Functional neurologic disorders
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
T/F: you have to exclude malingering to diagnose functional neurologic disorders?
false
is it possible for patients with FND to score normal range on psychological questionnaires?
yes, 39% of patients diagnosed scored within normal range
do symptoms usually come on gradually or rapidly?
rapid and suddenly
what are potential contributing factors to FND? (5)
- early life stresses (including in utero)
- injury
- illness with fatigue/bed rest
- anesthesia
- post panic attack
is it common for there to be spontaneous remission?
yes
can multiple functional symptoms occur concurrently?
yes
what is the overall treatment protocol?
- PT and OT 2x/day for 5 consecutive days
- SLP if needed
- eval by psychiatrist or psychologist early in the week
- assessment by neurologist at end of the week
what outcome measures should be done? (3)
- video at beginning and end of week
- patient and physician rated outcomes
- self rated disability scale
how can long term outcome measures be done?
- can mail questionnaires and phone call to follow up
what are positive diagnostic signs for functional limb weakness? (2)
- hoovers sign = hip ext weakness that improves with contralateral hip flexion contraction
- hip abductor sign = abductor weakness that improves with contralateral abduction contraction
what are positive diagnostic signs for functional movement disorders? (3)
- functional dystonia presenting in a clenched fist or inverted ankle
- facial dystonia presents with episodic contraction of orbicularis oculi
- left wrist tremor stops when copying examiners movements with right hand
what is the big picture on what you should look for when diagnosing?
- look for variability of symptoms especially when the patient is distracted
T/F: multidisciplinary approach is best?
true
what medications can be helpful?
- antidepressants
- anti-anxiety
T/F: it is important to acknowledge that the symptoms are real and that they are common?
true
can symptoms improve with FND? why or why not?
- yes because there is no irreversible damage to the nervous system
what are some factors that can trigger symptoms? (6)
- stress
- anxiety
- depression
- trauma
- illness
- injury
what is the goal of therapy?
re-training the nervous system
is every patient with FND appropriate for therapy?
no
how might you treat breathing techniques with a distraction component of FND treatment? (3)
- blowing bubbles
- blowing a pinwheel
- blowing with a straw
T/F: FND often occurs with other neurological disorders?
true
T/F: FND is exclusively a psychological problem caused by psychological problems?
false
T/F: prognosis of FND is usually good?
false
T/F: FND treatment is individualized and involves careful explanation and combinations of physical and psychological rehabilitation?
true
is there a consensus for frequency and duration of treatment OUTSIDE OF PROGRAMS?
- no consensus
- maybe 1-2x/week for 12-16 weeks
what is the physio4FMD trial?
- looking at a specialist physiotherapy protocol alone to treat rather than a multidisciplinary approach
- 9 sessions/3weeks
- found that there were better subjective reports of improvements despite there still being impairments
T/F: FND is an umbrella term?
true
what is FND?
- neurological condition caused by changes in how the brain networks work
- not changes in the structure of the brain
can physical symptoms of FND be explained by changes in brain structure?
-no, but that doesn't mean the symptoms aren't genuine
what 2 neurologic conditions is FND compared to?
- MS and ALS
can FND overlap with a neurologic disease?
yes
what is the diagnostic criteria for FND (4)
- 1+ symptoms of altered voluntary motor or sensory function
- clinical findings provide evidence for incompatibility between symptoms and recognized medical conditions
- another medical or mental disorder does not explain the symptoms presenting
- symptom or deficit results in clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other functional spaces
what is a functional movement disorder?
- involuntary but learned habitual movement pattern driven by abnormal self-directed attention due to a complex combination of physical, mental, and social influence on brain function
what is a common trigger of functional movement disorder?
- commonly triggered by physical or emotional event
- 40% of people dont have psychiatric history
what is a common presentation of adult with functional movement disorder? (5)
- tremor
- gait disorder
- dystonia
- weakness
- paralysis
what is a common presentation in children with functional movement disorder? (3)
- seizures
- sensory loss
- motor symptoms
what is ongoing research saying about FMRIs?
- FMRI are showing changes in brain structure with FND
what is agency?
- experience of being the cause of our own actions
- depends on comparison of sensory feedback with what was predicted
what happens with impaired self agency?
- brain is over aware of attention without voluntary control
what 2 events must occur to produce self agency?
1. the person must have the sense of willing the movement
2. the movement has to happen
what is interoception?
- perception of internal signals from the body
what is attention dysregulation?
- inappropriate self directed attention
what are key regions of the brain that are involved? (5)
- insula
- amygdala
- prefrontal cortex
- temporo-parietal junction
- supplementary motor area
what is the function of the insula? (5)
- sensory processing/interoception
- emotional functions/limbic system
- motivation/reward/defense systems
- cognitive systems
- neuromodulation
what is the amygdala?
- in the limbic system of the brain
- at the epicenter for emotions (mostly fear)
T/F: FND causes a top-down prediction error?
true
T/F: FND causes impaired integration of bottom up sensory imput?
true
what is entrainment?
- tremor changes to the same frequency as a cued rhythmic movement
what is a whack-a-mole sign?
- with restraint of affected body part, involuntary movement emerges or worsens in other parts of the body
what is a wheelchair sign?
- patient can sit and walk the wheelchair while seated but is unable to stand up and walk
what is the riverbanks analogy?
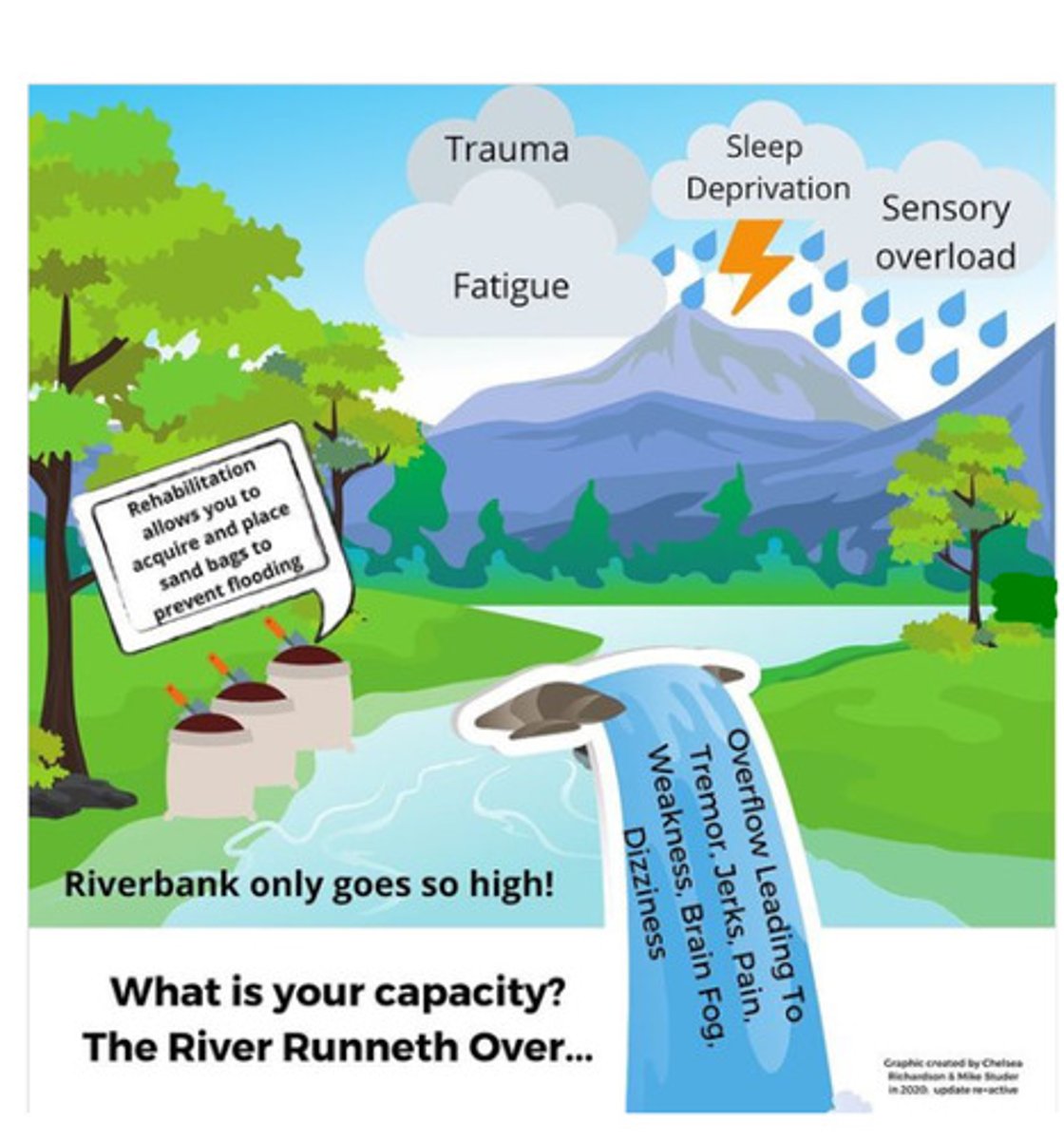
T/F: physical therapy for FND emphasizes task based interventions and self efficacy?
true
T/F: FND is associated with autonomic factors?
- true
- reports of fainting, rapid HR, dizziness, sweating, bowel and bladder issues
T/F: people with FND tend to have a decrease in PSNS activity
true
what can be done to measure increase in SNS?
- decreased PSNS means increased SNS
- if increased SNS, wrist or chest HR monitor can be used to gather objective data (HR and HR variability)