biological molecules
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
what are monomers
the smaller units from which larger molecules are made
what are polymers
Polymers are molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together in a chain
what are carbohydrates
molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (higher proportion of oxygen than lipids)
what are the different types of carbohydrates
monosaccharides
disaccharides
polysaccharides
define a monosaccharide, give an example, and state its function
definition- made up of a single sugar unit, and all monosaccharides are reducing sugars
examples:
ribose
glucose- alpha and beta glucose
function- source of energy in respiration, and are the building blocks for polymers
define a disaccharide and give examples
definition- a sugar formed from 2 monosaccharides, joined by a glycosidic bond in a condensation reaction
examples:
maltose- alpha glucose + alpha glucose (reducing sugar)
sucrose- glucose + fructose (non-reducing sugar)
lactose- glucose + galactose (reducing sugar)
define a polysaccharide, give an example, and state its function
definition- a polymer formed from many monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds in a condensation reaction
examples:
cellulose (made from beta glucose)
starch (made from alpha glucose in the form of amylose and amylopectin)
glycogen (alpha glucose)
function:
energy storage:
starch- in plants
glycogen- in animals
structural- cellulose makes up the cell wall in plants
what is a condensation reaction
when monomers combine together by covalent bonds to form polymers and a water molecule is removed
what is a hydrolysis reaction
polymers are broken down into smaller subunits as covalent bonds are broken when a water molecule is added
what is the difference between reducing and non reducing sugars
the classification depends on the sugars ability to donate electrons
reducing sugars can donate electrons (the carbonyl group becomes oxidised)
non-reducing sugars can’t donate electrons, so can’t become reduced
give examples of reducing and non-reducing sugars
reducing sugars:
glucose
fructose
lactose
galactose
non-reducing sugars:
sucrose
what is the test for reducing sugars and non reducing sugars
sugars are soluble
place sugars in benedict’s solution (blue) and heat up solution in a water bath
reducing sugars- will donate an electron which reduces cupric ions (Cu2+) into cuprous ions (Cu1+) - this causes a colour change to brick red
non-reducing sugars- can’t donate an electron, so cupric ions (Cu2+) aren’t reduced- solution stays blue
what is an oxidation reaction
gain of oxygen
loss of hydrogen
loss of electrons
what is a reduction reaction
loss of oxygen
gain of hydrogen
gain of electrons
how are sugars named
-Sugars end in OSE
3 carbon sugar = triose sugar
4= tetrose sugar
5= pentose sugar
6= hexose
7= heptose
what is an isomer
a molecule with the same molecular formula but a different structure
what is the molecular formula for glucose
C6H12O6
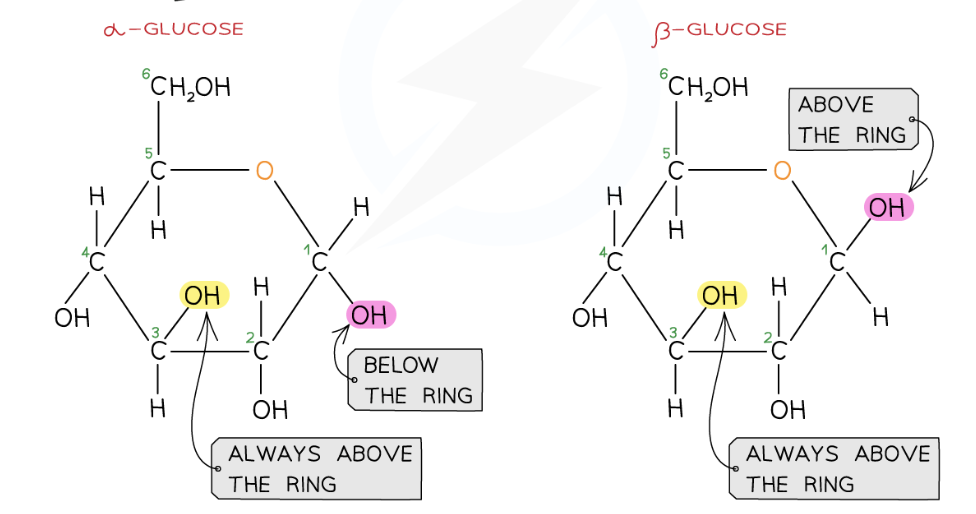
draw alpha and beta glucose
ABBA- for OH group
alpha- below (OH group is below)
beta- above (OH group is above
why are disaccharides more suitable for transport than monosaccharides
Less Reactive – Disaccharides are more chemically stable than monosaccharides, reducing the risk of unwanted reactions during transport in plants and animals.
Lower Osmotic Effect – They exert less osmotic pressure than monosaccharides, preventing excessive water movement that could disrupt cell balance.
Easier Storage & Controlled Breakdown – Disaccharides can be hydrolyzed into monosaccharides when needed, allowing for controlled energy release.
Efficient Energy Transport – In plants, sucrose (a disaccharide) is the main sugar transported in the phloem because it is stable and soluble.
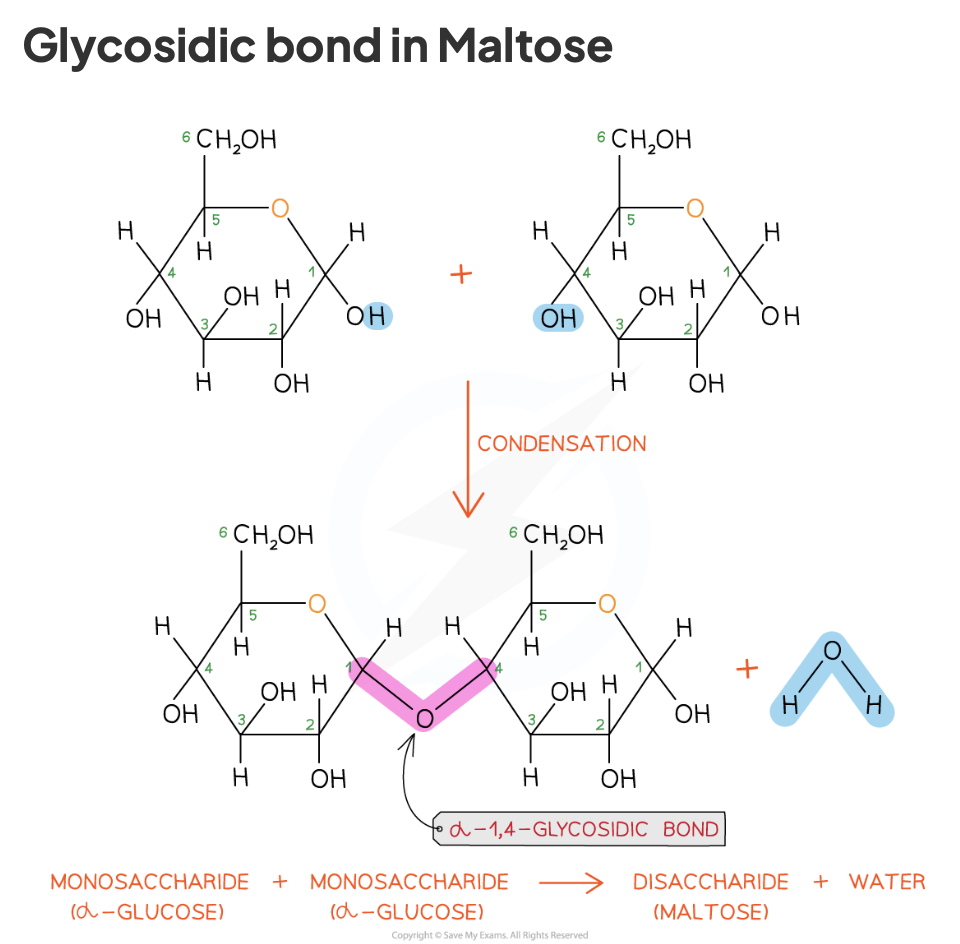
how are glycosidic bonds formed
when two hydroxyl (-OH) groups on different saccharides interact to form a 1-4 glycosidic bond via a condensation reaction
1-4 because carbon 1 on one saccharide and carbon 4 on the other saccharide
results in one water molecule being removed
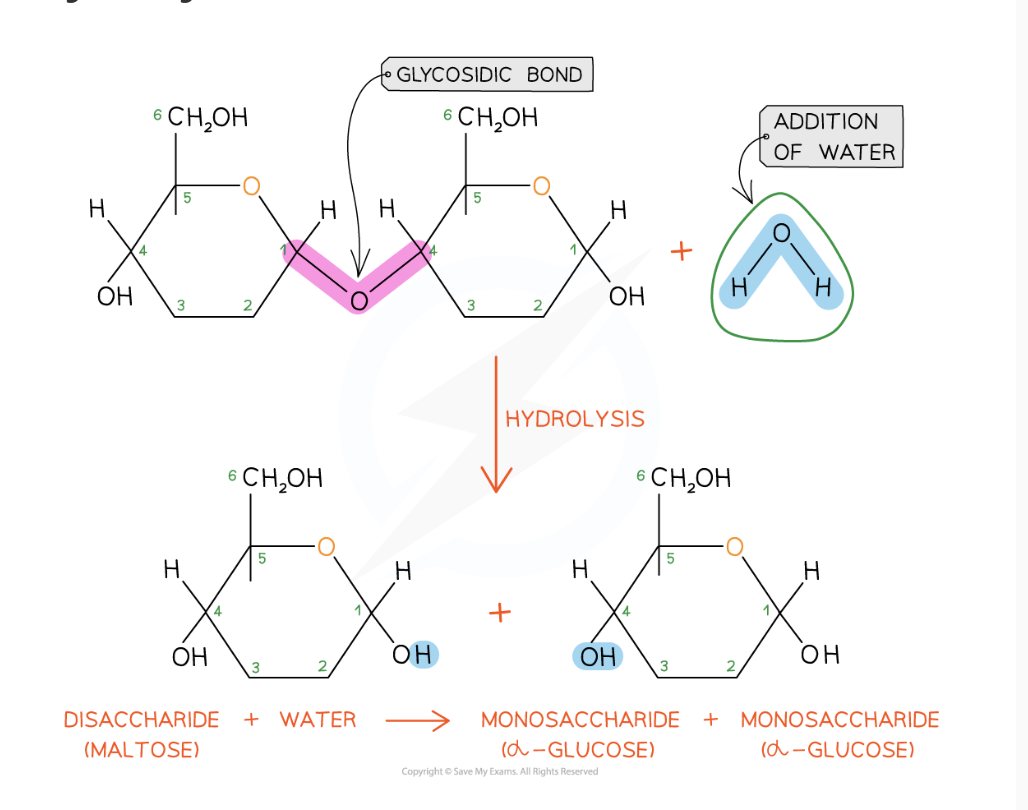
how are glycosidic bonds broken
hydrolysis reaction with the addition of a water molecule
compare the structure of monosaccharides and disaccharides
Compare the structures of monosaccharides and disaccharides
-monosaccharides are made up of 1 sugar unit e.g. Glucose and disaccharides are made up of 2 sugar units e.g. sucrose
-Disaccharides contain an alpha 1-4 glycosidic bond.
-Disaccharides require a condensation reaction to be formed, which releases a water molecule
-Both soluble in water
-Monosaccharides such as glucose can be used straight away for respiration, however disaccharides have to be broken down/digested before they can be used in respiration
why don’t plants and animals store glucose as glucose
glucose is soluble in water which could lead to the osmosis effect as it can decrease the water potential off cells causing water to be drawn in
need to store as starch or glycogen because they are compact molecules and are insoluble in water
describe the structure and function of starch
monomer- alpha glucose
used for storage of carbohydrates in plants
form- grains
two forms- amylose and amylopectin
amylose:
straight chain as it’s only made up of 1-4 glycosidic bonds
helix shape allows it to be more compact (can store more glucose in a certain area)
more resistant to digestion as it’s not branched (smaller surface area for hydrolysis- increases rate of hydrolysis)
amylopectin:
branched chain as it has 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
more easily and quickly digested because it’s branched so larger SA for hydrolysis
describe the structure and function of glycogen
monomer- alpha glucose
used for storage of carbohydrates in animals and fungi
form- granules in the liver and muscle cells
glycogen contains 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
glycogen is more branched (higher proportion of 1-6 glycosidic bonds than amylopectin so it’s more compact- animals can store more glucose than plants
The branching enables more free ends where glucose molecules can either be added or removed allowing for condensation and hydrolysis reactions to occur more rapidly
describe the structure and function of cellulose
monomer- beta glucose, joined together by 1-4 glycosidic bonds
has straight and unbranched chains which form hydrogen bonds between adjacent layers (because beta glucose has an -OH group on either side of the molecule
hydrogen bonds are weak individually but strong together
hydrogen bonds between layers creates microfibrils which in turn create fibres that provide the cell wall with immense strength- prevents the cell from bursting when there is high tutor pressure
strengthened walls provide support to the plant
what is the test for starch
add a few drops of iodine to the solution (orange/brown)
if starch is present then there will be a colour change to blue/black
what is a lipid
macromolecules which contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (lower proportion of oxygen than carbohydrates)
They are non-polar (molecules isn’t charged) and hydrophobic/insoluble in water
But they will dissolve in organic solvents such as ethanol
there are two different groups of lipids (triglycerides and phospholipids)
which stores more energy, carbohydrates or lipids
lipids store twice the energy than carbohydrates do, of the same mass
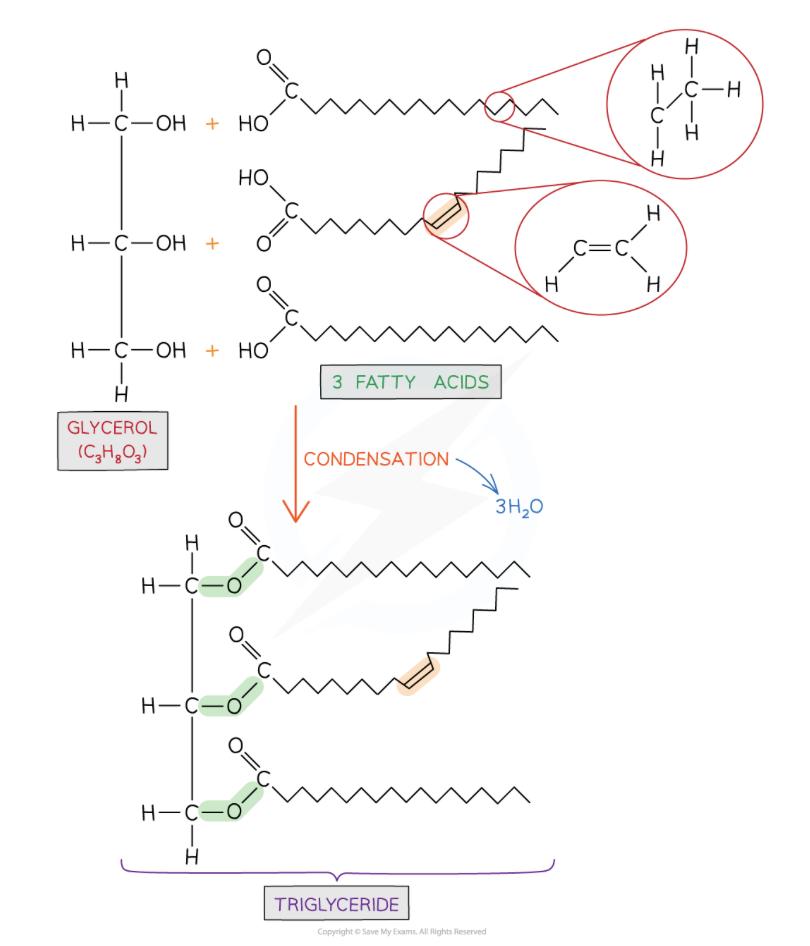
describe the structure of triglycerides
made up of 1 glycerol and 3x fatty acids which are joined by 3x ester bonds- formed via condensation reactions
describe the structure of fatty acids
they are made up of a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end (COOH) and a methyl group at the other end (CH3)
the hydrocarbon tail is known as the R group (chains of hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon atoms which are typically 2-20 carbon atoms long)
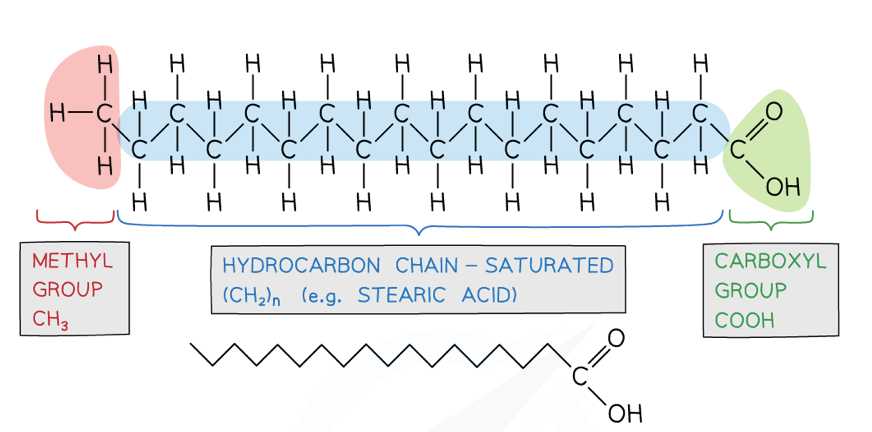
how can fatty acids vary
the length of the hydrocarbon chain (R group)
or they can either be saturated or unsaturated
what is a saturated fatty acid
the chain has no carbon-carbon double bonds because each carbon atom in the hydrocarbon chain has 4 strong covalent bonds
what is the general formula for saturated fatty acids
Cn H2n O2
what is an unsaturated fatty acid
where the hydrocarbon chain has at least one carbon-carbon double bond
what are the two types of unsaturated fatty acids
monounsaturated- where there is a single carbon-carbon double bond present in the hydrocarbon chain
polyunsaturated- where there is more than one carbon-carbon double bond present in the hydrocarbon chain
describe the bonding present in triglycerides
an ester bond forms between a hydroxyl group (-OH) on the glycerol molecule and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the fatty acid molecule
a H from the glycerol combines with an OH from the fatty acid to make water
ester bonds are formed via condensation reactions where a water molecule is released
three fatty acids join to one glycerol molecule- so three water molecules are released
how does the melting point differ between fats and oils
fats are more saturated than oils
the carbon-carbon double bond results in a kink in the hydrocarbon tail
the kink pushes carbon molecules further apart from each other which makes the fatty acid more fluid- so it has a lower melting point
what are the different functions of triglycerides
energy storage
insulation
buoyancy
protection
how is the structure of triglycerides suited for energy storage
the hydrocarbon tails contain many carbon-hydrogen bonds which release energy when they are oxidised and broken which can be used to produce ATP
triglycerides are also hydrophobic so when they are stored, they don’t affect the water potential and lead to osmosis
the oxidation of carbon-hydrogen double bonds releases large numbers of water molecules during cellular respiration (useful for desert animals as they can retain this water when there is a limited supply of water to drink)
how is the structure of triglycerides suited for insulation
electrical insulation- don’t conduct electricity -> make up the myelin sheath which is wrapped around nerve cells -> increases action potential transmission via saltatory conduction
thermal insulation- doesn’t conduct heat -> layer under the skin which prevent heat leaving the body via the skin -> keep us warm
how is the structure of triglycerides suited for buoyancy
the low density of fat tissue can increase the ability of animals to float more easily
how are triglycerides suited for protection
fats can be stored around organs to help protect them from damage and impact
why are triglycerides energy reserves
they store more energy than carbohydrates per gram due to their hydrocarbon chains containing less oxygen than carbohydrates
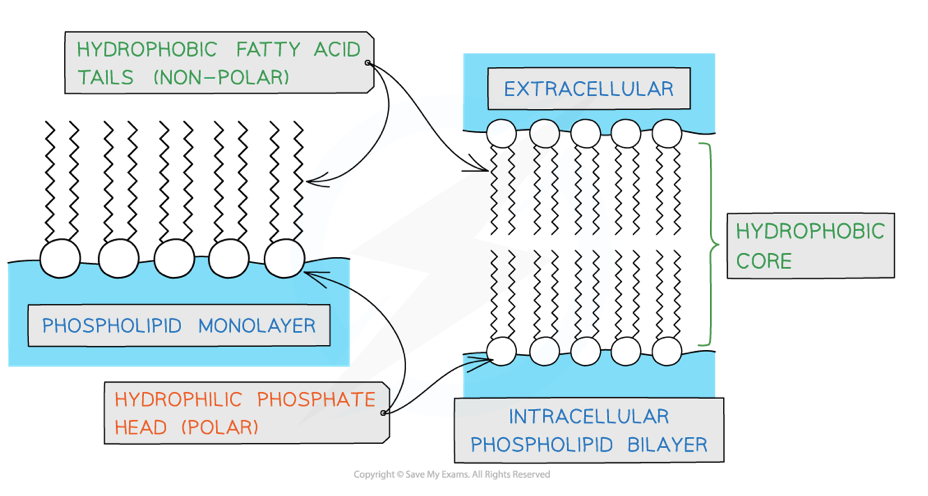
describe the structure of a phospholipid
made up of:
2 fatty acids (non-polar) forms hydrophobic tail
one glycerol
one phosphate ion (polar)- forms hydrophilic head
2x ester bonds between fatty acids and glycerol
1x ester bond between glycerol and the phosphate ion
overall 3x water molecules are released
how do phospholipids form a bilayer
phospholipids make up the cell membrane- allows the cell membrane to act as a barrier and control what substances enter and leave the cell
the ‘hydrophobic tails’ orientate themselves inwards away from the water forming the hydrophobic core
the ‘hydrophilic heads’ form hydrogen bonds with water
how does the composition of phospholipids contribute to the fluidity of the cell membrane
if the phospholipid bilayer has mainly saturated fatty acids then it will be less fluid (less carbon-carbon double bonds)
if the phospholipid bilayer has mainly unsaturated fats then it will be more fluid (more carbon-carbon double bonds)
what is the test for lipids
add the lipid sample to the test tube- if food sample is solid it should be ground up first
add ethanol to the test tube and shake to mix it
then add the firs mixture to a different test tube with water in it
Results:
if lipids are present then a layer of milky/cloudy emulsion will form at the top of the test tube
if no lipids present then the solution will remain clear
what are proteins
they are polymers made of repeating monomers called amino acids
the type, number, and order of amino acids will determine the shape of the protein and therefore its function aswell
describe the structure of an amino acid
they have a central carbon atom which is bonded to:
an amino group (-NH2)
a carboxyl group (-COOH) - an acidic group
a hydrogen atom
an R group
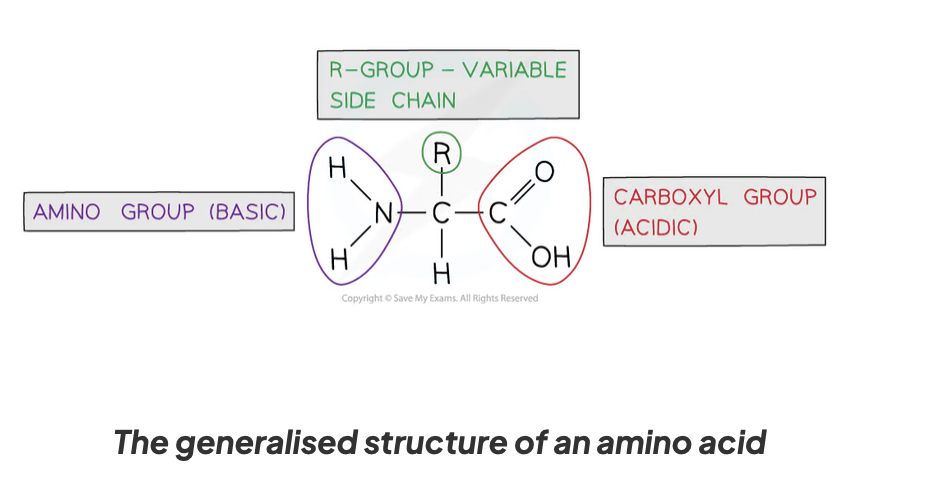
what is the R group in an amino acid
the part of an amino acid that differs- 20 different amino acids
the R group of the amino acid depicts it’s properties
what are the bonds present in proteins
peptide bonds
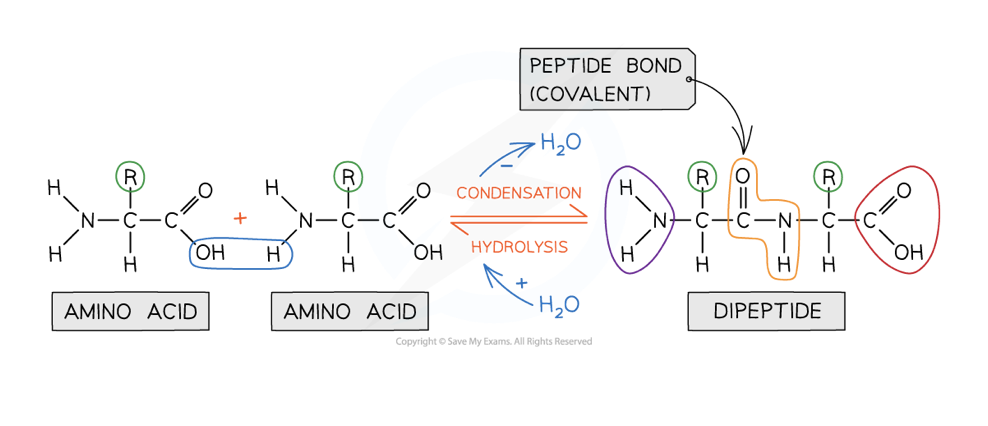
how are peptide bonds formed between amino acids
formed via a condensation reaction
a hydroxyl (-OH) is lost from the carboxyl group of one amino acid and a hydrogen atom is lost from the amino group of another amino acid
water is released
what is a dipeptide
consist of two amino acids
formed via one condensation reaction
what is a polypeptide
the sequence of at least more than two amino acids joined together by peptide bonds that are formed through condensation reactions
draw hydrolysis and condensation reactions to show how dipeptides and amino acids swap between each other
describe how chromatography works
Chromatography is a technique that can be used to separate a mixture into its individual components
Chromatography relies on differences in the solubility of the different chemicals (called ‘solutes’) within a mixture
All chromatography techniques use two phases:
The mobile phase
The stationary phase
The components in the mixture separate as the mobile phase travels over the stationary phase
Differences in the solubility of each component in the mobile phase which affects how far each component can travel
Those components with higher solubility will travel further than the others
This is because they spend more time in the mobile phase and are thus carried further up the paper than the less soluble components
what is the mobile phase in paper chromatography
The mobile phase is the liquid that carries the sample through the chromatography system.
It moves through or over the stationary phase, carrying the components of the mixture with it.
Different compounds in the sample travel at different speeds depending on how strongly they interact with the mobile phase versus the stationary phase.
e.g. water or ethanol
what is the stationary phase in paper chromatography
The stationary phase is the material that stays fixed inside the chromatography system. e.g. the paper
It provides a surface for the components of the sample to interact with, leading to separation.
Some compounds adhere to the stationary phase more strongly than others, causing them to move slower.
describe the primary structure of a protein
the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
The DNA of a cell determines the primary structure of a protein by instructing tRNA molecules to join amino acids in a specific order
peptide bonds form between amino acids via condensation reactions
the primary structure of a protein determines the structure and function of the protein
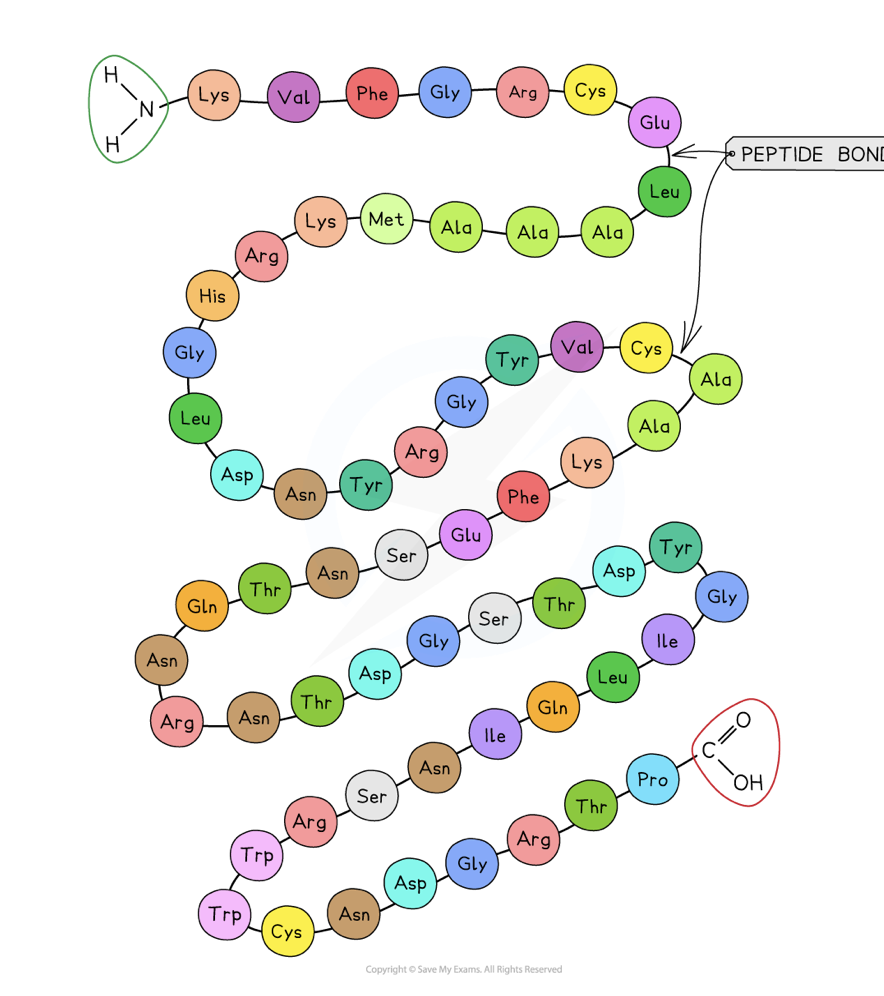
describe the secondary structure of a protein
the secondary structure of a protein is held together by hydrogen bonds that form between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
these hydrogen bonds can lead to:
α-helix
β-pleated sheet
hydrogen bonds are individually weak but strong together
what can hydrogen bonds in the secondary structure of a protein be broken by
high temperatures and changes in pH
describe the tertiary structure of a protein
additional bonds form between the R groups of amino acids which gives the protein its 3D structure
still contains peptide bonds and hydrogen bonds between amino and carboxyl groups
the 3D structure allows proteins to have a specific function e.g. a specific shaped active site
the additional bonds include:
hydrogen bonds between strongly polar R groups
disulfide bonds/bridges between cystine amino acids
ionic bonds between amino and carboxylate groups on different R groups
weak hydrophobic interactions between non-polar R groups
describe the quaternary structure of a protein
occurs in proteins that have more than one polypeptide chain working together as a functional protein e.g. haemoglobin
each polypeptide chain is referred to as a subunit of the protein
proteins can either be:
functional (globular) e.g. haemoglobin
structural (fibrous) e.g. collagen
describe ionic bonds in the tertiary structure of a protein
ionic bonds form between positively charged amino groups and negatively charged carboxyl groups on different R groups
ionic bonds are stronger than hydrogen bonds but weaker than disulfide bonds
they are easily broken by changes in pH
describe disulphide bonds in the tertiary structure of a protein
disulphide bonds are strong covalent bonds that form between two cystine R groups
this is because cystine is the only amino acid that has an available sulfur atom in its R group
these are the strongest bonds in the tertiary structure
describe hydrophobic interactions in the tertiary structure of a protein
hydrophobic interactions form between the non-polar R groups
describe the difference between hydrogen bonds in the secondary and tertiary structure of a protein
in the secondary structure of a protein hydrogen bonds only form between carboxyl and amino groups on different amino acids
whereas,
in the tertiary structure, hydrogen bonds form between strongly polar R groups (they are the most common bond in the T structure because they are able to form between a wide variety of R groups)
how do you test for proteins
biuret test
a liquid solution containing the sample is treated with sodium or potassium hydroxide to make it alkaline
a few drops of copper II sulphate is added to the sample (blue colour)
if a colour change from blue → lilac/purple is observed then protein is present
what are the problems with using biuret to test for proteins
test doesn’t work on amino acids or dipeptides- must be more than two peptide bonds present
colour change is subtle so its recommended to hold the test tube up against a white tile
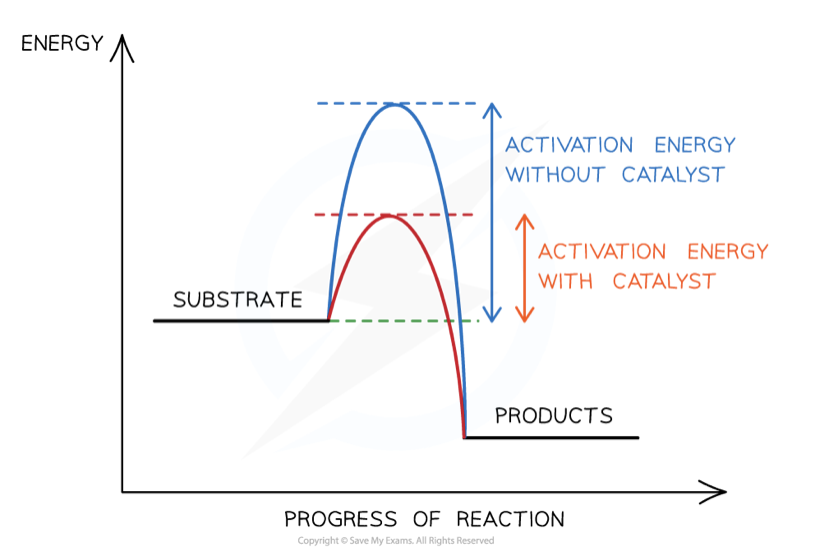
what is an enzyme
an enzyme is a biological catalyst that speeds up the rate of reaction but aren’t used up in the process
they do this by lowering the activation energy for the reaction
how are enzymes specific
the shape of the enzymes active site is complimentary to its substrate
the shape of the active site is determined by the enzymes/proteins tertiary structure
Proteins are formed from chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds
The order of amino acids determines the shape of an enzyme
If the order is altered, the resulting three-dimensional shape changes
what does the term denaturation mean
when extreme heat or pH disrupts the bonds in the tertiary structure of the enzyme causing it’s 3D structure to change → changes the shape of the active site → prevents substrate from binding as it’s no longer complimentary
what is the difference between catabolic and anabolic enzyme reactions
catabolic- the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler products
single substrate is drawn into the active site and broken apart into two or more distinct molecules
anabolic- the building of more complex molecules from simpler molecules
two or more substrates are drawn into the active site, and bonds are formed between them which forms and releases a single product
define activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required for a reaction to occur
how do enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction
they provide an alternate energy pathway
this means that reactions can take place at lower temperatures (hence why the human body’s temperature is 37.7 .C
what is collision theory
states that the enzyme and the substrate must collide at the correct orientation with sufficient energy for the reaction to occur
describe the lock and key theory
Enzyme has a specific active site – The enzyme's active site has a fixed shape that is complementary to the substrate.
Substrate specificity – Only a specific substrate can fit into the active site, like a key fitting into a specific lock.
Enzyme-substrate complex forms – The substrate binds to the active site, forming an enzyme-substrate complex.
Reaction occurs – The enzyme catalyzes the reaction, converting the substrate into the product(s).
Products released – The product(s) no longer fit the active site and are released, leaving the enzyme unchanged and free to catalyze another reaction.
describe the induced fit hypothesis
before the reaction the enzymes active site isn’t a perfect fit for the substrate
the active site undergoes a conformational change becoming fully complimentary to the substrate as the substrate molecule enters the active site and the enzyme substrate complex begins to form
the binding process distorts the bonds in the substrate which lowers the activation energy for the reaction and the products are produced
after this the enzyme returns to its original shape
how can we measure enzyme catalysed reactions
we could measure:
the formation of products of the reaction
the disappearance of the substrate
how does temperature affect enzyme action
as temperature increases, the kinetic energy of the substrate and the enzyme increase
this leads to an increase/higher frequency of successful collisions between the enzyme and the substrate due to collision theory (correct orientation and sufficient energy)
leads to an increase in the number of enzyme substrate complexes forming
therefore, an increase in rate of reaction
as temperature starts to increase beyond 35 degrees celsius bonds (hydrogen bonds) in the enzymes tertiary structure begin to break, so the tertiary structure changes
this can change the shape of the enzymes active site making it more difficult for the substrate to bind to the active site (decreased rate of reaction)
after 60 degrees celsius the enzyme denatures (substrate can no longer bind to the enzymes active site)
how does pH affect enzyme action
all enzymes have an optimum pH which they work best at
enzymes are denatured at extremes of pH values- this can break hydrogen and ionic bonds in the tertiary structure of an enzyme
low pH caused by increase of H+ ions
high pH caused by increase of OH- ions
this will change the enzymes tertiary structure → active site will change shape → the substrate will no longer be complimentary to the active site so enzyme substrate complex’s can’t be formed (no products formed either)
how does the concentration of substrate affect enzyme activity
at low substrate concentration there are lots of empty/unsaturated active sites- so an increase in substrate concentration will lead to more enzyme substrate complex’s forming → increase rate of reaction
rate of reaction increases until there is an excess of substrate and all the active sites are fully saturated (Vmax)
any further increase of substrate won’t increase the rate of reaction (substrate has nowhere to bind)- enzyme concentration is now the limiting factor
how does the concentration of enzymes affect enzyme activity
when there is low enzyme concentration there is an excess of substrate molecules as they have no active sites to bind to
so an increase in enzymes → greater number of active sites available for binding → greater number of enzyme substrate complex’s forming → increased rate of reaction
rate of reaction increases until there is an excess of enzymes and all of the active sites are occupied (Vmax) - substrate concentration is now the limiting factor
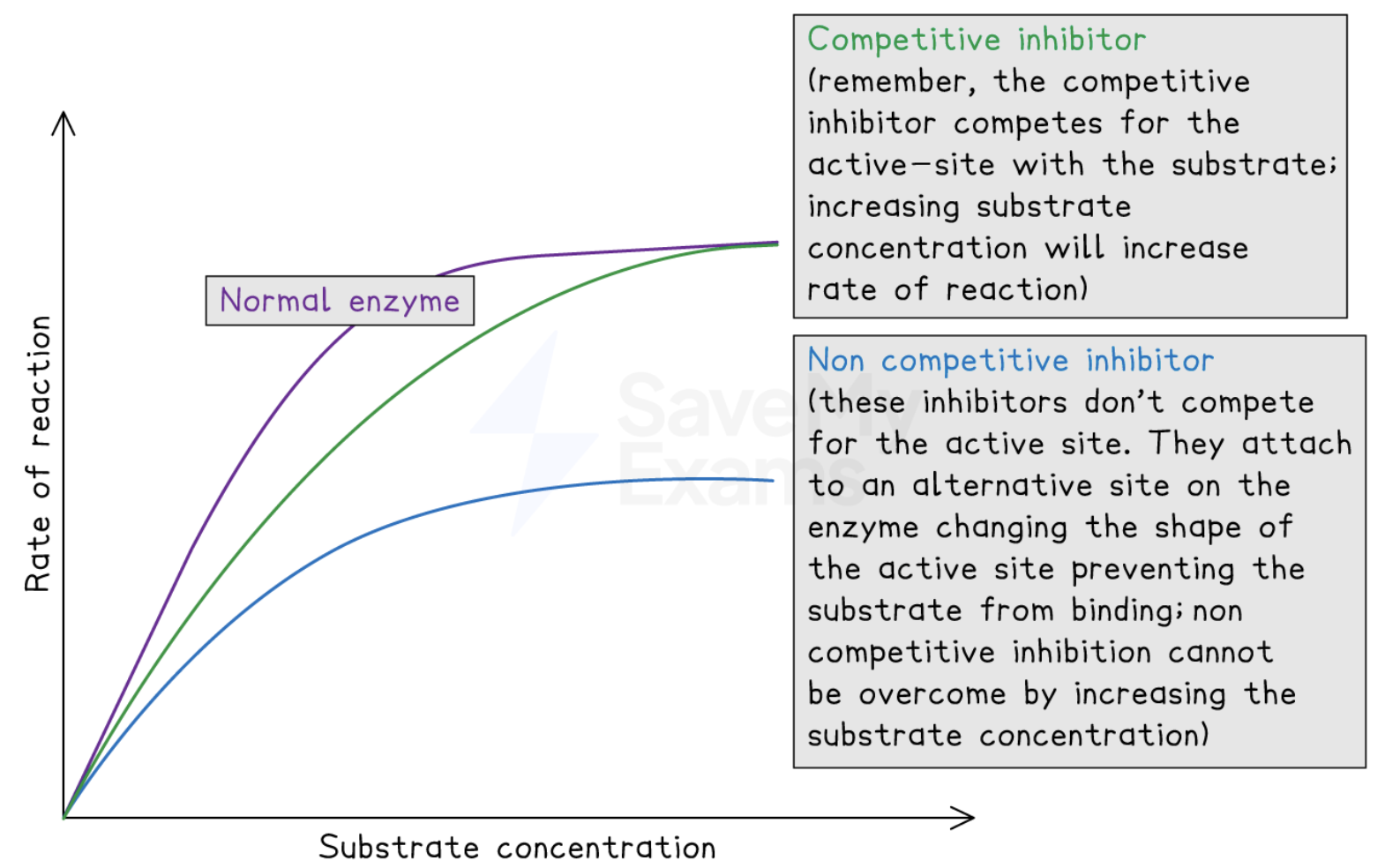
what are competitive inhibitors
they have a similar shape to the substrate molecule and compete with the substrate for the active site
what are non-competitive inhibitors
they don’t compete with the substate for the active site. They bond to an allosteric site (another site that’s different from the active site) which causes a conformational change to the enzymes active site, preventing the substrate from binding to it
how do competitive inhibitors affect the rate of reaction
competitive inhibitors have a similar shape to the substrate is they can directly compete with the substrate for the active site
when they bind they will temporarily block the enzymes active site, preventing the substrate from binding to it
this leads to less enzyme-substrate complex’s from forming → decreasing the rate of reaction
how do non competitive inhibitors affect the rate of reaction
Non-competitive inhibitors bind to an allosteric site, which is another site on the enzyme, which is different from the active site
This binding causes a conformational change to the enzyme’s 3D structure → changing the shape of the enzyme’s active site so that the substrate is no longer complementary to the active site
This means that no enzyme-substrate complex’s can form, so the reaction can’t occur
This change is usually permanent
how can the effect of competitive inhibitors on rate of reaction be reduced
by increasing the concentration of the substrate (dilutes the effect of the inhibitor)
This means that the substrate is more likely to collide with the enzyme’s active site instead of the inhibitor molecule
draw graphs for how both types of inhibitors affect the rate of reaction compared to no inhibitor molecule