PCOL:3102 NSAIDs, Allergies, and Asthma
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
prostaglandin synthesis
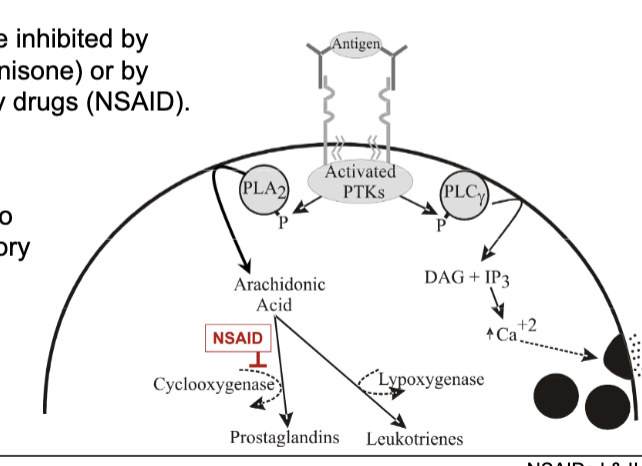
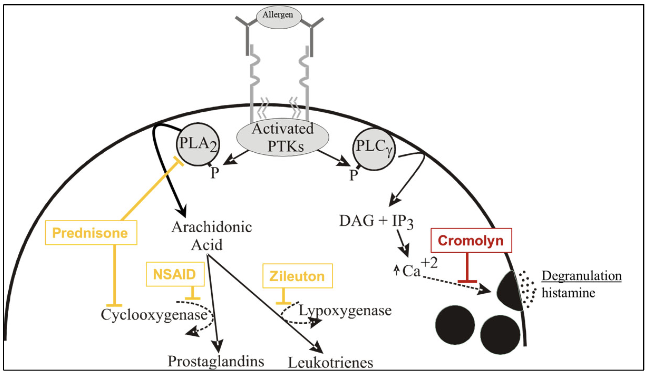
antigen activates PTKs which will phosphorylate PLA2
PLA2 makes arachidonic acid which depending on enzyme will make prostaglandin or leukotrienes
COX → prostaglandin
lipoxygenase → leukotrienes
types of prostanglandins made
PGE2
PGI2
TXA2
effects depend on where it’s released. prostanglandins have short half-life so they don’t travel far which is why its effects are tissue specific
prostaglandin effect on blood vessels
PGI2 and PGE2 cause vasodilation → increase blood flow
TXA2 cause vasoconstriction → decrease blood flow
prostaglandin effect on platelets
TXA2 increase blood clotting
PGI2 decrease blood clotting
prostaglandin effect on sensory nerves
PGI2 and PGE2 lower threshold for pain stimulation (hyperalgesia) which can convert normally non-painful stimuli into painful stimuli
prostaglandin effect on brain
PGE2 in hypothalamus cause increase in body temp → fever
prostaglandin effect on uterus
can cause uterine contraction and relaxation
difference between where COX1 and COX2 work?
COX1 is only one involved in platelets and stomach & GI, so main culprit in blood clotting and helps secrete mucus to protect stomach lining
COX 2 is only one involved in inflammation, so COX2 main culprit in inflammation responses
both in uterus and kidney
where are the diff prostaglandins released in?
PGE2 in most tissues
PGI2 in endothelium of vessels
TXA2 in platelets
NSAIDs
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
COX inhibitors so can inhibit both COX-1 and 2
reduces inflammation by inhibiting COX-2
many adverse effects from inhibiting COX-1 like stomach irritation
non-selective and selective types
non-selective NSAIDs
aspirin
better at treating blood clots than others because it’s an irreversible COX inhibitor so platelets have to wait till a new COX is born for it to get its clotting ability back
ibuprofen
naproxen
non-selective NSAIDs
celecoxib — inhibits COX2
what are NSAIDs used for?
reduce inflammation from injury/stress (mild to moderate) as glucocorticosteroids more effective in that aspect
reduce fever by immune or inflammatory activities
analgesia (pain caused by inflammation)
reducing CV events since it prevents TXA2 from platelets for blood clots (ONLY ASPIRIN USED)
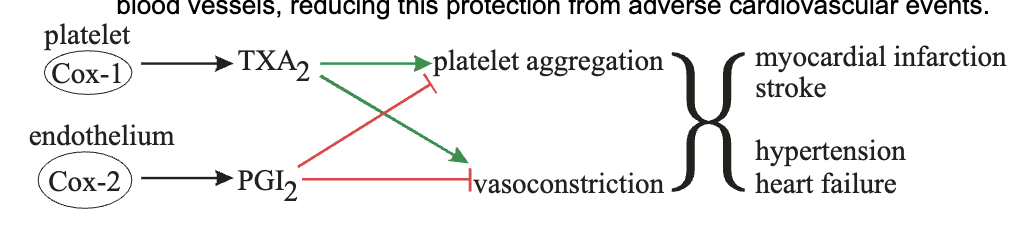
why is there only one selective NSAID and why is it not used as much?
celecoxib only one out there and has less toxic side effects than others
it selectively inhibits COX-2 which is primarily involved in inflammation
but it also prevents synthesis of PGE2 which causes vasodilation and prevent platelet aggregation
platelets ONLY express COX1 which can make TXA2 to cause platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction
without PGE2 made from COX2 in endothelium, there’s no brake pedal on COX1 and its TXA2 production → more adverse CV events
acetaminophen
NOT NSAIDs
non-selective COX1 and 2 inhibitor but its activity is substantially reduced in presence of peroxides that are often elevated at inflammatory sites
so does not help with inflammation
also not active in platelets and stomach/GI tract so it can’t affect blood clotting or GI disturbances
still has the same analgesic and antipyretic effects
associated with liver toxicity
histamine
molecule synthesized and stored in most cells in body
stored in intracellular vesicles
released when vesicles fuse with plasma membrane
binds to two main types of receptors: H1 and H2
histamine effecst and function
acts as NT on H1R in CNS to promote wakefulness and nausea
vasodilation causing increased blood flow to sites where histamine was released → anaphylaxis during systemic release of histamine which drastically decreases BP
makes capillary walls leaky allowing plasma to seep into surrounding tissues
increased fluid in tissue causing swelling (edema)
increased fluid in nasal passages → congestion
increased fludi in lungs → difficulty breathing
histamine stimulates peripheral nerves causing itchy sensation
bronchoconstriction → difficulty breathing
triple response
aka wheal and flare
response of combo of H1 effects of histamine on blood vessels and nerves that produces hives
red spot from capillary dilation
flare (axon reflex) from histamine stimulation of sensory nerves which releases vasodilators and irregular reddening
wheal: edema from leaky capillaries
first gen antihistamines
diphenhydramine
dimenhydrinate
doxylamine
diphenhydrinate
used for motion sickness and nausea
better at preventing new symptoms then on-going symptoms
combo of 2 drugs including diphenhydramine
dimenhydramine
allergies / nasal congestion / hives
drug of choice where histamine is primary mediator
doxylamine
in sleep aids and cold medicine
sedation!
in nyquil
main adverse effects of antihistamines
only for first gen
sedation from blocking H1R in CNS cuz they can easily cross BBB
anti-muscarinic effects from interacting with non-H1 receptors in periphery — dirty drugs!
second gen antihistamines
loratadine
modified to not be able to cross BBB → no sedation
more selective for H1R → less anti-muscarinic and other receptor side effects
asthma
recurrent episodic bouts of coughing and difficult breathing from airway inflammation
who are more at risk for asthma?
people with allergies
genetic factors
people with no siblings and live in clean environment cuz they’re immune system isn’t trained → hygiene hypothesis
how do asthmatic episodes happen?
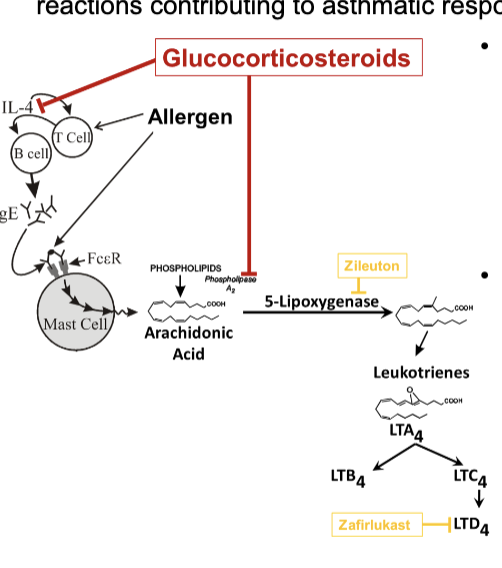
starts with an allergen which triggers Th2 response characterized by IL-2 and IgE release
IgE activates mast cell and eosinophils thru Ab receptor which causes histamine and leukotriene release (first wave)
causes bronchoconstriction and mucus build up → difficulty breathing
mast cells and IL-4 release attarcts other immune cells to trigger pro-inflammatory mediators (second wave)
now at late phase so more constriction, mucus, and overall pro-inflammatory environment in airway
if chronic → establishes hyperresponsive state
how is asthma managed?
not curable
immunosuppresive and anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce effects of mediator elease and reduce immune cells in airway
bronchodilators to open up bronchia
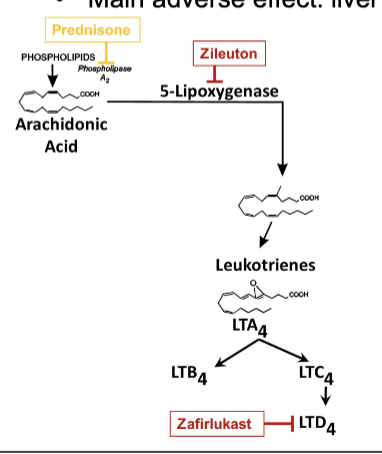
how do leukotrienes mediate airway inflammation?
leukotrienes produced by mast cells and eosinophils are primary mediators of bronchial constriction and edema
leukotrienes made from arachidonic acid by lipoxygenases
two types of leukotrienes: LTB4 and LTD4
LTB4 attracts neutrophils
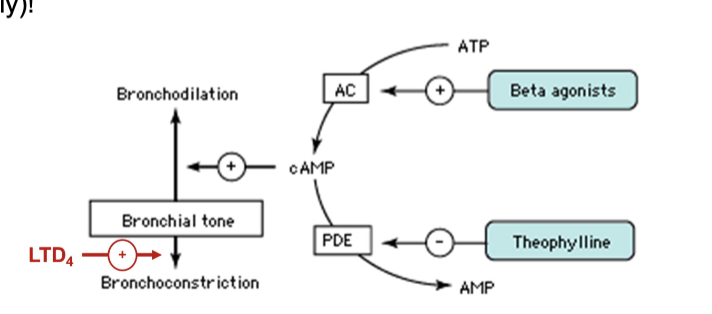
LTD4 major factor in airway inflammation and difficulty breathing (major culprit) and attracts eosinophils
bronchoconstriction, increased capillary permeability
asthma maintenance therapy with glucocorticosteroids
inhibits cytokine expression (IL-4) to reduce Th2 response
this reduces IgE production and mast cell + eosinophil proliferation which release inflammatory mediators
inhibits PLA2 which prevents leukotrienes from being made
administered at lowest doses to prevent adverse effects
ex. budesonide, fluticasone, prednisone
topical administration of glucocorticosteroids for asthma
aerosolized version
daily inhalation can produce long-term reduction in asthma symptoms
budesonide and fluticasone
systematic administration of glucocorticosteroids for asthma
oral / IV
provide burst of anti-inflammatory and immunosuppresive activity → intermediate term relief
reduction in airway inflammation can cause reduction in airway responsiveness sufficient to gain control of disease
your reg glucocorticosteroid side effects
prednisone
asthma maintenance therapy with inhibition of leukotriene pathways
zileuton: inhibits lipoxygenase
zafirlukast and montelukast: inhibits LTD4 receptor; preventing LTD4 release
asthma maintenance therapy with degranulation inhibitors
cromolyn used to prevent mast cell degranulation → no vesicular histamine release
administered as powder aerosols so can cause irritation and cough
asthma maintenance therapy with bronchial dilators
DO NOT reduce inflammation ONLY cause bronchodilation
B2-adrenergic receptor agonists which is Gs-linked and dilates muscle
long acting: vilanterol
short acting: albuterol
theophylline: inhibits cAMP breakdown from PDE which helps with muscle relaxation in bronchial muscles
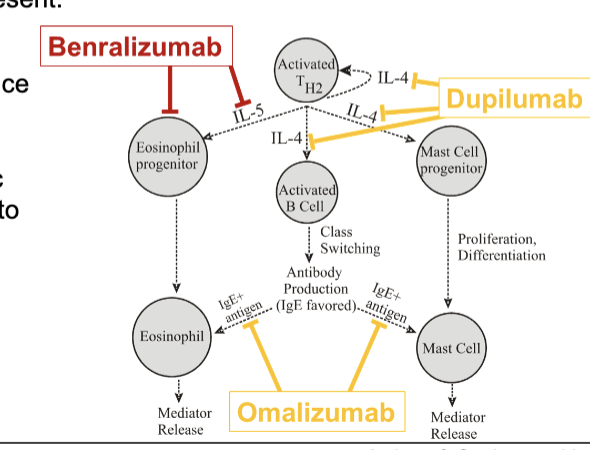
asthma maintenance therapy with Th2 targeted immune responses
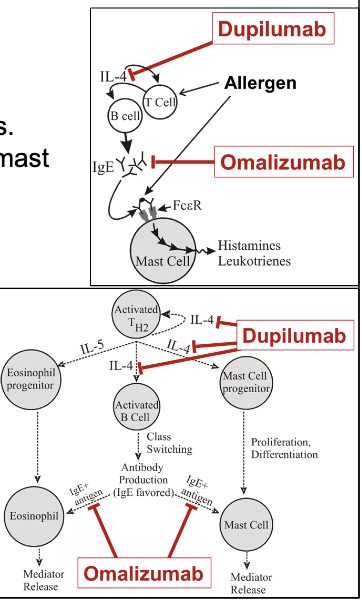
dupilumab
omalizumab
dupilumab
Ab that binds IL-4 and prevent interaction with receptor
reduces mast cell recruitment and mediator release along with reduced production of IgE
increase risk of parasitic infections and anaphylactic rxns
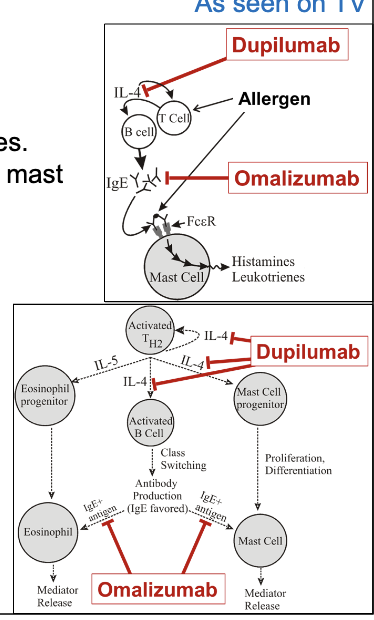
omalizumab
Ab binding to Fc domain of IgE to reduce IgE-mediated allergic responses
prevents IgE from interacting with mast cells and eosinophils
reduces levels of free IgE
increase risk of parasitic infections and anaphylactic rxns
asthma maintenance therapy with eosinophil targeting
benralizumab
Ab that binds to IL-5 receptor
blocks IL-5 from binding which is involved in eosinophil recruitment
opsonizes eosinophil and depletes them by ADCC
increase risk of parasitic infections and anaphylactic rxns