Week 3 - Biological Foundations of Behaviour - Neurons and Action Potentials
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
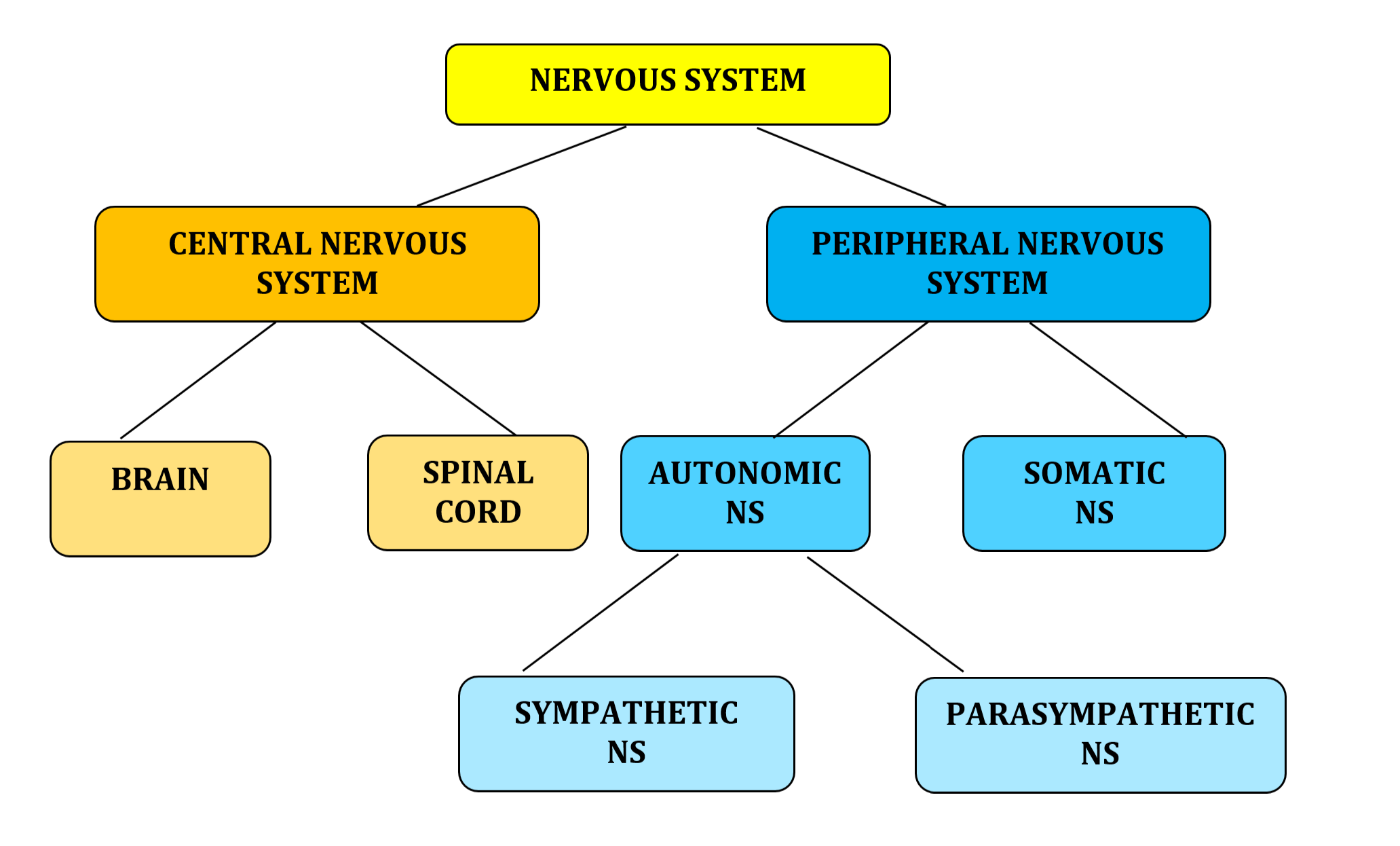
The Nervous System (create a chart)
Central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Nerves are always encased in bone
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Branches that go outwards from the spinal cord
No encased in bone
Types of systems
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Neurons
what are they
How do they operate
How to communicate with other neurons
The Types of neurons
3
are the basic units of the nervous system
Operate through electrical impulses
Communicate with other neurons through chemical signals
Types of neurons
Sensory neurons: toward the central nervous system
Motor neurosurgeon : away from the central nervous system to glands muscles, etc
Interneurons: between sensory and motor neurons (back and forward)
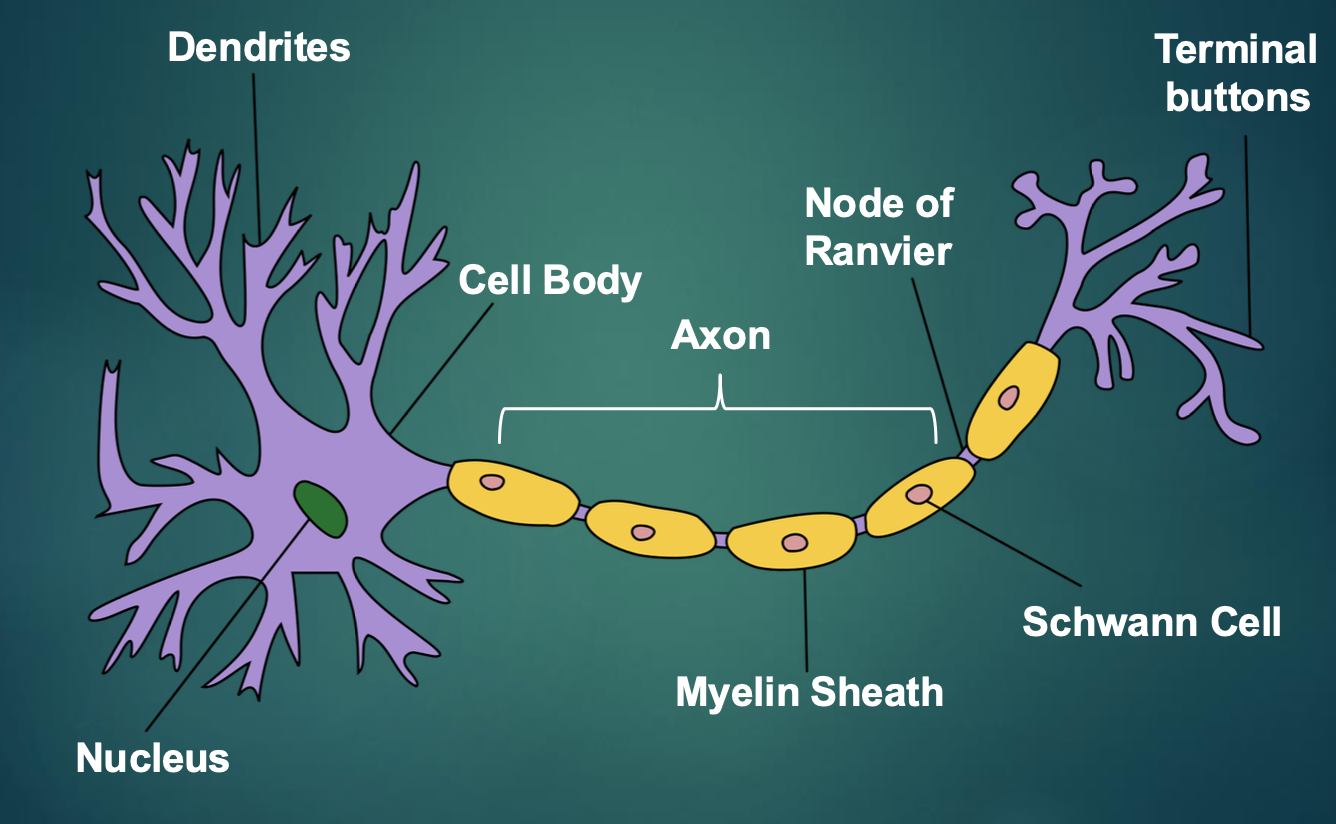
Parts of the neuron
Dendrites: branch-like sensations from the neuron and detect information from other neurons (increase receptive feel with the increase of branches)
Cell body: collecting all the information coming in from the thousand of neurons sending information
Nucleus
Axon: transmit to other neurons (the connection) (axon can be as long of the base of the spine to the base of the foot)
Myelin Sheath (myelinated axon): an insulating layer around axons that increases conductions between neurons and rapid transmutations of action potentials
very helpful if you need to react to burns, heat, pain faster
Glial cell (Schwann cell): help form the myelin sheet
Nodes of Ranvier: information jumps on node of ranvier
Terminal buttons: when firing an action potential, information goes to the synaptic cleft
Neurons Communicate via Action potentials
When do neurons fire?
types of signals
What is resting potential
excitatory signals will make the neurons less negative, depolarize, increasing the likelihood that the neuron will fire
Inhibitory signals will hyper polarize and decrease the likelihood of the neuron firing
When do neurons generate an action potential
only if the extort input will reach a certain threshold
What is the all-or-none principle
a neuron will fire with the same magnitude each time
Will or will not fire
but the frequency of firing will vary
What occurs during the resting potential
the ions
Neurons are polarized at rest (-70 mV)
More sodium ions outside
more potassium ions inside
Contributes to the polarized nature of the cell
More negative inside than outside
gated channels
Sodium channels: closed
Potassium channel: closed
Prevent them from moving around to balance the solution
Na+ and K+ transporter ion moves Na out and K in
Depolarization
sodium channels open up
Sodium ions come into the cell, into the axon
shifts the electric potential: making inside more positive
Peace action potential and hyper polarization
Potassium gates open: potassium will flow up, and the gate quickly closes - creating hyperpolarization
Will make the inside more negative
the refractory period: 3 Na out and 2 potassium inside with one ATP molecule
Allows to restore resting potential for another action potential
Local current
the flow sodium ions isn’t enough for the action potential begins
Therefore must reach -55 mV
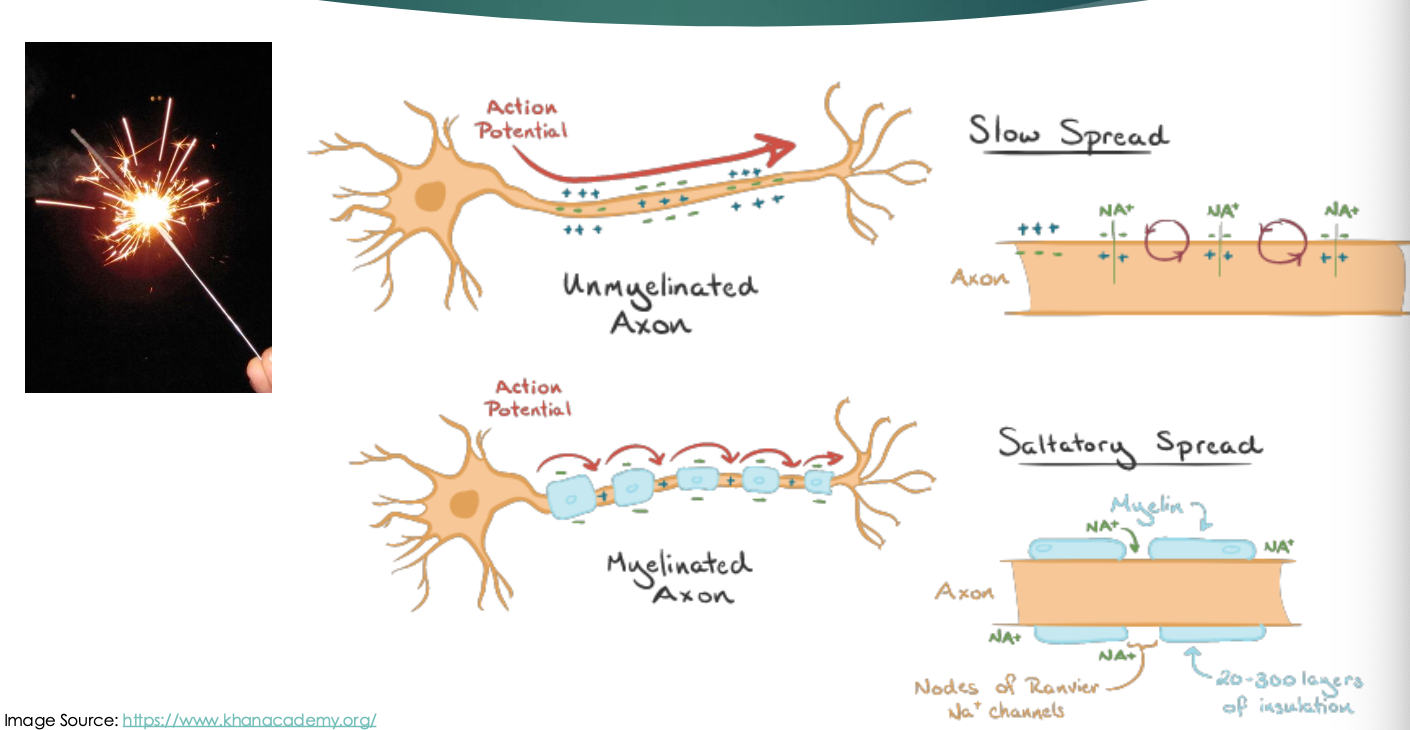
Saltatory Conduction
myelated vs unmyelinated axons
Saltatory spread: slow spread of information travelling for unmyleated
Results in the jumping
Up to 50 times faster
Slow spread