Ovarian Tumors: Surface Epithelial Tumors
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are ovarian tumors and what are the types?
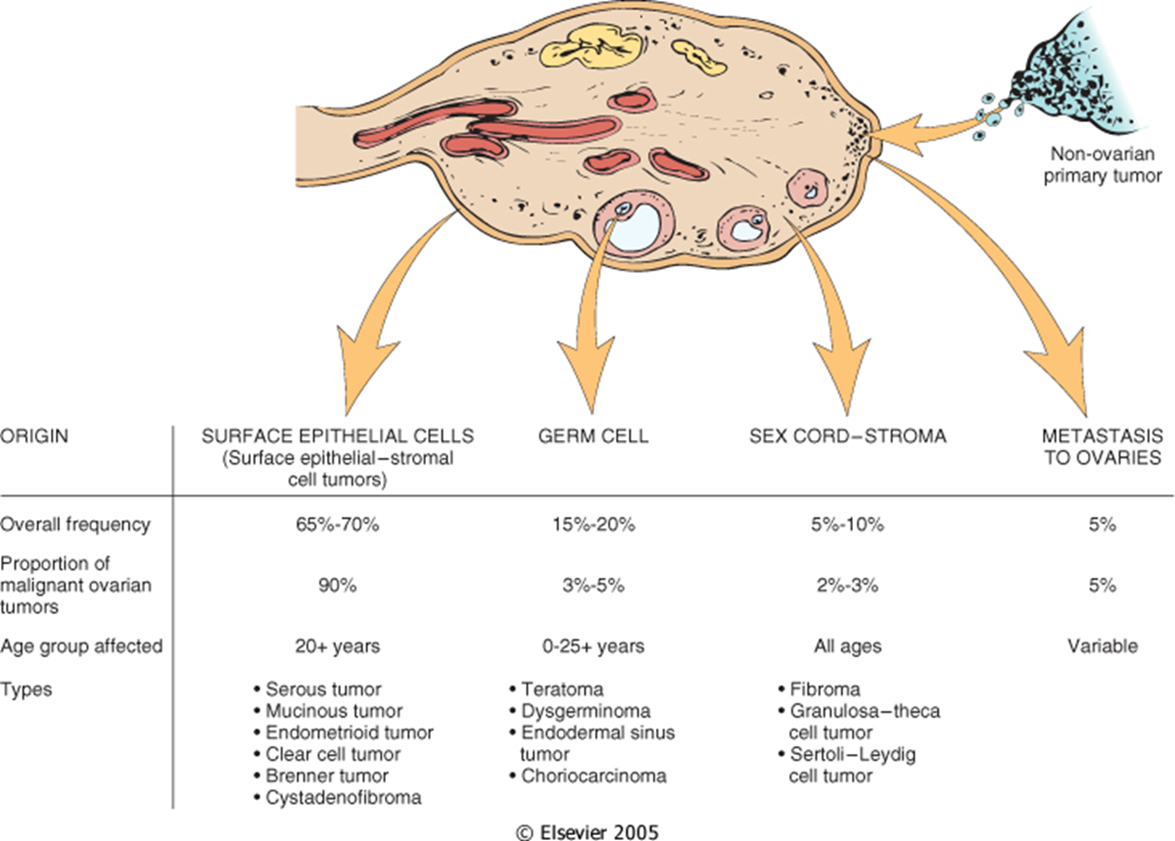
Ovarian tumors are often non-hormonally active and will reach large size before detection subdivided into four different tissues of origin
→ often times symptoms arise before clinical presentation of symptoms
Germ Cell
→ most common ovarian tumor in childrenSex-Cord Stroma
→ third most commonSurface Epithelium or the Mullerian Surface Epithelial Tumors
→ most common form of ovarian tumor, seen in patients older than 20Metastasis
→ least common
What are the five surface epithelial tumors of the ovaries? What marker is elevated in all of these?
Surface epithelial tumors are the most common ovarian tumor and are subdivided into five groups
Serous - the most common
serous cystadenoma
serous borderline
serous carcinoma
Mucinous
mucinous cystadenoma
mucinous borderline
mucinous adenocarcinoma
Endometroid
Clear Cell
Brenner
CA-125 is associated with surface epithelial tumors but is non-diagnostic
What are the characteristics of metastatic tumors to the ovaries?
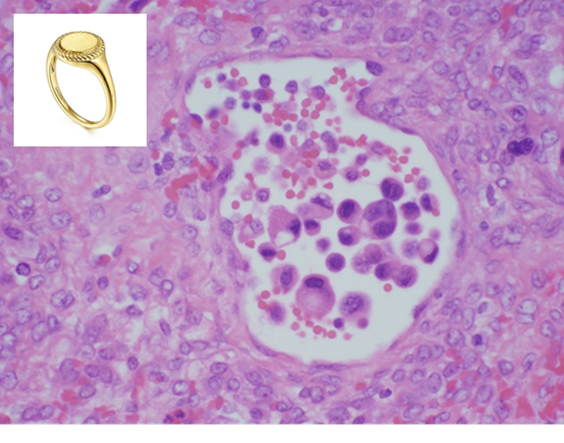
Metastatic tumors to the ovaries are the least common but will originate from organs adjacent to the ovaries like the uterus and fallopian tube
1) breast and colorectal are most common organs outside of the GU tract to the ovaries
2) can also be Krukenberg’s tumor where gastric carcinoma metastasizes to ovaries bilaterally
→ these are mucin producing and forms signet ring cells on histopathology
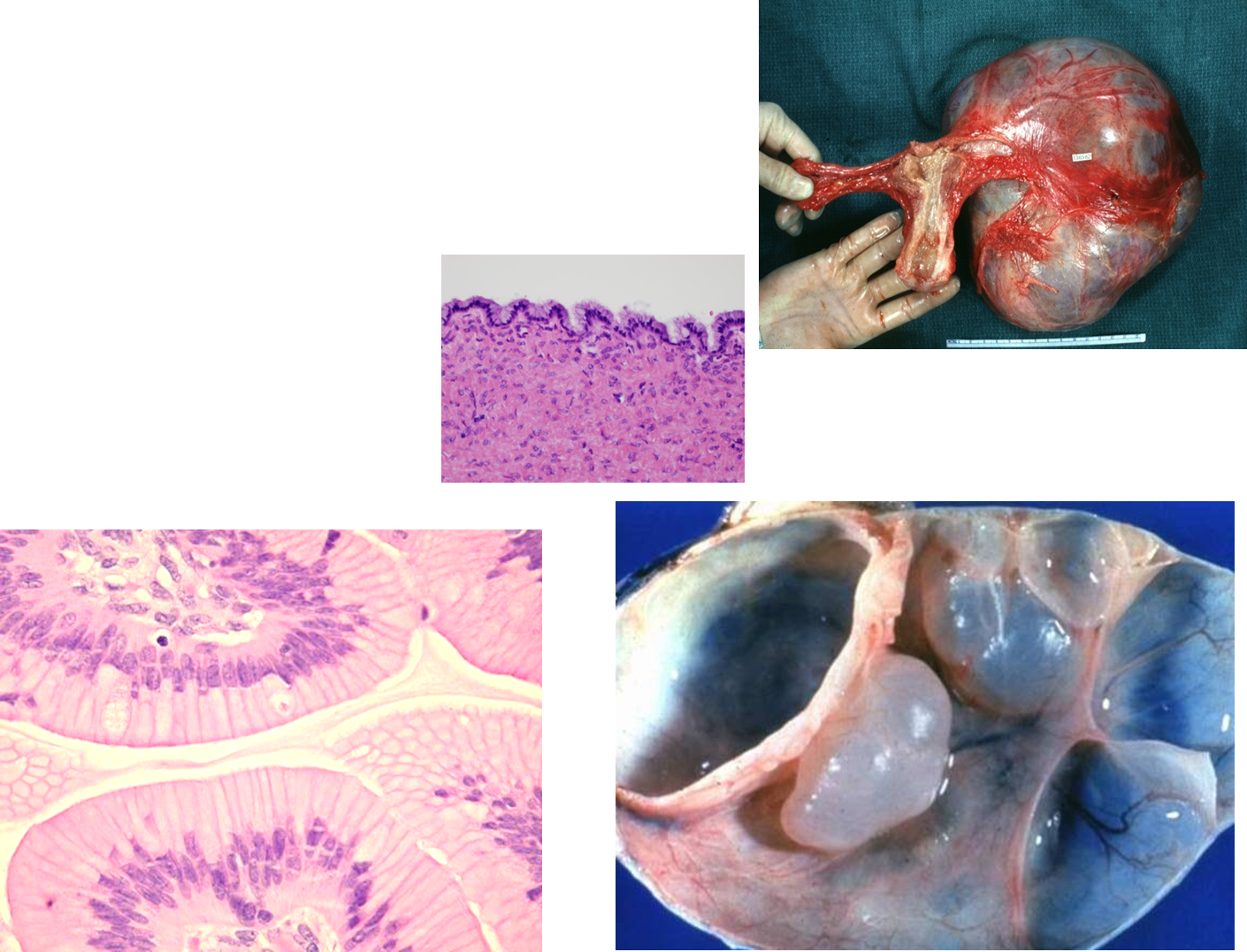
What is Serous Cystadenoma?
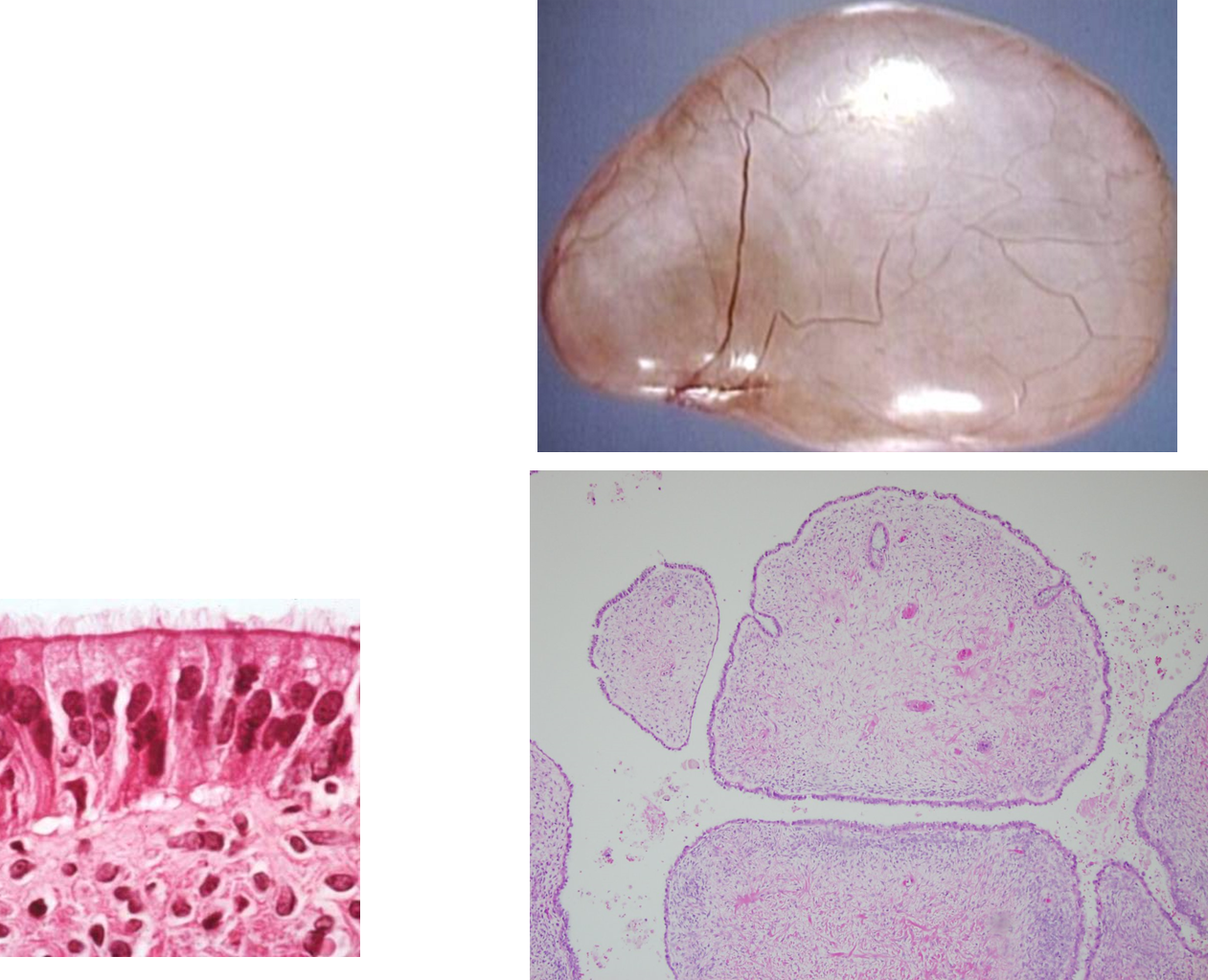
Serous Cystadenoma is a benign tumor of the simple serous lining
presents as a simple fluid filled cysts that histologically have bland looking cells
often looks like a small water-balloon
the epithelium mimics the fallopian tube epithelium: a single simple line of pseudostratified with cilia
What is Serous Borderline Tumor
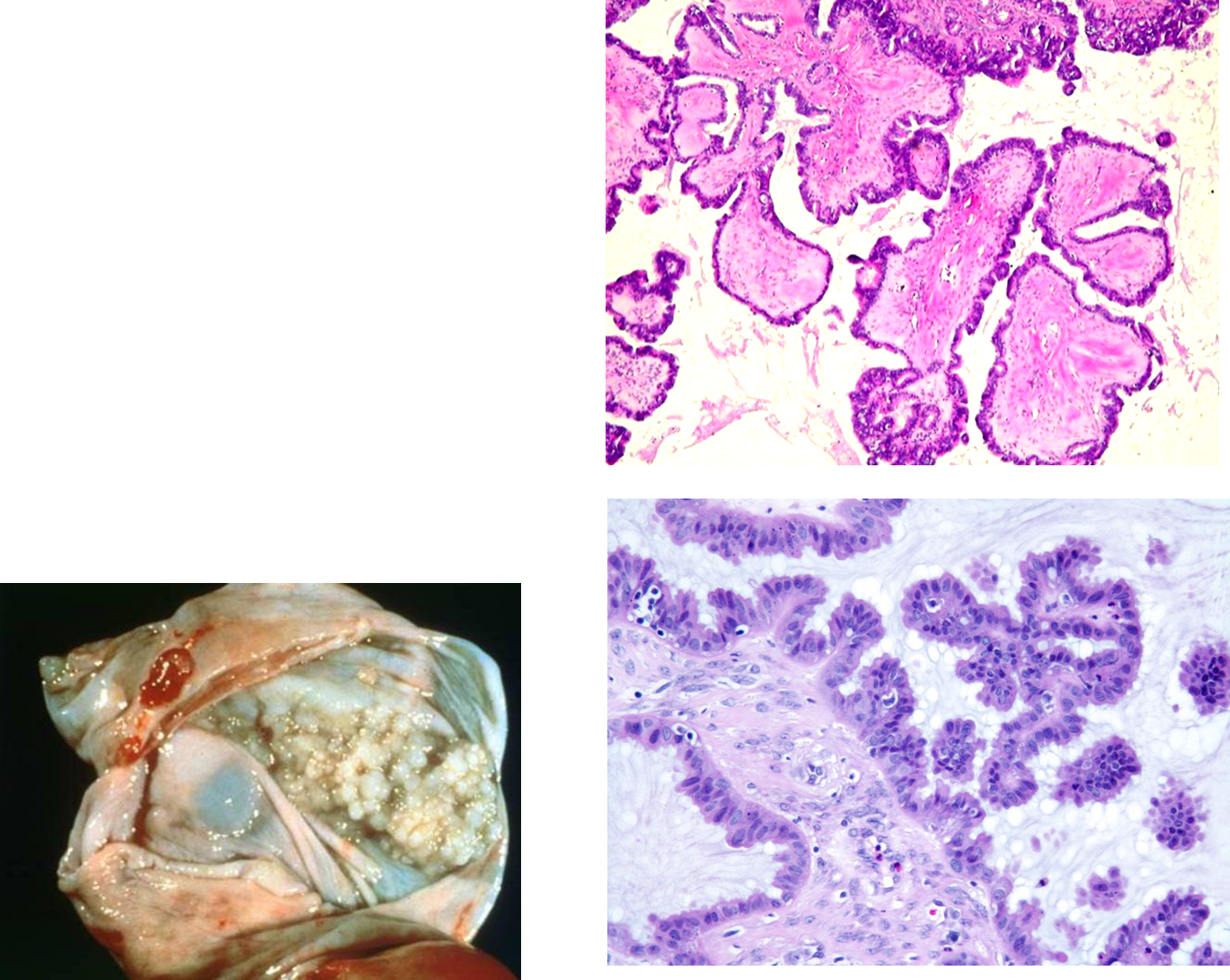
Serous Borderline Tumor is a superficial epithelial tumor of the ovaries
These are classified by papillae exophytic growth within the ovaries
→ these are non-invasive
What is Serous Carcinoma?
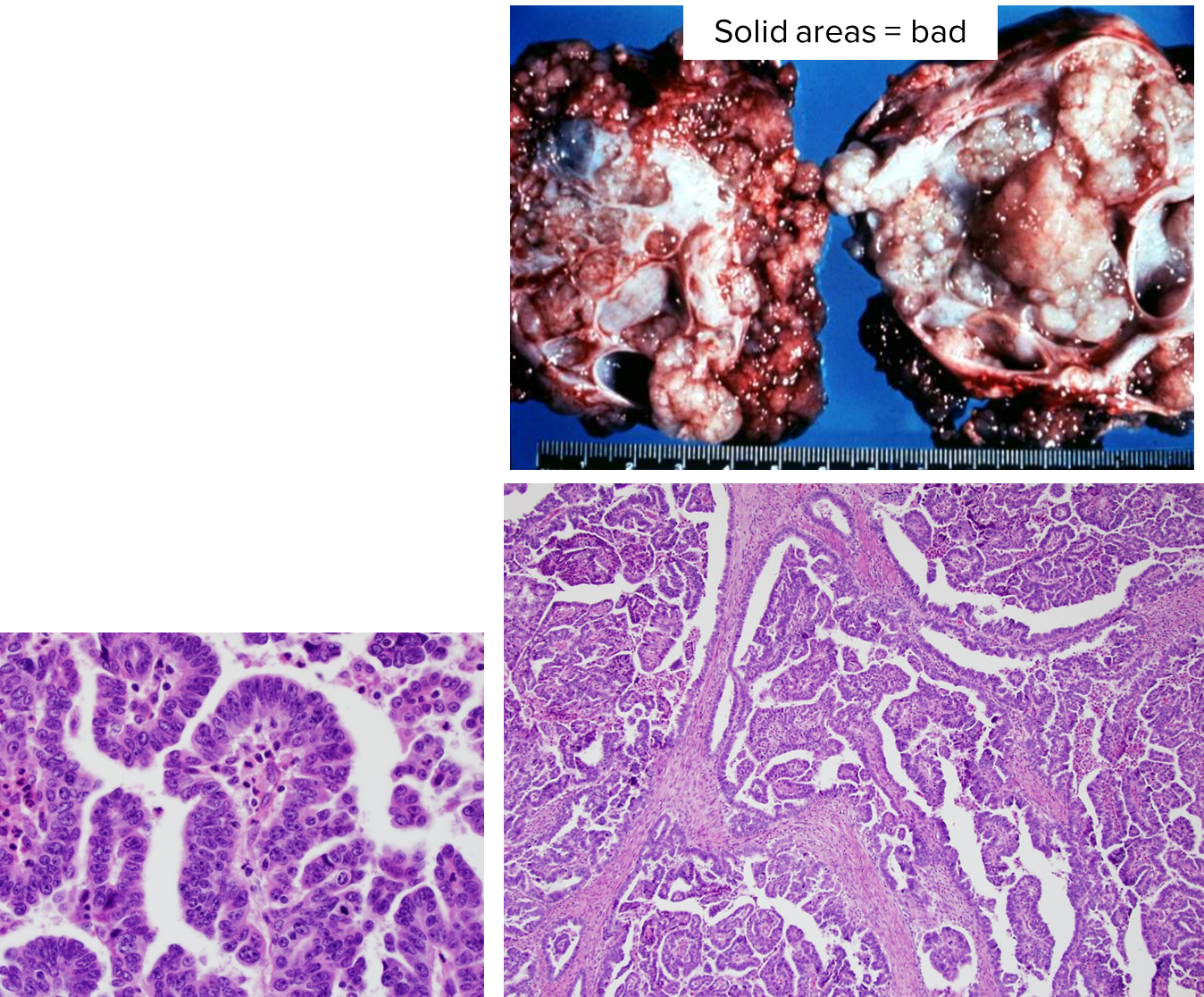
Serous Carcinoma is the most common malignant surface epithelial tumor
1. Often metastatic and bilateral in presentation
What is Mucinous Cystadenoma?
Mucinous Cystadenoma are benign large multi-loculated cysts
Typically presents unilaterally and are histologically simple and smooth
What is Mucinous Borderline Tumor?

Mucinous Borderline Tumors are cysts with proliferation of the epithelium and complex architecture
→ is non-invasive
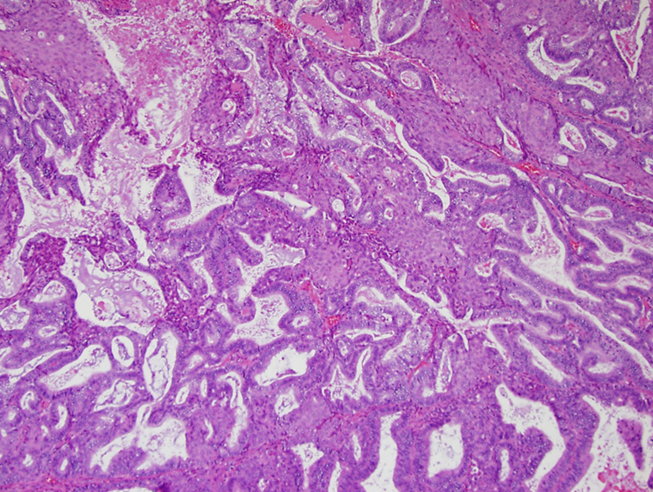
What is Mucinous Adenocarcinoma?
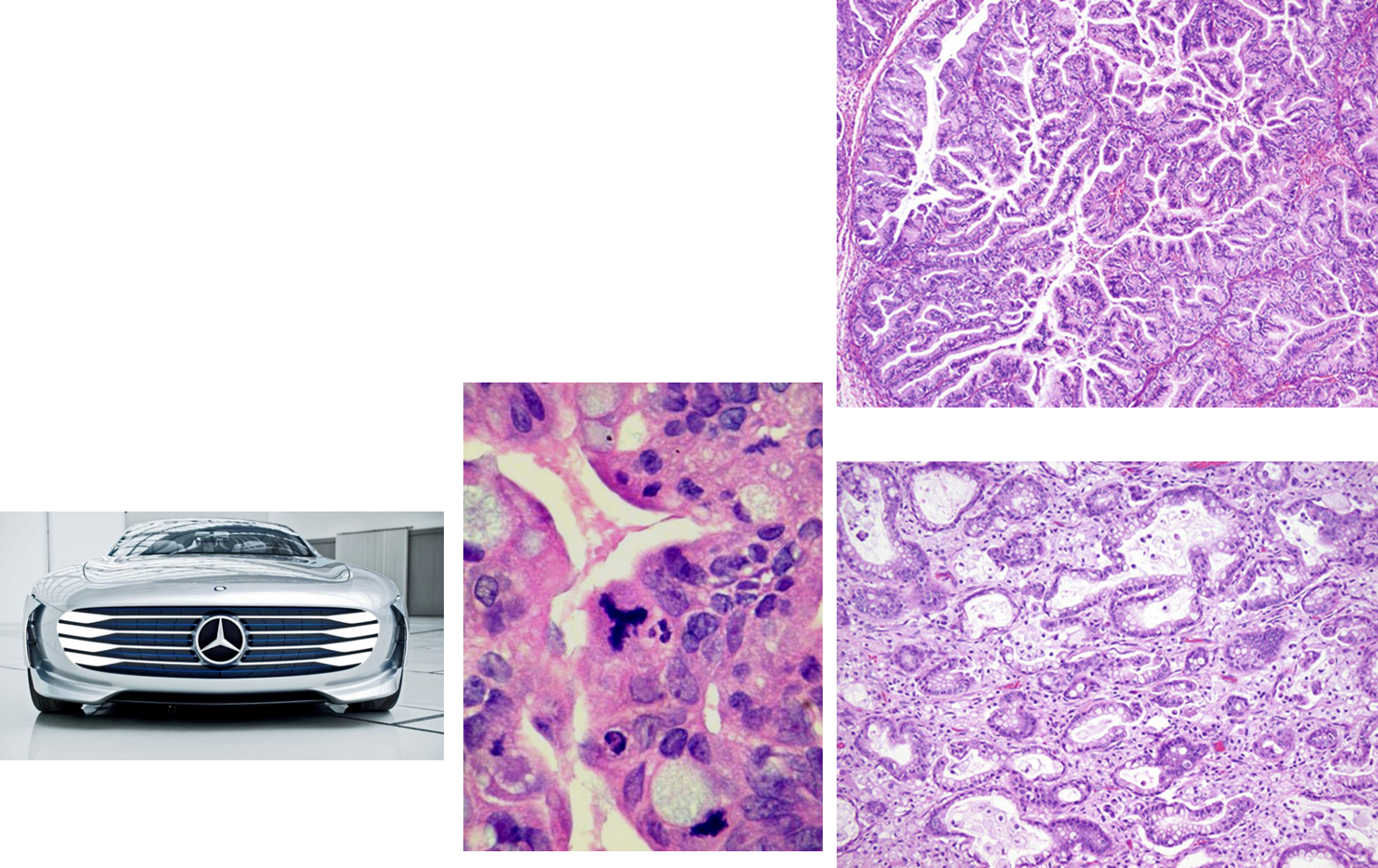
Mucinous Adenocarcinoma is an invasive form of mucinous superficial epithelial carcinoma
1. Often solid masses with complex nuclei and high levels of invasion
→ exhibits a tri-polar mitosis
What is Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma?
Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma mimics endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the uterus
→ associated with synchronous endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the uterus
What is Clear Cell Carcinoma?
Clear Cell Carcinoma of the ovaries are a always malignant and invasive for of superficial epithelial ovarian cancer
→ is often associated with endometriosis
What is Brenner Tumor?
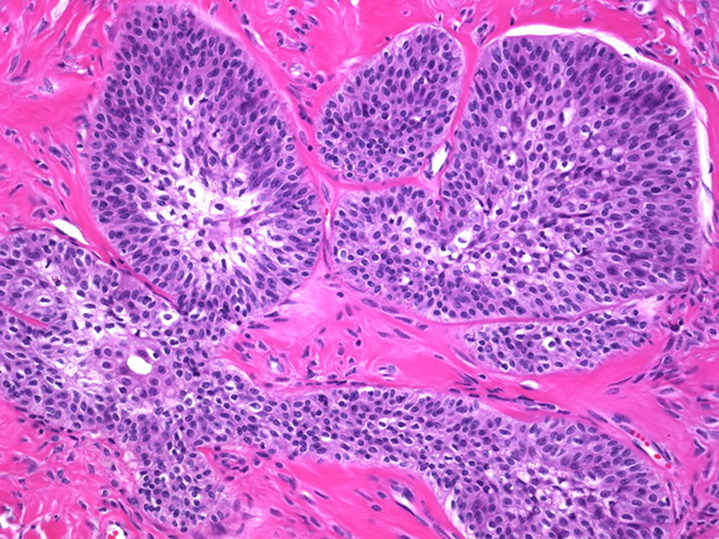
Brenner Tumor presents as urothelium nests within the ovary
→ are benign and are associated with mucinous cystadenoma