conduction disorders
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
p wave duration
0.08-0.11 seconds
p-wave progression
SA node, internodal pathways, bachmann bundle, atrial myocytes
PR interval duration
0.12-0.2 seconds
QRS complex duration
0.06-0.12 seconds
QT interval duration
female ≤0.44 seconds
males ≤0.40 seconds
arrhythmia reasons HIS DEBS
hypoxia, ischemia, sympathetic stimulation, drugs, electrolyte disturbance, bradycardia, stretch
CHF diagnostic requirement
echo
first evaluation of EKG
P wave for every QRS and is there a T wave
sinus bradycardia threshold
<60 bpm
sinus tachycardia threshold
>100 bpm
hyperkalemia consequence
bradycardia or asystole
hypokalemia consequence
ventricular tachycardia
sinus brady CP
asymptomatic
dizziness, (pre)syncope, fatigue, weakness, confusion
when to intervene with sinus brady
HR <50-55 WITH SYMPTOMS
sinus brady diagnostics
EKG with rate <60, CBC, BMP, TSH
sinus brady causes
athletes, hypothyroidism, early MI (inf/post), high K+, rate limiting agents (nCCB, BB)
sinus brady tx
tx underlying cause IF SYMPTOMATIC
atropine, catecholamines (dopamine), dobutamine, epi, temporary pacer, permanent pacemaker
sinus tach considerations
anemia, hypovolemia, fever, pain, HF, hyperthyroidism, EtOH, lung disease
sinus tach CP
CP, SOB, dizziness, palpitations, heart racing
sinus tach conditions
sepsis, dehydration, anxiety, COPD, asthma
atropine action
speeds up HR
dopamine action
positive inotrope and speeds up HR
sinus tach diagnostics
EKG with rate 100-149, CBC, BMP, TSH
sinus tach tx
tx underlying cause IF SYMPTOMATIC
r/o arrhythmias, can add rate limiting agents (BB, nCCB)
supraventricular arrhythmias
afib, aflutter, PSVT, PAT, MAT, WPW
sinus arrhythmia
NSR but slightly irregular rate, benign
atrial fibrillation
arrhythmia with disorganized, rapid, irregular atrial electrical activation with loss of organized mechanical contraction
afib RF
aortic/mitral stenosis, CHF (systolic), DM, HTN, age >75, hx stroke, CAD/ischemia, EtOH, hyperthyroidism, OSA, obesity, post cardiac surgery, medications
afib types
paroxysmal, persistent, permanent, RVR, SVR
afib CP
palpitations, heart racing/flipping/butterlfy, SOB, dizziness, CP, fatigue, CHF sx
afib complications
stroke
afib PE
irregularly irregular rhythm, irregular pulse, tachy, CHF signs (edema)
afib EKG
irregular rhythm with NO P WAVE
afib labs
CBC, BMP, thyroid studies, trop
afib echo
look for valvular issues and establish EF
holter monitor
portable EKG to capture rhythms throughout the day over 24, 48, 72h
event monitor
small portable device recording electrical activity of heart for 2 weeks or 30 days
MUST BE ACTIVATED with symptoms, not continuous
paroxysmal afib
self terminating, maybe recurrent
persistent afib
fails to terminate, lasts >7d
permanent/chronic afib
persistent afib >1y
afib RVR
atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response
afib SVR
atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response
afib tx
rate control with BB or CCB
restore sinus with cardioversion, antiarrhythmic meds, or catheter ablation
stroke risk stratification
CHADS2 score
action if CHADS >2
DOAC to prevent clots
stable low risk afib management
rate control - IV diltiazem (MC) or amiodarone
rhythm control - electrical cardioversion if antiarrhythmics don’t work
DOAC
stable low risk afib
<48h, hemodynamically stable
high risk STABLE afib management
rate control - IV diltiazem (MC) or amiodarone
rhythm control - electrical cardioversion if antiarrhythmics don’t work for 4-6 wks, TEE cardioversion
DOAC
TEE cardioversion
transesophageal echocardiogram with cardioversion to ensure no LA clot
high risk UNSTABLE afib management
ATTEMPT rate control - IV diltiazem (MC) or amiodarone
URGENT electrical cardioversion
anticoagulation - IV heparin or LMWH
CHADS-VASc oral antiarrhythmics
metoprolol, diltiazem, amiodarone, sotalol
unstable afib complications
increased risk of thromboembolism with emergent cardioversion (unstable pt outweighs risk)
cardioversion
synchronised, quick, low energy shocks to heart to restore typical heartbeat
afib ablation
catheter resets faulty electrical circuits in persistent afib
watchman device
left atrial appendage occluders, can prevent stroke in pts unable to do long term anticoags
atrial flutter
rapid, regular tachycardia with 2 to 1 block in AV node and ventricular rate 150 bpm
aflutter RF
COPD, valvular/structural heart disease, atrial septal defect, surgically repaired congenital heart disease, HTN, thyroid, afib
aflutter CP
palpitations, fatigue, mild dizziness, CHF sx, near syncope, DOE, SOB at rest, CP
aflutter PE
often normal
tachy, CHF signs (edema)
aflutter EKG
“sawtooth”pattern, look at inferior leads II, II, aVF
aflutter labs
CBC, CMP, thyroid, troponin
aflutter echo
look at valvular issues and EF baseline
aflutter tx
if CHADS-VASc >2 DOAC, cardioversion, BB, nCCB, amiodarone, sotalol
ablation definitive tx
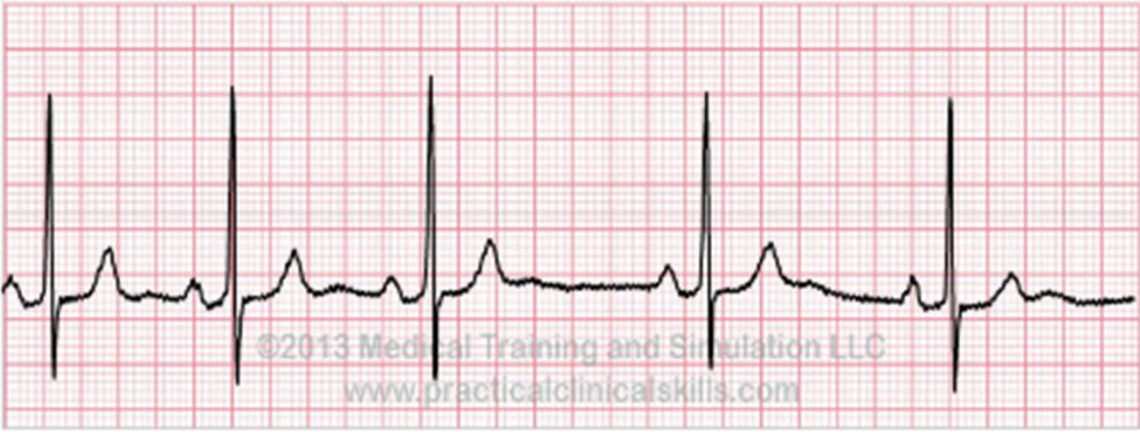
rhythm?
sinus arrhythmia
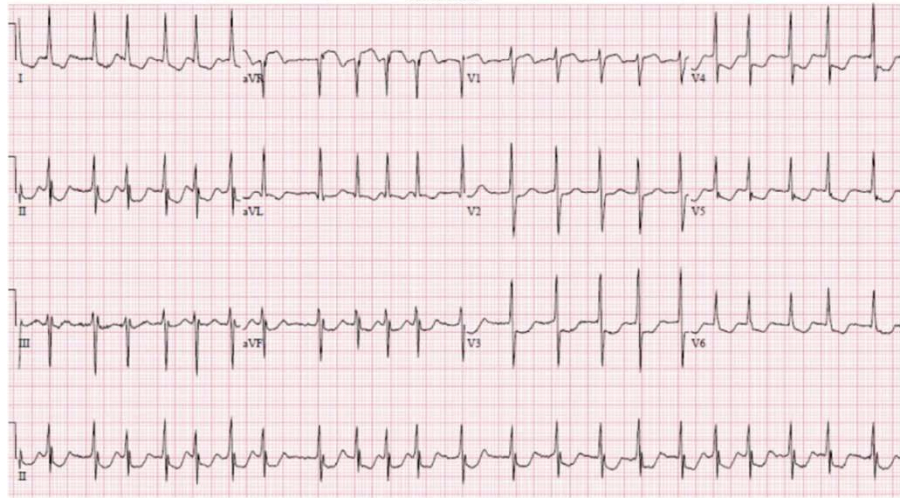
rhythm?
atrial fibrillation
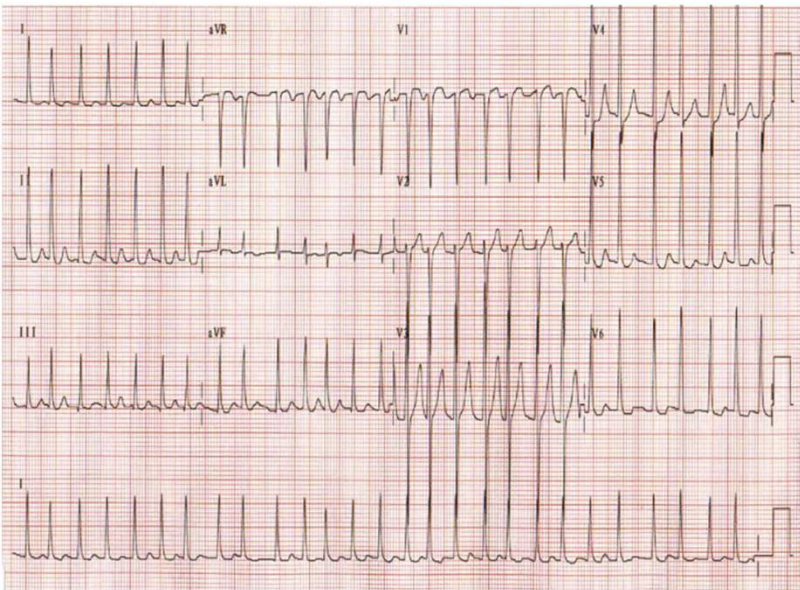
rhythm?
atrial fibrillation
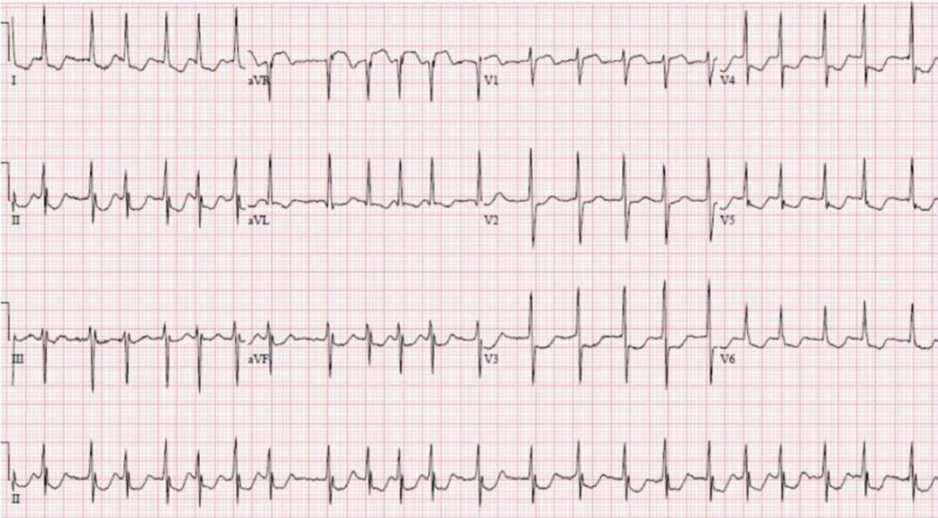
rhythm?
atrial fibrillation
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT)
tachyarrhythmia originating above ventricles
ventricular activation over purkinje system, narrow-complex tachycardia
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) population
young adults, no structural heart disease
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) RF
high caffeine intake, EtOH, marijuana
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) CP
palpitations, diaphoresis, dyspnea, dizziness, CP, syncope (rare)
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) EKG
regular narrow QRS tachycardia (QRS <120ms)
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) EKG types
AVNRT, AVRT
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) AVNRT
AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia with SVT p waves buried in QRS and rate 140-200
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) AVRT
AV reciprocating tachycardia with p waves hidden in QRS and T wave inversion and ST depression, rate 200-300
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) AVRT conditions
wolf-parkinson white or lown-ganong-levine syndrome
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) stable tx
1 - valsalva maneuver (bear down, cough, hold breath, carotid sinus massage)
2 - adenosine IV push or BB/nCCB
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) unstable tx
synchronized cardioversion
if recurrence refer to EP for ablation (very effective)
paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) patient edu
reduce caffeine and EtOH
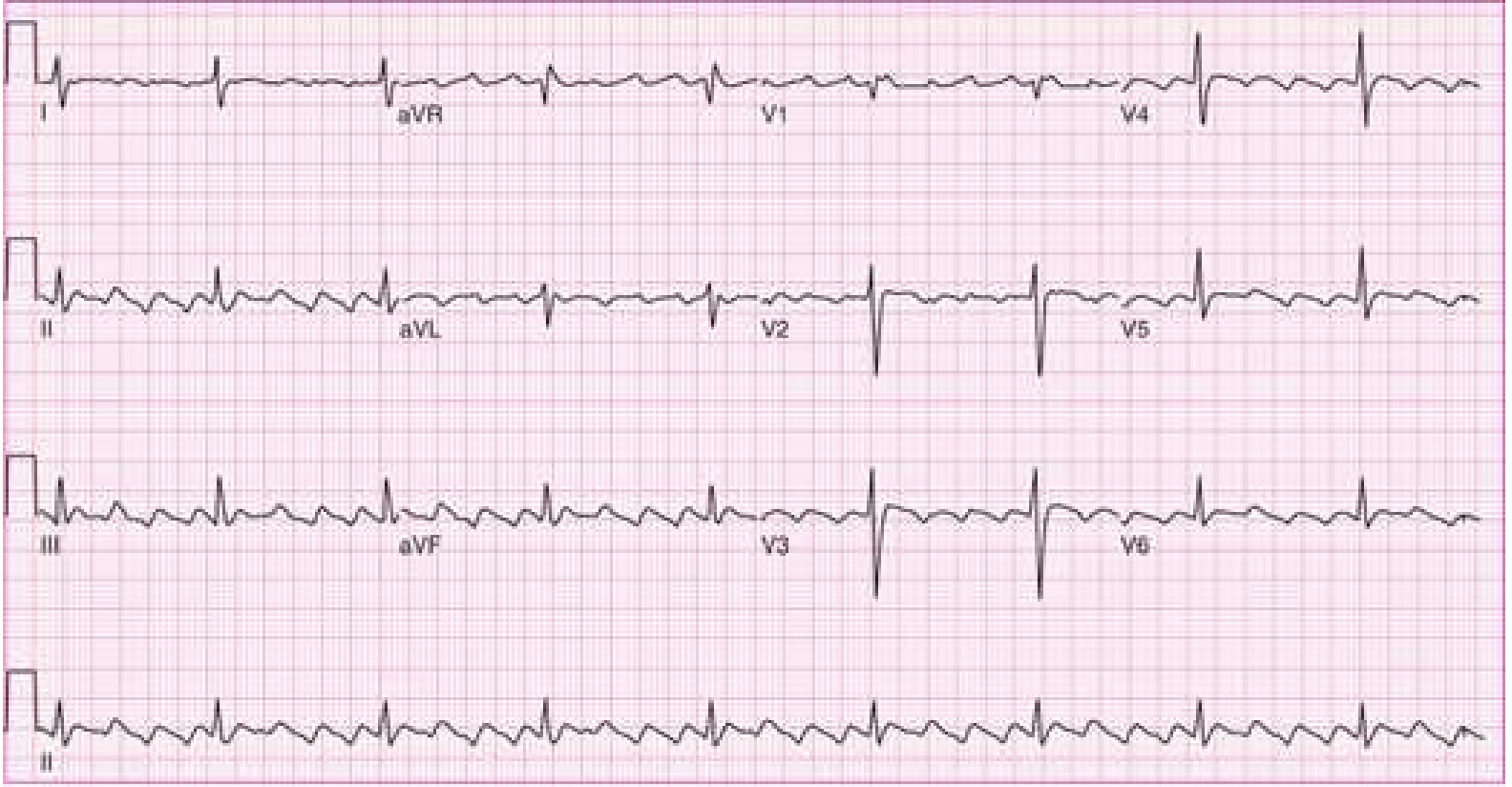
rhythm?
atrial flutter
multifactorial atrial tachycardia (MAT)
distention of RA from elevated pulm pressure causes multiple electrical firing with ventricular rate <150
must have 3 different p wave morphologies
multifactorial atrial tachycardia (MAT) RF
COPD, respiratory failure, alcohol + lung disease, infection, electrolyte disturbance
multifactorial atrial tachycardia (MAT) CP
DOE, dizziness, syncope, palpitations, CP, tachy
MAT vs afib
afib NO p waves, MAT HAS p waves with different shapes
wandering atrial pacemaker
same as MAT (3 different p wave morphologies) but rate <100
multifactorial atrial tachycardia (MAT) PE
irregularly irregular rhythm, rhonchi/wheeze, hypoxia
multifactorial atrial tachycardia (MAT) EKG
irregularly irregular narrow complex tachy with rate >100
multiple p wave morphologies w/at least 3 distinct within 1 lead
multifactorial atrial tachycardia (MAT) tx
nCCB (verapamil DOC)
tx underlying condition
wolff parkinson white (WPW)
congenital heart condition with extra accessory pathway (bundle of Kent) causing no delay in ventricular contraction leading to pre-excitation of ventricles
wolff parkinson white (WPW) considerations
genetic, typicaly not life threatening, can lead to SVT
wolff parkinson white (WPW) CP
asymptomatic
fluttering/pounding HB, palpitations, CP, SOB, dizziness, fainting, fatigue, anxiety
wolff parkinson white (WPW) EKG
shortened PR interval causing delta wave
wolff parkinson white (WPW) tx
ablation if symptomatic
cardioversion if unstable
wolff parkinson white (WPW) mnemonic
WPW wave (delta), PR short, wide (QRS base)
atrioventricular block (AVB)
conduction disturbance between atria and ventricles that can be physiologic (d/t vagal tone) or pathologic (ischemia, myocarditis, fibrosis)
blocks in AV node
first degree, second degree Mobitz type 1 (wenckebach)
blocks below AV node
second degree Mobitz type 2, third degree
first degree AVB
prolonged delay in AV conduction, common in sleep or well trained athletes
first degree AVB considerations
can be normal or d/t meds (CCB, BB, digitalis, antiarrhythmics)
first degree AVB CP
rarely symptomatic, often found incidentally on EKG