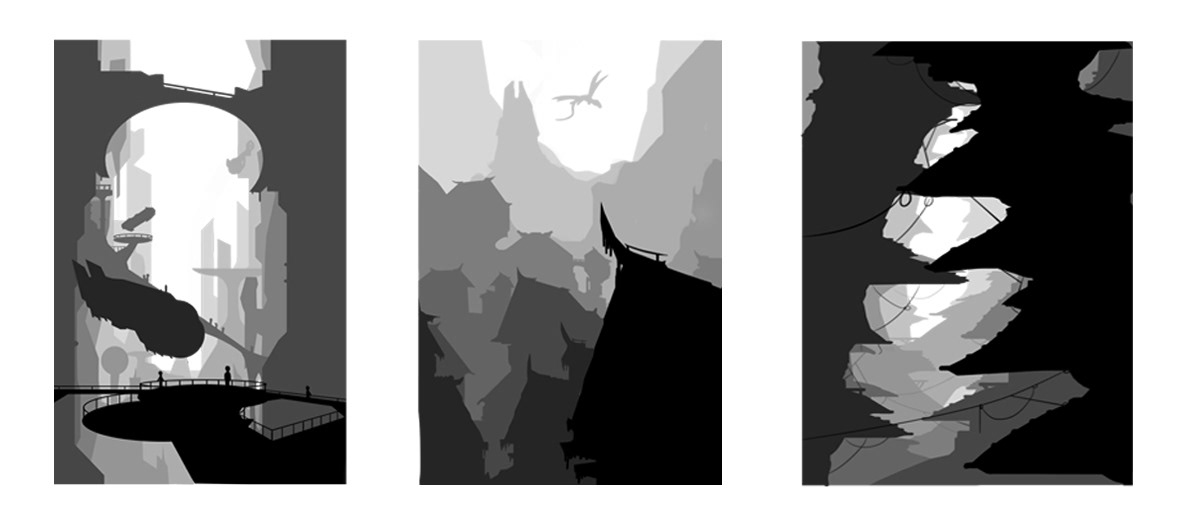
Value Study
Drawing Technique: simplifying a scene into shapes of light and dark to understand composition, guide the eye, and add dimension. Often starting with just 2-3 values (black, white, gray) to block out big shapes before adding detail.
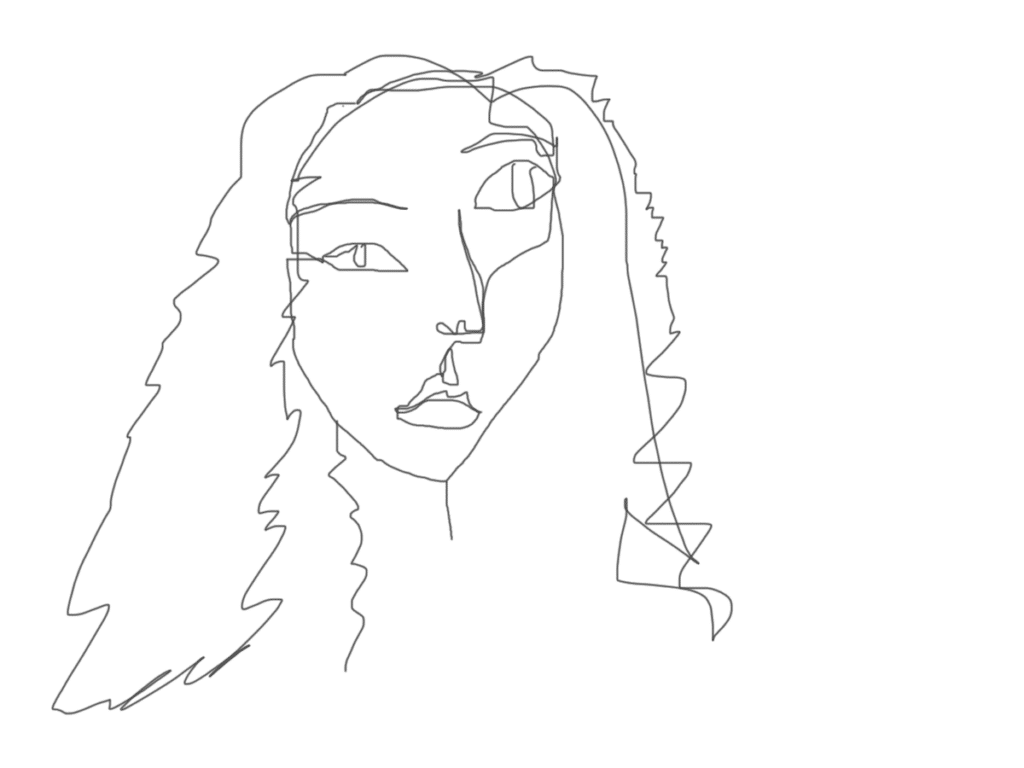

Blind Contour
Drawing Technique: a method of drawing where the artist sketches the outline of a subject without looking at the paper, focusing solely on the subject's contours, often using a single, continuous line to develop observation skills, hand-eye coordination, and loosen up your drawing style by bypassing the critical brain
Postive/Negative
Drawing Technique: a method that utilizes the contrast between the positive shapes (the subject) and negative spaces (the background) to create a balanced composition, enhancing the overall visual impact.
Graphite, Ebony, Generals Extra Black
Mediums: types of pencils known for their varying hardness and darkness, commonly used for creating detailed sketches and shading in drawings.
Sketch and Wash
Medium: water soluble graphite performs like traditional graphite when dry. If you run a wet brush over the pencil lines, however, they completely dissolve, and you can brush the liquid graphite throughout your design like paint
Tempera Paint
Medium: a fast-drying paint made from colored pigments mixed with a water-soluble binder, such as egg yolk, typically used for its vivid colors and smooth application.
Oil Pastel Resist
Medium: an art technique where oil pastels, due to their oil/wax base, repel water-based paints like watercolors or acrylics, creating a separation effect where the paint doesn't cover the pastel marks
Watercolor color pencils
Medium: Look like regular colored pencils but contain water-soluble binders and pigments that dissolve with water.
Markers, Micron, Sharpie, Posca
Medium: alcohol or water-based inks for vibrant illustrations, blending, and detailed work, featuring dual tips for broad and fine strokes, and serving as essential mediums for sketching, design, and mixed media art
Colored Pencil
Medium: thin, pigmented core (wax, oil, or water-soluble)
Color Pencil Layering
Art Medium: Layering colors together using colored pencil to get the desired color
Colored Pencil Saturation
Art Medium: The intensity and richness of color achieved by applying multiple layers of colored pencil, resulting in a vibrant and deep hue. The thing is from color pencils
Shade
The darkness of a color. Add more black to increase the shade
Tint
The whiteness of something. Add white to increase tint
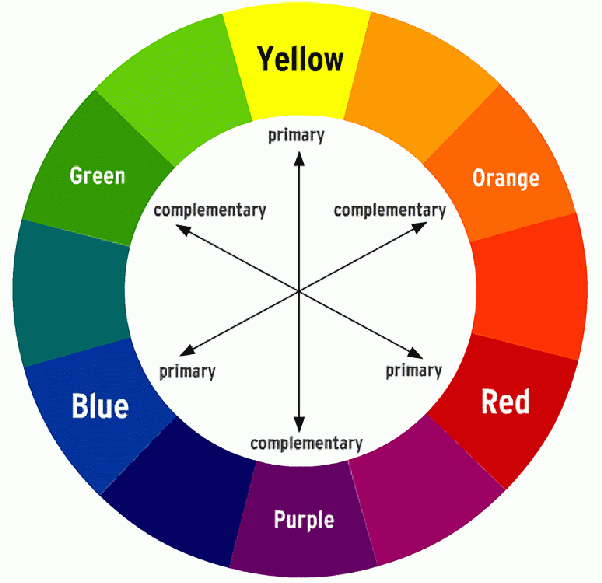
Complimentary
pairs (like red/green, blue/orange, yellow/purple) directly opposite on the color wheel, creating high contrast that makes them appear brighter side-by-side or mix to form neutral grays/blacks
Grid Portrait
Portrait made using the grid method; an art technique that involves dividing a reference image into smaller sections using a grid, and then replicating those sections onto a separate drawing surface
Self Portrait
A portrait the artist made of themselves
Portrait
A painting, photo, sculpture, etc of a person or animal
Still Life
a work of art depicting inanimate subjects, typically with a story or title that adds meaning to it
Gradation/Gradient
the smooth, gradual transition between colors, tones, or values (lightness/darkness) to create depth, volume, and realism, guiding the viewer's eye through a composition
Tempera Paint
a fast-drying, water-based paint known for its bright, opaque colors
Craftsmanship
The quality of the artwork
Blending Stump
tightly rolled paper tool used to smudge, blend, and smooth out drawings
Ebony
The super duper super dark pencil
Sketchbook
The book that we practice drawing techniques in
Critique Step 1: Description
detailing what you see (subject, colors, shapes, medium, artist, title)
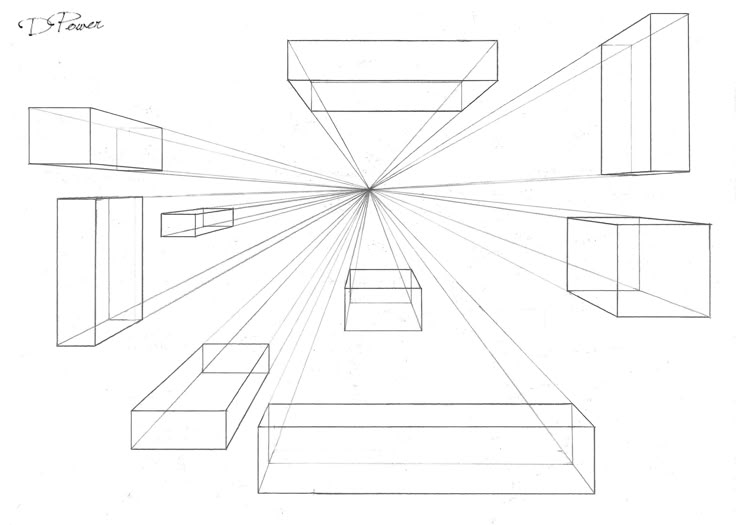
Linear Perspective 1 Point
Uses 1 vanishing point on the horizon line. Made up of horizontal, vertical, and orthogonal lines.
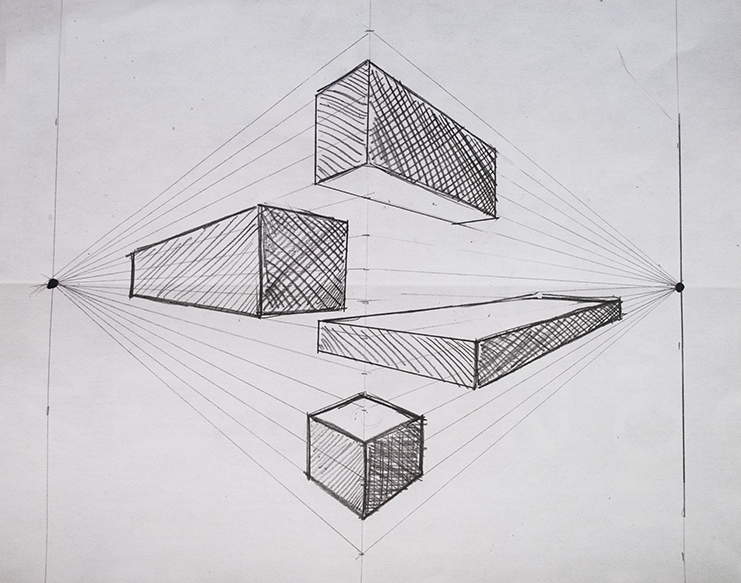
Linear Perspective 2 Point
Uses 2 vanishing points. Made up of vertical and orthogonal lines
Vanishing Point
the spot on the horizon line where lines seem to converge and disappear
Vertical Line
Line that goes up and down. In 1 and 2 point perspective
Horizontal Line
Line that goes side to side. Only in 1 point perspective
Horizon
a horizontal imaginary line that represents the viewers eye level where the sky meets the ground
Orthogonal Lines
diagonal parallel lines that recede from the viewer to the vanishing point. In all perspective points.