Chapter 10 CSF
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
where is CSF formed
lateral, 3rd, and 4th ventricles of the brain
what is the normal volume of CSF present (adult & infant)
90-150 mL in adults
10-60 mL in infants
how much CSF is produced (per day and per hour)
500 mL/day
20 mL/hour
what are 3 major functions of CSF
supply nutrients to nervous tissue and remove metabolic waste
maintain intracranial pressure
provide a mechanical barrier to cushion the brain and spinal cord against trauma
where is a lumbar puncture/spinal tap performed?
intervertebral space between L3-L4 or L4-L5
CSF tube 1
frozen
chemistry (glucose, protein), serology
CSF tube 2
room temperature
gram stain, AFB stain (tuberculosis), india ink preparation, bacterial culture (BA, CHOC), fungal culture, culture for tuberculosis
CSF tube 3
may refrigerate up to 4 hours
hematology (total cell count, differential count)
CSF tube 4
may refrigerate up to 4 hours
cytology, immunology, additional tests
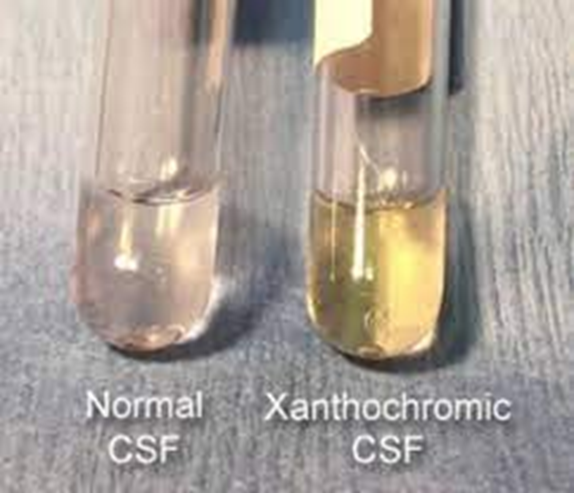
what does normal CSF look like
clear and colorless, viscosity similar to water
CSF that is turbid, hazy, milky, or cloudy may contain….?
WBCs, microorganisms, protein
could indicate meningitis or disorders affecting BBB
CSF that is oily-appearing may contain…?
radiographic contrast media
CSF that is clotted may contain…?
protein & clotting factors
associated with a traumatic tap
disorders affecting the BBB including neurosyphilis (dementia) and meningitis
CSF that is bloody red, pink, or smoky may contain…?
RBCs
traumatic tap
CSF that is xanthochromic may contain…?
bilirubin, carotene, protein, melanin, hemoglobin, or protein and associated with various disorders
CSF that is pellicle may contain….?
protein or clotting factors
define xanthochromia
CSF is yellow, pink, or orange
what causes xanthochromia
RBC degradation
pink - slight amount of oxyhemoglobin
orange - heavy hemolysis
yellow - conversion of oxyhemoglobin to unconjugated bilirubin
elevated serum bilirubin
carotene
increased protein
melanoma pigment
A xanthochromic CSF specimen appears:
yellow and clear
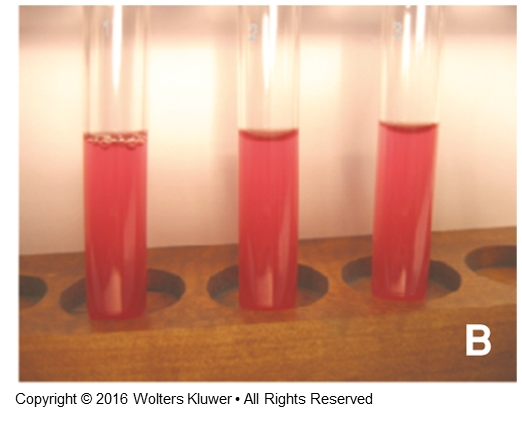
what is the main difference between CSF specimens due to a hemorrhage and CSF specimens due to a traumatic tap?
hemorrhage specimens will all appear the same amount of pink or red
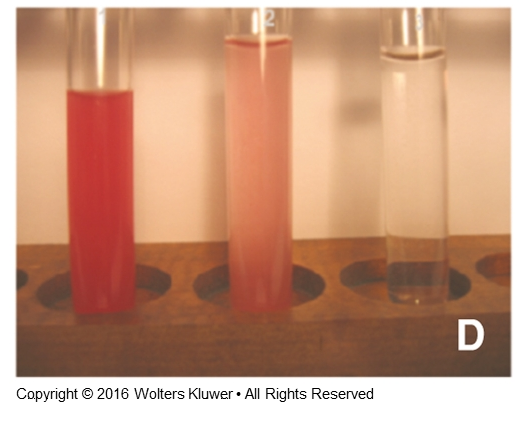


traumatic tap specimens will gradually become more clear
Differential counts on CSF are performed on:
stained smears prepared form concentrated specimens
what are the lab results for normal CSF
(appearance, WBC, protein, glucose, lactate, and other tests)
clear
< 8 WBCs
15-45 mg/dL protein
50 -80 mg/dL glucose
11-22 mg/dL lactate
what are the lab results for bacterial meningitis CSF
(appearance, WBC, protein, glucose, lactate, and other tests)
turbid
elevated
> 1000-2000 WBCs
neutrophils
elevated protein
decreased glucose
lactate level >35 mg/dL
positive gram stain and bacterial antigen tests
what are the lab results for fungal meningitis CSF
(appearance, WBC, protein, glucose, lactate, and other tests)
clear
elevated
<500 WBCs
lymphocytes AND macrophages/monocytes present
moderate-elevated protein
normal-decreased glucose
lactate level >25 mg/dL
positive for Cryptococcus neoformans (PCR, imm test, india ink)
what are the lab results for viral meningitis CSF
(appearance, WBC, protein, glucose, lactate, and other tests)
clear
elevated
<300 WBCs
lymphocytes present
moderate protein elevation
normal glucose level
normal lactate level
PCR test positive for enterovirus, herpes simplex, or parechovirus
what are the lab results for tubercular CSF
(appearance, WBC, protein, glucose, lactate, and other tests)
pellicle
elevated
lymphocytes and monocytes present
moderate to elevated protein
decreased glucose
lactate > 25 mg/dL
PCR positive for Mycobacterium tuberculosis
identify this cell and what it indicates
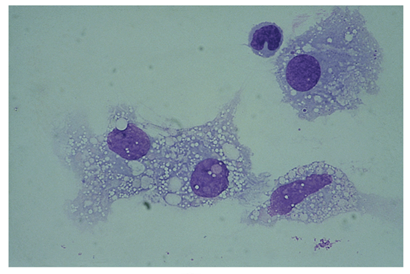
macrophage
appears within 2-4 hours after RBCs enter CSF
frequently seen after repeated taps
identify this cell and what it indicates
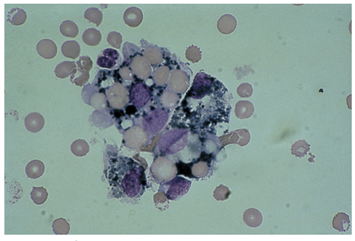
increased macrophages
previous hemorrhage
identify this cell and what it indicates
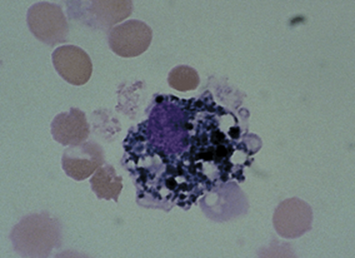
dark blue or black iron-containing hemosiderin granules
degradation of phagocytized RBCs
identify this cell and what it indicates
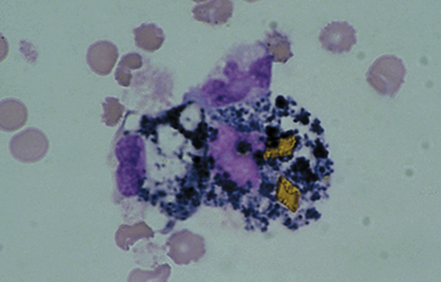
yellow hematoidin crystals inside macrophages
further degeneration
identify this cell
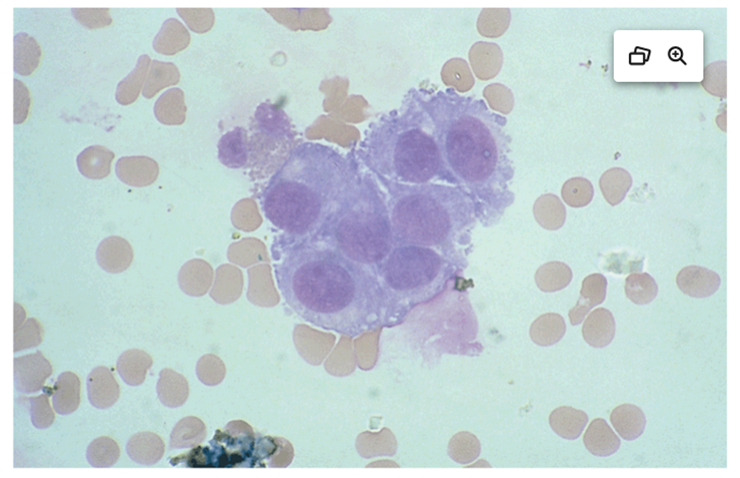
choroidal cells and capillary endothelial cells (from spinal wall)
Increased and vacuolated macrophages are seen in the CSF following:
previous hemorrhage
Which cells are considered an abnormal finding in CSF
tumor/blast cells
what is CSF protein normal range
15 mg/dL - 45 mg/dL
what are some proteins present in CSF
albumin
prealbumin (transthyretin)
alpha globulins
transferrin
gamma globulins
fibrinogen
beta lipoprotein
what can cause elevated CSF protein
damage to BBB
immunoglobulin production within the CNS
decreased normal protein clearance from fluid
neural tissue degradation
what can cause abnormal elevated CSF protein
meningitis
hemorrhage
primary CNS tumors
multiple sclerosis
neurosyphilis
Guillan-Barre syndrome
Cushing disease
diabetes
what can cause abnormal decreased CSF protein
CSF leakage/trauma
recent puncture
rapid CSF production
water intoxication
CSF/serum albumin index
CSF albumin (mg/dL) / serum albumin (g/dL)
normal CSF/serum albumin index
< 9
A complete breakdown of the blood–brain barrier is indicated by a CSF/serum albumin index of…?
> 100
What laboratory finding is most suggestive of blood-brain barrier damage in a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis?
CSF/serum albumin index >9
an IgG index value of > 0.70 indicates…?
IgG production within the CNS
typically becomes an autoimmune disease
Primary purpose for performing CSF protein electrophoresis is to?
detect oligoclonal bands, which represent inflammation within the CNS
gamma region
The presence of two or more oligoclonal bands in the CSF that are not present in the serum can be a valuable tool in diagnosing?
Multiple sclerosis, accompanied by increased IgG index
presence of what protein in CSF indicates recent destruction of the myelin sheath (demyelination) → MS
Myelin basic protein (MBP)
The normal CSF glucose is:
60 to 70% of the blood glucose
50-80 mg/dL
what is normal lactate level of CSF
11-22 mg/dL
CSF lactate level >35 mg/dL indicates…?
bacterial meningitis
elevated CSF lactate level can also indicate…?
tissue destruction due to hypoxia or any condition that decreases oxygen flow to tissues
how is glutamine produced
ammonia and a-ketoglutarate by brain cells
removes toxic metabolic waste product ammonia from CNS
what is normal CSF glutamine level
8-18 mg/dL
CSF glutamine test is often ordered for patients with …?
coma of unknown origin
what organism is associated with positive india ink test
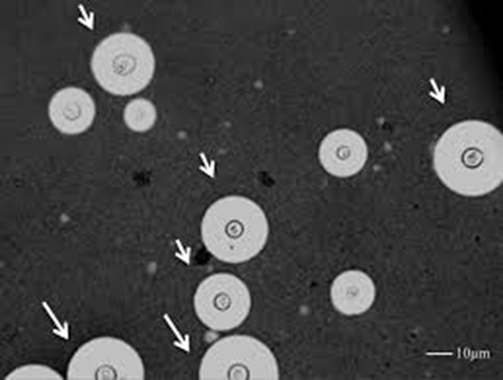
Cryptococcus neoformans
fungal meningitis
AIDS
thickly capsulated
identify this organism
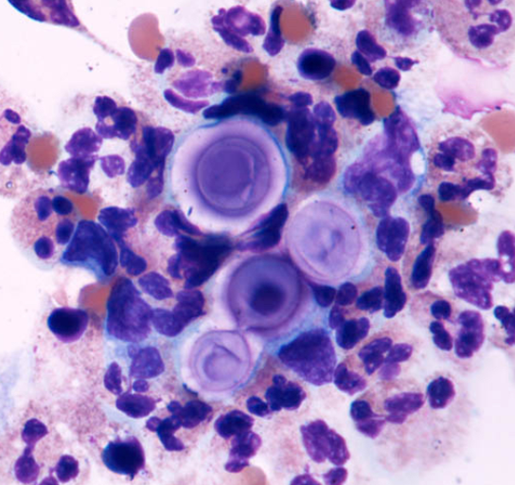
star-burst pattern gram stain
Cryptococcus neoformans
causes infection in immunocompromised (AIDS/HIV) patients after breathing in the fungus
what is a more sensitive test than india ink to detect Cryptococcus neoformans
latex agglutination tests are more sensitive, but should be confirmed with a positive india ink stain AND culture
what are some advantages of PCR molecular diagnostic testing in meningitis
–detect the cause of meningitis with a small amount of the pathogen’s DNA
–Universal PCR detects pathogens with increased sensitivity and specificity.
does PCR test for DNA or RNA
–PCR assays are based on the amplification of regions of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes to detect and differentiate causative pathogens of meningitis.