Bio unit 3: intergration of body systems
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/17jhC3hq8t35ZbFEb4n_3dwULh2e5HYY_g31guy40P1Q/edit#slide=id.g2ae189293de_0_207
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
nervous system (slide 5, 10, 14)
overview:
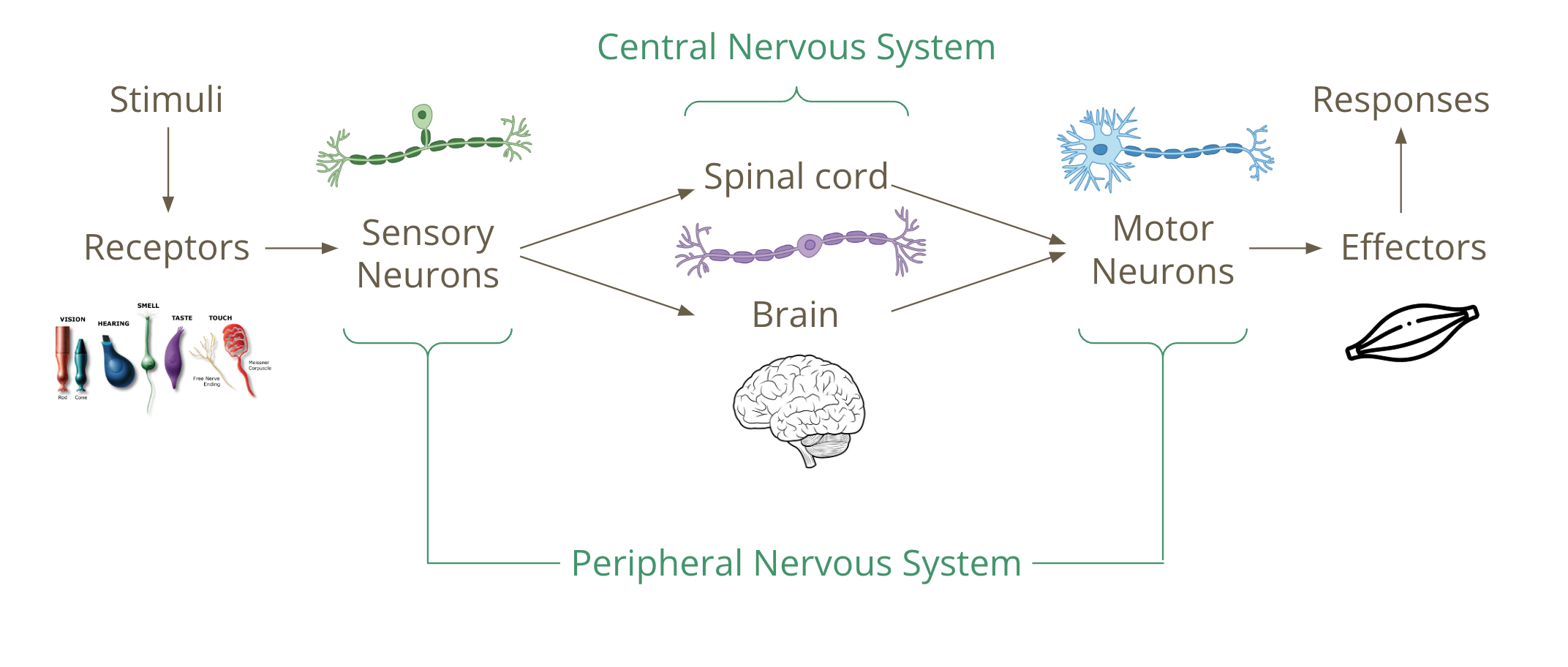
stimuli (environment) received by receptors → activates action potential in sensory neurons → relay neurons pass on information to spinal cord and brain → motor neurons bring signals from CNS (brain and spinal cord) to effectors →projects axon (indirectly or directly) to control effectors (glands or muscles)
Characteristics:
composed of many neurons
interact together sending messages throughout the entire body
made of 2 systems
central nervous system
peripheral nervous system
system is interdependent with endocrine system
Endocrine system
composed of glands (a system of glands)
they secrete (Release) (into the blood stream(transport system)), produce, and store hormones (chemical signals)
glands are not connected (do not need to know all the glands)
controlled by the hypothalamus of the brain (CNS)
via a neural and hormonal connection to the pituitary gland (the master gland, secretes hormones, controls other glands)
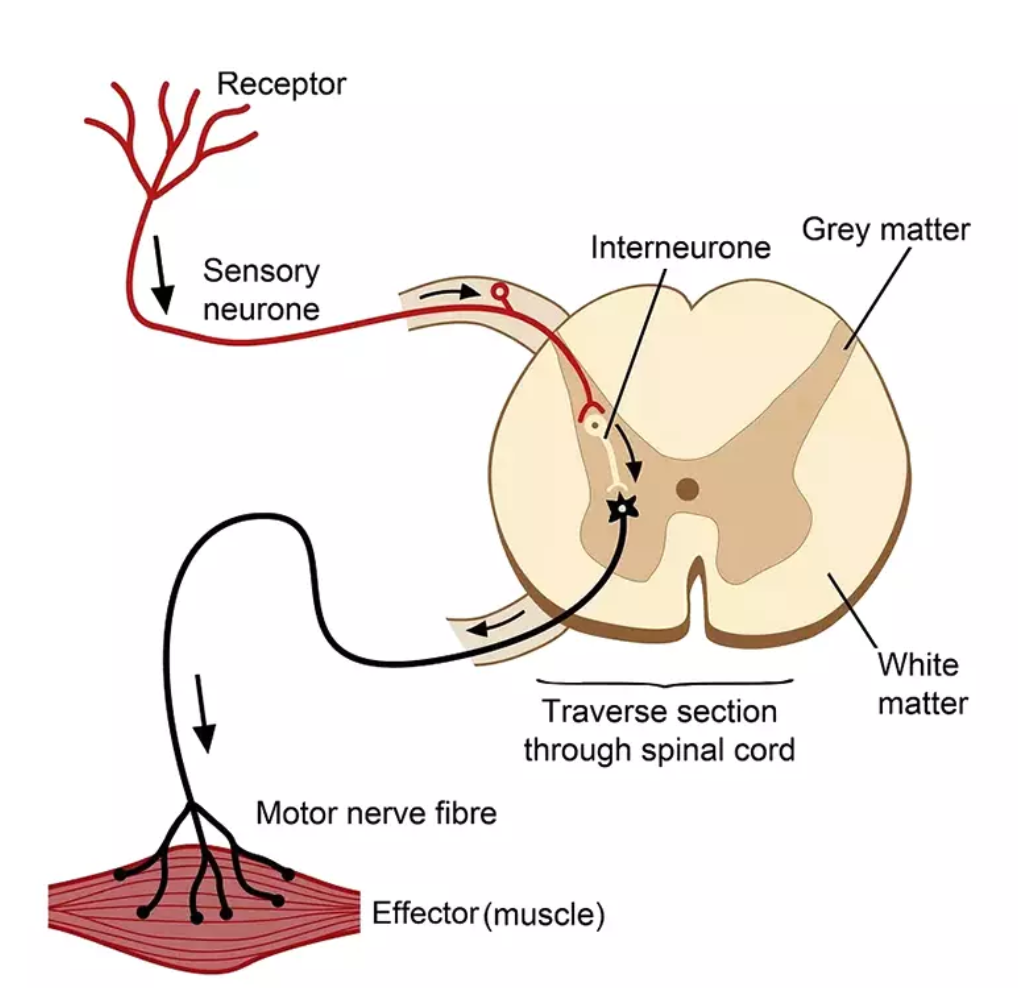
withdrawal reflex (pain reflex arc) (slide 9)
automatic response enacted to withdraw a limb from a painful stimulus (involuntary)
free nerve ending sensory neurons are activated from sensory input from environment
input is detected via receptors (nocireceptor) → initiates a nerve impulse (activation, action potential)
interneurons then relay (relay neuron) the action potential from sensory neuron to the motor neuron
motor neuron (cell body in the CNS (central nervous system) axon projects directly or indirectly to control effector (gland or muscle)))
other characteristics:
intensity of reflex is proportional to the intensity of the pain
polysynaptic reflex
synapses are located in the grey matter of the spinal cord
sensory receptors (slide 11)
any type of cell that can detect numerous types of stimuli (sound, touch, taste)
main function is to send signals via sensory neurons to the CNS (central nervous system)
the brain (slide 13, 14)
core structure:
cerebrum
left cerebral hemi(half)sphere
right cerebral hemisphere
makes up most of the brain
Brain stem
midbrain
pons
medulla
Cerebellum
motor control and coordination
significant part of the brain
helps with balance
function:
central coordinator of information
unconscious and consicous processes
recieve complex sensory inputs
learns (formation of new synapses and strengthening synaptic connections)
form memory (stores learning, stores conscious memory and unconscious memory)
spinal cord (slide 14)
coordinates unconscious responses (e.x. reflexes)
conveys signals to and from the brain
brain and motor control (slide 15)
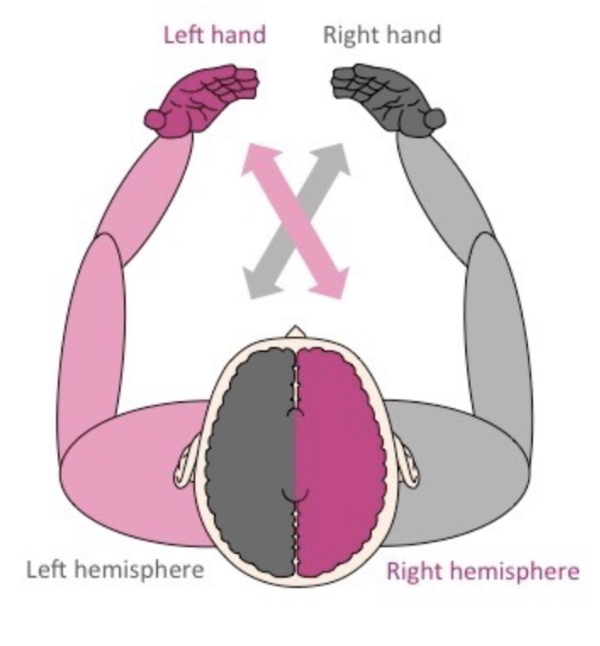
left and right cerebral hemispheres control muscles via motor neurons
cause muscles to contract (ex. skeletal muscles, smooth muscles of intestines, blood vessels, irises of the eye)
left controls right side of the body and vice versa
cerebellum (slide 16)
found at the base of the brain
functions: coordination of contraction of skeeltal muscles
overall control of body movement (percision and timing) (e.x. balance, posture, walking, running)
unable to intiate muscle contraction
recieves input from cerebral hempisheres (cerebrum)
involved in motor learning (learning new motions)
Nerves (Slide 17)
bundles of axons of neurons
sensory and motor neurons
myelinated and unmyleniated
nerve fibers are bundled togther inside protective sheaths of connective tissue
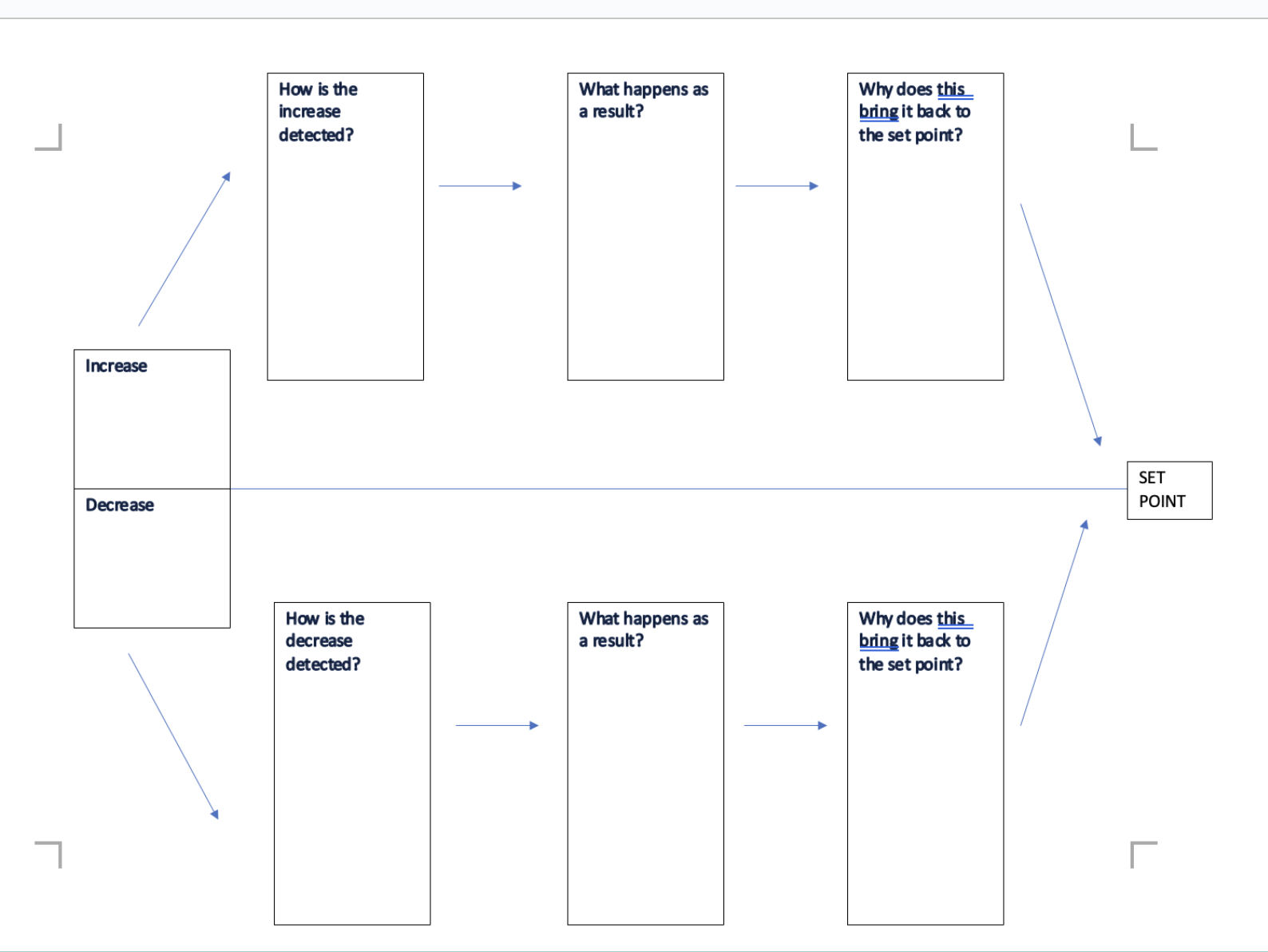
feedback loop
a response
in a system, an output is measured to provide input t o the system
negative feedback
if an output increases, the system reacts to decrease it, and vice versa
negative means in the opposite direction
used for homeostasis (maintaining conditions within set limits)
ex. if blood oxygen conc. decreases, the brain detects this and reacts by increasing the breathing rate which increases oxygen
positive feedback
increase of an output causes an even greater increase in the output
ex. uterine contractions during birth: contractions cause an increase in contractions
medulla oblongata
part of brainstem (base of the brain)
regulates cardiovascular and respiratory systems via nerve impulses
increases & decreases heart rate and ventilation rate based on
sensory input from baroreceptors and chemoreceptors
located in carotid arteries and the aorta
the medulla can increase or decrease:
heart rate
stroke volume
ventilation rate
stroke volume
the volume of blood pumped by the left ventricle in one contraction
ventilation rate
contraction of exterior intercostal (located in ribcagge) muscles and diaphragm for inhalation and interior intercostal muscles and abdominals for exhalation
baroreceptors and chemoreceptors
Chemoreceptors are cells that detect concentrations (sensory input) of O2, CO2, and blood pH
increased cell respiration increases CO2 conc., and decreases O2 conc. & pH
chemoreceptors detect this and send signals to the medulla
the medulla sends signals to the heart to increase heart rate and to the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to increase ventilation rate
Baroreceptors (aka stretch receptors) are cells that detect the changes in the circumference of arteries (the degree that they are stretched by blood pressure)
high blood pressure increases circumference/stretch
baroreceptors signal the medulla and the medulla decreases heart rate and stroke volume and dilates blood vessels
peristalis
coordinated contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle in the digestive tract that moves materials through the digestive system
swallowing: voluntarily controlled by the CNS (brain + spine)
peristalsis from esophagus to rectum: involuntary control by the ENS
enteric nervous system (ens)
collection of nerves from esophagus top the rectum
functions independantly fo the CNS
coordinates movement of material throuhh the gut
egestion of feces: voluntarily controlled by the CNS
hormones (part of the endocrine system)
bind to receptors on target cells/organs
control and coordinate other organs
pituitary gland
the pituitary gland secretes hormones
that control other endocrine glands
(known as the “master gland”)
Vasopressin (ADH)
hormone (need to know)
Adrenal Gland
renal refers to kidney
the hormone epinephrine/adrenaline is released from adrenal glands
in response to stress (the trigger) (fight or flight response)
affects various organs
prepares for vigorous activity with intense muscle contractions
increased:
heart rate
blood pressure
ventilation
blood glucose conc
fatty acid conc
blood flow to skeletal muscles
dialates blood vessels supplying skeletal muscles
constricts other blood vessels
brain and sense organs become more alert
Circadian rhythm
24 hour pattern of physiological changes
mainly affected by light-dark cycle:
light → photoreceptors (detect change in light activity)→ optic nerve → pineal gland → dec. melatonin
dark → photoreceptors → optic nerve (part of nervous system), sends electrical signal → pineal gland (endocrine system) secretes → inc. melatonin (hormone)
also affected by:
food intake, stress, physical acitivty, social environment, temperature
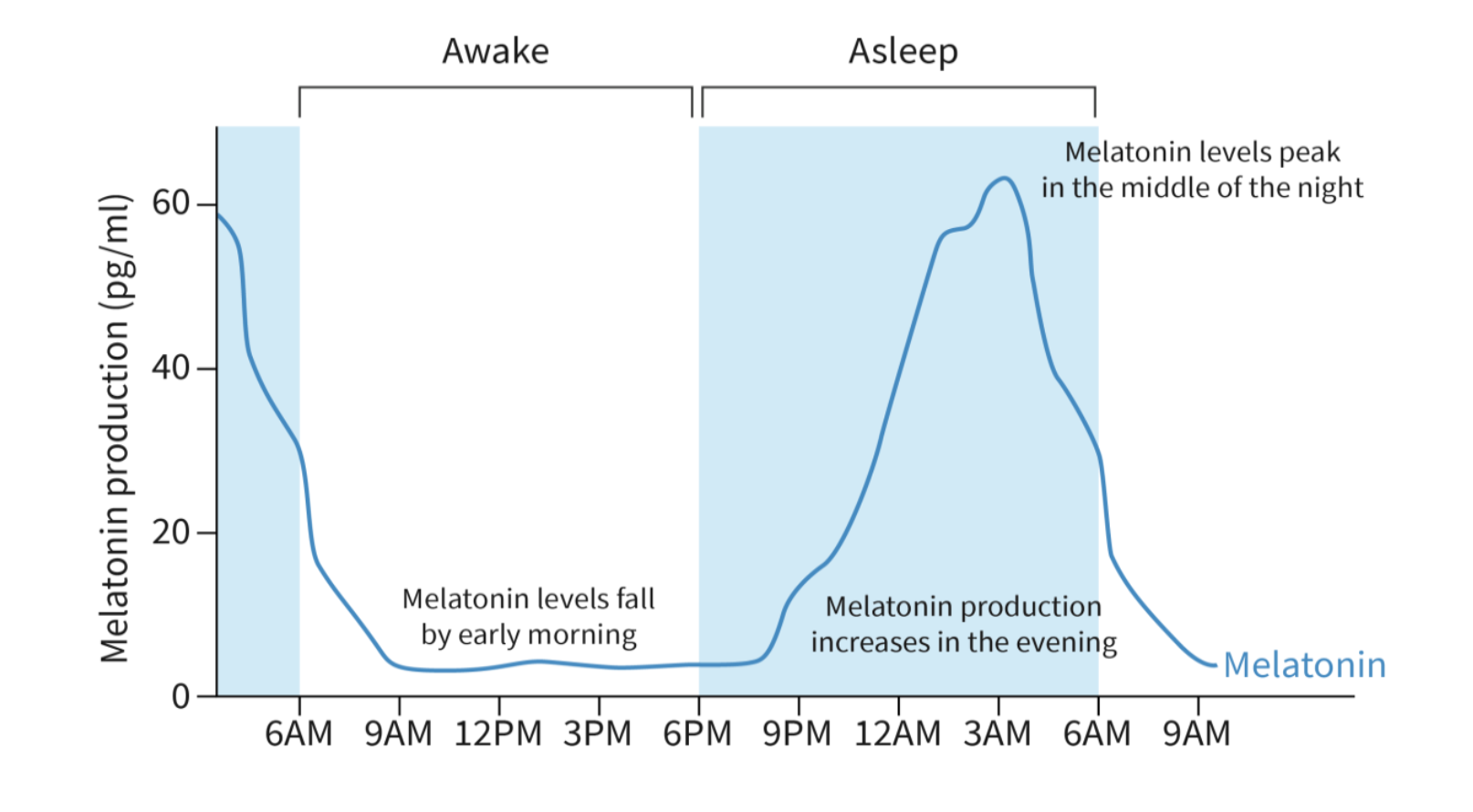
melatonin
hormone
regulate the sleep/wake cycle
diurnal (daily) pattern of melatonin secretion by the pineal gland
induces sleep by dec brain acitivty, temperature, other hormones (ex. cortisol)
during adulthood and adolesence,
systems
human body is collection of systems
system:
interacting and intedependant parts that create emergent properties
e.g. neuron could not sustain itself or achieve coordination without other cells and systems
interaction and interdependance rquires coordination
the nervous or endcrine systmes coordinate body systems
cardiovascular system
heart + blood vessels
aids in the interaction and interdepndance between body systems
carries materials and energy (like a highway):
hormones from glands to targets
chemical energy in nutrients
o2
waste products (e.g. co2)
distributes heat energy arnd the body
transportation system and heat system
hierarchy of subsystems
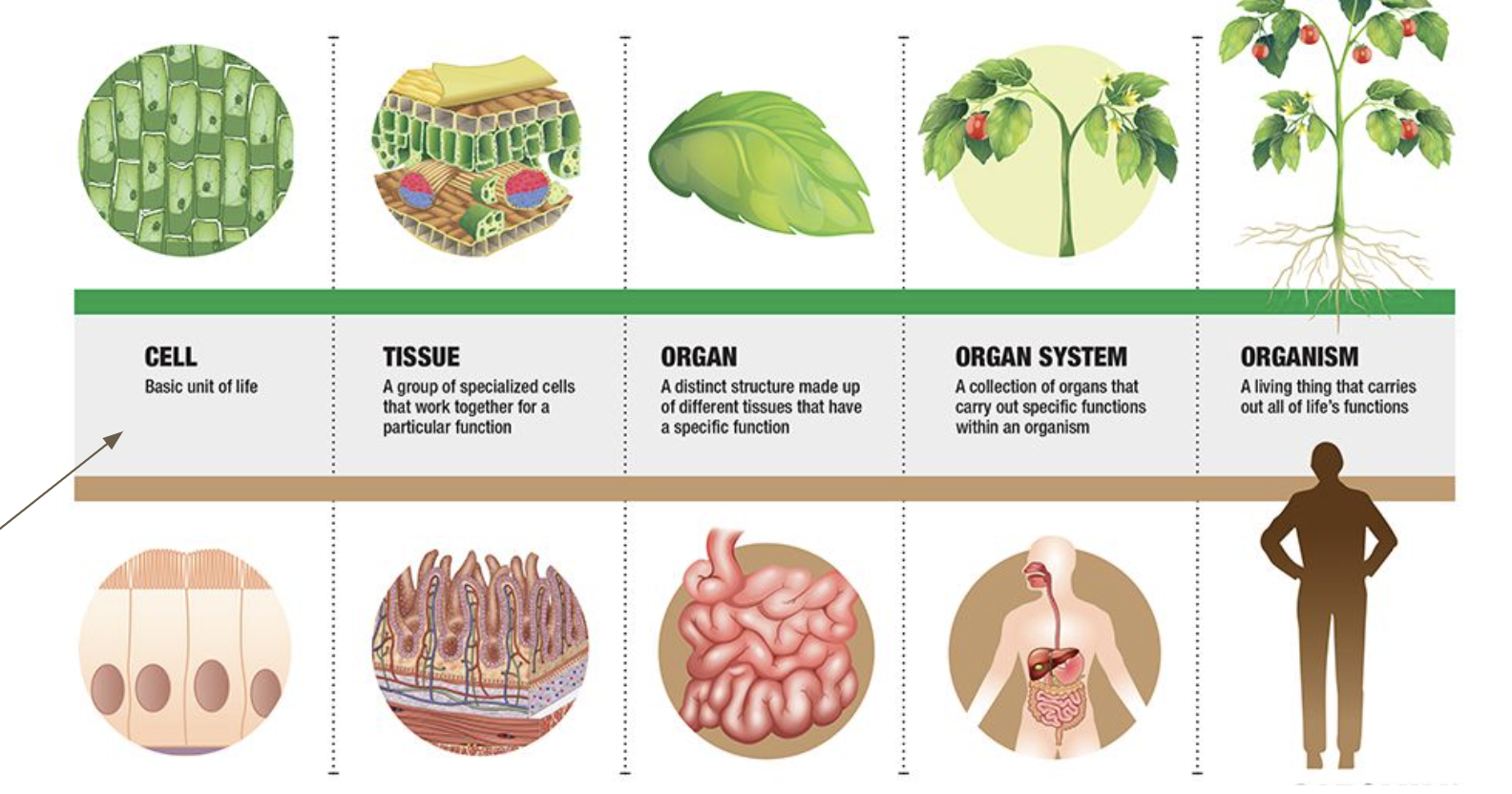
Hierarchy: cells → tissues → organs → body systems → organism
Each level is a subsystem of the next level.