Eukaryotic Pathogens and Their Characteristics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
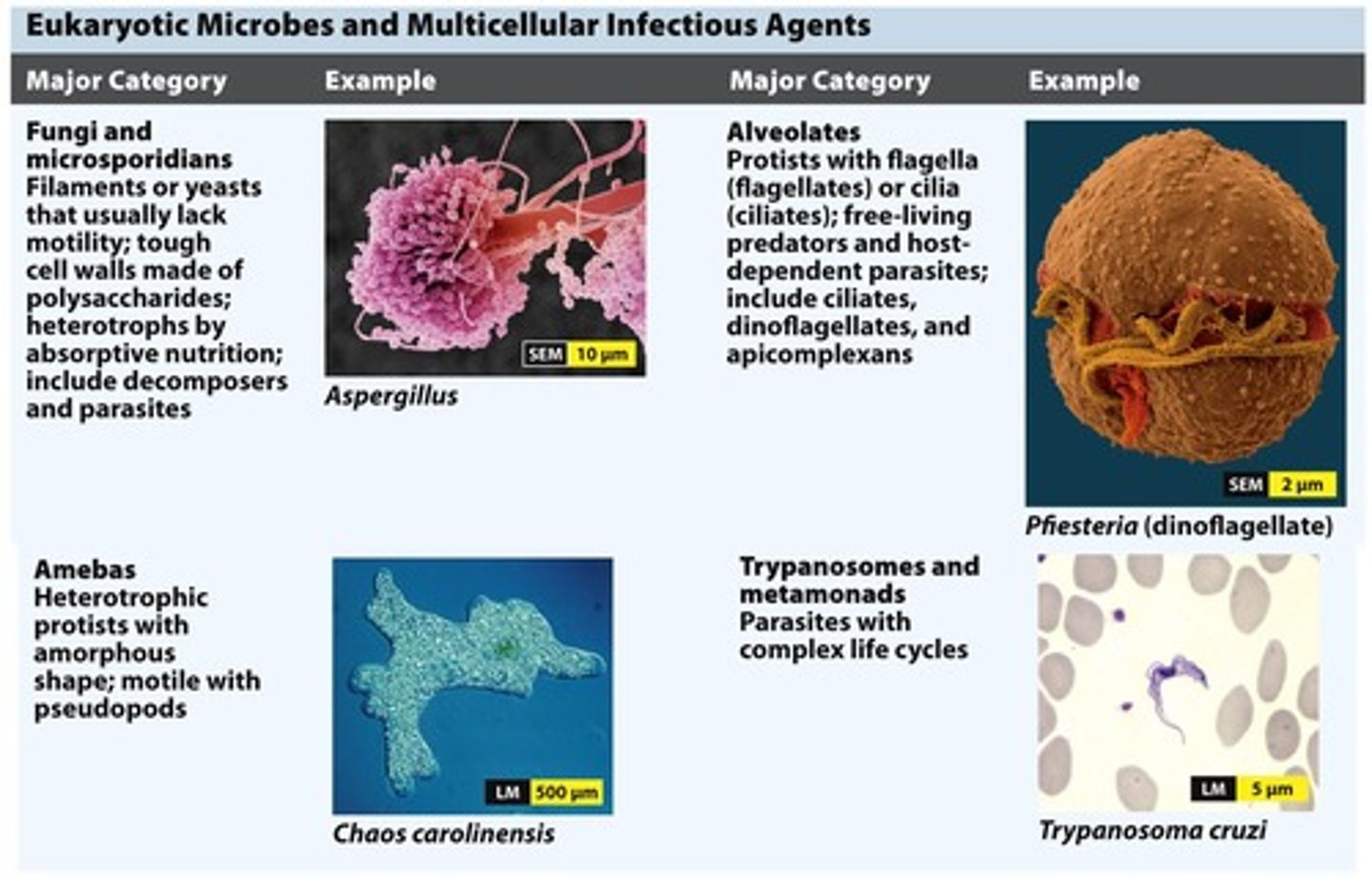
Eukaryotic Pathogens
Organisms with complex cells causing diseases.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells with a nucleus and organelles.
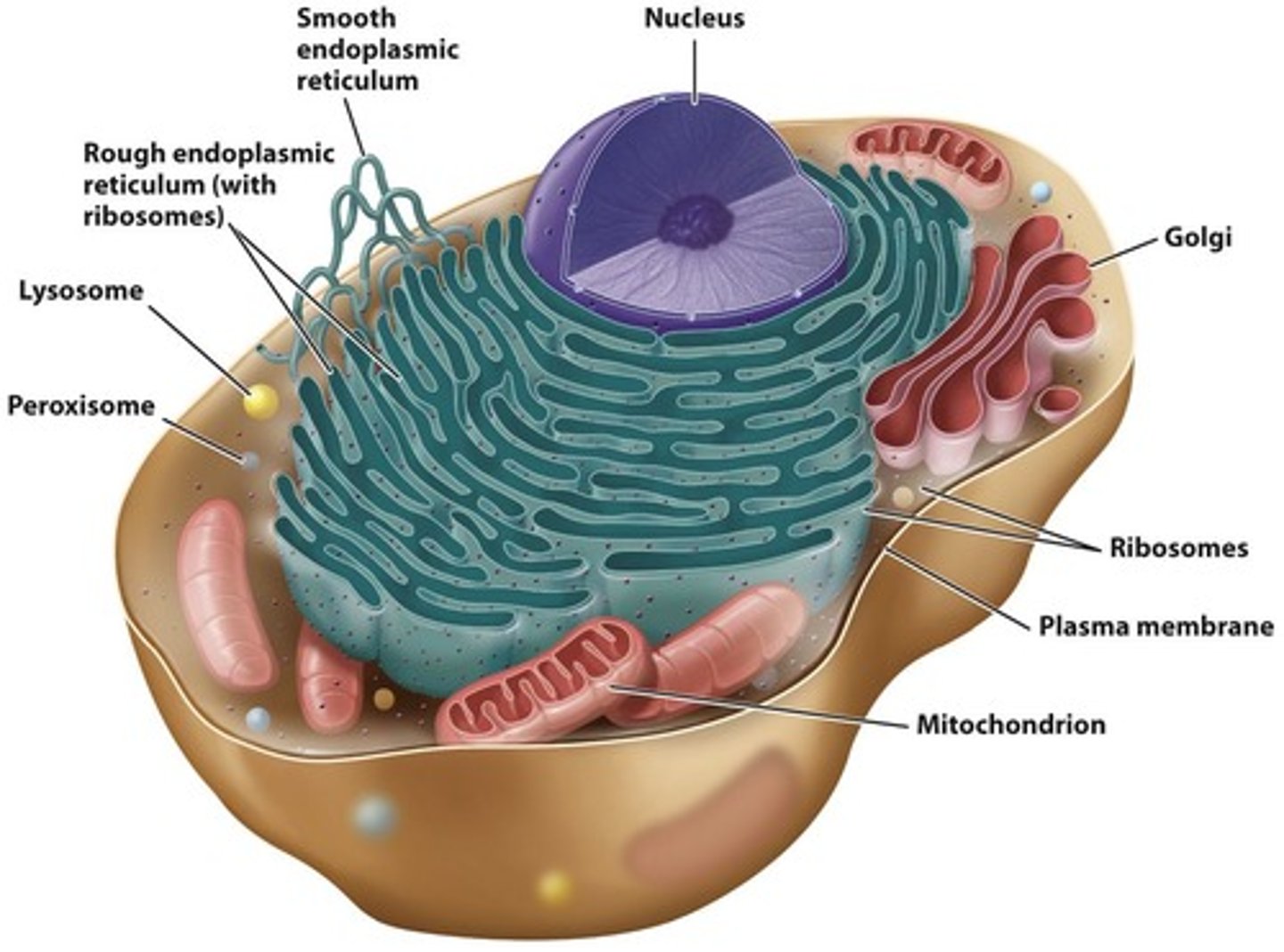
Mitochondria
Energy-producing organelles in eukaryotic cells.
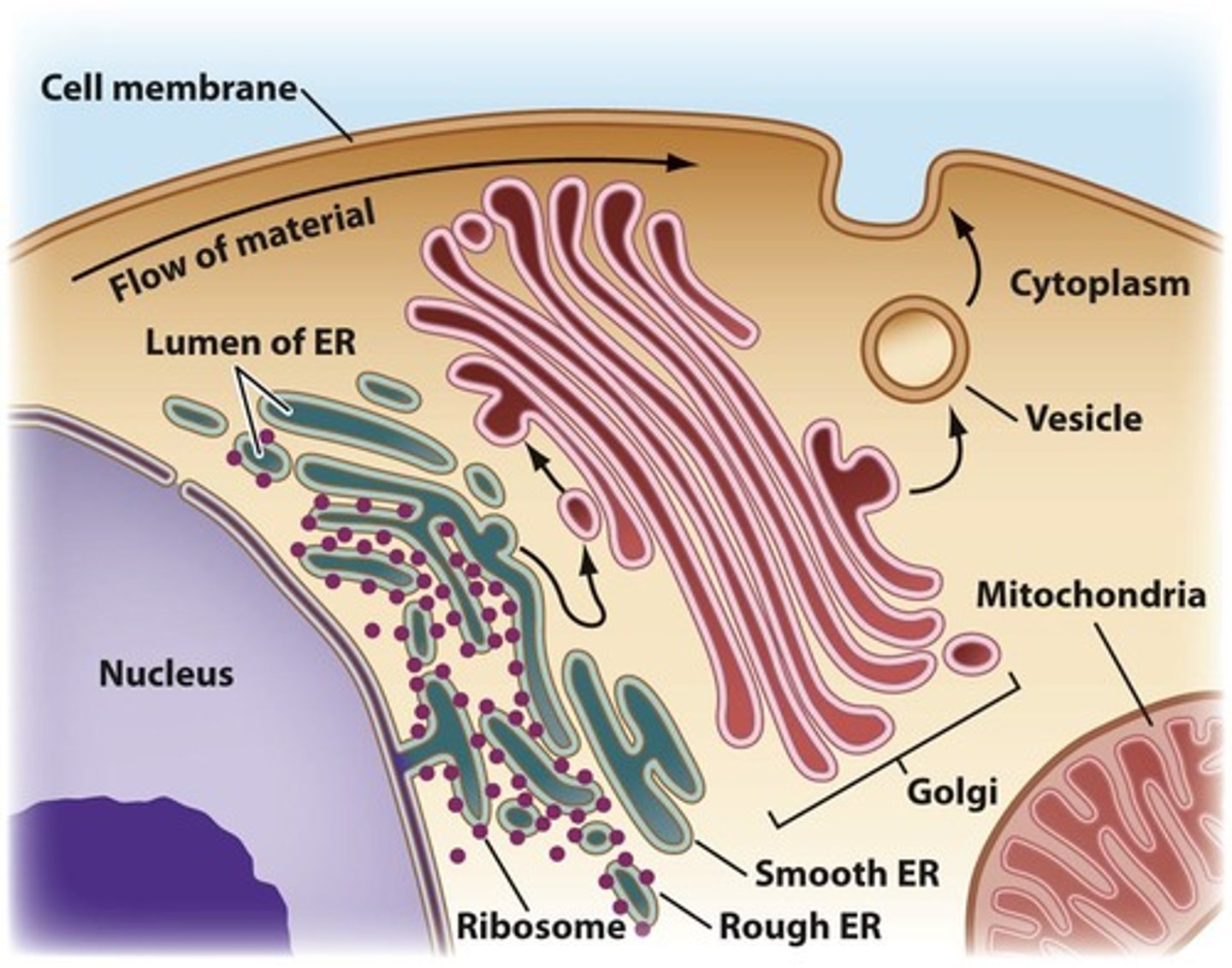
Endomembrane System
Network of membranes for cellular processes.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Site of protein synthesis with ribosomes.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification.
Lysosomes
Organelles containing enzymes for digestion.
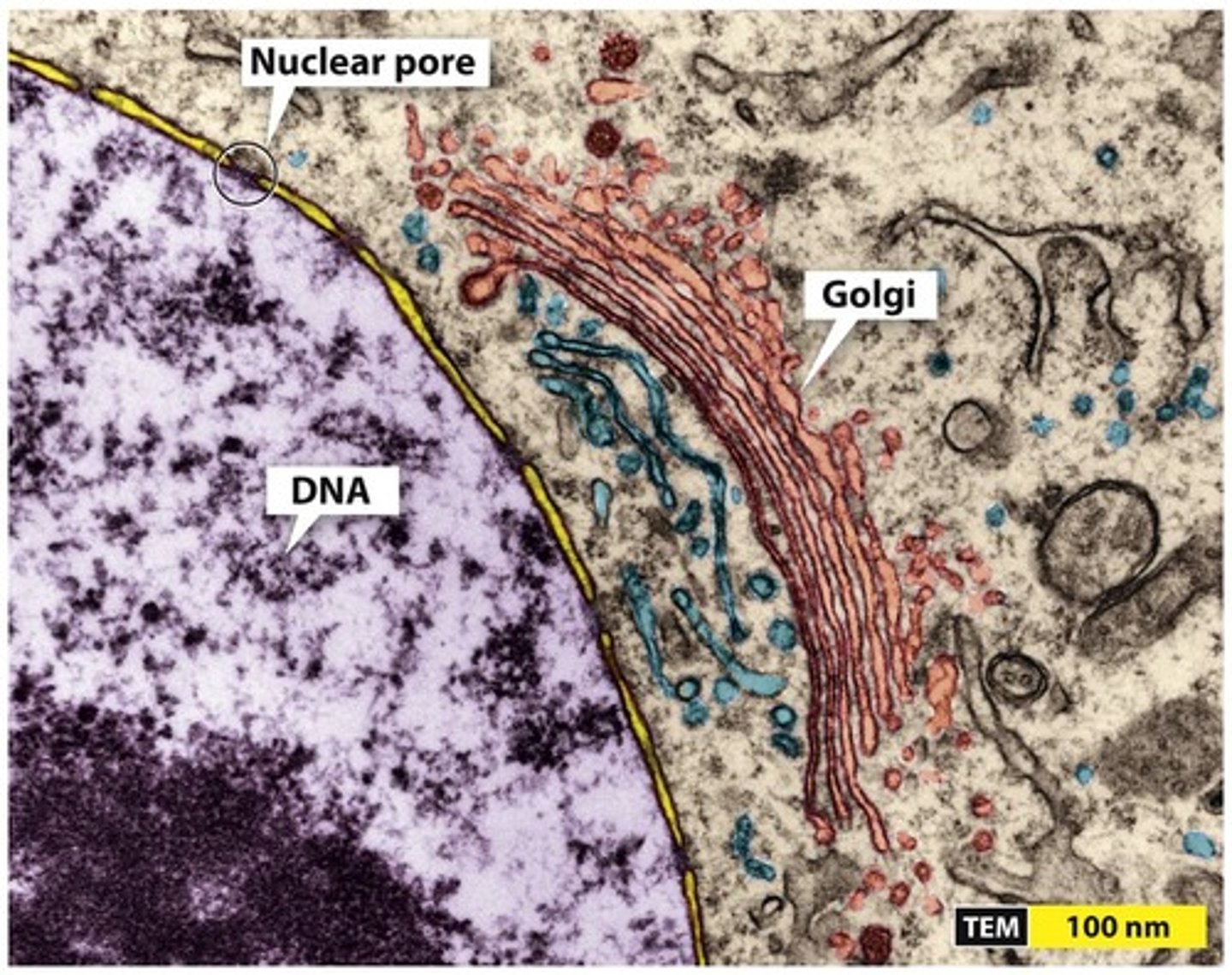
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies and packages proteins for transport.
Mitosis
Process of cell division in eukaryotes.
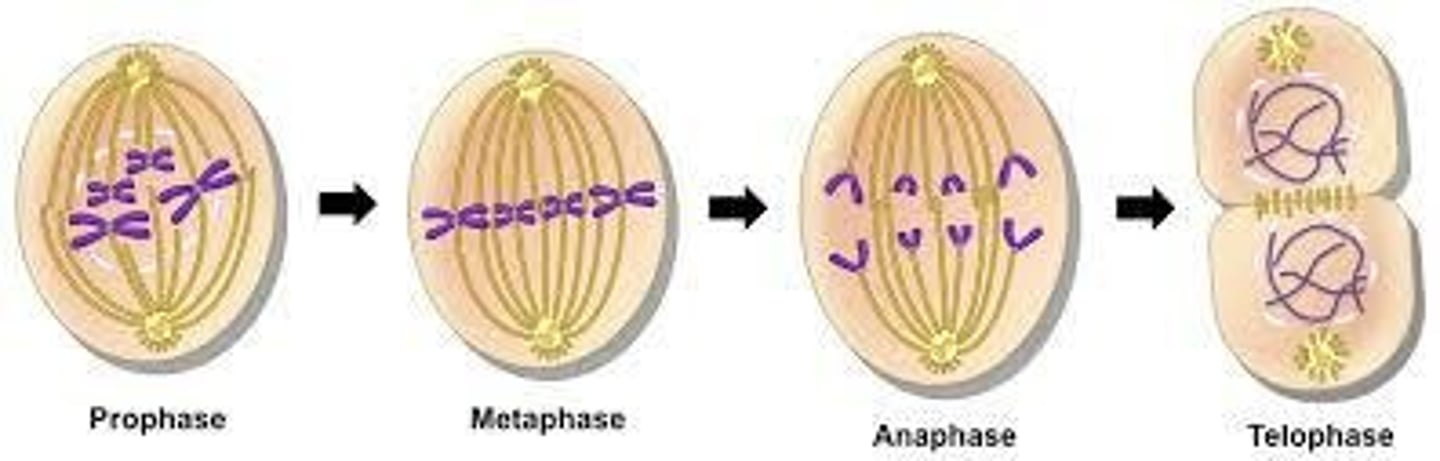
Prophase
First stage of mitosis, chromosomes condense.
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the cell's equator.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids are pulled apart.
Telophase
Nuclear membranes reform around separated chromosomes.
Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms, often decomposers or pathogens.
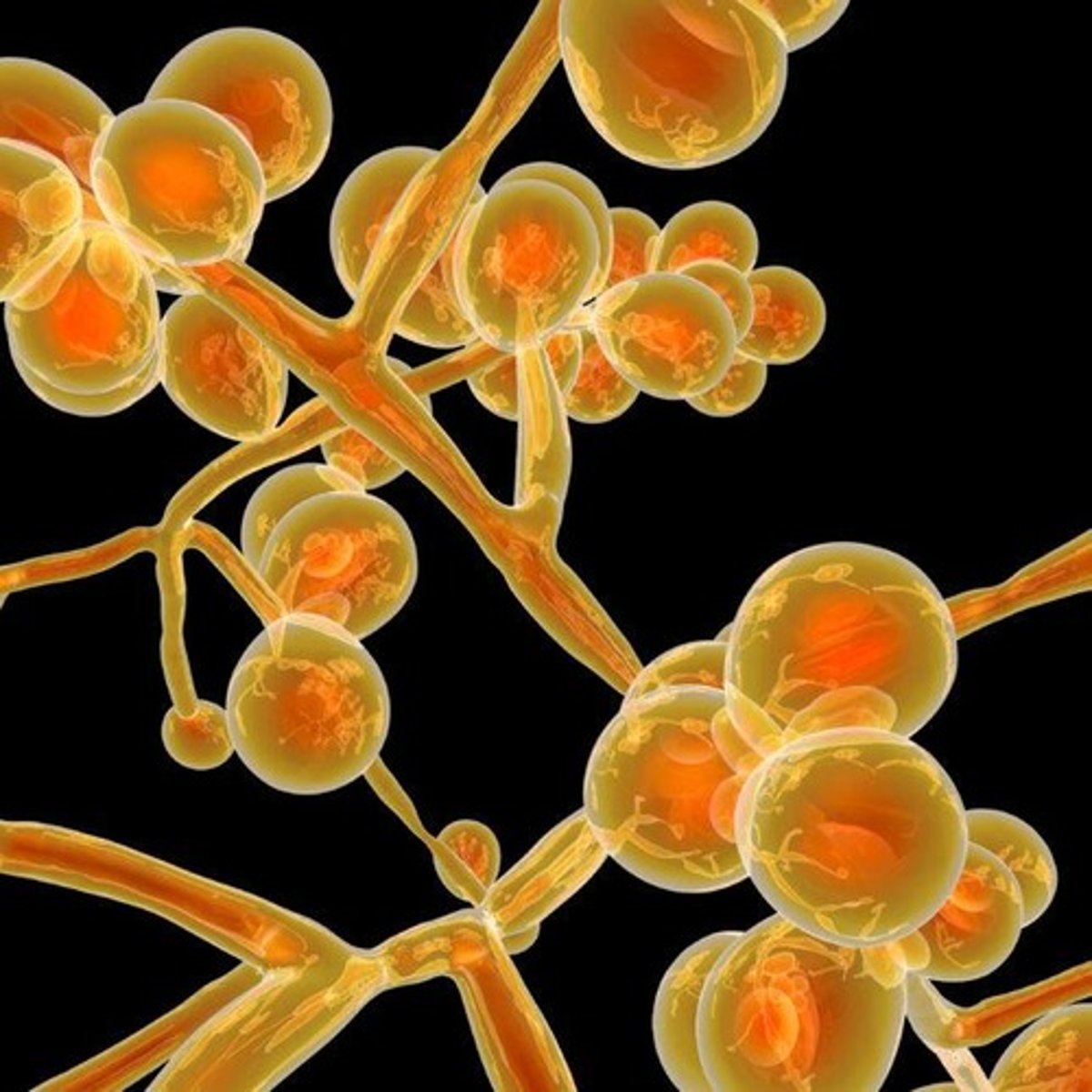
Mycoses
Fungal infections in humans and animals.
Superficial Mycoses
Fungal infections affecting outer skin layers.
Candidiasis
Infection caused by Candida species.
Protozoa
Single-celled eukaryotic organisms, often pathogens.
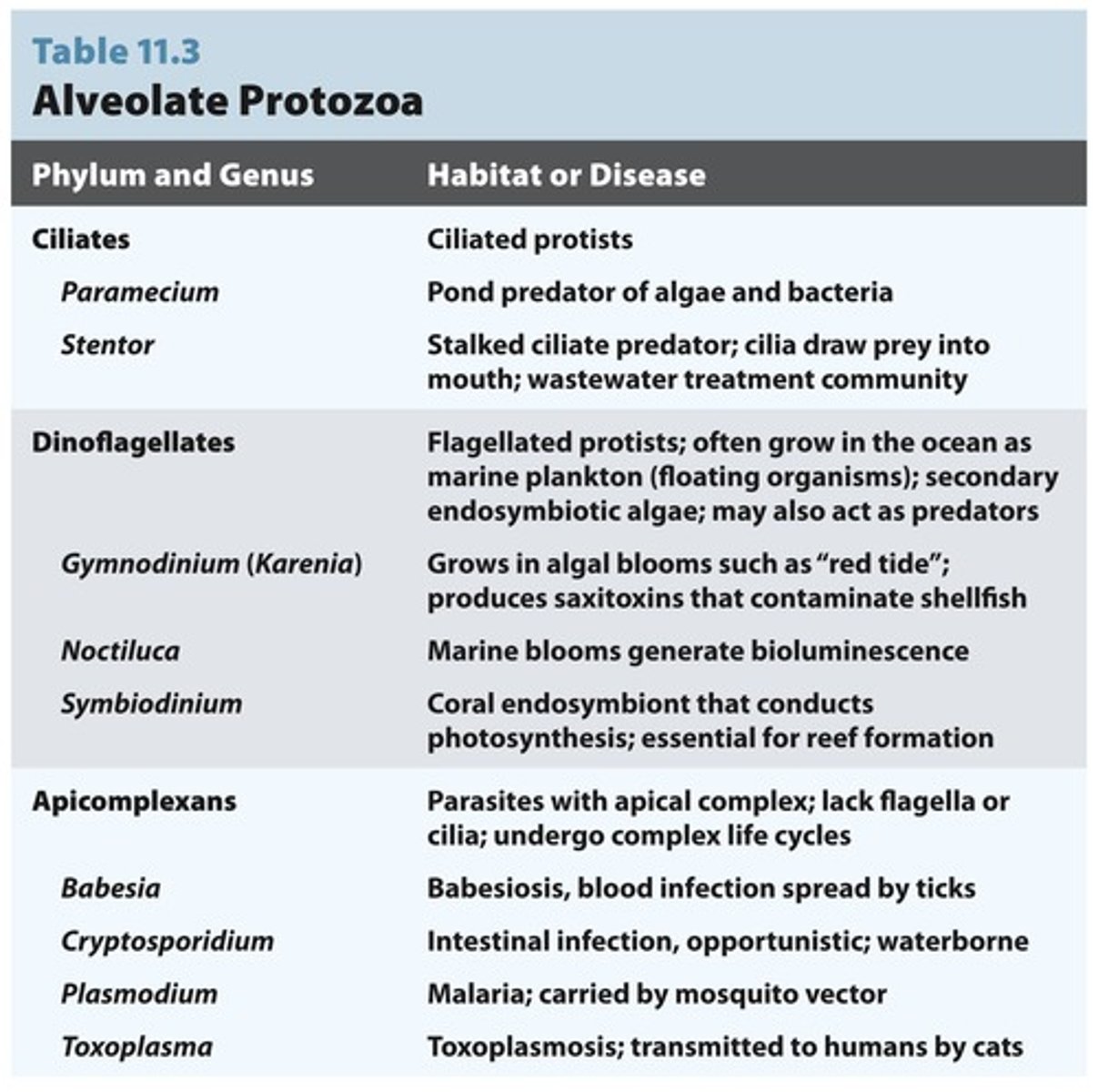
Dinoflagellates
Marine protozoa causing red tides and toxins.
Apicomplexans
Parasites with specialized structures for host entry.
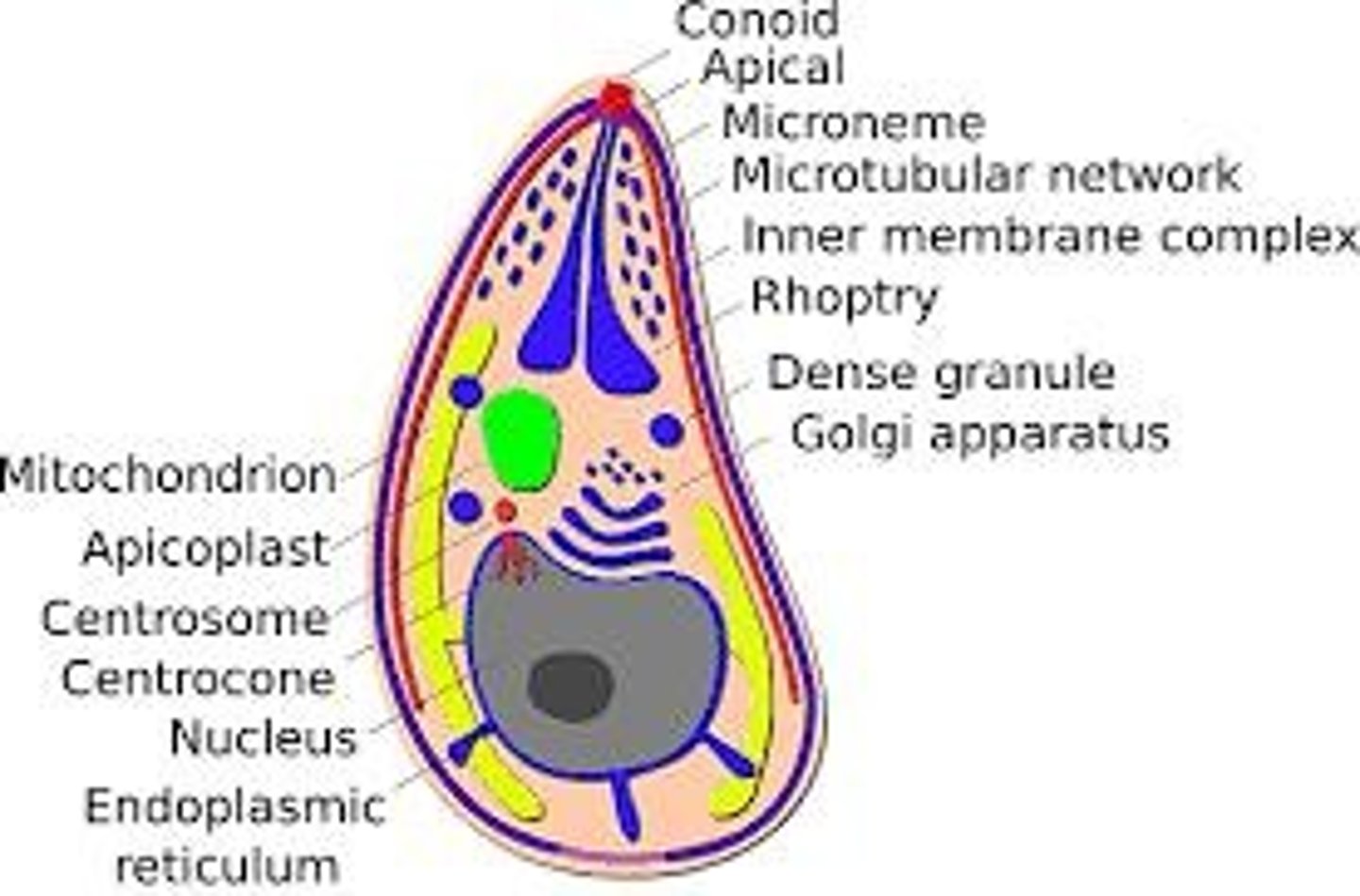
Malaria
Parasitic disease caused by Plasmodium spp.
Toxoplasmosis
Disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii.
Cryptosporidium parvum
Waterborne pathogen causing diarrhea in immunocompromised.
Giardia lamblia
Causes intestinal giardiasis, transmitted via feces.
Helminths
Multicellular parasitic worms affecting human health.
Nematodes
Roundworms with cylindrical bodies and digestive tubes.
Trematodes
Flatworms with branched digestive systems.
Cestodes
Tapeworms that absorb nutrients through skin.
Cyst Formation
Stable form of parasites in the environment.
Saprotrophic
Organisms that obtain nutrients by decomposing organic matter.