Diabetes
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
How does glucagon increase the amount of glucose in the bloodstream?

What does insulin do to glucose levels and explain?

What is diabetes?
It is a common endocrine disorder. It is characterised by persistent hyperglycaemia due to impaired insulin secretion, with or without insulin resistance. it can be classified as type 1 or type 2, with 90% of people having type 2 diabetes mellitus.
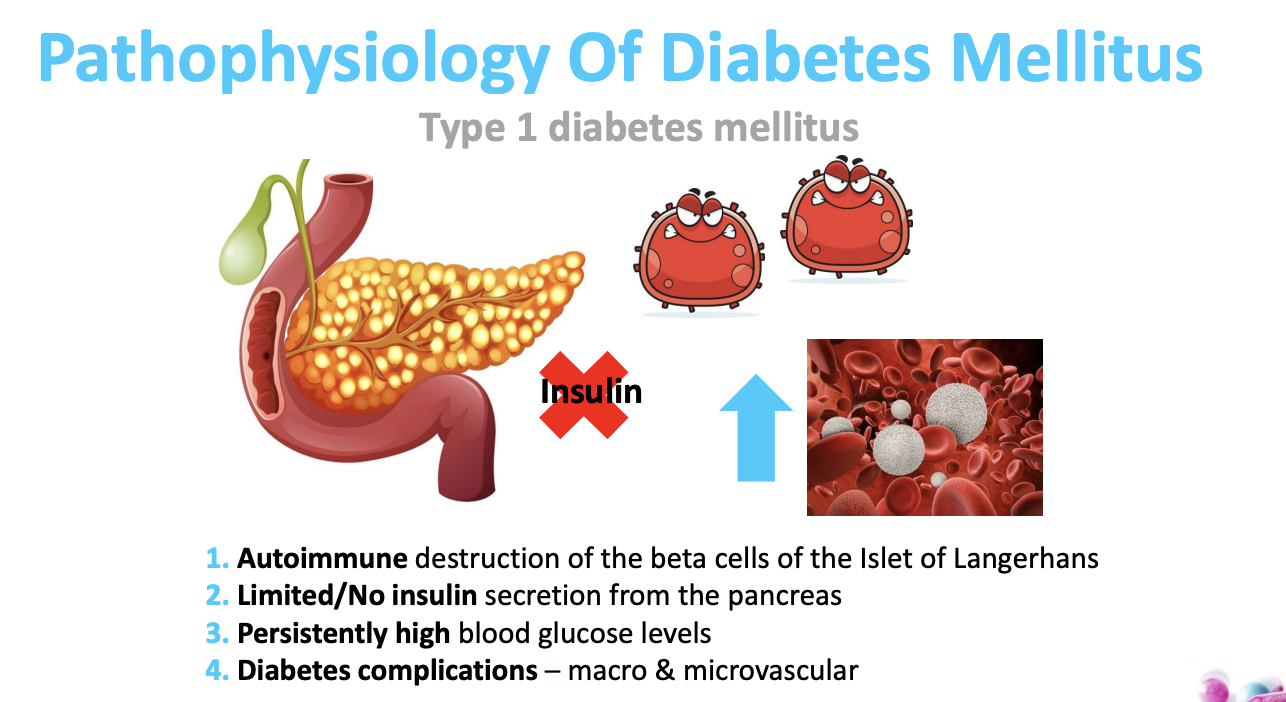
What is the pathophysiology of type 1 diabetes?
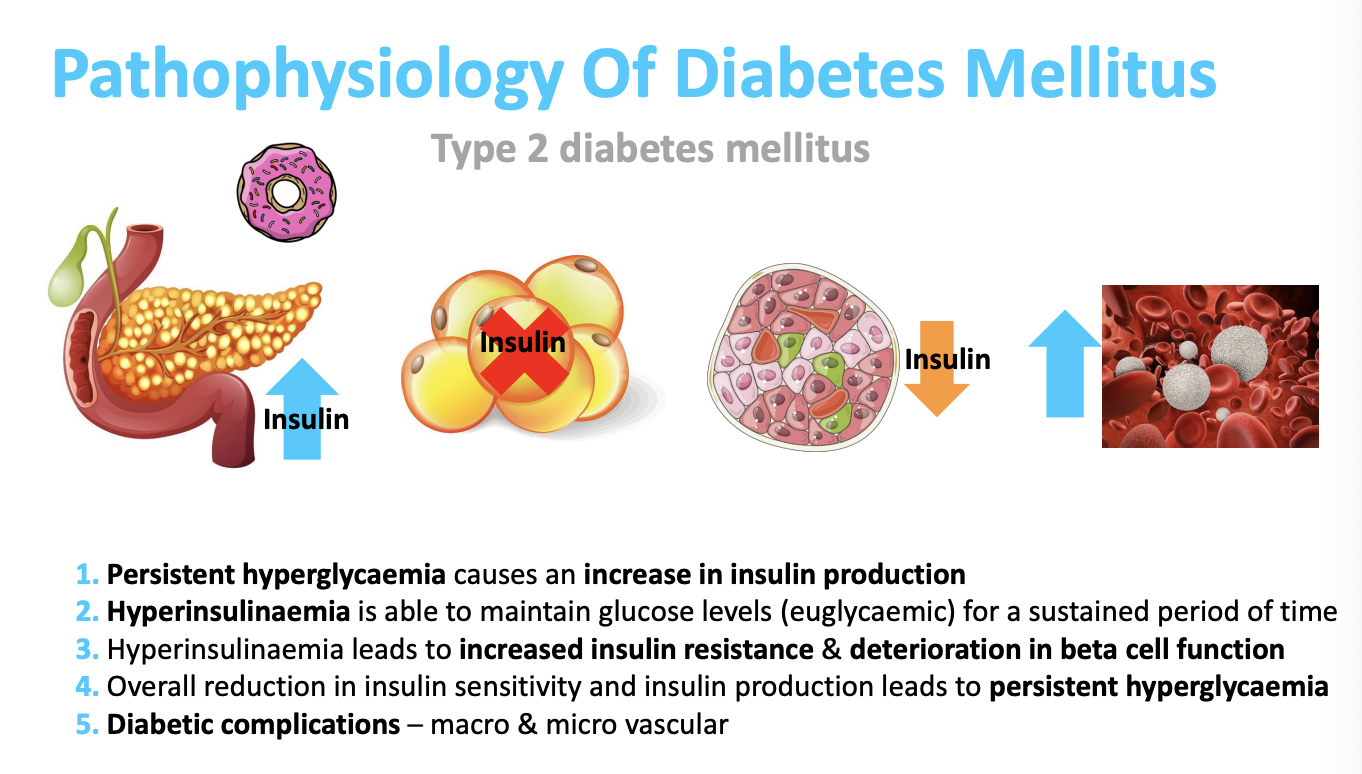
Describe the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes?
Describe and explain the clinical features of diabetes mellitus?
Polyuria
Polydipsia
Polyphagia
fatigue
weight loss
blurred vision
increased infection rate
poor wound healing
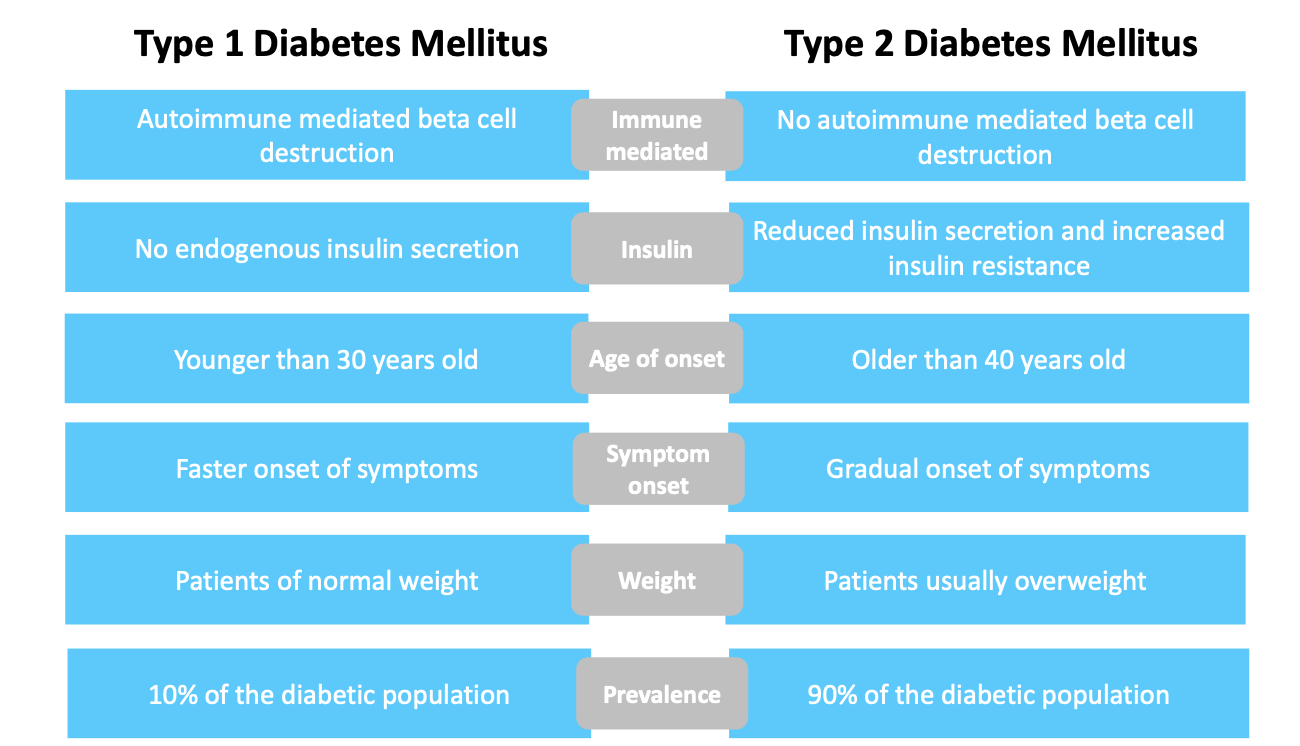
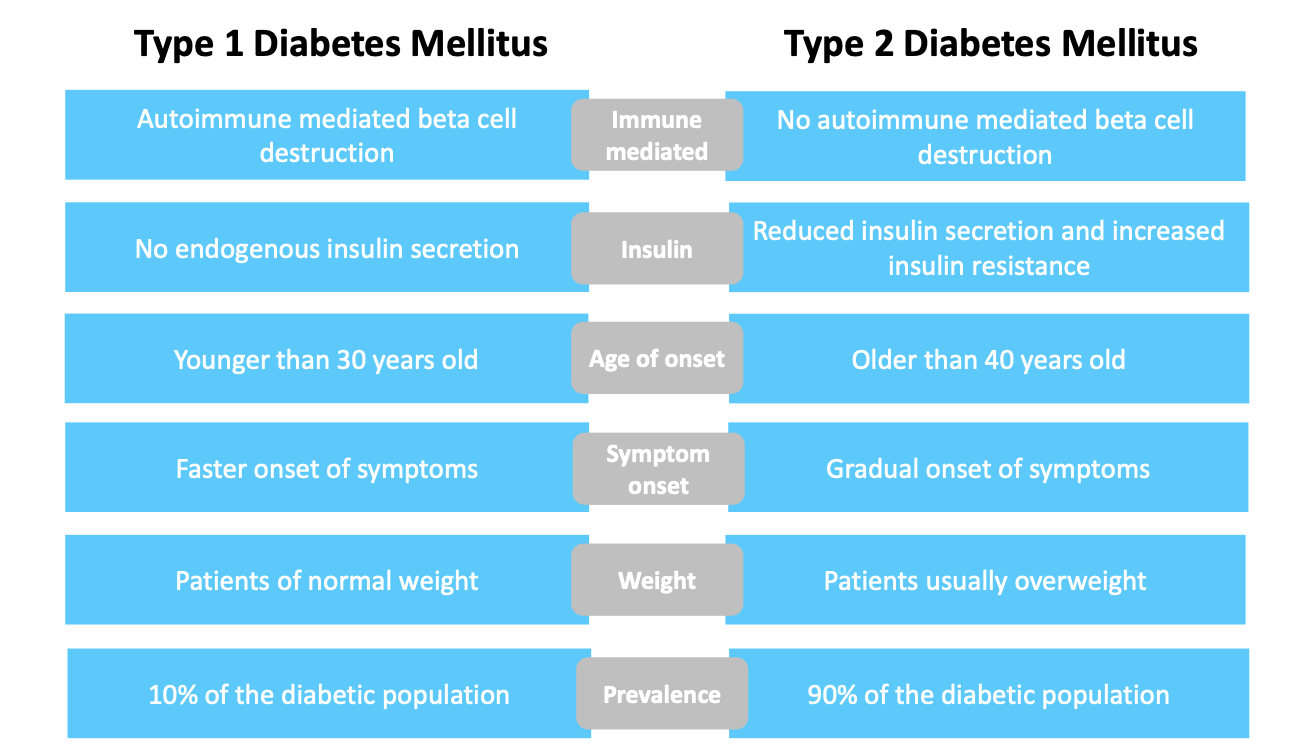
Describe the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
What are the macrovascular and microvascular complications related to diabetes?
Macrovascular: affecting large blood vessels- coronary arteries, aorta
Ischaemic stroke (x2 more likely) (causes 1 in 5 strokes)
Myocardial infarction (MI) (x2.5 more likely)
Other CVD HF (x2.5 more likely)
Microvascular: small large vessels- capillaries
nephropathy (10,350 have end stage kidney failure in uk)
retinopathy (responsible for 5% of sight loss)
neuropathy
What interventions can be made to reduce a persons CV risk if a person has a 10 year QRISK3 score of 10% or more?
Offer atorvastatin 20mg (primary prevention of CVD)
What interventation would you give someone with T1DM for primary prevention of CVD regardless of their QRISK3 score: older than 40, diabetes more than 10 years, established nephropathy, other CVD risk factors.
Atorvastatin 20mg OD
What is the diagnositic criteria for persistent hyperglycaemia?
HBA1c of 48 mmol/mol or more
fasting glucose level of 7.0 mmol/l or more
random plasma glucose of 11.1 mmol/l or more with presence of signs + symptoms
What is the diagnostic criteria of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
What is considered a diabetic emergency?
blood glucose <4 mmol/l
hypoglycaemia
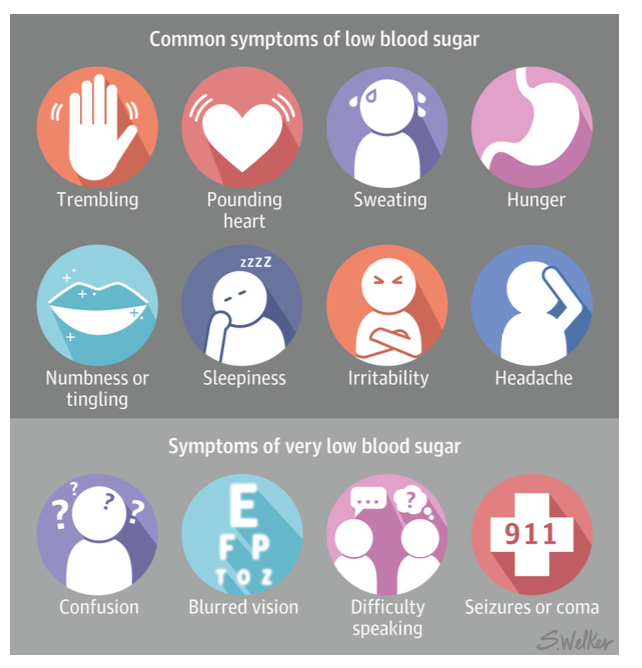
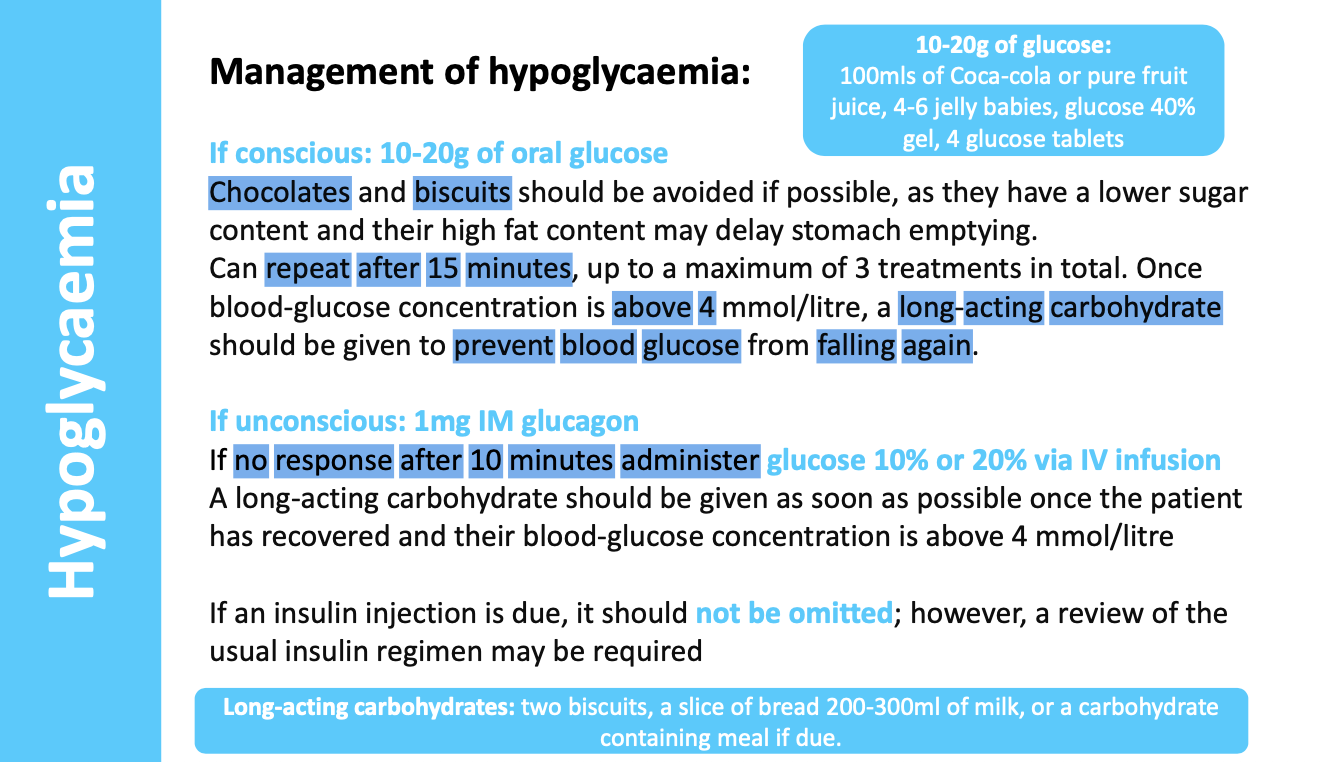
what are the non-pharmocological and pharmacological management treatment for hypoglycaemia?
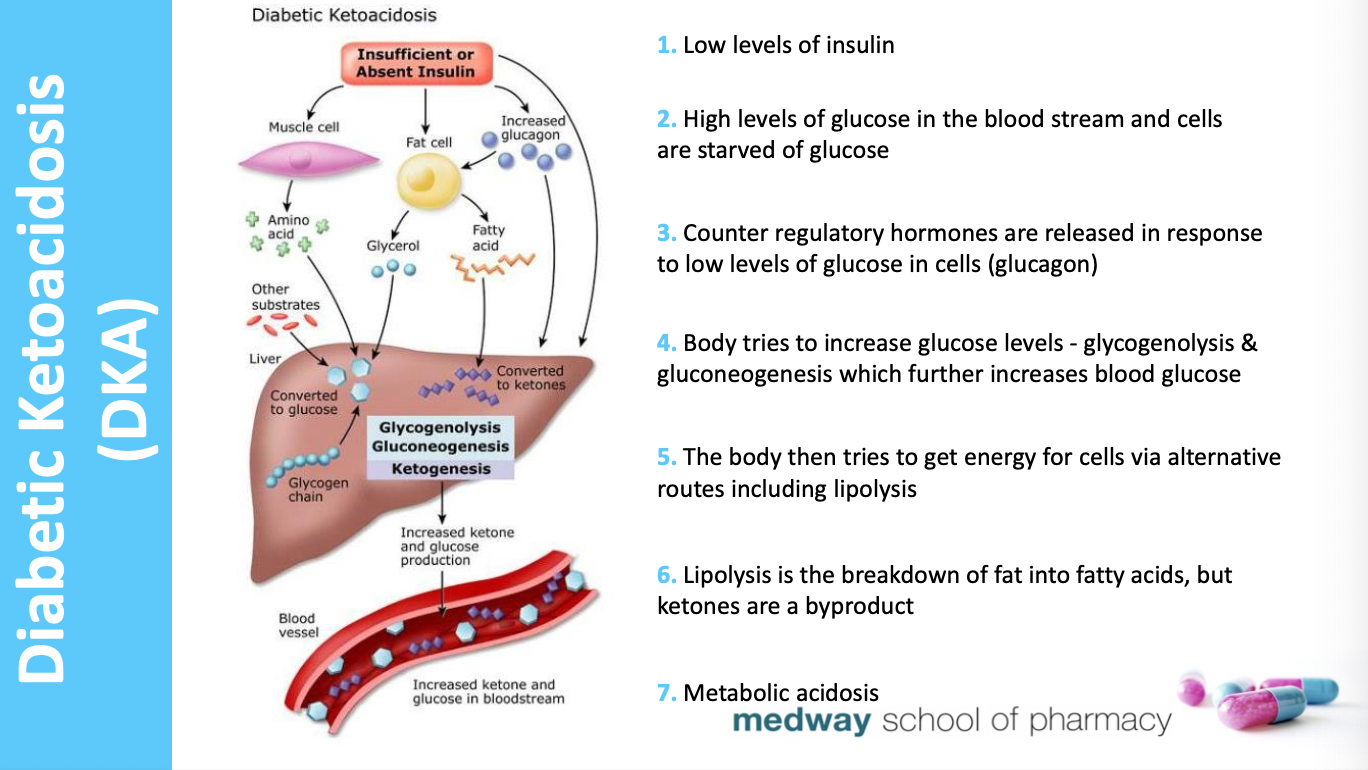
How does diabetic ketoacidosis arise and what is the diagnosis?
Diagnosis:
Blood sugar > 11mmol/l + clinical symptoms + ketones are high (2+ urine, 3mmol/l blood)
preventable but associated with mortality. most seen in T1DM as severe insulin deficiency.
can be first presentation of T1DM.
Management of DKA
insulin
intravenous fluids
potassium + other electrolyte supplementation. insulin binds to cells… movement of potassium allowed, blood stream to cells… leads to hypokalaemia.
How are insulin injections delivered?
Subcutaneously, 90 degrees