Earth Systems Exam
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
metamorphism:
heat, pressure, and fluids
-convert a parent rock into a metamorphic one
-transformation of rock WITHOUT melting
-changes their mineral composition
-all occurs under the melting point
where does metamorphic activity usually occur?
below the surface
how are metamorphic rocks distributed across the world?
1) shields: oldest part of the continental crust
2)cores of large mountain ranges
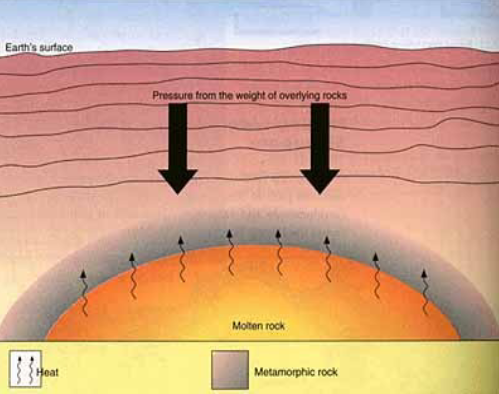
Agent of change—> temperature
-the heat comes from the interior of the earth
-the heat helps speed up reactions, producing a different rock
agent of change—> pressure
1) confining/ lithostatic
2)directed/ differential
confining/ lithostatic pressure
equal pressure in all directions due to overlying rocks
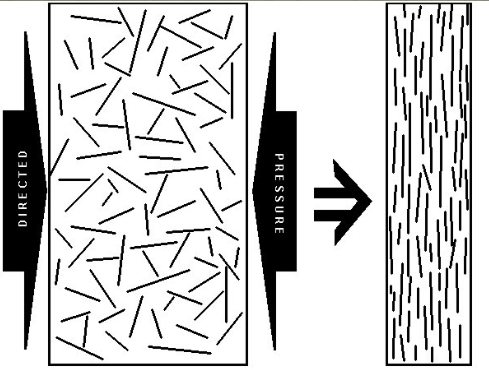
directed/ differential pressure
pressure is more in one particular direction
Agent of change—> chemically active fluids
hydrothermal fluids: water can accelerate chemical changes. aids in recrystallization of minerals by dissolution and deposition
metamorphic environments
1)hydrothermal (divergent zones)
2)contact/ thermal
3)dynamic
4) regional
hydrothermal (divergent zones) metamorphic environment:
hot, iron rich fluids move through cracks in the rock
contact /thermal metamorphic environments
rocks surrounding a molten, igneous body are “baked”.
-form under high temp and low pressure
dynamic metamorphic environments:
caused by faults where crust fractures due to tectonic activity
-increased pressure due to convergence, high pressure builds up but temp is low
regional metamorphic environments:
-most common
-broad range. temp and pressure both act as driving forces for metamorphic reactions

foliated texture classification:
banded appearance, associated with regional metamorphism.
-crystals are elongated or plated
-form a graded series of gran size and the development of foliation

Non-foliated texture classification
associated with contact metamorphism.
-crystals are equidimensional
-do not exhibit preferred orientation of minerals
ex) marble
grade
described by the degree to which a rock has undergone metamorphic change
“how much was this parent rock effected by the agents of change?”
what are the metamorphism grade scale transitions?
1)slate
2)phyllite
3)schist
4)gneiss
5)quartzite
6)marble
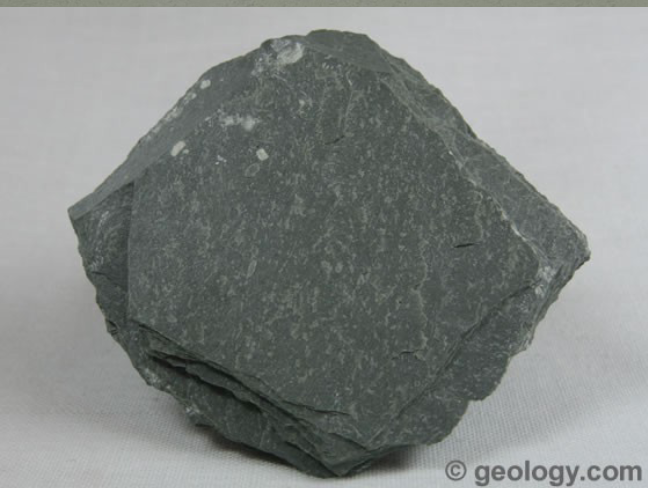

features of metamorphic slate
-parent rock is shale and sandstone
-foliated
-low grade
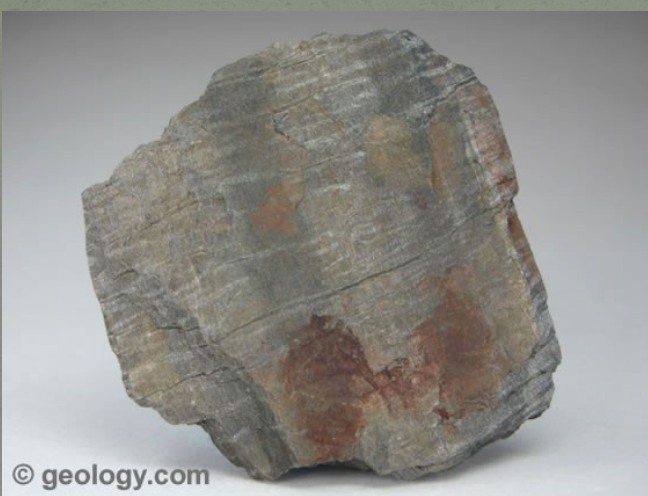

features of metamorphic phyllite
-parent rock is shale/ sandstone
-foliated
-low-medium grade
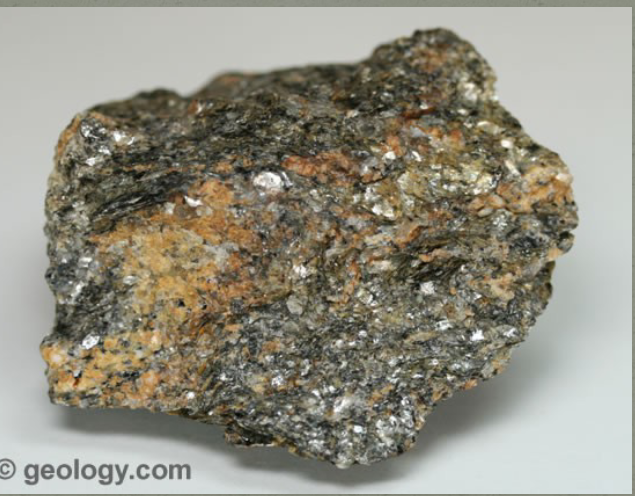

features of metamorphic schist
-parent rock is shale and sandstone
-foliated
-low-high grade
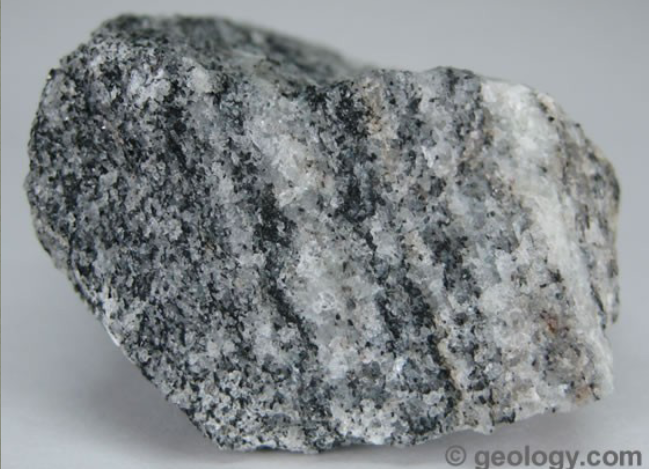

features of metamorphic gneiss
-parent rock is shale/ sandstone
-foliated
-high grade
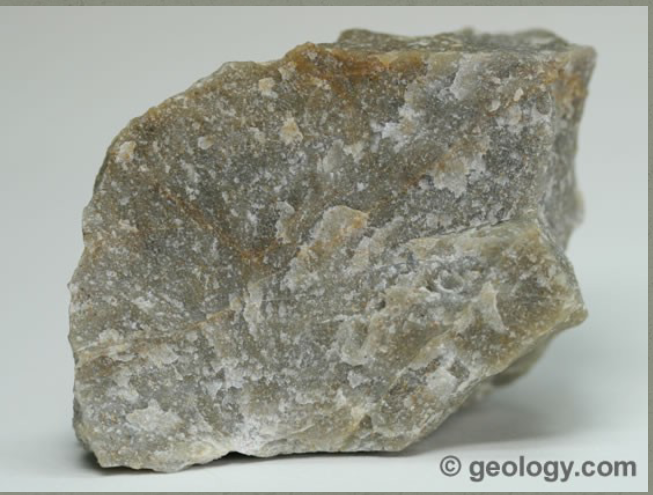

features of metamorphic quartzite
-parent rock is sandstone
-non foliated
-medium-high grade
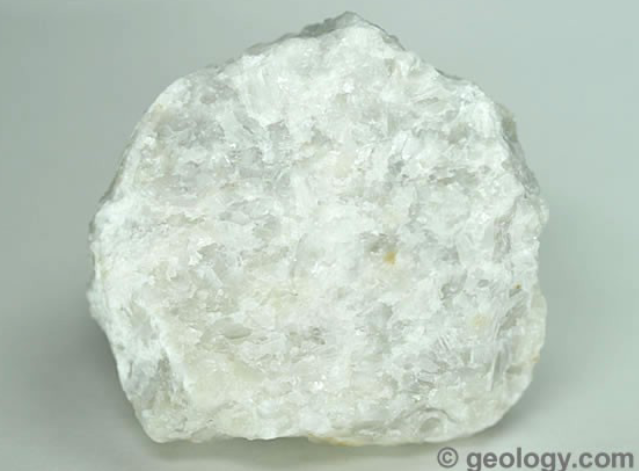

features of metamorphic marble
-parent rock is limestone
-nonfoliated
-low-high grade
lakes represent what depositional environment?
continental
if a sedimentary rock contains particles at least 2mm in size, what is it grained?
fine grained
biochemical/ bioclastic
classified by the presence of once living organisms contained within the rock
chemical classification of sedimentary rock
classified by the minerals found within the rock as they were precipitated from solution
how are detrital rocks classified
classified on size of the particles of sediment
what sedimentary rocks are derrived from biochemical limestone?
-coquina
-chalk
what sedimentary rocks are derived from chemical chert?
flint and jasper
is rock salt igneous, metamorphic, or sedimentary?
sedimentary
what is the most abundant chemical/ biochemical rock and also derived from calcite?
limestone
cross bedding
changing drn of flow of wind or water that changes the direction of sediment buildup
silicates
-90% of earths crust
-basic building block of silicon-oxygen tetrahedron
silicon-oxygen tetrahedron
-building block of all silicate minerals
-overall charge of +4
common dark silicates (ferromagnesian)
-olivine
-pyroxene group (augite)
-hornblende
-micah
common non-ferromagnesian (light) silicates
-muscovite (light micah)
-feldspar
-quartz
light silicates
have lower specific gravity
-light in color
dark silicates
-higher specific gravity
-rich in iron and magnesium
what common mineral has a conchoidal fracture?
quartz
feldspar
-2 planes of cleavage
-white and pink type
-hardness of 6
olivine group
forms small round crystals with no cleavage
granular look in large samples
pyroxene group (augite)
cleaves at 90 deg
dominant mineral in basalt
amphibole group (hornblende)
cleaves at 60 or 120 deg
found in continental rock
volatiles
gasses dissolved in the melt , including H20, CO2, and SO2
Basaltic (mafic) magma
most common
-dark silicate
-hottest
andesitic (intermediate) magma
-intermediate temp
-has a mix of dark and light silicates
rhyolitic (felsic) magma
-coolest
-light silicates
what are igneous rocks classified by?
-texture
-location of formation
-cooling process
-composition
phaneritic (intrusive) igneous rock textures
slow cooling
-coarse grained
-large crystals
aphanitic / extrusive igneous rock texture
rapid rate of cooling of lava
-small crystals
-fine grained texture
glassy aphanitic igneous texture
microscopic crystals
-cools instantly with contact with water
vesicular aphanitic igneous rock texture
contains vesicles (holes from gas bubbles)
porphyritic igneous rock texture
formed at different temps and rates throughout the rock
-large crystals are called phenocrysts (rest is the groundmass)
pyroclastic igneous rock texture
rocks form from explosive volcanic activity