enzymes
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
transition state
old bonds are incompletely broken and new bonds are incompletely formed
has a different geometry from either reactants or products
how do enzymes affect the transition state?
proximity
orientation
microenvironment
cofactors
a non protein compound that must be bound either tightly (prosthetic group) or loosely (coenzyme) to an enzyme in order for it to function during catalysis.
eg metal ions
many are vitamin derivatives, required in diet as not synthesised
eg thiamine and cobalamin
coenzyme
binds reversibly
they are chemically changed during the course of enzyme activity
many are vitamin derivatives
feedback vontrol of enzyme pathways
operate within pathwats
many metabolic pathways areeeecontrolled by feedback mechanisms
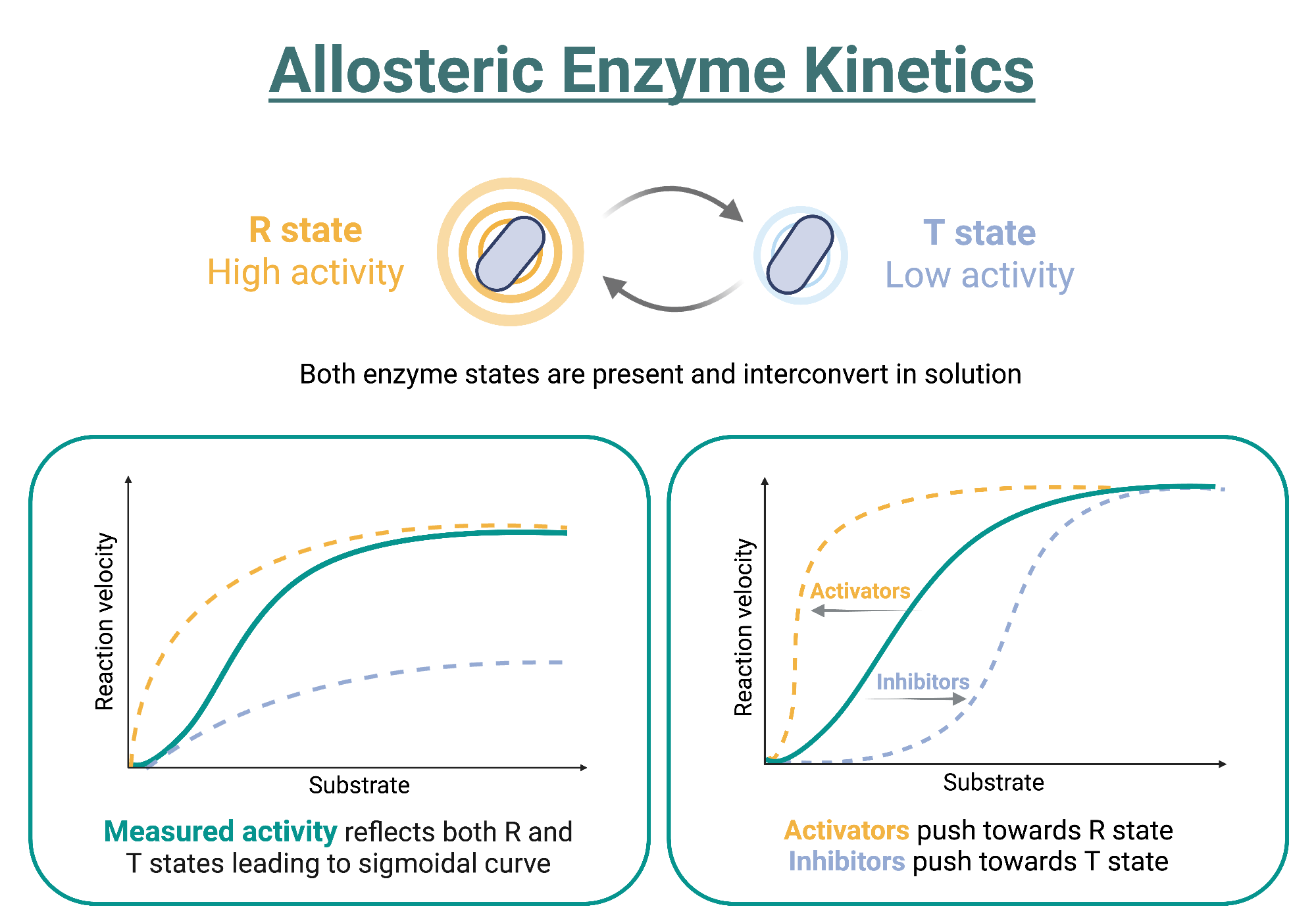
allosteric enzymes
close to beginning end or branch point of metabolic pathways
bind products of remote reactions in the same or related pathway
at allosteric site
have a quaternary structure
display s shaped kinetic profiles- cooperitivity
can be affected by inhibitors or activators
covalent modification
phosphorylation/dephosphorylation
phosphorylation- kinases
de- phosphatases
serine/threonine kinases and tyrosine kinases are the 2 types
phosphorylation reactions usually requie ATP as a phosphate donor producing ADP in addition to covalently linking a phosphate group to serine threonine or tyrosine on the target protein
control by regulatory proteins or nucelotides
enzymes can be activated or inhibited through binding of nucleotides or other proteins to site remote from active site
eg regulatory subunit of cAMP dependent protein kinase requires nucleotide cAMP binding for activation
control by ion binding
only calcium ions
in an E-F hand the calcium binding site is located in a tight loop connecting two alpha helices E and F
control through proteolysis
blood clotting pathway- protease cascade
enzymes break down proteins to regulate cellular processes
sequential activation of protease actiivty through proteolysis ensures rapid signal amplification
mechanisms to stop protease is required
allosteric regulation of enzyme activity
allosteric inhibitors stablise the inactive state
so decreases affinity of enzyme for substrate
allosteric activators stabilise the active site
so incereases affinity of enzyme for substrate