Reproductive and urinary systems
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Gonads
Sex organs that contain germ cells and produce gametes and sex hormones
Testosterone
principle male sex hormone
Potent androgen
Synthesized within the leydig cells of the testes
Some synthesized in the adrenal cortex - in both f and m
What is testosterone responsible for ?
development and maintenance of the male secondary sexual characteristics
Primary hormone from which other sex hormones can be produced
DHEA
dehydroepiandrosterone - weaker version of testosterone
Responsible for the early development of pubic / body hair in boys and girls
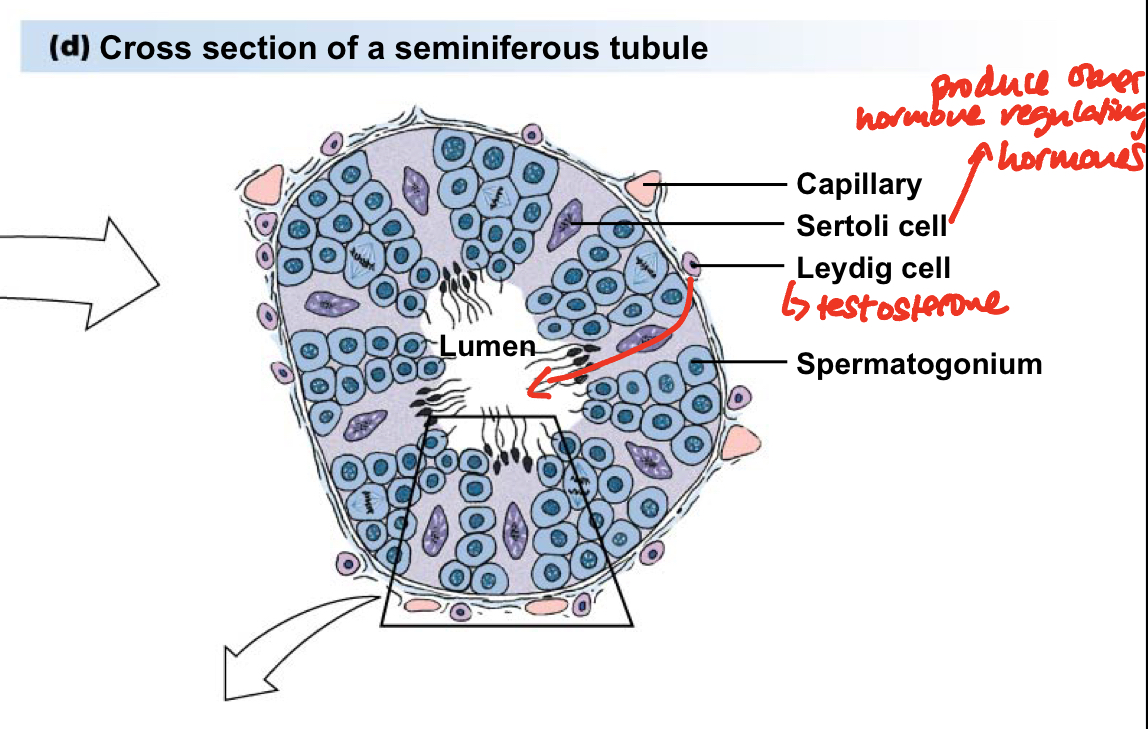
Describe the anatomy from which testosterone is produced
highly folded seminiferous tubules excrete testosterone from leydig cells
Sertoli cells produce other hormone regulating hormones
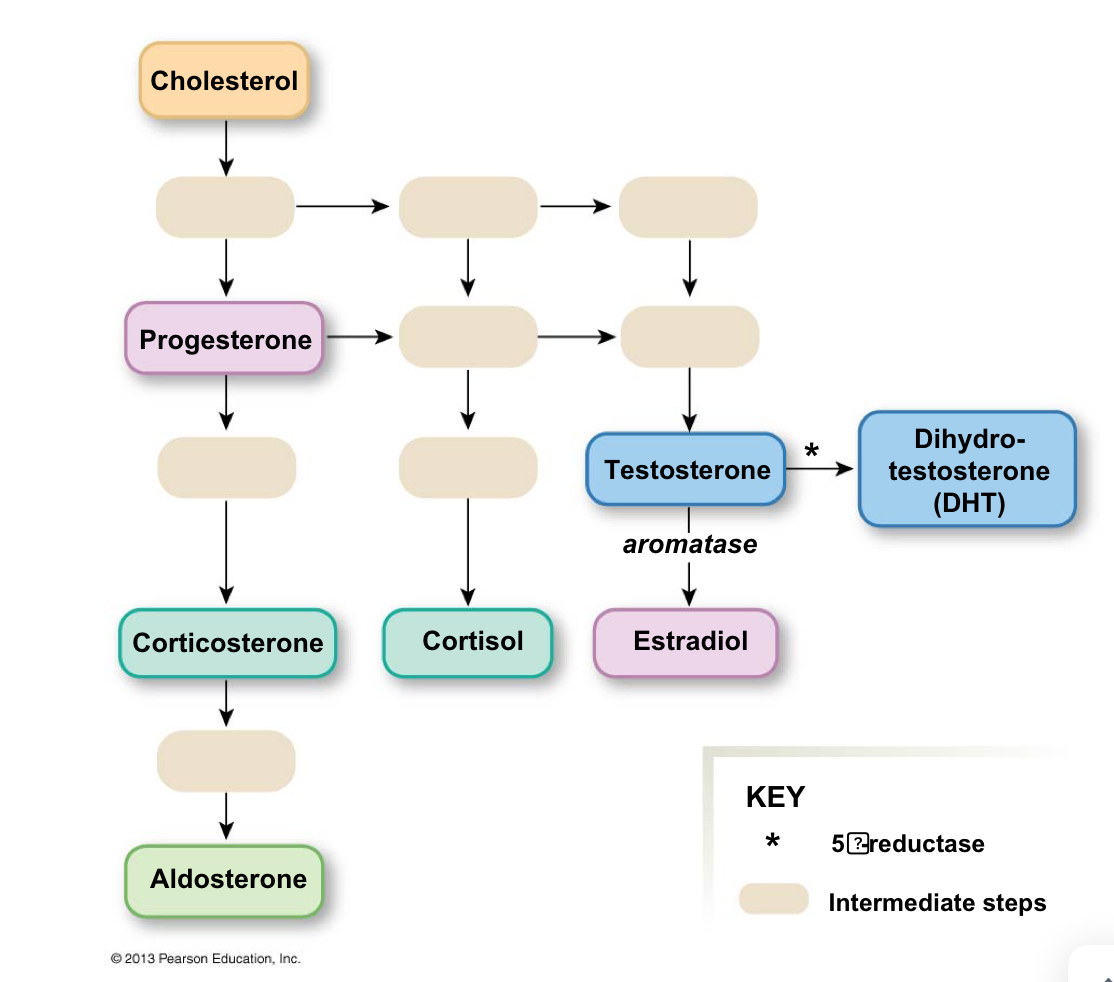
What hormones is testosterone a precursor for ?
in men - dihydrotestosterone (active metabolite)
In women - estrodiol (active metabolite)
Androsterone ( inactive)
Etiocholanolone (inactive)
Synthesis pathway for steroid hormones
Actions of Testosterone
stimulates enlargement of tastes and male accessory organs
Stimulates development of male secondary sex characteristics
Male secondary sex characteristics
Increased growth of body hair
Enlargement of the larynx and thickening of vocal chords
Thickening of the skin
Muscle growth, widening of shoulders, narrowing of waist
Thickening and strengthening of bones
Action of DHT
binds to cytoplasmic androgen receptors
Binding promotes release of heat shock protein (hsp)
Steroid receptor complex migrates to nucleus
Binds to specific regions of DNA that contain Androgen response elements (ARE)
Drives expression of genes that determine male phenotype
Why Androgen receptors and AREs important to women too ?
help with the development of pubic and axillary hair
How do Testosterone levels of men and women change throughout their lives ?
mini puberty at 6 months
Hormone levels unchanged until puberty
Increased during puberty
Maintain throughout adult life - decline in old age
What organs does testosterone target ?
Brain
Skin
Kidney
Male sex hormones
Bone
Bone Marrow
Fat
Liver
Muscle
How does Testosterone affect the brain, skin and kidney
Brain - libido, aggression, cognition
Skin- Male pattern body, facial hair, balding and increased sebum production
Kidney- stimulation of erythropoietin production
How does Testosterone affect the Male sexual organs, bone and bone marrow ?
Male sexual organs - penile growth, spermatogenesis, prostate growth and function
Bone - accelerated linear growth, closure of epiphyses, maintains BMD
Bone Marrow - Stimulation of stem cells
How does Testosterone affect fat, liver and muscle ?
fat - decrease in mass
Liver - synthesis of serum proteins
Muscle - increase in strength and volume
Which organs secrete hormones in males ?
hypothalamus
Anterior pituitary gland
Testes
Which hormones does the brain use to control reproduction in both sexes ?
GnRH - gonadotropin releasing hormone - acts on the hypothalamus - triggers short-loop negative feedback
Triggers lutenizing hormone (LH) and Follicle Stimulating hormone (FSH) - which act on the gonads
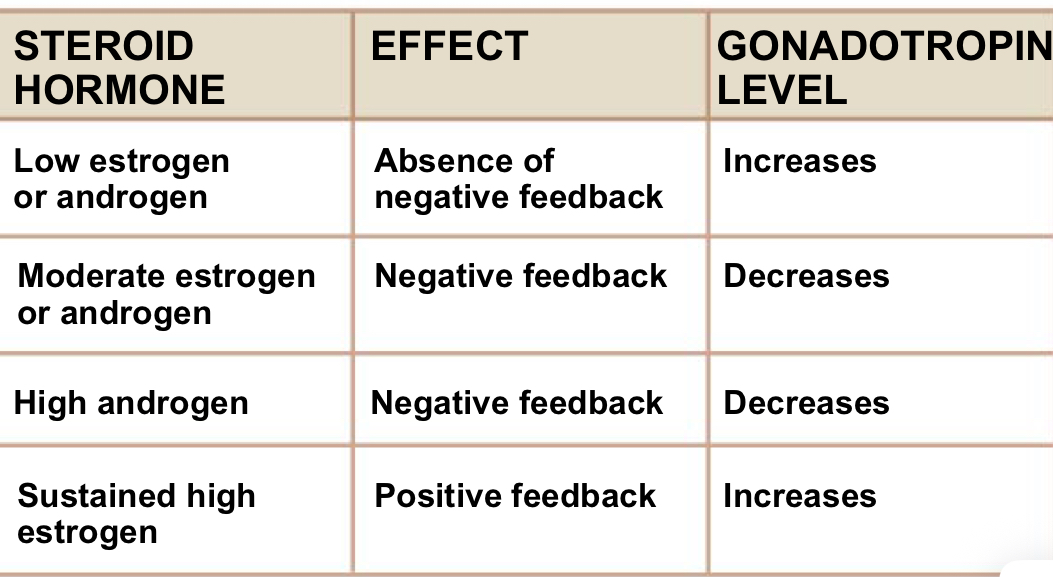
Describe the feedback effects of sex steroids on gonadotropin release
What do the ovaries produce ?
Female sex hormones and female germ cells
Describe the evolution of the ovum throughout the menstrual cycle
Primary follicle
Theca
Antrum
Ovulation
Corpus luteum formation
Mature corpus leteum
Corpus albicans
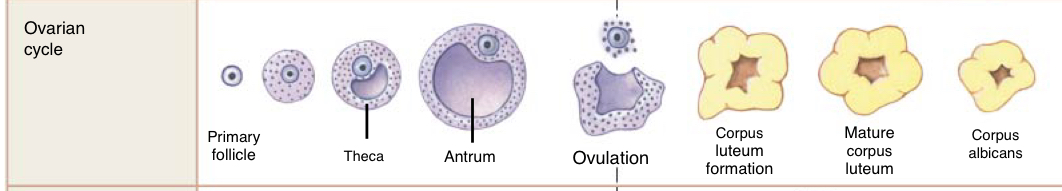
Describe the cellular structure of the antrum (Tertiary follicle)
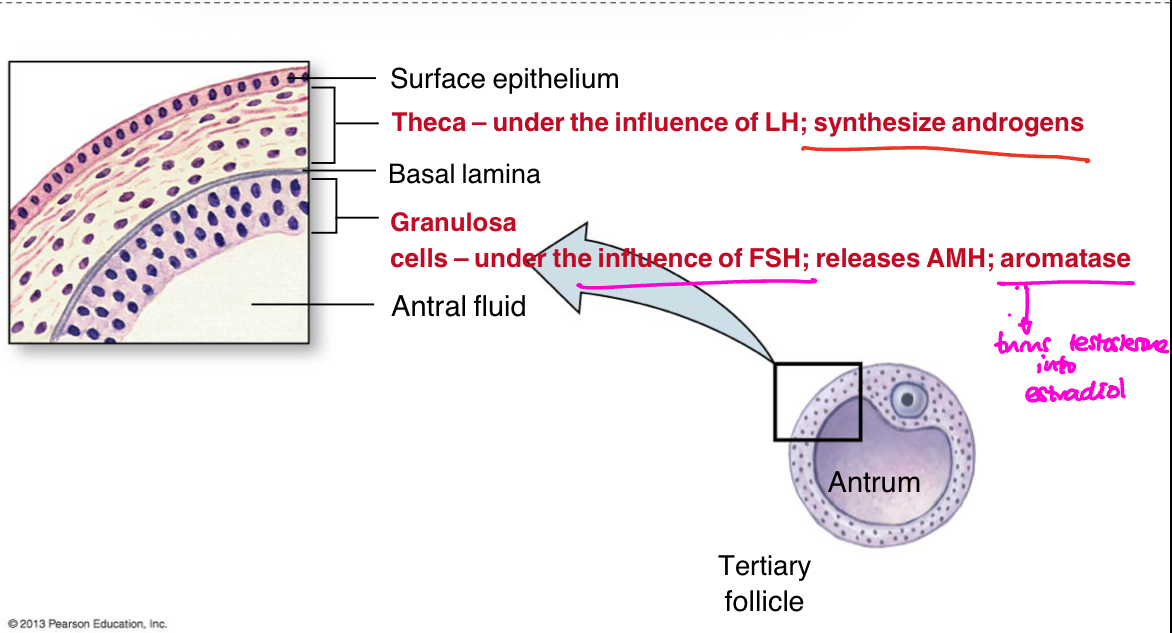
Describe the 3 categories of Ovarian Steroid Hormones ?
Estrogens C18 (produced by Granulosa cells)
Progestagens C21 ( produced by Corpus Luteum Cells)
Androgens C19 ( produced by Theca cells)
Estrogens C18
17 B-Estradiol (E2) - most potent type of estrogen - regulates menstrual cycle - present from puberty to menopause
Estrone (E1) - post menopause - weaker type of estrogen - synthesized from fat
Estriol - E3 - present in pregnancy
Progestagens C21
Pregnenolone
Progesterone
17 OH Progesterone
Androgens C19
DHEA
Androstenedione
Testosterone
Dihydrotestosterone
How are the actions of estrogen mediated ?
Estrogen Receptor (ER) is a dimeric nuclear protein that binds to DNA and controls gene expression
Estrogen:ER complex binds to specific DNA sequences called hormone response element to activate the transcription of target genes
Main actions of Estrogen
Development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics
Provision of the hormonal timing for ovulation
How does estrogen affect the brain, breasts and skin of the female body ?
Brain - helps adjust body temp, increase memory, adjusts libido
Breast - grows and shapes breast, preparation for breast feeding
Skin - makes skin young
How does estrogen affect the Bone, Vagina nd Uterus of the female body ?
Bone - strengthens bone and increases its density
Vagina - moistens, protects from infection
Uterus - monthly preparation for pregnancy or menstrual cycle