Normal Profits, Supernormal Profits & Losses
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
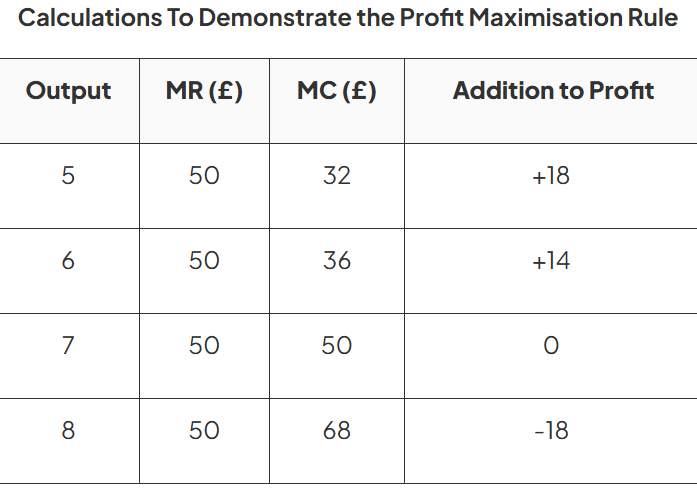
To maximise profit firms should produce up to the level of output where marginal cost (MC) = marginal revenue (MR)
Observations
With the 7th unit of output, MC = MR and no additional profit can be extracted by producing another unit
Up to the 6th unit of output, MC < MR and additional profit can still be extracted by producing an additional unit
From the 8th unit of output, MC > MR and the firm has gone beyond the profit maximisation level of output
It is making a marginal loss on each unit produced beyond the point where MC = MR
Explicit costs
Explicit costs are the costs which have to be paid e.g raw materials, wages etc.
Implicit costs:
Implicit costs are the opportunity costs of production
This is the cost of the next best alternative to employing the firm's resources
E.g. if an investor puts £1m into producing bicycles and they could have put it in the bank to receive 5% interest, then the 5% represents an implicit cost
Why must implicit costs be considered?
Implicit costs must be considered as entrepreneurs will rationally reallocate resources when greater profits can be made elsewhere
Profit = total revenue (TR) - total costs (TC)
Total costs include explicit and implicit costs
Normal profit occurs when TR = TC
This is also called breakeven
When does a Supernormal profit occur
Supernormal profit occurs when TR > TC
A loss occurs when TR < TC
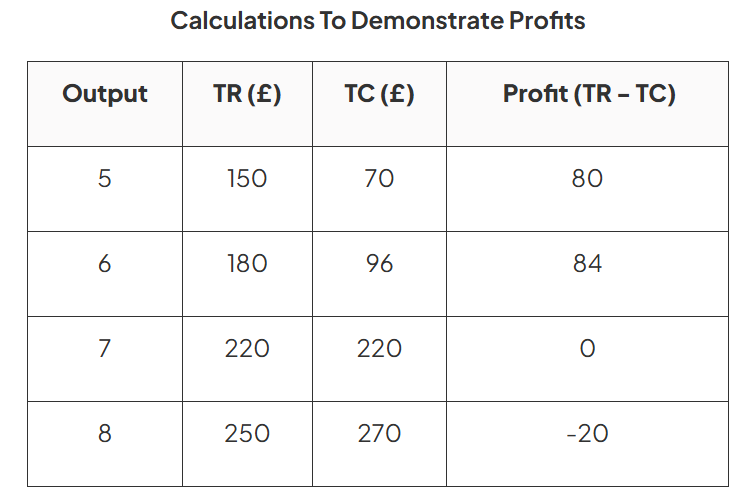
Observations
Supernormal profit occurs up to the 6th unit of output
Normal profits occur at the 7th unit
From the 8th unit, the firm is making a loss
Short-run & Long-run Shut-down Points
Firms do not always make a profit and may endure losses for a period
Entrepreneurs often keep firms going in the hope that market conditions will change and demand for their products will increase leading to profitability
This raises the question, 'when is it the best time for a firm to shut down?'
The shut-down rule provides the answer by considering both the long-run and short-run periods
The short-run shut down point
In the short-run, if the selling price (average revenue) is higher than the average variable cost (AVC), the firm should keep producing (AR > AVC)
If the selling price (AR) falls to the AVC it should shut down (AR = AVC)
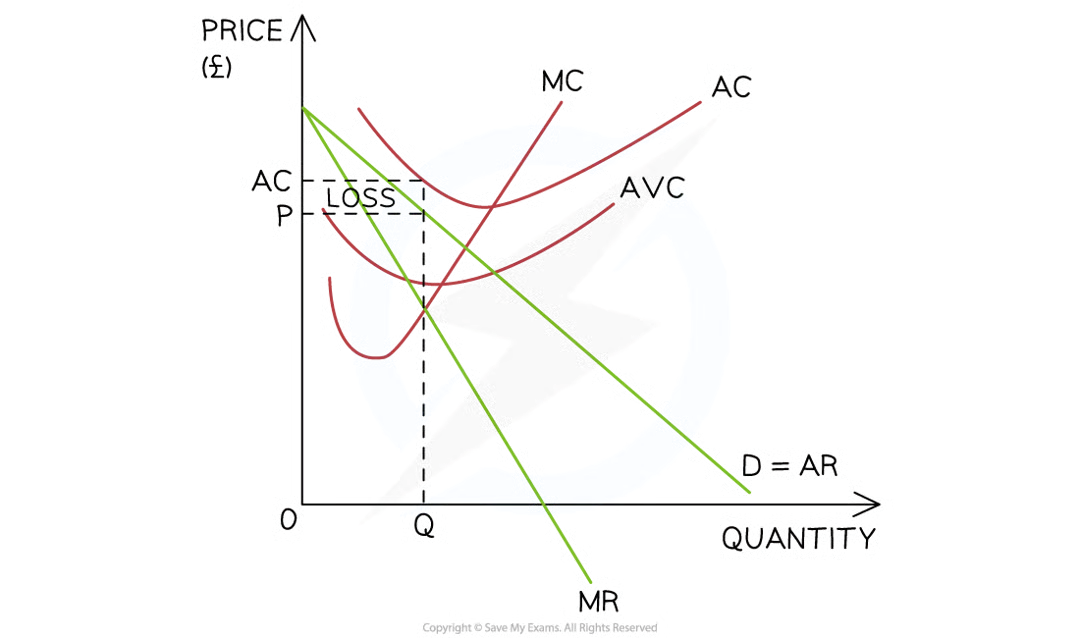
Diagram analysis
The firm produces at the profit maximisation level of output (Q) where MC=MR
At this level, the P = AVC
This means that there is no contribution towards the firm's fixed costs
The selling price literally only covers the cost of the raw materials used in production
There is no point in continuing production and the firm should shut down
The long-run shut down point
In the long-run, if the selling price (AR) is higher than the average cost (AC) the firm should remain open (AR > AC)
if the selling price (AR) is equal to or lower than the average cost (AC), the firm should shut down (AR = AC)
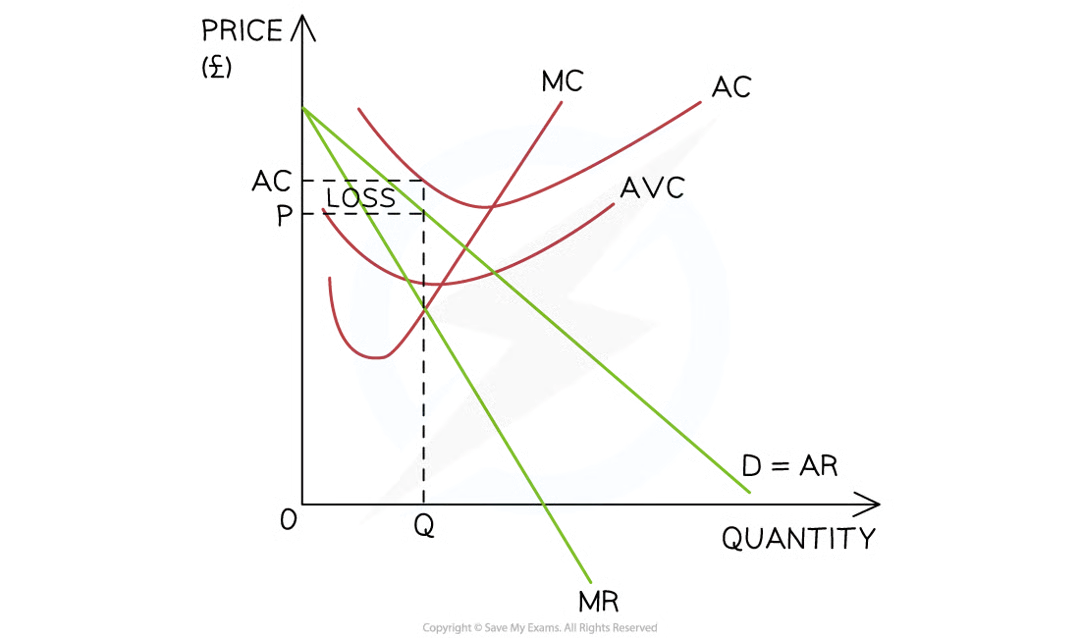
Diagram analysis
The firm produces at the profit maximisation level of output (Q) where MC=MR
At this level, P < AC
It could continue operating in the short-run as the AR > AVC, but in the long-run they are making a loss and the firm will shut down