MLSP 5214 Final practical notes/study
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
myelocyte notes
confused w/ monocytes
- myelocyte = pink cytoplasm
- monocyte = blue cytoplasm
usually in BM, presence in PB = left shift
- assoc w infection (bacterial), sepsis, CML
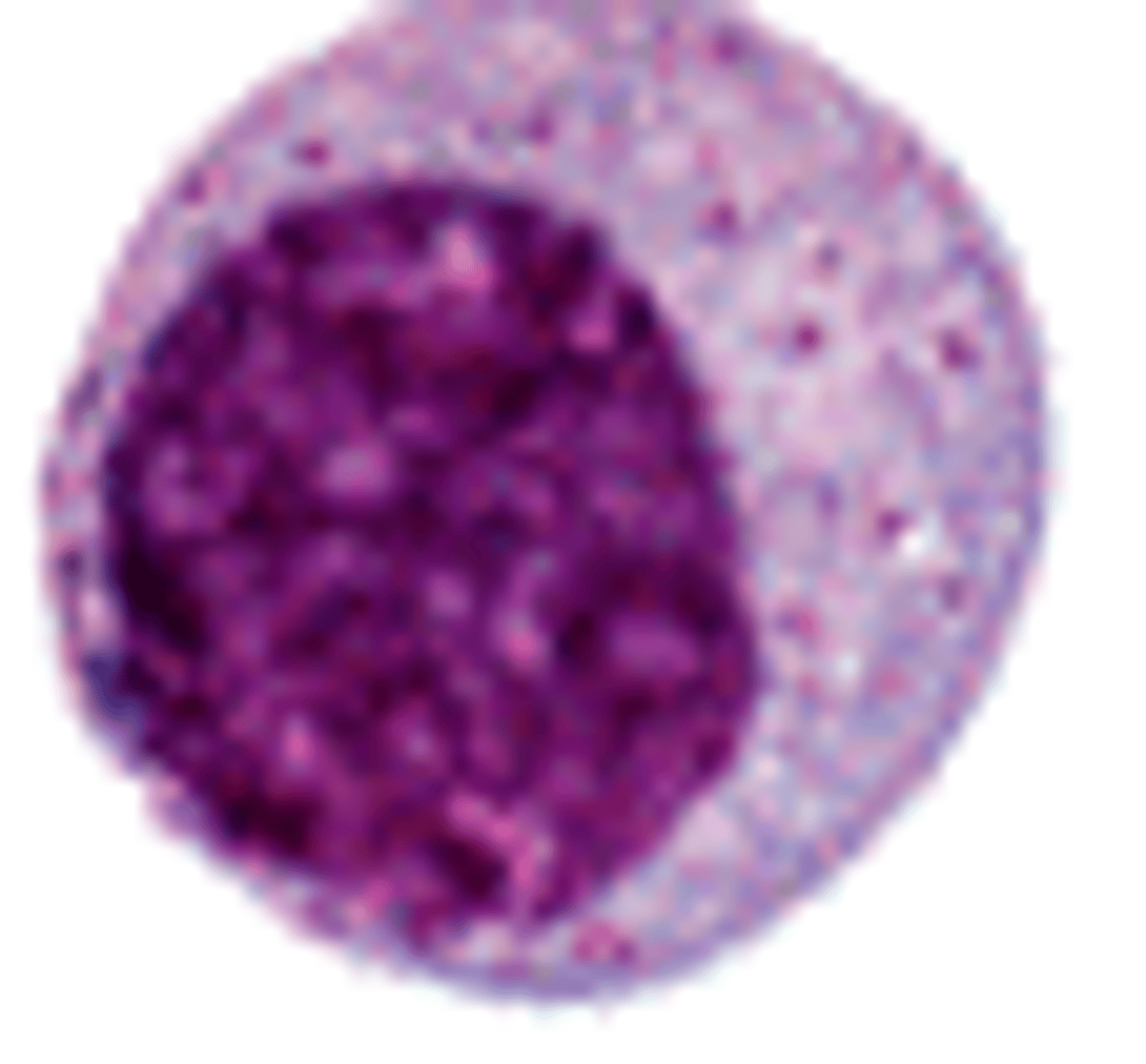
You think you saw an immature micromegakaryocyte?
- SIZE! in comp to other cells
- HAVE to see abnormal plt morphologies
- blebs + perinuclear blue granules
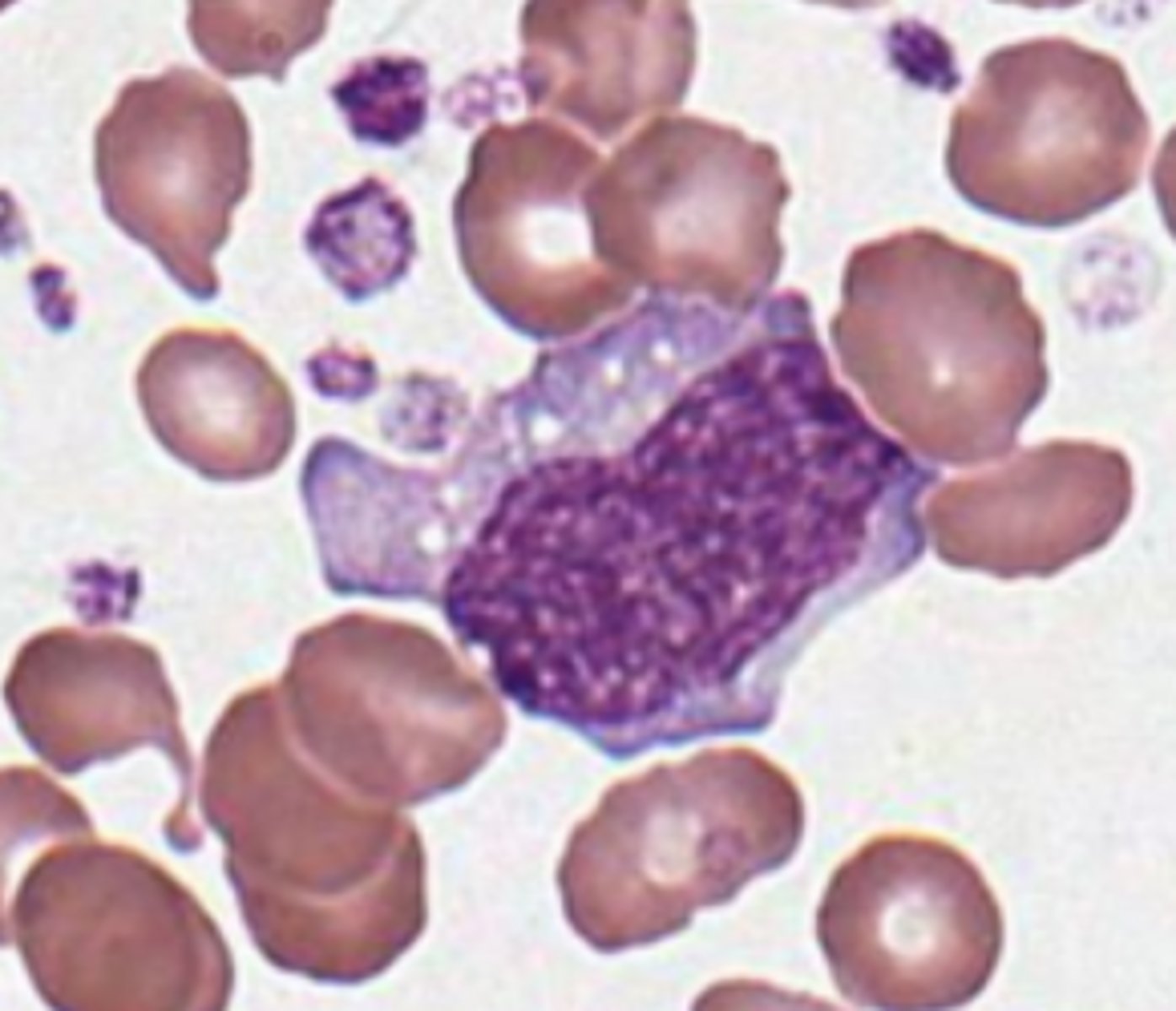
You think you saw immunoblast?
- radial basophilia
-- streaks of basophilia
- remember:
immunoblast --> plasma cell
NO stretched chromatin
increased in lympho-prolif
- viral illness like infectious mono, hepatitis
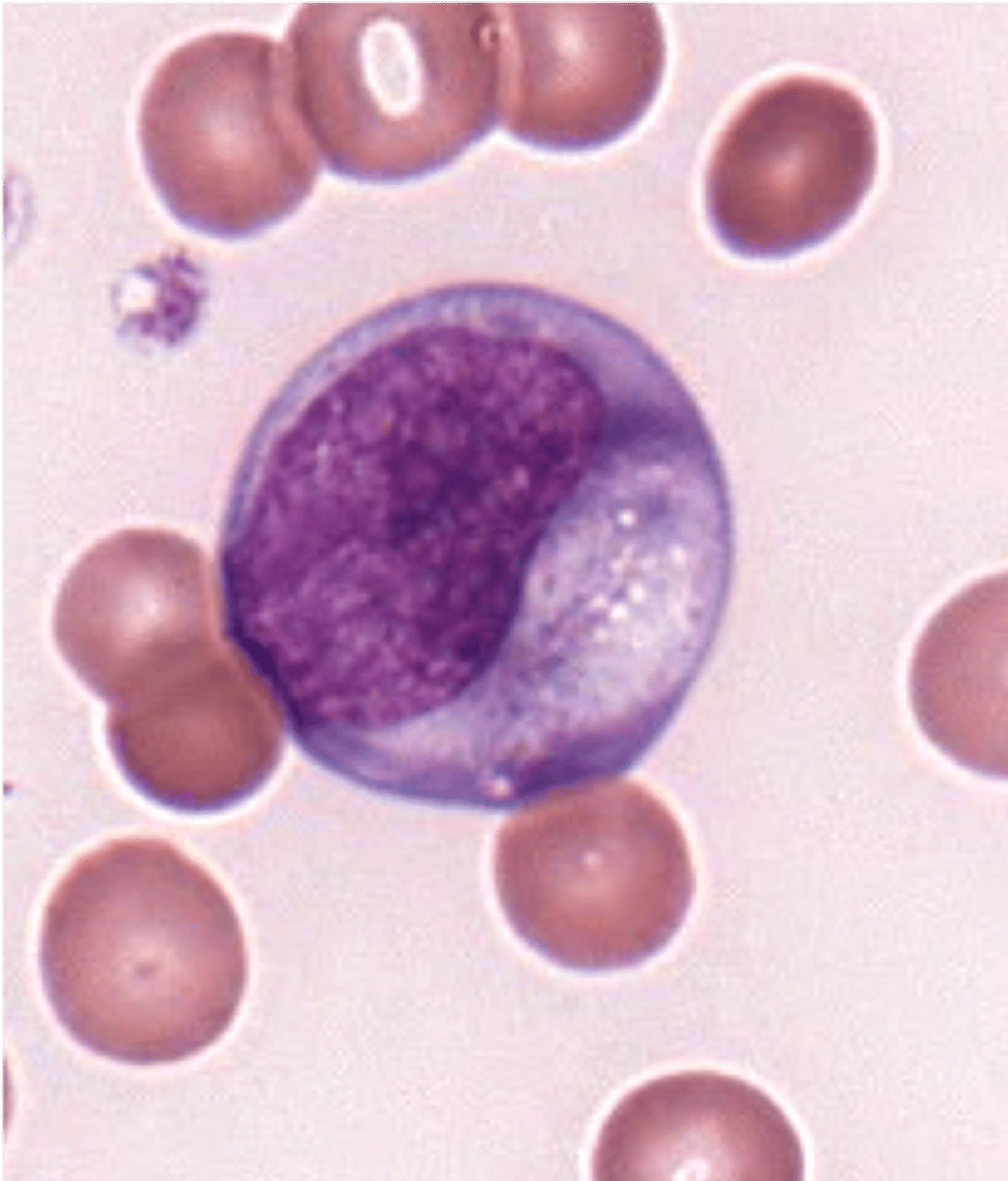
Immature basophilia notes
can see nucleus most of the time
- can't in a mature basophil
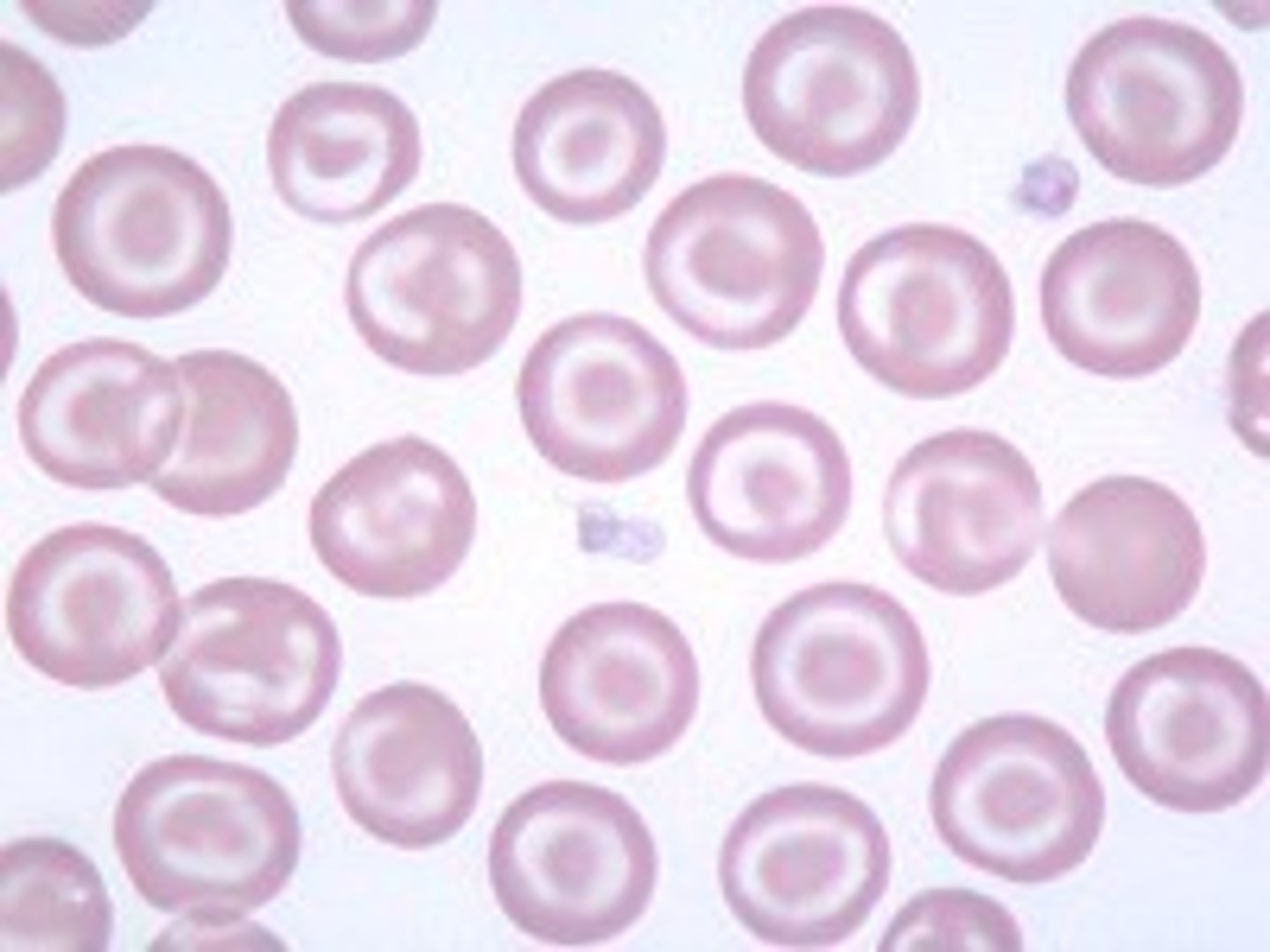
Target cells associated with
in hypo/micro = beta thalassemia (hgbinopathies), IDA
in macro = liver disease
sideroblastic anemia
RBC fragments + normo/normo =
Hemolytic anemia, DIC, other microangiopathic (TTP), HUS
Spherocytes associated with
RBC spheres containing more than normal amounts of hgb
seen in:
- AIHA
-- Ab-mediated hemolysis
- DIC
- hereditary spherocytosis (defect in spectrin)
- some infections (lecithinase bacteria like C. perfringens)
-- lecithin is apart of RBC membrane
treatment: splenectomy
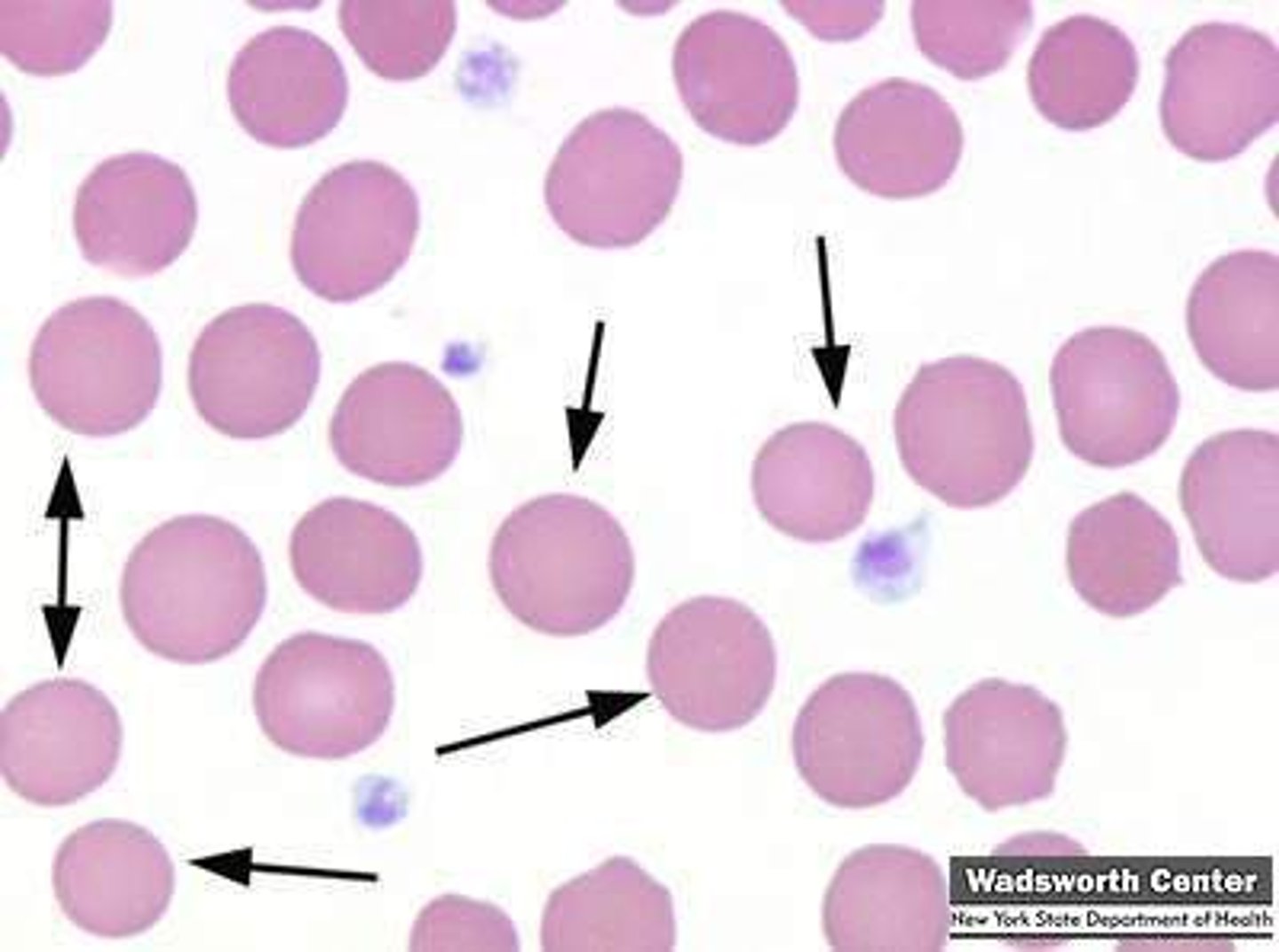
Helmet cell associated with
blister rupture of membrane
- G6PD deficiency
- pulmonary embolism
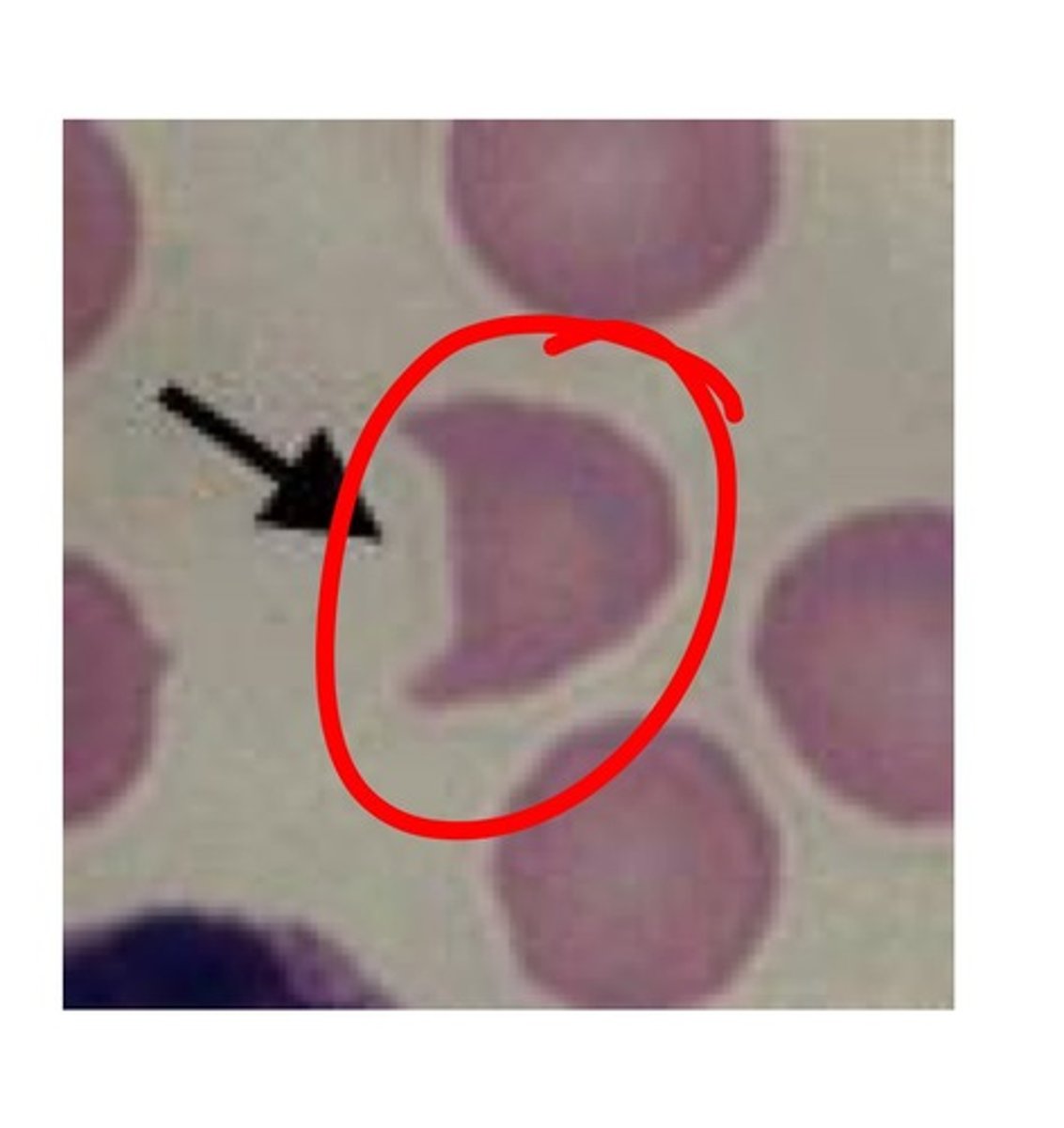
Teardrops associated with
squeezing of RBCs, crowded BM or spleen
- splenomegaly
- MDS
- Severe anemia
- Fibrosis
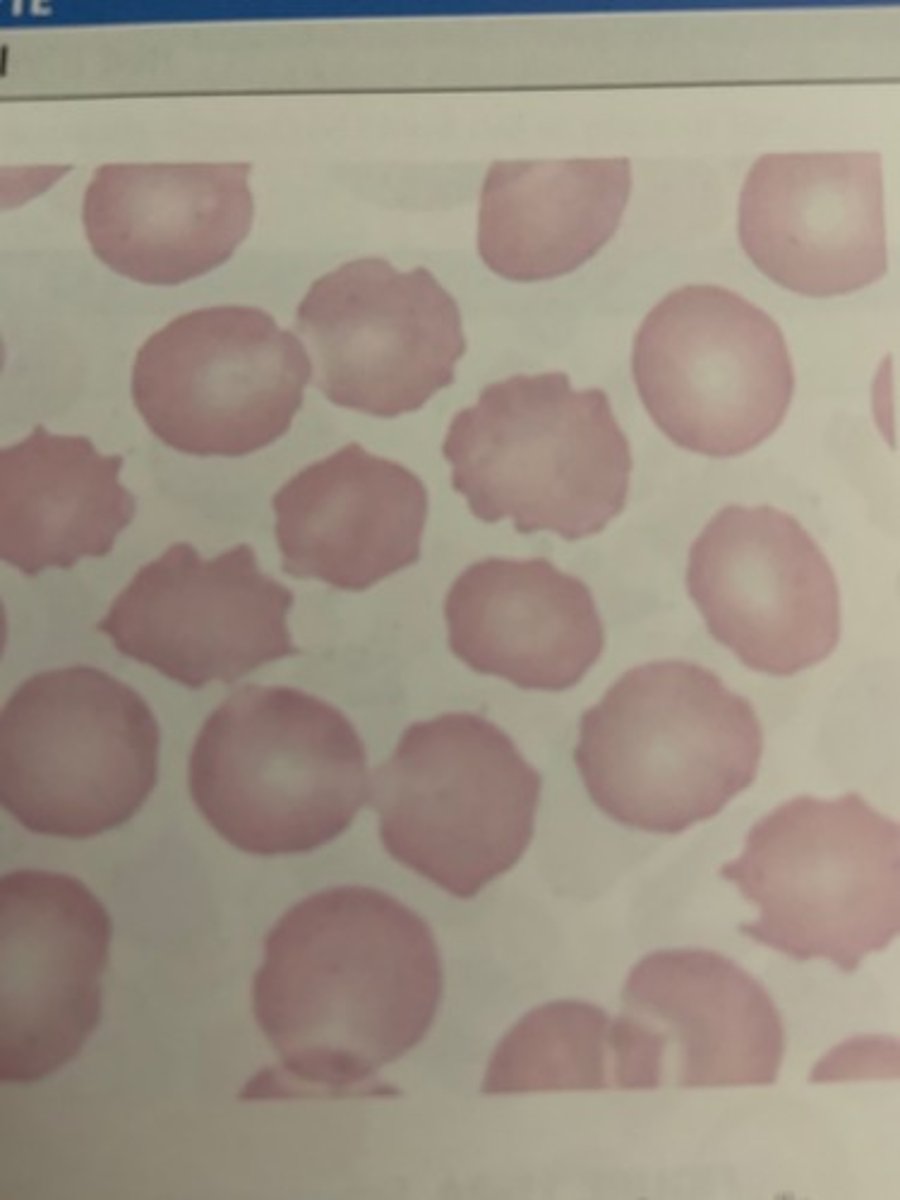
Echinocytes associated with
aka burr cells. grooves in perimeter, osmotic imbalance
- usually drying artifact
- kidney and liver disorders
-- HUS (Shiga toxin from E. coli)
- dehydration
- HUS (Shiga toxin from E. coli)
- severe burns, gastric ulcers
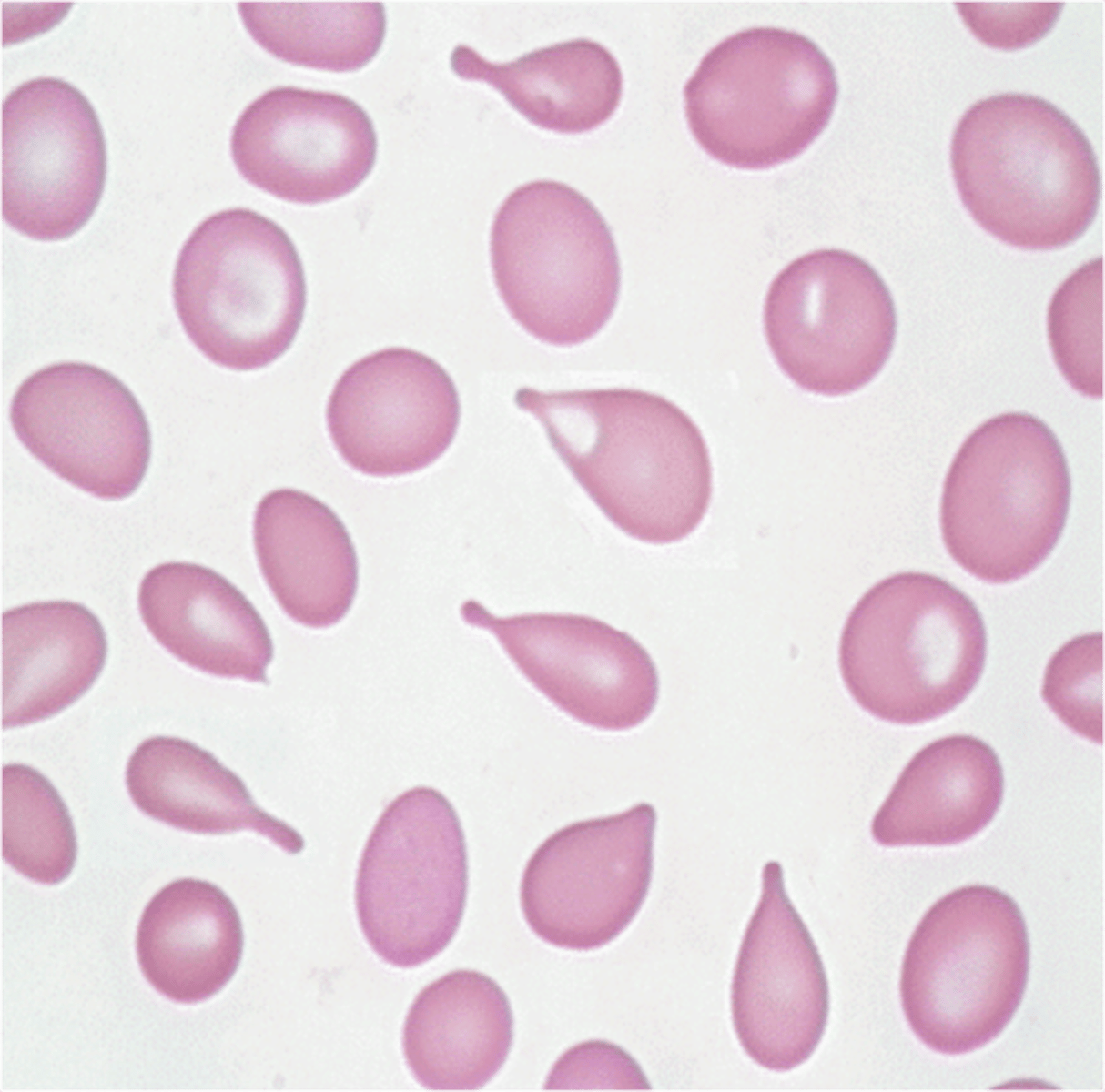
Acanthocytes associated with
spikes. liver disease, lipid defects, loss of membrane changes (micro, no pallor)
- cirrhosis, hepatitis, alcoholism
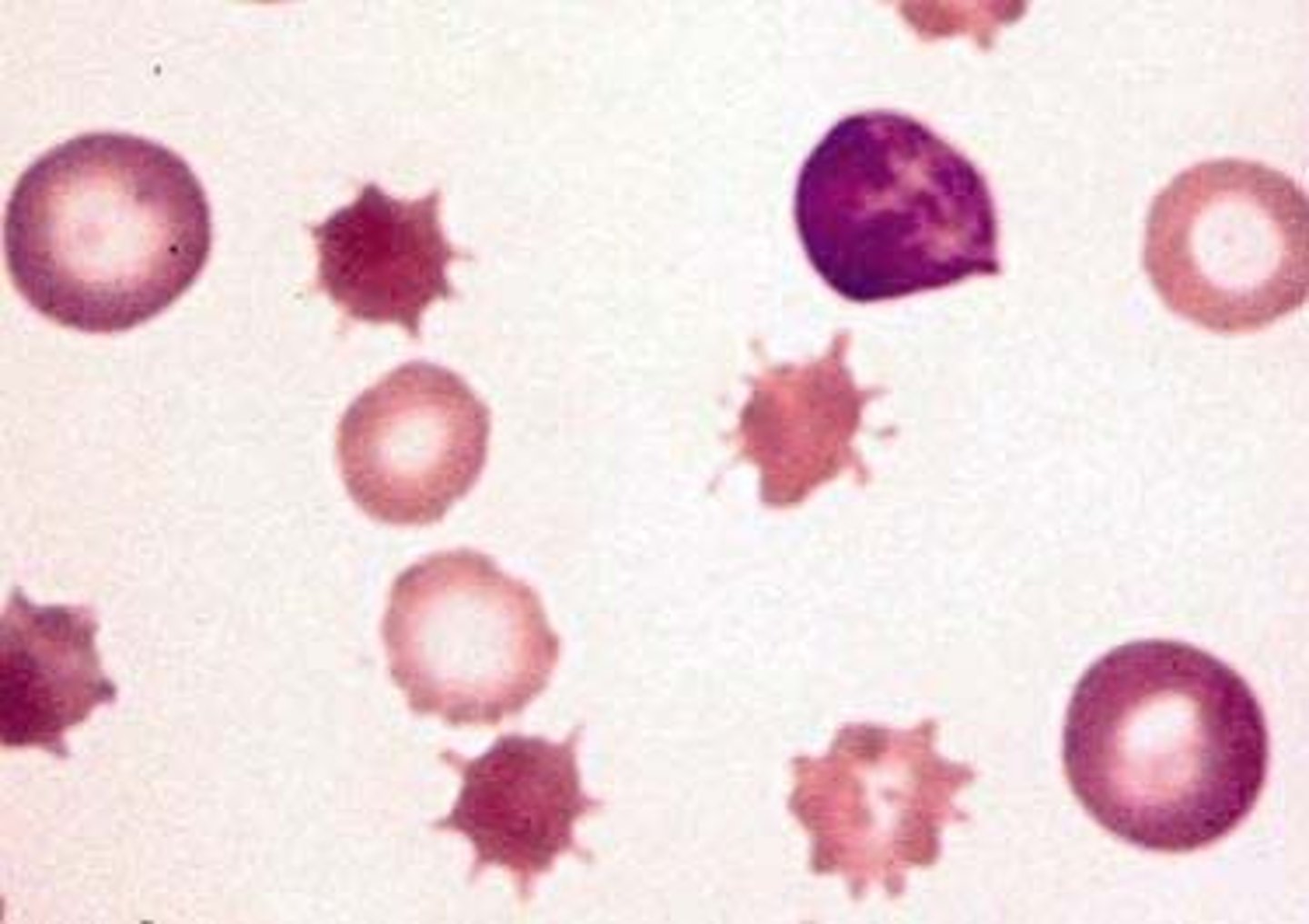
Bite cells associated with
heinz body (hgb remnants) removed by spleen
- thalassemia
- G6PD def
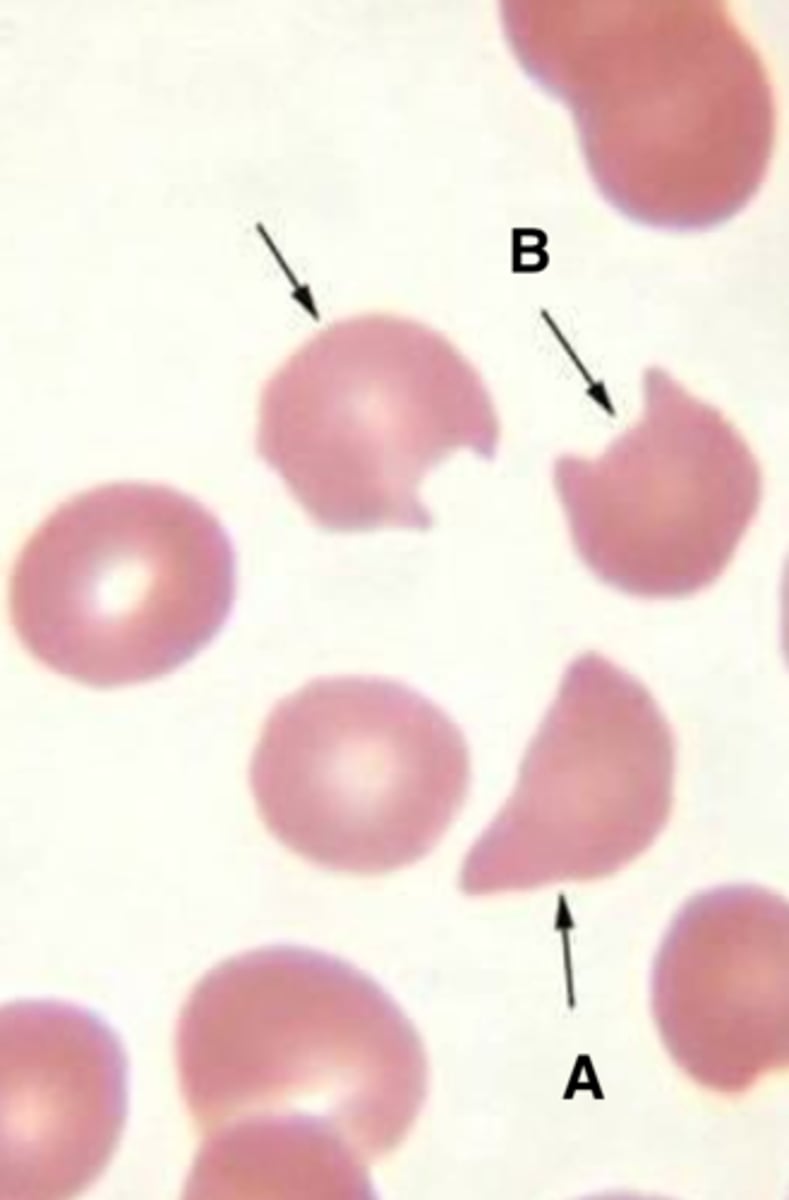
Elliptocyte associated with
- hereditary elliptocytosis
- thalassemia
- IDA (early)
ovalocytes associated with
- macrocytic anemia
- hypersegmented neus
- B12 or folic acid deficiency
- malabsorption, intrinsic factor def, dietary def
Gaucher disease
glucocerebrosidase def. = ↑ glucocerebroside
- crumpled tissue paper look
- hepatosplenomegaly
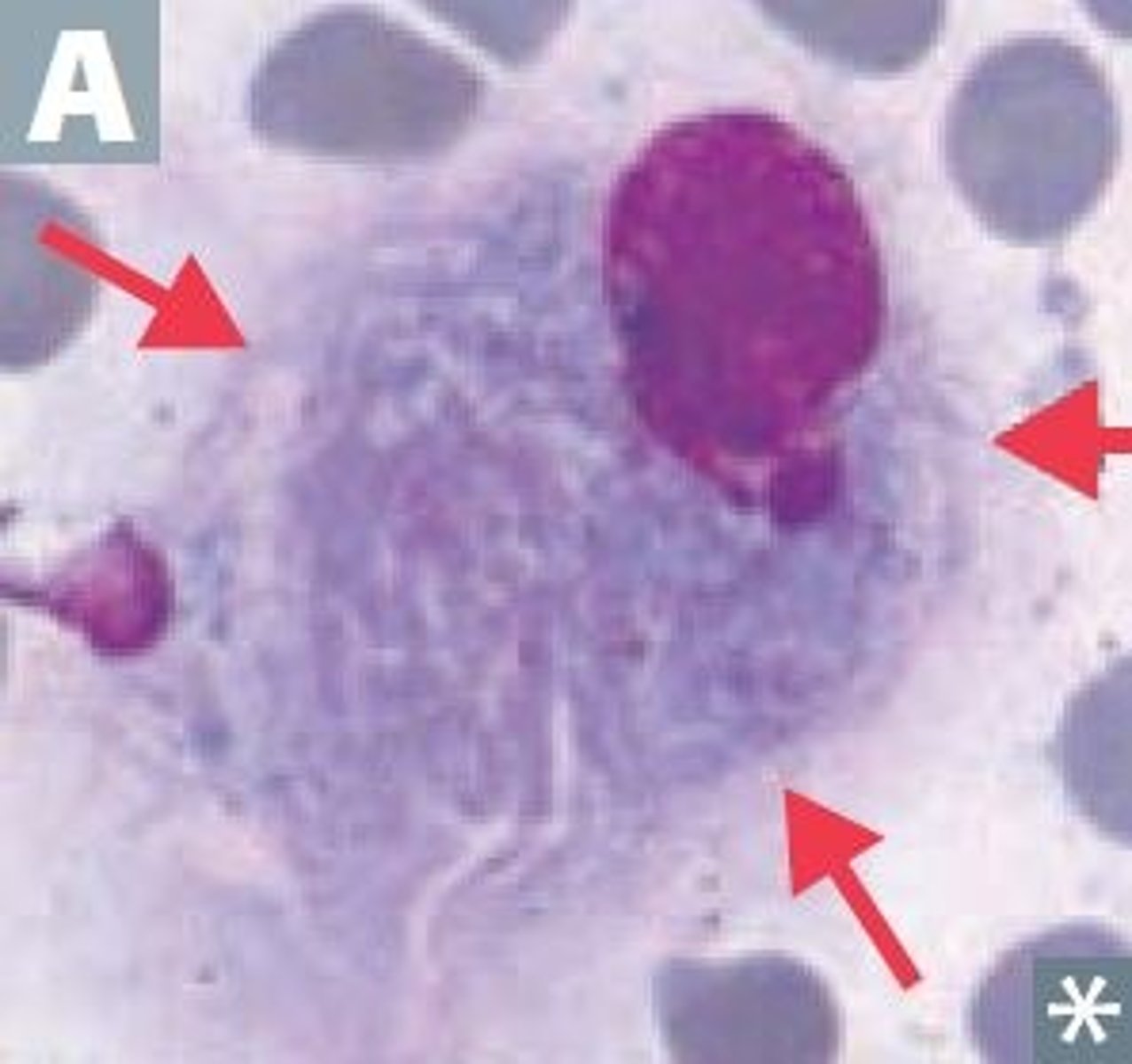
May-Hegglin Anomaly
- neutrophils have blue-staining inclusions that resemble Dohle bodies
- thrombocytopenia
- giant abnormal platelets
Alder-Reilly Anomaly
a mucopolysaccharidosis
- every leukocyte seen exhibits dense, basophilic coarse granulation
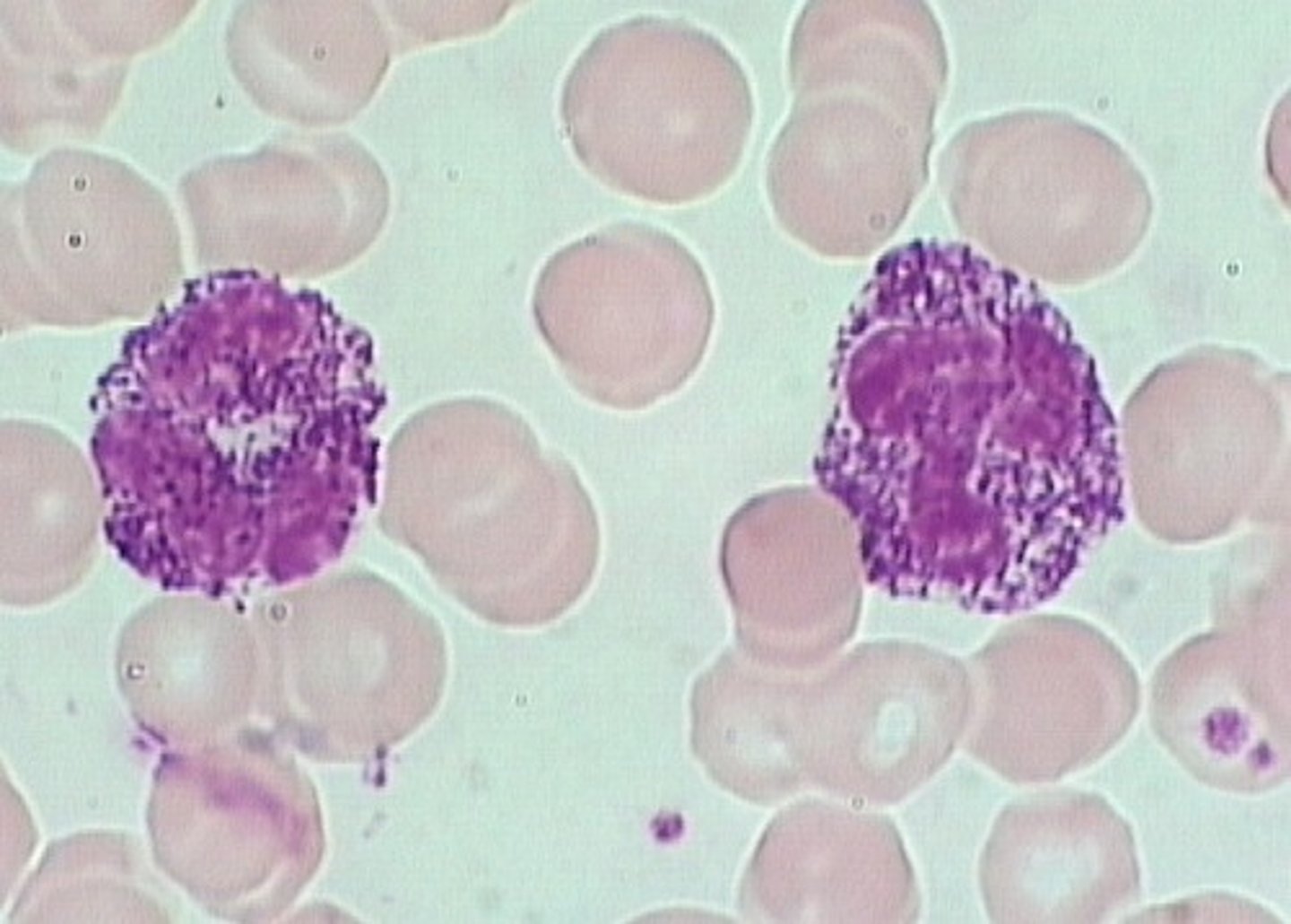
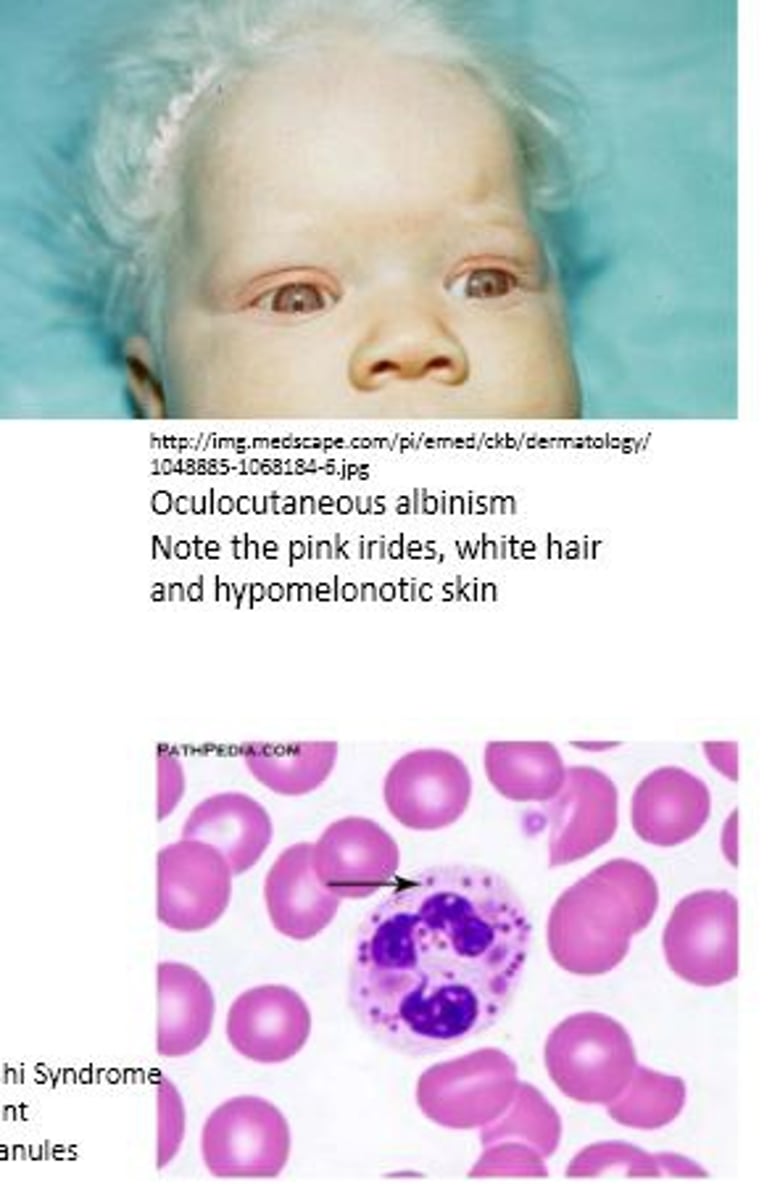
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
- defect in microtubule polymerization
- infection prone
- Giant granules in neutrophils
- oculocutaneous albinism
Niemann-Pick disease
Sphingomyelinase deficiency = increase sphingomyelin
RBC nuclei contain sphingomyelin
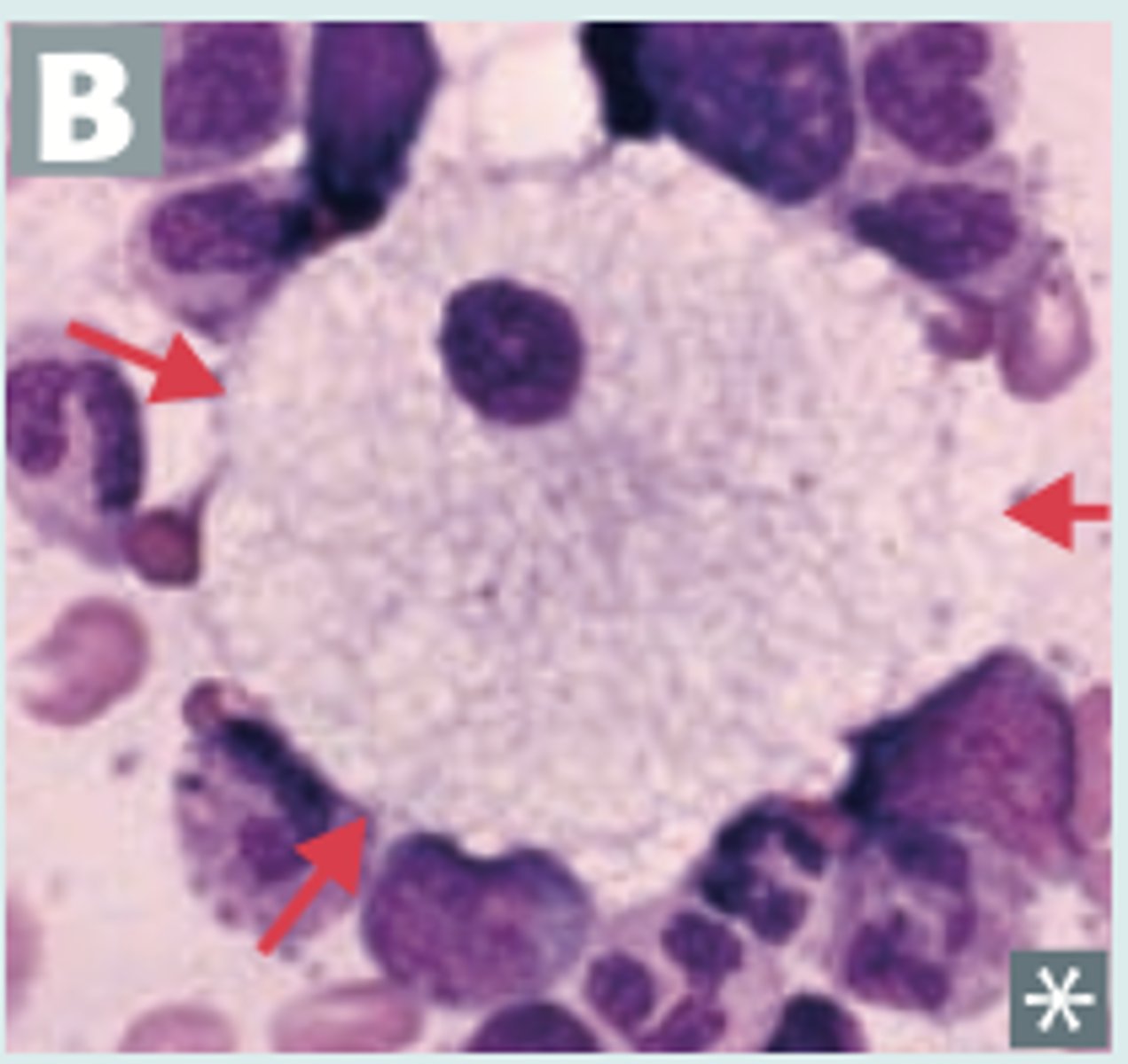
Mucopolysaccharidoses present as
inclusions with halo in lymphocytes
neurological disability
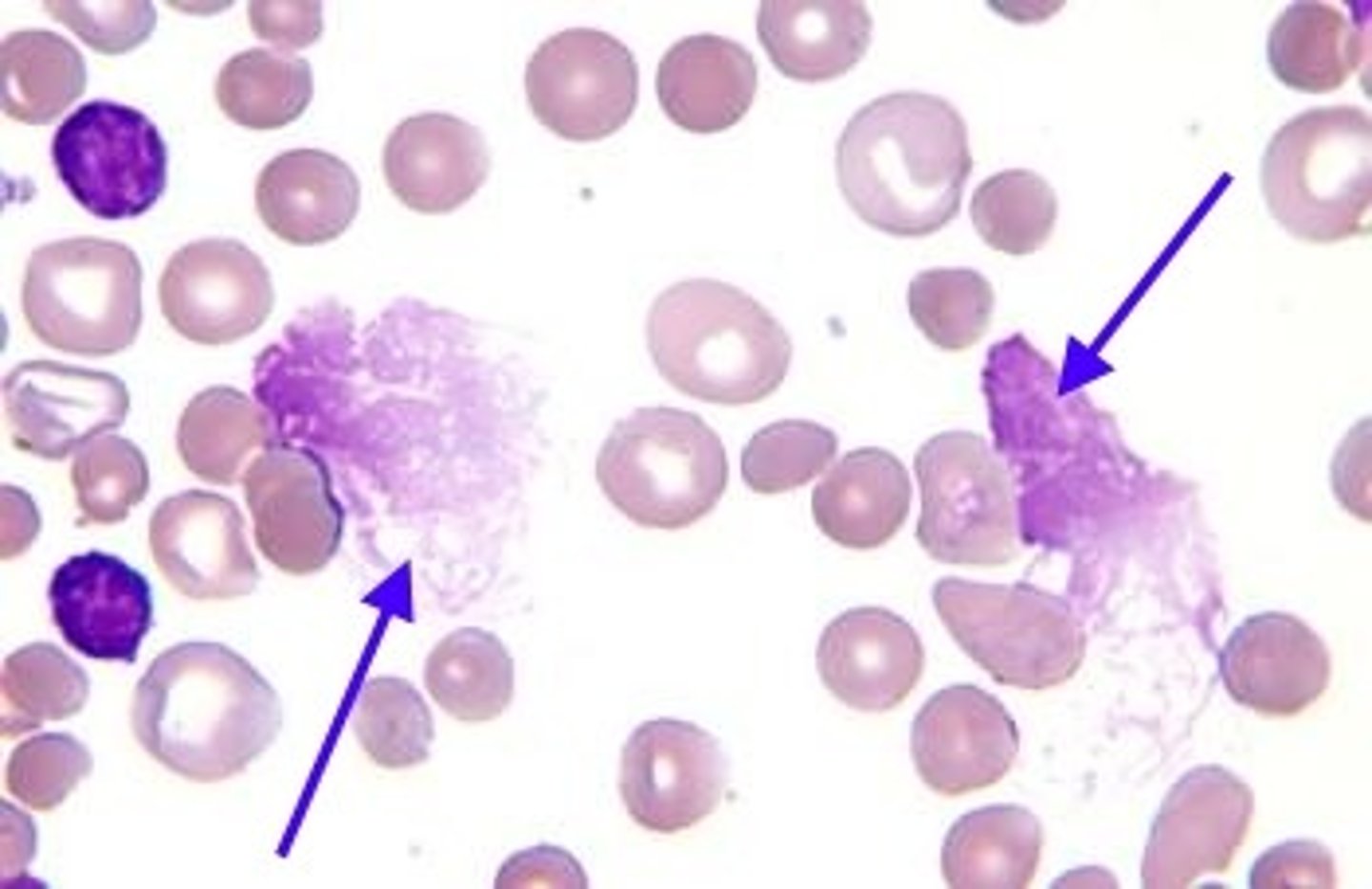
Smudge cells associated with
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
- only in PB
- any cell thats partially ruptured
An increase in eosinophils or hybrid eos-baso cells in BM vs PB
BM = inv(16)
PB = CML
Pseudo Chediak-Higashi granules
seen in any leukemia
- usually wherever Auer rods are (AML)
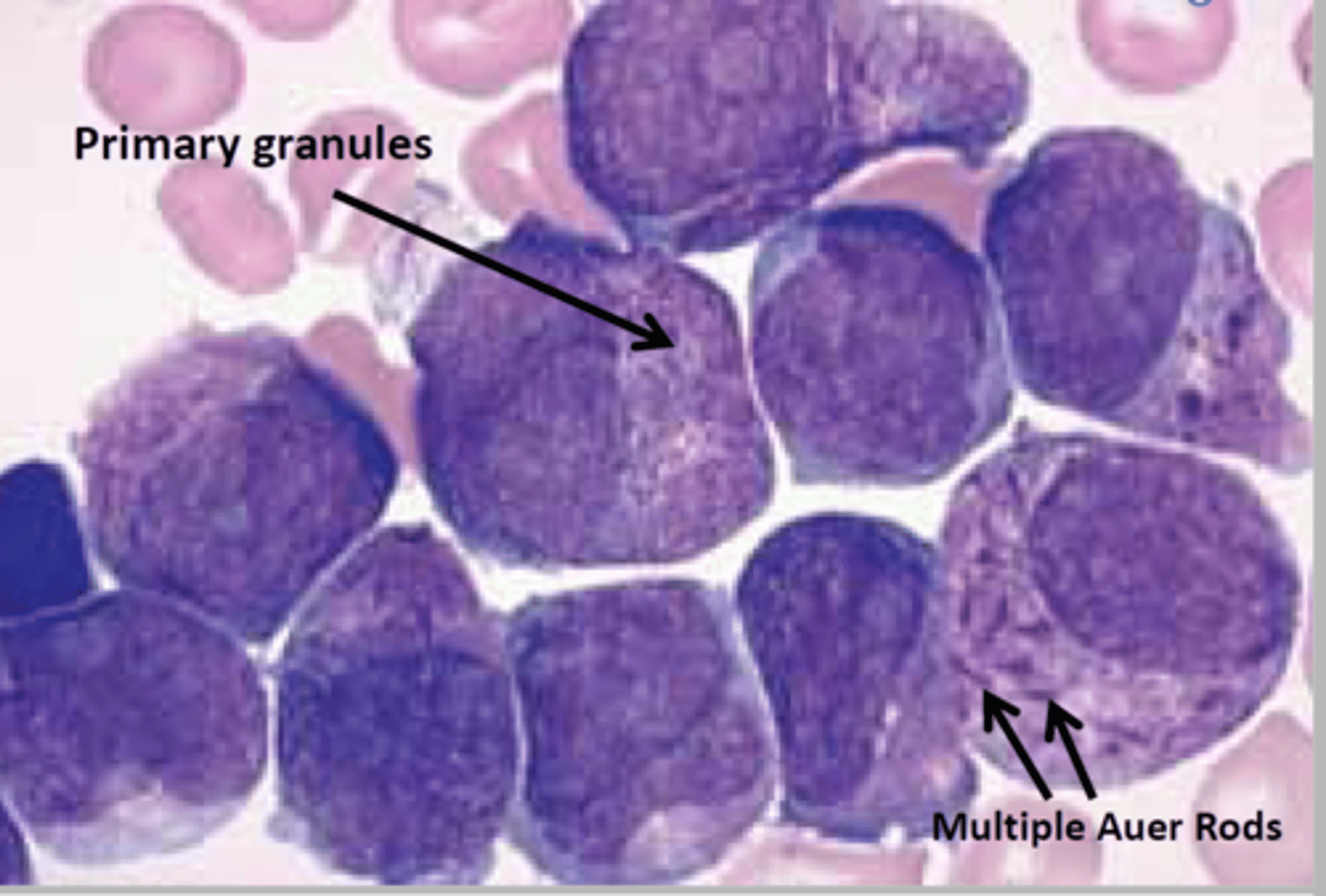
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)
promyelocytes with intracytoplasmic Auer rods
- clefted nucleus (hourglass-shape)
- can be hypogranular
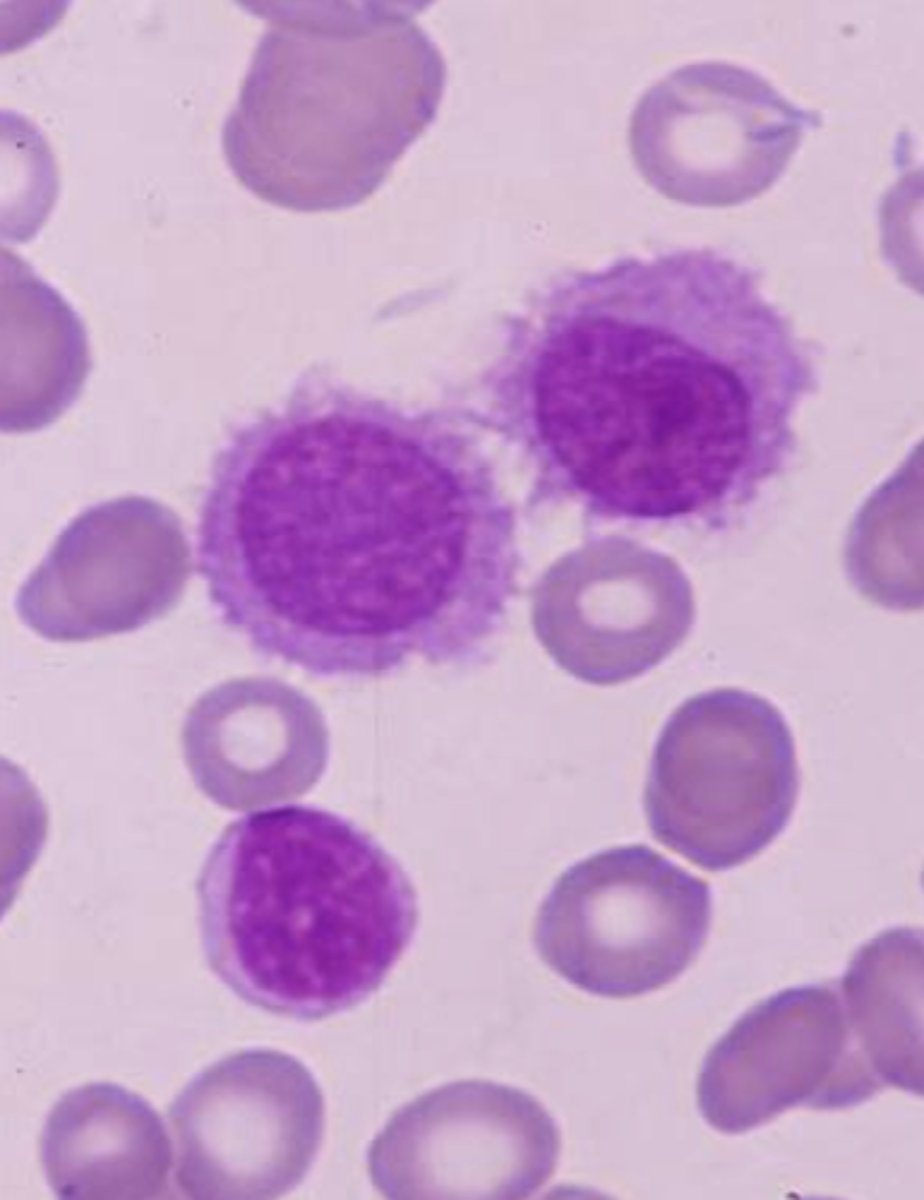
Hairy Cell Leukemia
Neoplastic proliferation of mature B cells in BM
- cells have filaments, making them look hairy
- affects spleen, BM tap usually dry
- monocytopenia
- CD19, 20, 25!, 103!
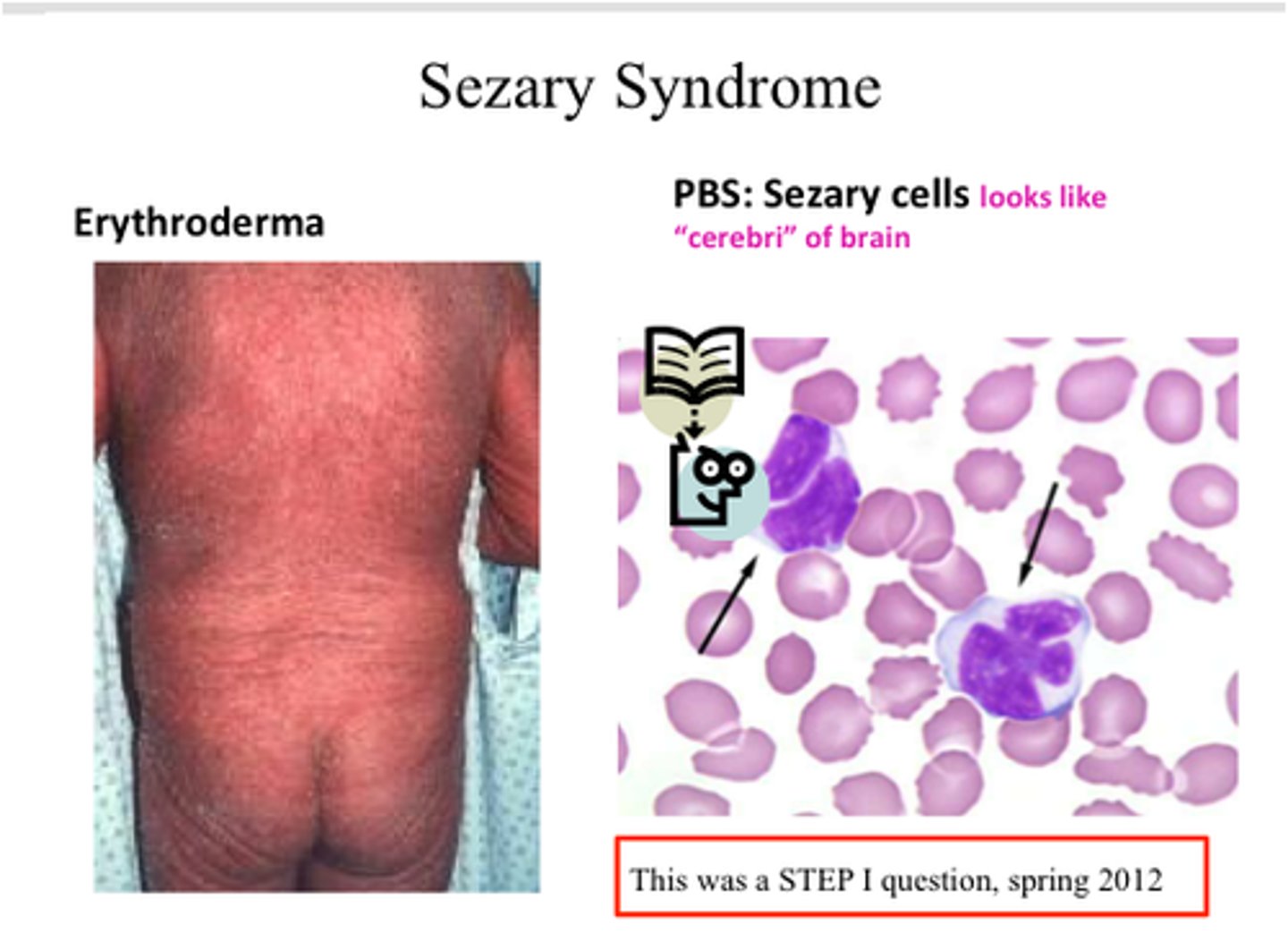
Sezary syndrome
leukemic phase of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides)
looks like clover leaves
- itchy RASH
- CD4 (T helper)
- CD3, 7, 2!
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)
immature lymphocytes predominate
- kids, sudden onset
smaller lymphos, can get into spinal fluid easier
lymphoblasts = malignant
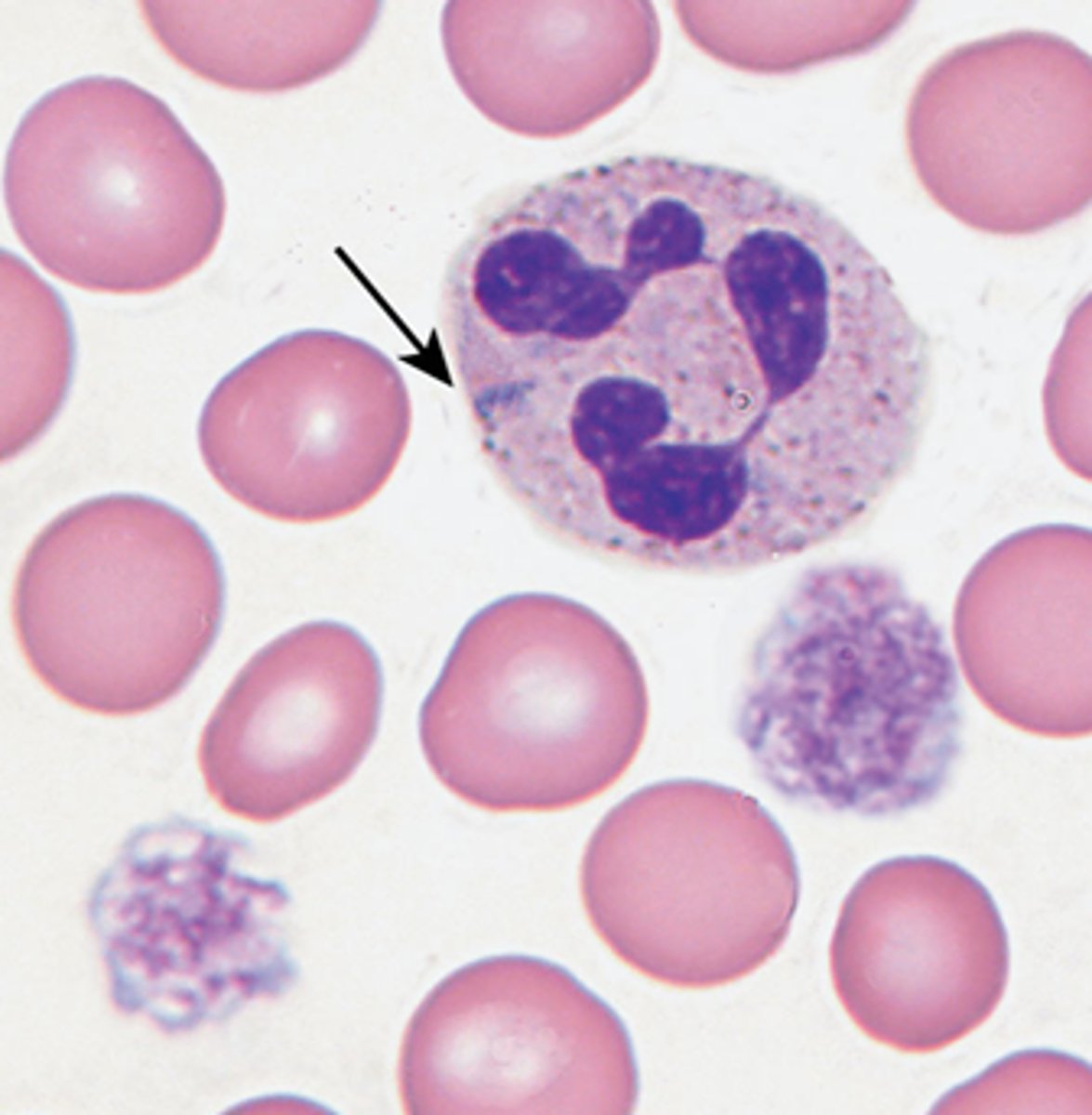
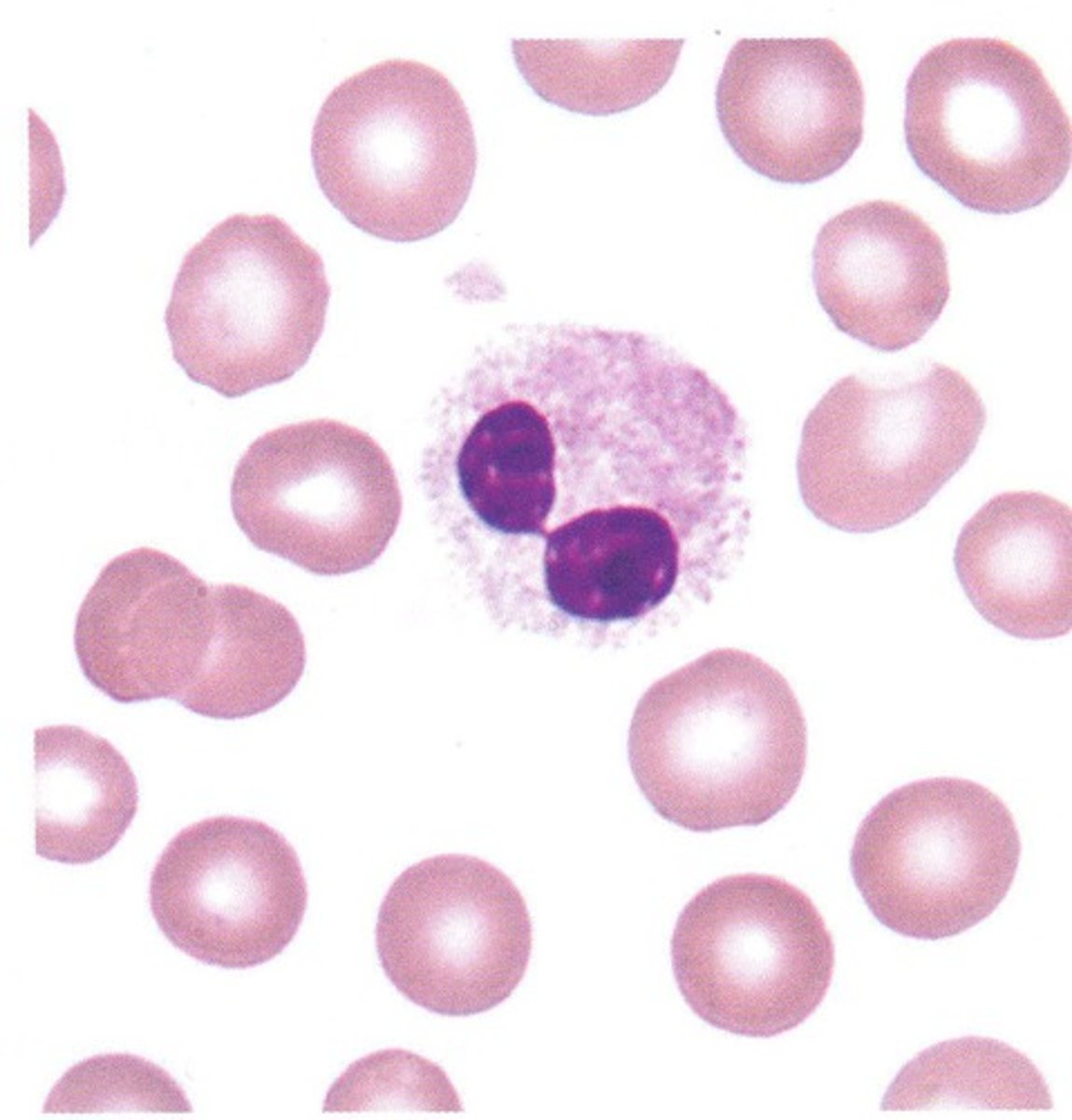
Pelger-Huet anomaly vs. pseudo Pelger-Huet
inherited, bi-lobed neutrophils in PB
- benign condition with no clinical manifestations
Pseudo Pelger Huet = only some neutrophils have bilobed nuclei
- a toxic change
- assoc w toxic granulation, degranulation, left shift, MDS, etc.
Epstein Syndrome
splenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, prolonged bleeding time, giant platelets with abnormal structure
Diseases associated with abnormally large platelets
Epstein syndrome
Bernard-Soulier
Bernard-Soulier syndrome
genetic GPIB deficiency; platelet ADHESION impaired
- thrombocytopenia with enlarged platelets (enlarged bc more immature)
Dimorphic blood picture
two pop of size and color
- sideroblastic anemia: hypo/micro and normo
- treated IDA: transfused RBC and pt RBCs
Howell-Jolly bodies
nucleus remnants
- post-splenectomy (or nonfunctional spleen), usually seen with nRBCs
- splenomegaly
Basophilic stippling associated with
Lead Poisoning
Thalassemias
Anemia of Chronic Disease
coarse stippling = pappenheimer, sideroblastic anemia
Hypochromasia
low hgb conc
- low MCHC
IDA, megaloblastic anemia, thalassemias
Polychromasia
immature RBCs, bluish-purple
few = normal
increase = excess demand OR recovery from deficiency
Rouleaux associated with
multiple myeloma (plasma cells)
Agglutination associated with
cold agglutinins disease
mast cells
found in the CT of the dermis
respond to injury, infection, or allergy by producing and releasing substances
- including heparin and histamine
seen in sideroblastic anemia in tissues
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
Autoimmune platelet destruction
- thrombocytopenia
platelet satellitism, edta platelet clumping
Pseudothrombocytopenia
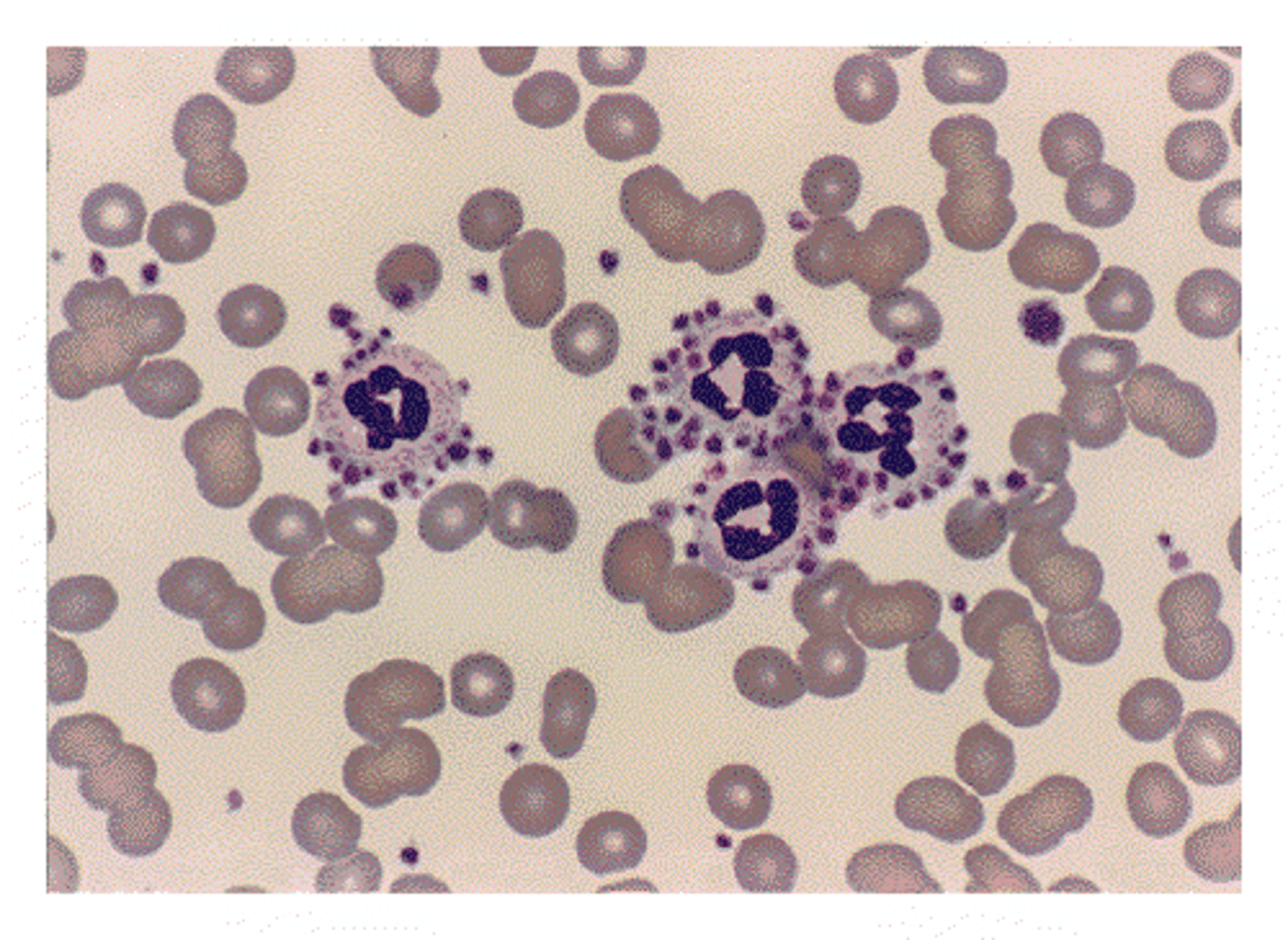
Primary Myelofibrosis (PMF)
NRBCs and early granulocyte progenitors = leukoerythroblastosis + basophilia
Teardrop-shaped RBC's (dacryocytes)
cells damaged during the birthing process in the fibrotic marrow
Heinz body vs. Howell-Jolly body
Heinz - G6PD deficiency
Howell-Jolly - asplenia
Ehrlichiosis
Obligate intracellular pathogens of host phagocytes
bruising and petechiae
-Cytoplasmic inclusions
- leuko and thrombocytopenia
Ehrlichia chaffeensis causes human monocytic ehrlichiosis (HME)

Cabot ring associated with
miotic spindles
- megaloblastic anemia
- thalassemia
- post-splenectomy
sickle cell due to
polymerizations due to amino acid substitution
Stomatocytes associated with
usually artifact
- alcoholism
- ion pump defects
- malignancies
Sudan Black B (SBB)
only pos rxn is significant
- strongly pos = auer rod = AML not ALL
Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
malignant erythroid precursor = strongly pos
Fagg*t cell
cells that contain many auer rods
- freq found in PML, t(15:17)