🧟 DNA Mutations
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Importance of Mutations
Sustain life but also cause suffering
Source of all genetic variation (providing raw material for evolution)
Source of diseases/disorders
Useful for probing fundamental biological processes
Identifying mutant genes that alter development are useful for identifying function of gene
When mutant genes alter development, they help scientists figure out what normal processes or structures require the gene to function properly
e.g. Wnt genes involved in patterning of vertebrate axis are now known to be at the center of colon cancer
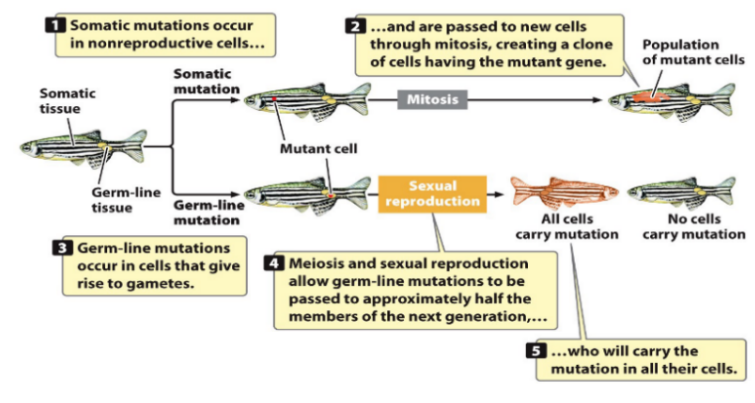
Somatic/Germ-Line Mutations - NOT TESTED
Somatic
Occur in nonreproductive cells
Are passed to new cells through mitosis, creating clone of cells with mutant gene
e.g. Melanoma
Germ-line
Occur in cells that give rise to gametes
Meiosis/sexual reproduction allow germ-line mutations to be passed to ~half of next generation, who will have the mutation in all of their cells
Types of Gene Mutations
Base substitutions
Transition
Transversion
Insertions/Deletions
Frameshift mutations
In-frame insertions/deletions
Expanding nucleotide repeats
Increase # of copies of set of nucleotides
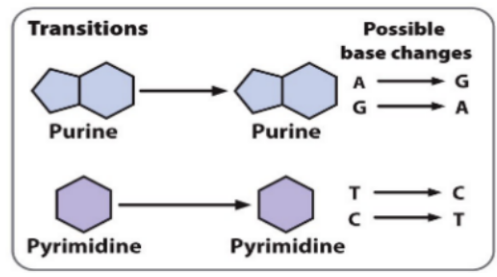
Substitutions - Transitions
Like for like
Purine to purine (A to G, G to A)
Prymidine to prymidine (T to C, C to T)
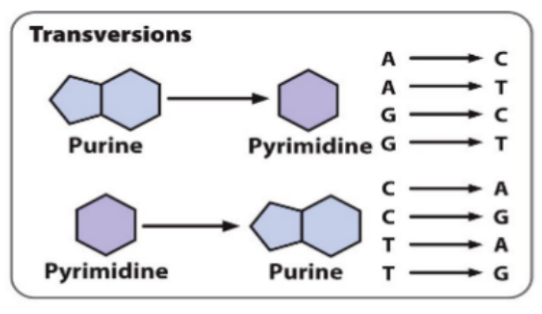
Substitutions - Transversions
Like for non-like (switching versions)
Purine to pyrimidine (A to T)
Pyrmidine to purine (T to G)
Base Substitutions
One codon changed when a base is added, no frameshift, only that codon is affected

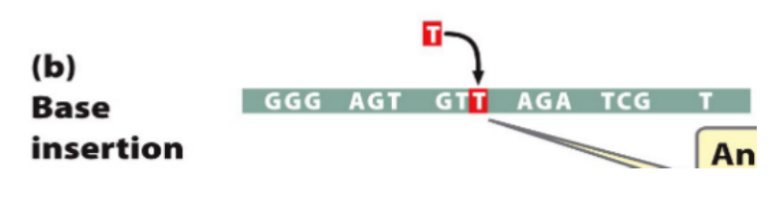
Frameshift - Base Insertions
Base is inserted and entire frame shifts, altering every codon after the insertion
Frameshift - Base Deletions
Base is deleted and entire frame shifts, altering every codon after deletion

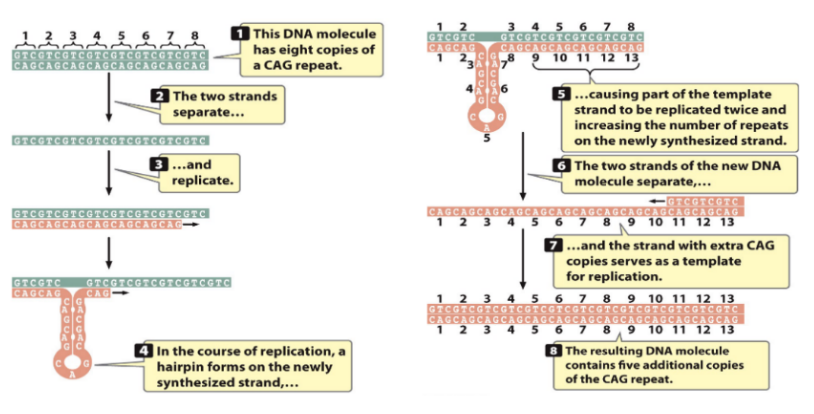
Expanding Nucleotide Repeats
e.g. CAG is normally repeated 12 times, but mutation causes 300 repeats instead
Repeats increase with generations (i.e. Parent might have 300 repeats, child will have 4000)
DNA has 8 copies of CAG
Strands separate and replicate
Hairpin forms on synthesized strand
Part of the template ends up being repeated on the synthesized strand
DNA strands separate
Strand with extra CAG repeats becomes template for replication
Resulting DNA molecule contains extra copies of repeats
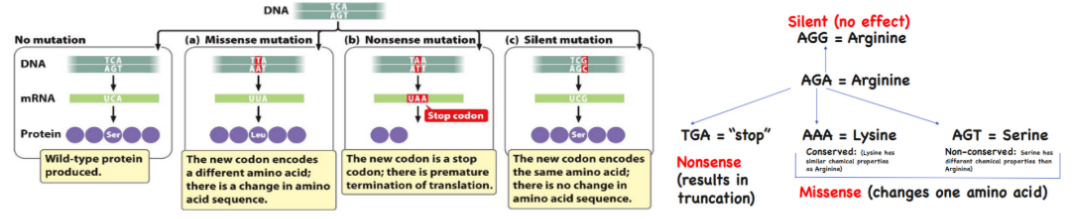
Phenotypic Effects of Mutations
Forward - Wild to mutant
Reverse - Mutant to wild
Missense - Amino acid to another amino acid
Nonsense - Sense codon to stop codon
Silent mutation - Codon to another codon that codes for the same amino acid
Neutral mutation - No change in function (e.g. many amino acids have the same properties/functions, so mutations don’t affect the protein too much)
Forward Mutation
Wild type to mutant
Reverse Mutations
Mutant to wild type
Missense Mutations
Amino acid to another amino acid
Silent Mutations
Codon to another codon that codes for the same amino acid
Neutral Mutations
No change in function (e.g. many amino acids have the same properties/functions, so mutations don’t affect the protein too much)