lecture 10, bone structure and composition
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
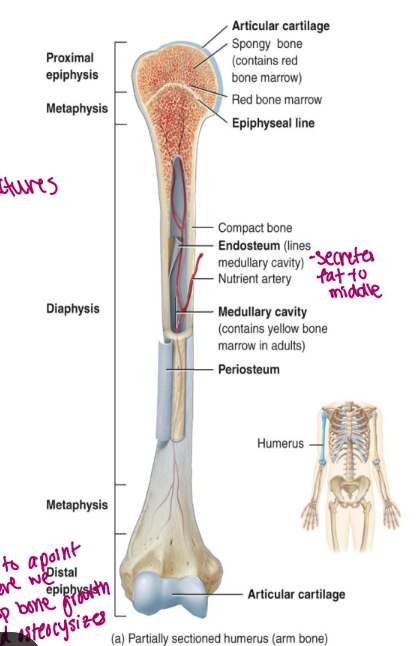
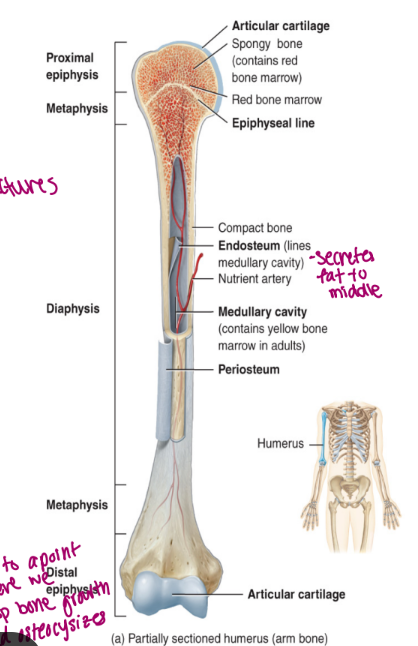
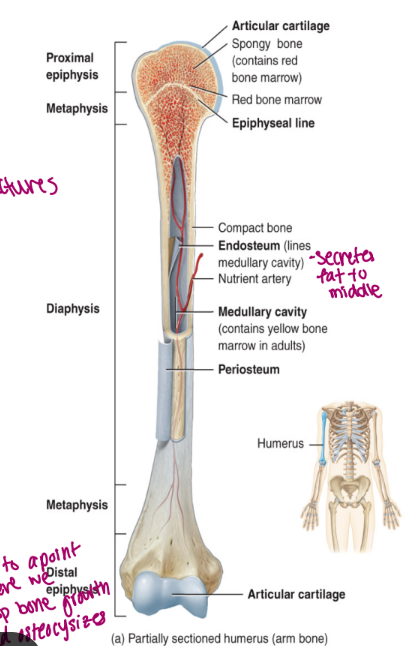
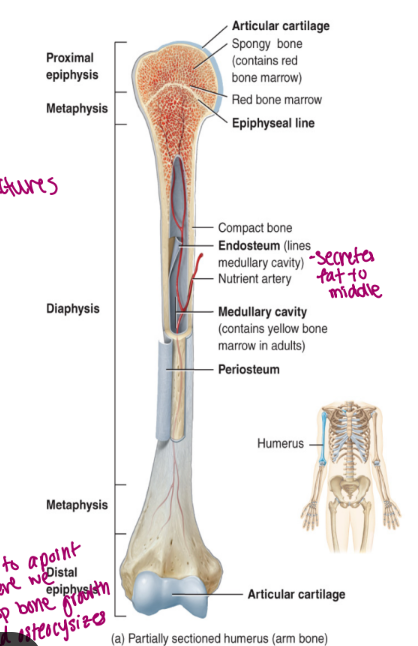
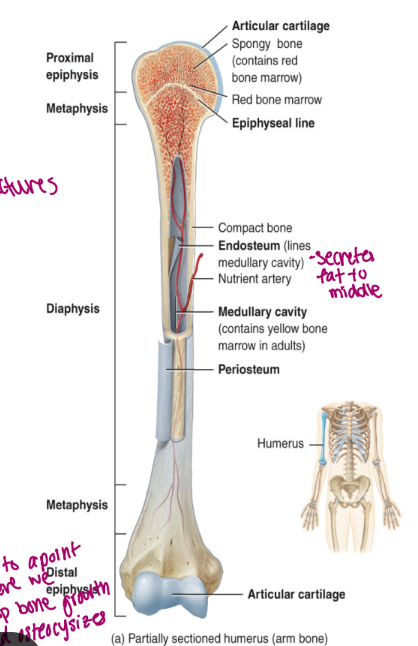
components of long bone
each of these bones is composed of a
diaphysis
the medullary cavity of the diaphysis (hollow)
epiphysis
epiphyseal plate
epiphyseal line
endosteum
periosteum membrane
articular cartilage
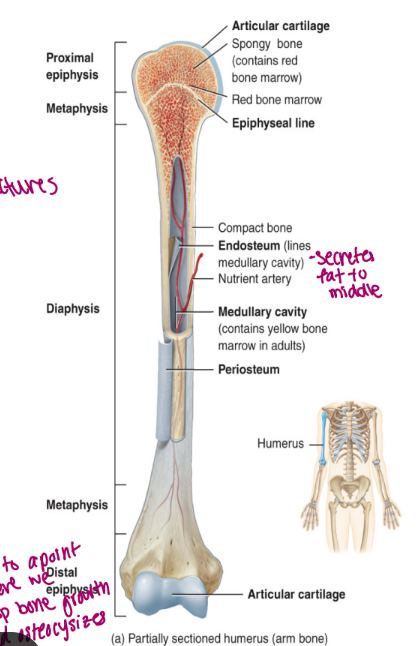
diaphysis
the shaft/body of the bone
composed of compact bone
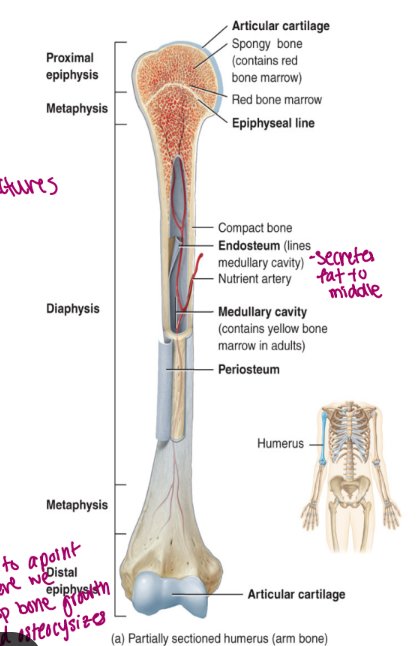
the medullary cavity of the diaphysis (hollow)
contains red bone marrow in a child
contains yellow bone marrow in an adult
contains fat
lined by endosteum
lines the cavity
“outer” “bone”
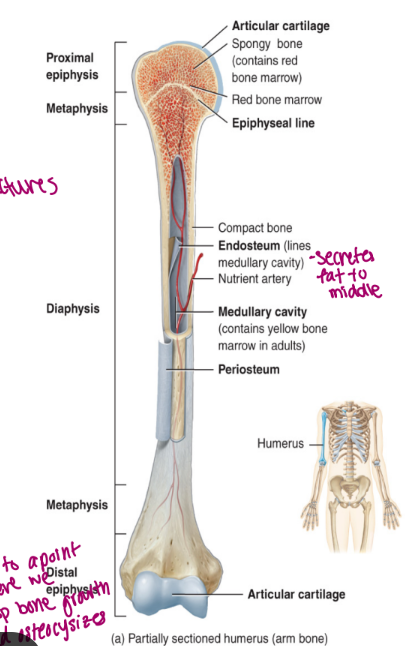
epiphysis
these are the proximal and distal entities (end part of long bone)
epiphysial plate: growth plate (cartilage, in between epiphysis and diaphysis, found in kids/teen)
epiphysial line: ossified remnant of growth plate (in adults, bone stops growing)
epiphyseal plate
composed of hyaline cartilage
bone growth in length occurs at this plate
bone growth is called endochondral ossification
epiphyseal line
replaces the epiphyseal plate when growth is finished
appears as a line because it is the junction of the diaphysis and the epiphysis
endosteum
connective tissue
very delicate (but it inside a hard long bone)
lines the internal surfaces of bone and canals (points of contact for delivery, allows for more access to nutrients)
contains osteoblasts and osteoclasts
“wallpaper”
periosteum membrane
composed of fibrous connective tissue
allows the bone to grow in diameter via intramembranous ossification
is a double membrane that covers the entire bone surface (except for the joint)
the outer layer is dese irregular connective tissue (good for movement)
the inner layer is osteogenic
bone forming and consists of osteoblasts (build it bigger) and osteoclasts (hollows out) increase size of cavity when bone grows
articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage that functions to prevent friction
found on the epiphyseal surfaces of long bone
tissues of the skeletal system
there are two primary tissues of the skeletal system
bone
cartilage
bone
bone is either compact (dense) or spongy (holes)
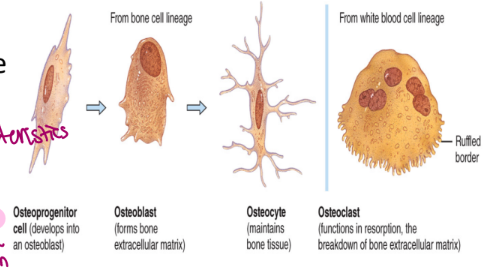
osteoprogenitor cells (like stem cells of the bone world, unspecialized) are cells that give rise to one of the following three cells
osteoblasts: build the matrix
osteocytes: maintain the matrix
osteoclasts: resorb (breakdown) the matrix (because want it fresh)
the cells of the connective tissue are separated by a matric that consists of
collagen fibers for flexibility
ground substances: hydroxyapatite crystals for strength → made from insoluble calcium phosphate salts
gives bone its characteristic strength
insoluble → otherwise bones would liquidify
water
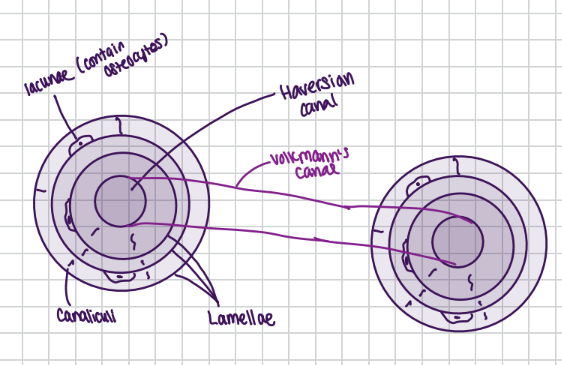
compact bone is found on the exterior surface of all bones
it is composed of individual structural units called osteons or Haversian systems
an osteon is composed of
osteocytes found within special spaces called lacunae
lamellae which are concentric circles of bone matrix
osteocytes are present between the lamellae
canaliculi connect cells and blood vessels (connection)
Haversian canals contain blood vessels and the nerves
lined with endosteum
Volkmann’s canals are found at a right angle to blood vessels found in Haversian canals
these connect the periosteum to the endosteum providing blood supply to the medullary cavity and the Haversian canals
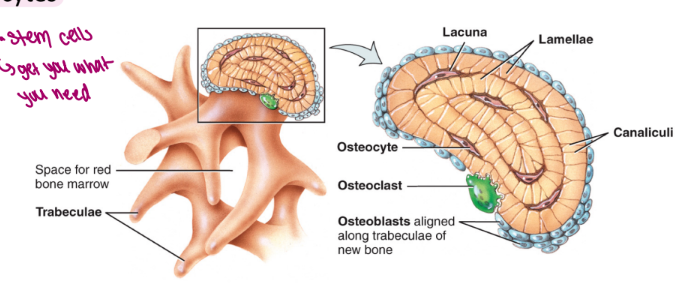
spongy bone is not organized into osteons
plates of bone are called trabeculae
irregularly arranged lamellae containing osteocytes
osteocytes are located in lacunae and are connected by canaliculi
found in epiphyses of long bone as well as in flat bones such as the skull and the ribs
the spaces of the spongy bone contain red bone marrow
these spaces produce blood cells and provide a blood supply to developing osteocytes
stem cells → get you what you need
(compact bone is like an and aero bar, hard chocolate on top and bottom and bubbles in between)
hyaline cartilage
the cells of the cartilage are chondrocytes and are found within lacunae
the matrix is composed of
collagen fibers
ground substance consisting of chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid
water (more water in cartilage than in bone)
avascular tissue
harder to heal
look ugly when healed (sometimes)
articulations and joints
points of contact between two or more bones
these can be classified on either structure or function
functional classification
this is based on degree of movement
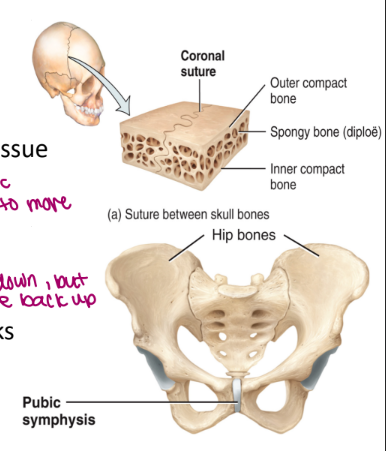
a. synarthrotic: immovable joints
ex. sutures
b. amphiarthrotic: slightly moveable joints
ex. pubic symphysis (not free but ex. when jump it moves slightly)
c. diarthrotic: freely moveable joints
ex. hip, knee, elbow, shoulder
structural classification is based on
the presence of the absence of a joint cavity and the type of tissue connecting two bones
there are three structural classifications of joints
fibrous joints
no joint cavity, composed of fibrous connective tissue
ex. sutures on the skull
fibers create the joint
fibrous characteristic because don’t need to move
cartilaginous joints
no joint cavity, composed of cartilage
ex. pubic symphysis and intervertebral disks
jump → compress down, but then come back up
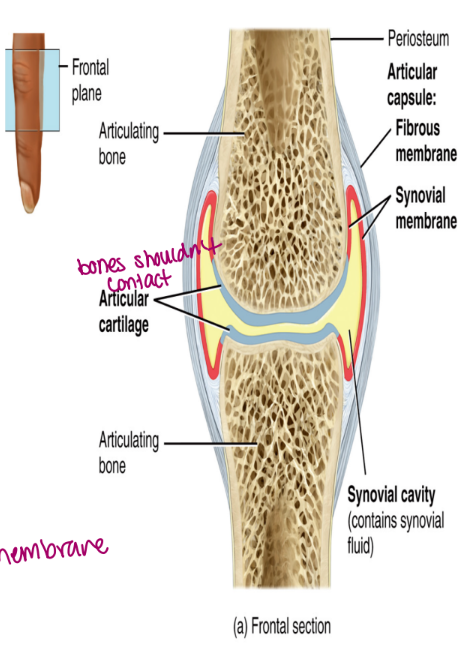
synovial joints
contain a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid
bones are held together by a joint cavity and associated ligaments
all diarthrotic joints are synovial joints (freely move)
ex. knee, shoulder, hip, elbow
synovial joints
all contain
articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage located on the ends of the bones
reduces friction
joint cavity
contains synovial fluid
joint capsule
contains an outer layer of fibrous connective tissue that attached to the periosteum
an inner synovial membrane which secretes synovial fluid
needs to come from the inner membrane (secretes it)
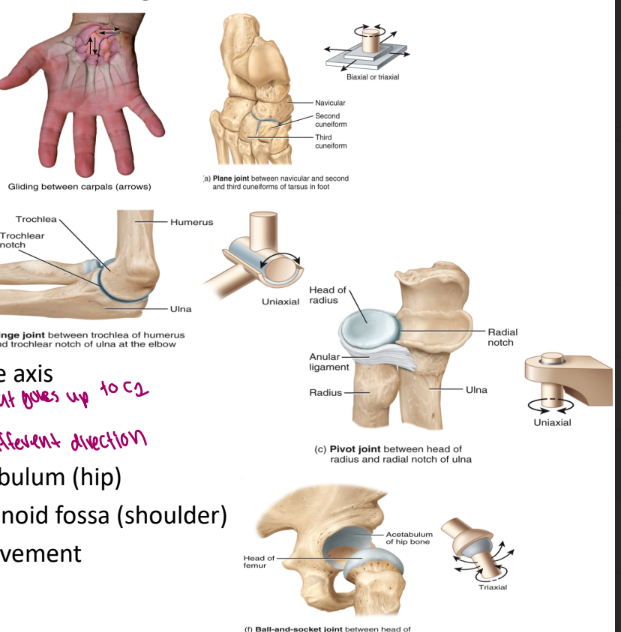
four primary types of synovial joints
grouped according to the shape of articulating bones
gliding (plane)
flat surfaces
ex. sacroiliac joint
hinge
concave and convex surface
ex. elbow, knee
ligament and cartilage
pivot
ex. odontoid process of the axis
ability to pivot
on the axis of C2 that goes up to C1
ball and socket
head of femur and the acetabulum (hip)
head of the humerus and the glenoid fossa (shoulder)
allows for a large freedom of movement
can move a lot in different directions