Biol 226 (A&P II) Lab Exercise 1 - General Senses, Smell, and Taste
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Inferior orbital fissure
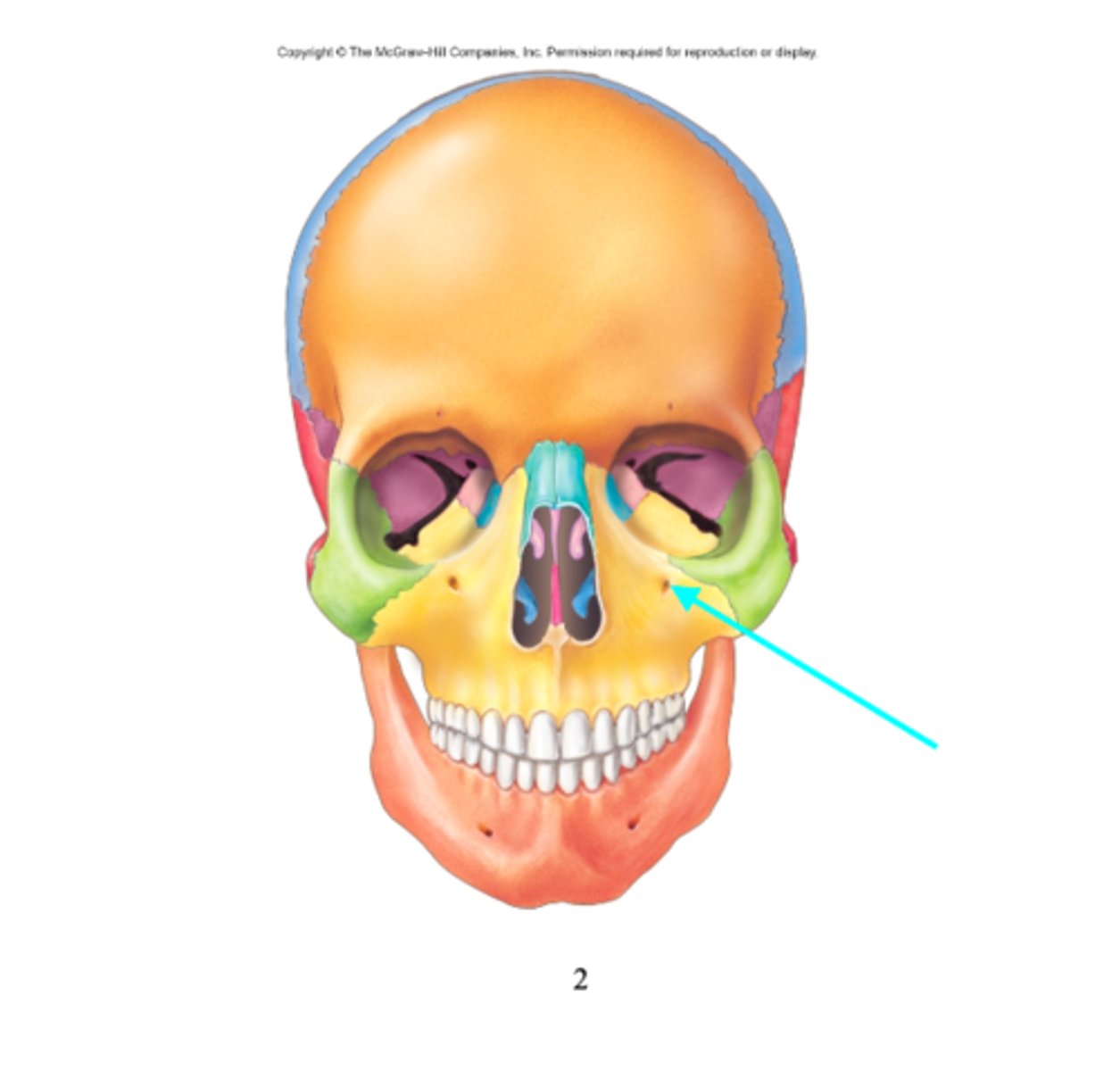
What feature is the blue arrow pointing at?
Infraorbital foramen
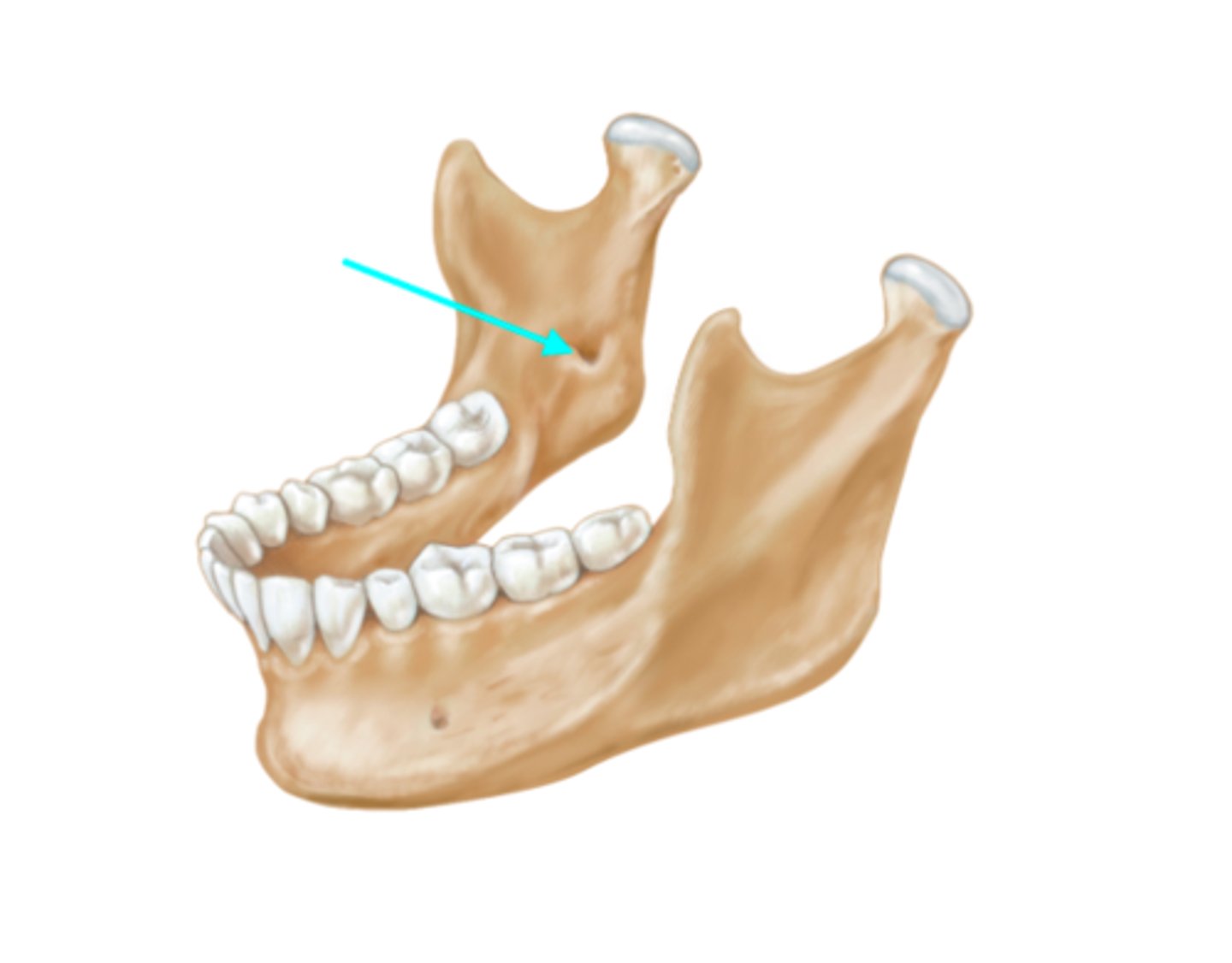
What feature is the blue arrow pointing at?
Mandibular foramen
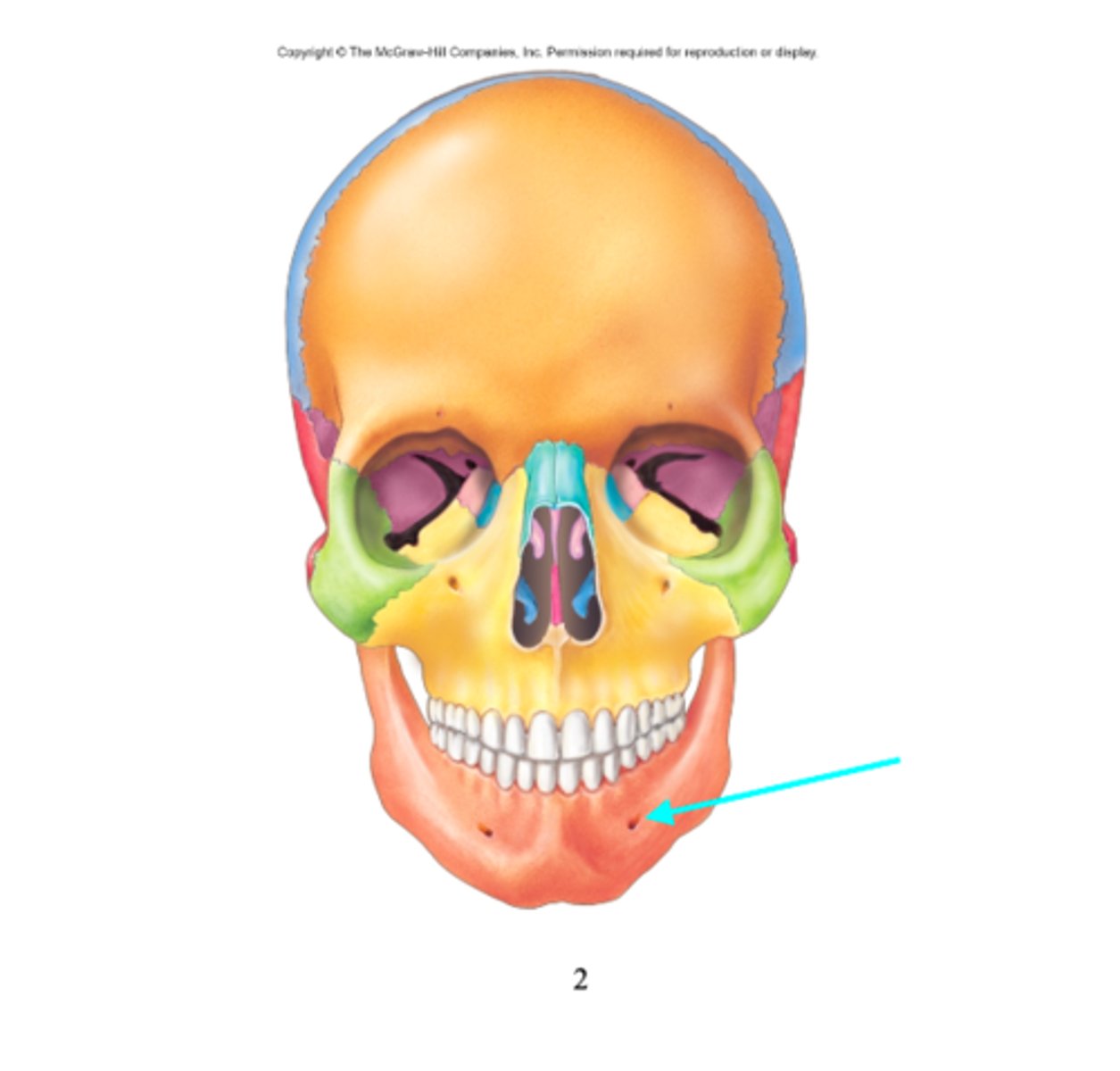
What feature is the blue arrow pointing at?
Mental foramen
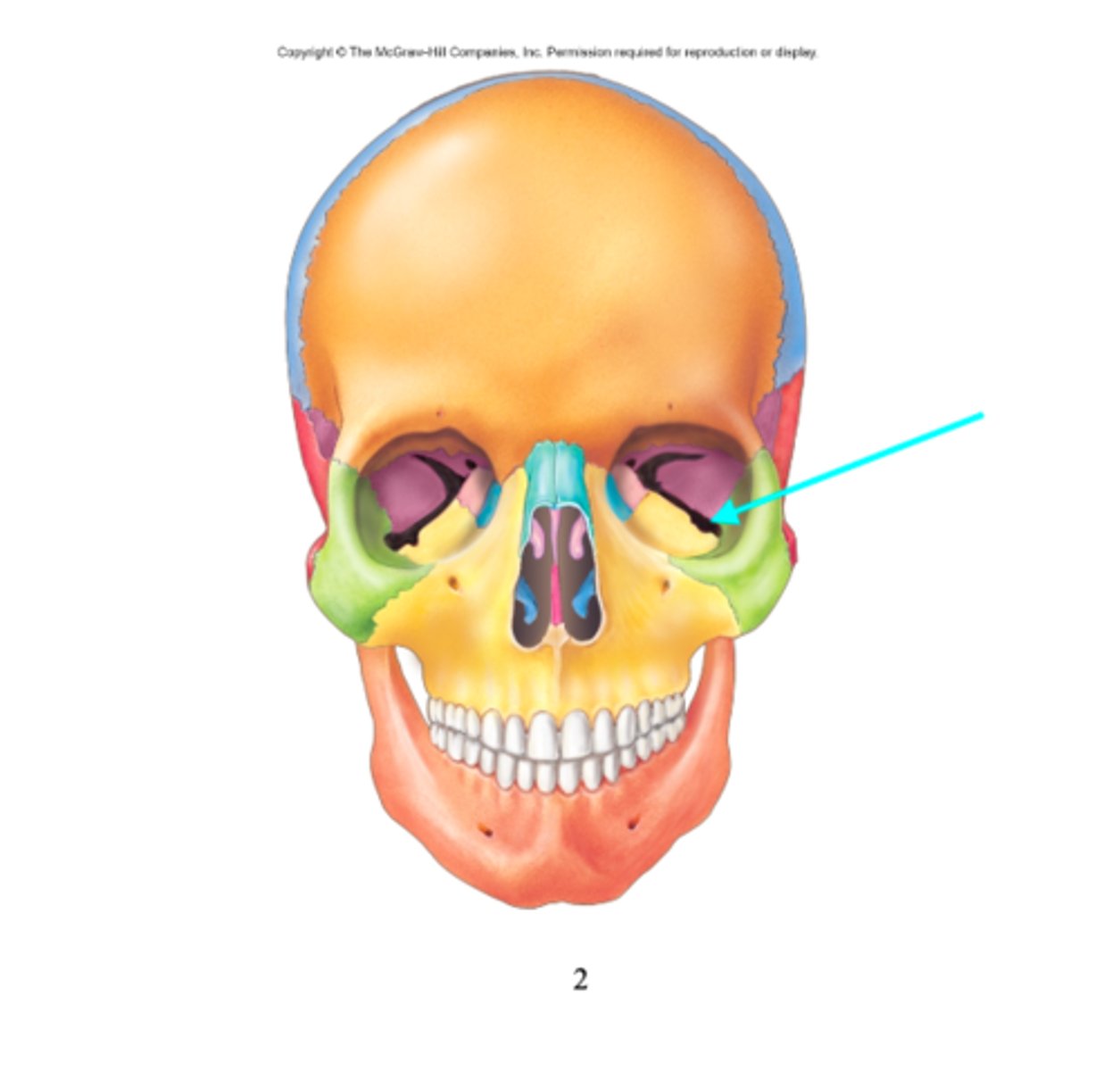
What feature is the blue arrow pointing at?
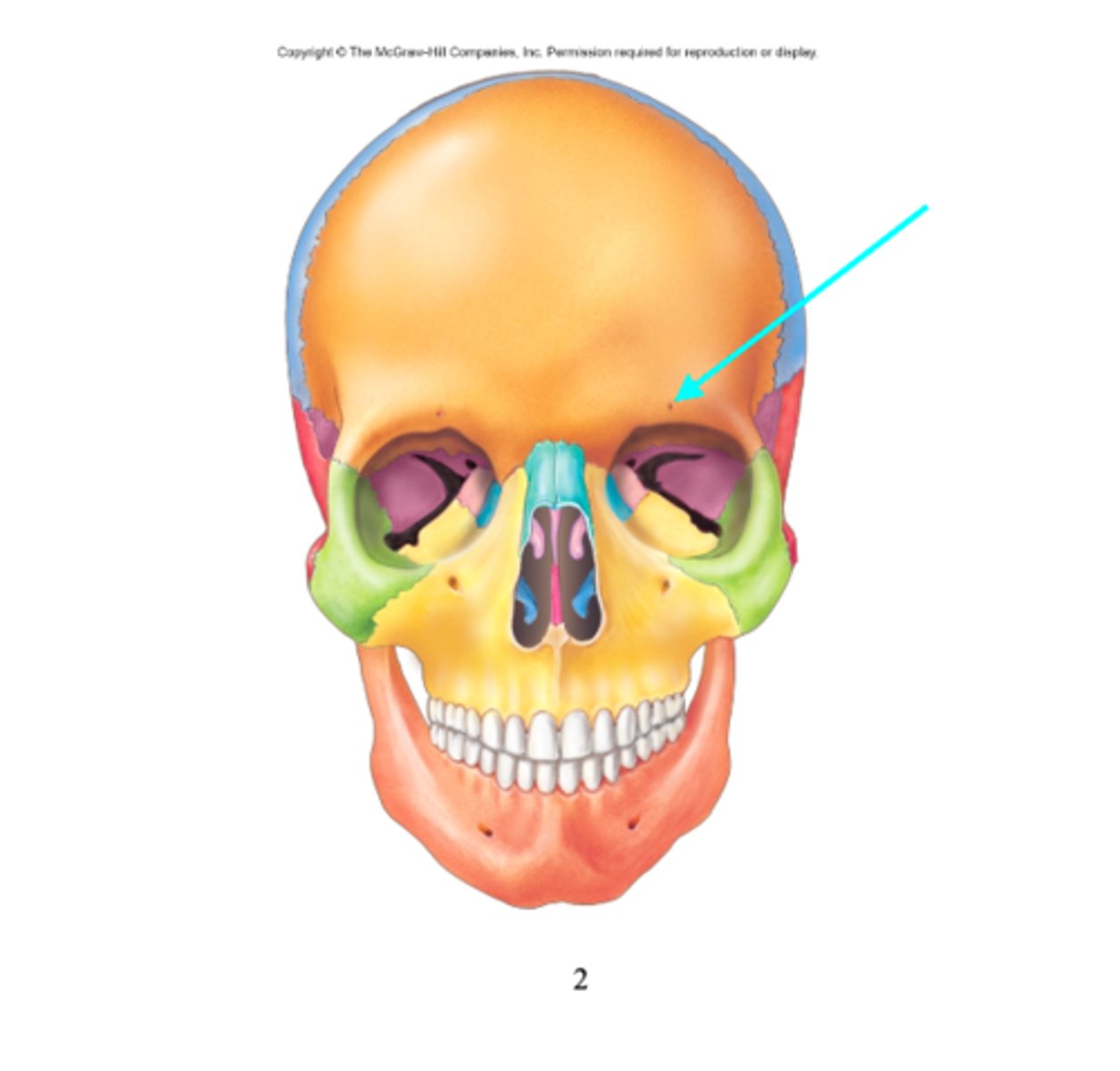
Superior orbital fissure
What feature is the blue arrow pointing at?
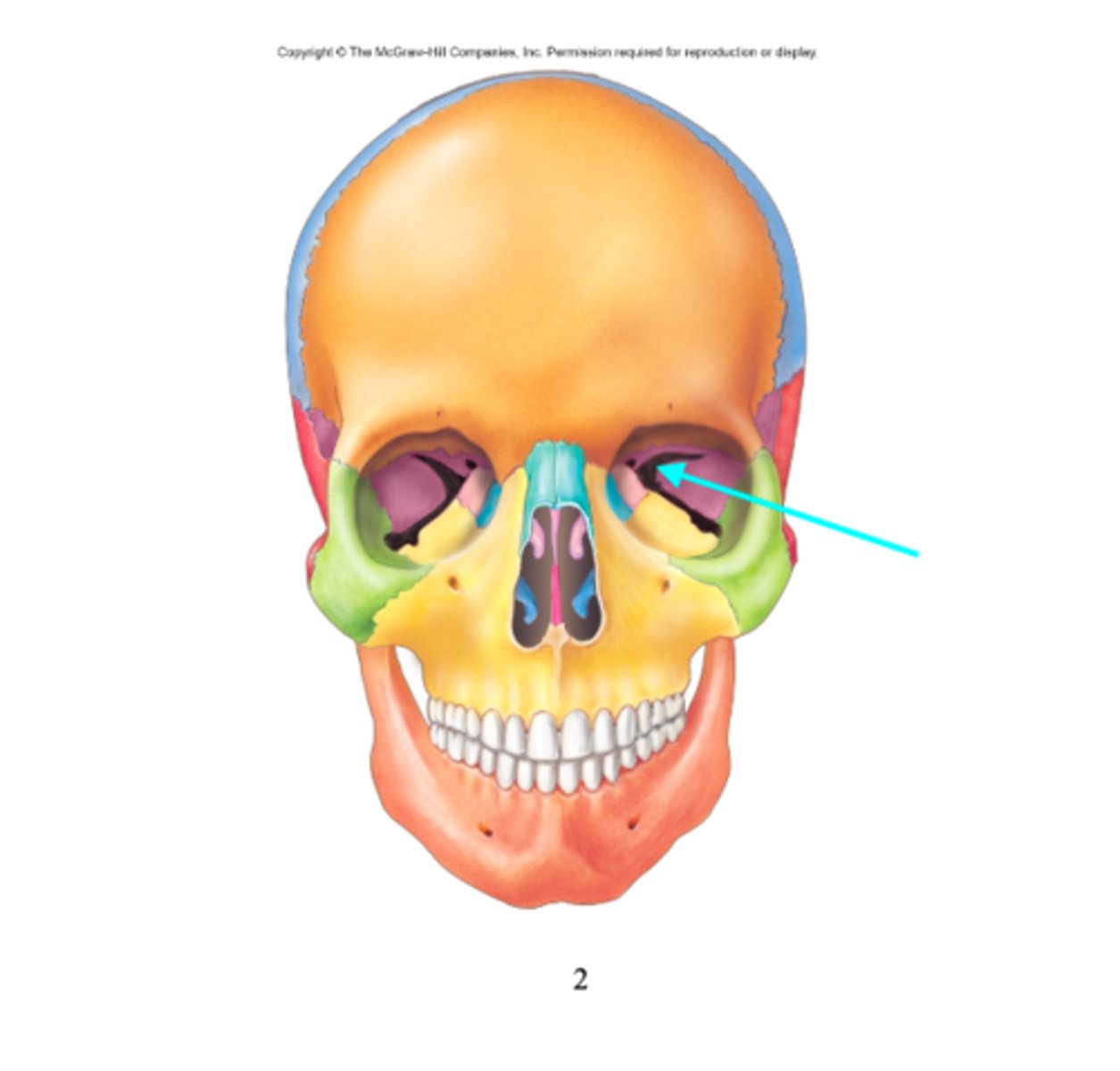
Supraorbital foramen
What feature is the blue arrow pointing at?
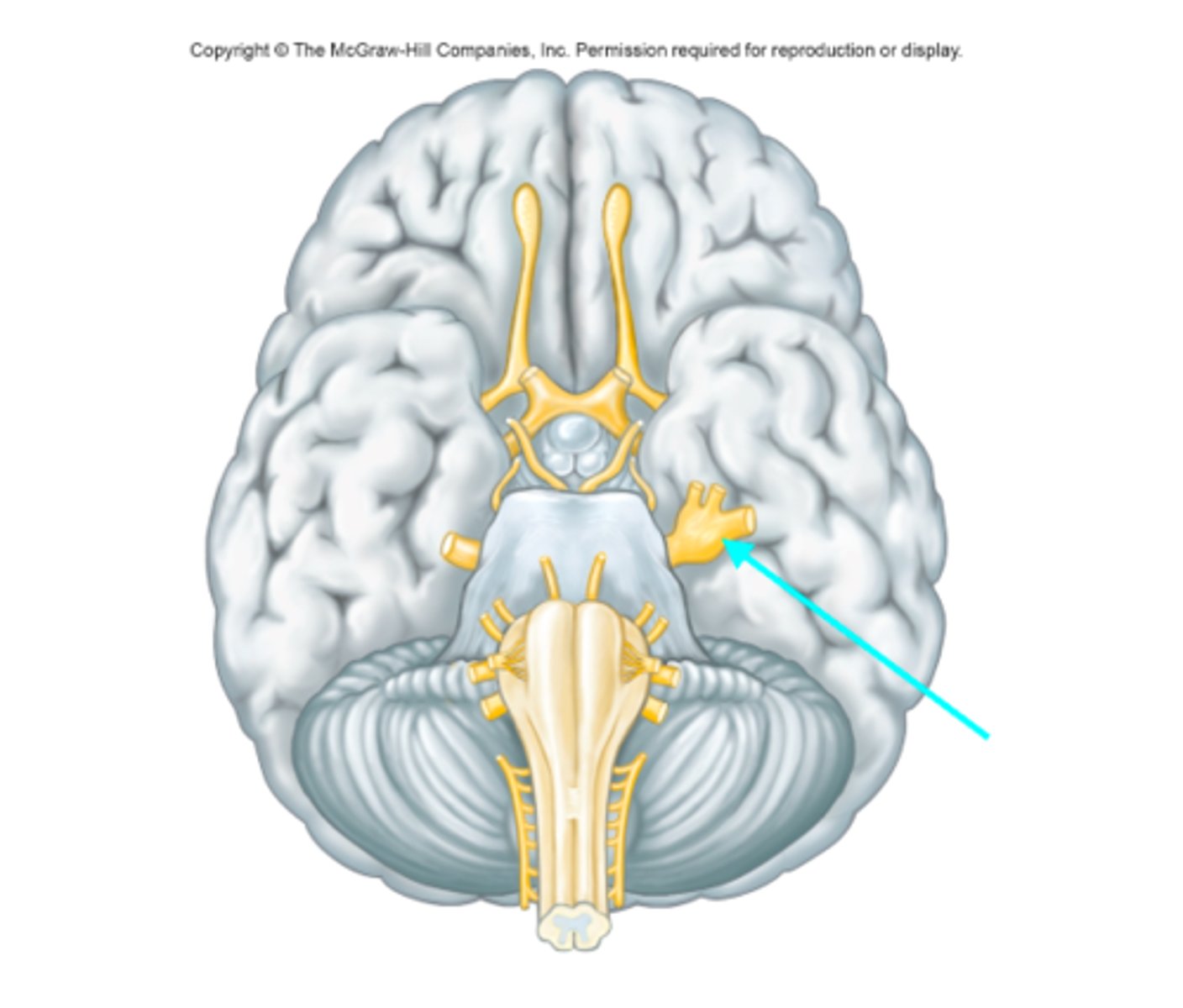
Trigeminal nerve (Cranial nerve V)
What cranial nerve is the blue arrow pointing at?
Ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular
What are the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve?
Ophthalmic division
Which division of the trigeminal nerve is associated with general senses from the surface of the eye, tear glands, forehead, and upper eyelid?
Maxillary division
Which division of the trigeminal nerve is associated with the general senses from the upper teeth, upper gum, and upper lip, and cheeks?
Mandibular division
Which division of the trigeminal nerve is associated with the general senses from the skin of the jaw, lower teeth, lower gums, lower lip, and the tongue?
Supraorbital foramen and superior orbital fissure
What two openings in the skull does the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve pass through?
Infraorbital foramen and inferior orbital fissure
What two openings in the skull does the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve pass through?
Mandibular foramen and mental foramen
What two openings in the skull does the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve pass through?
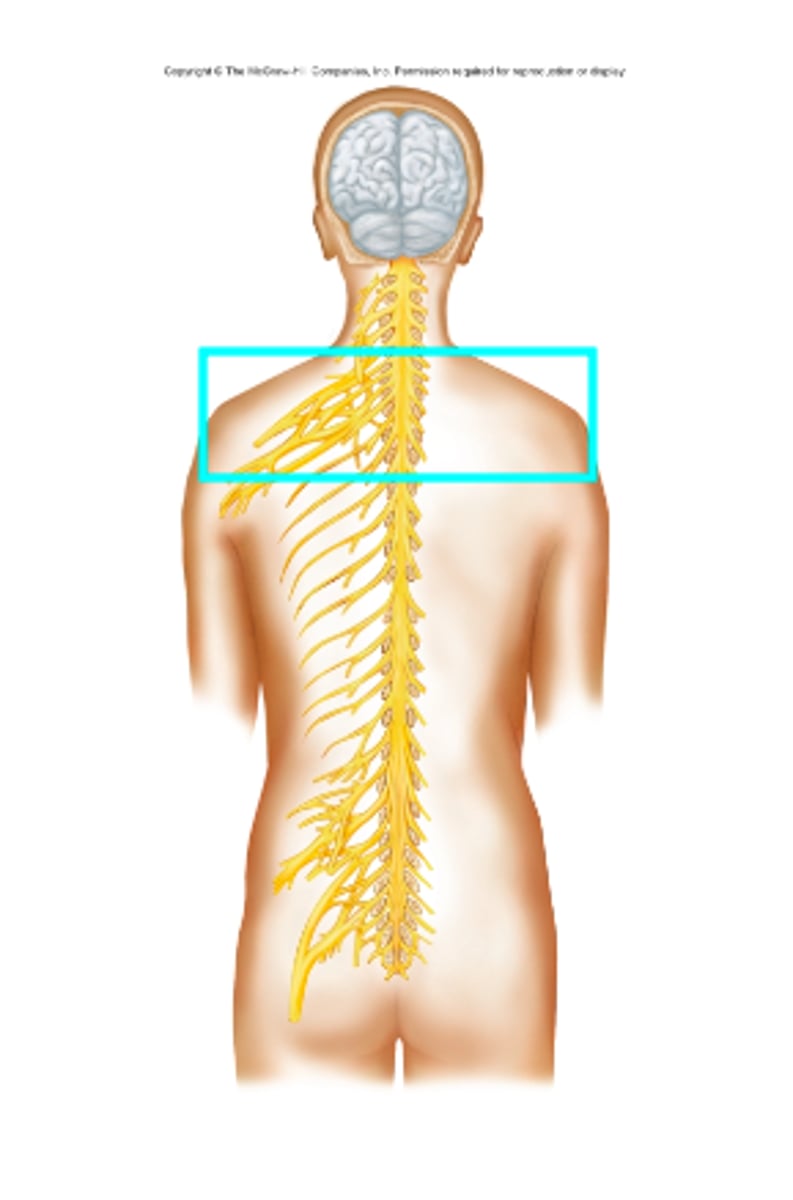
Cervical plexus
What nerve plexus is the blue box surrounding?
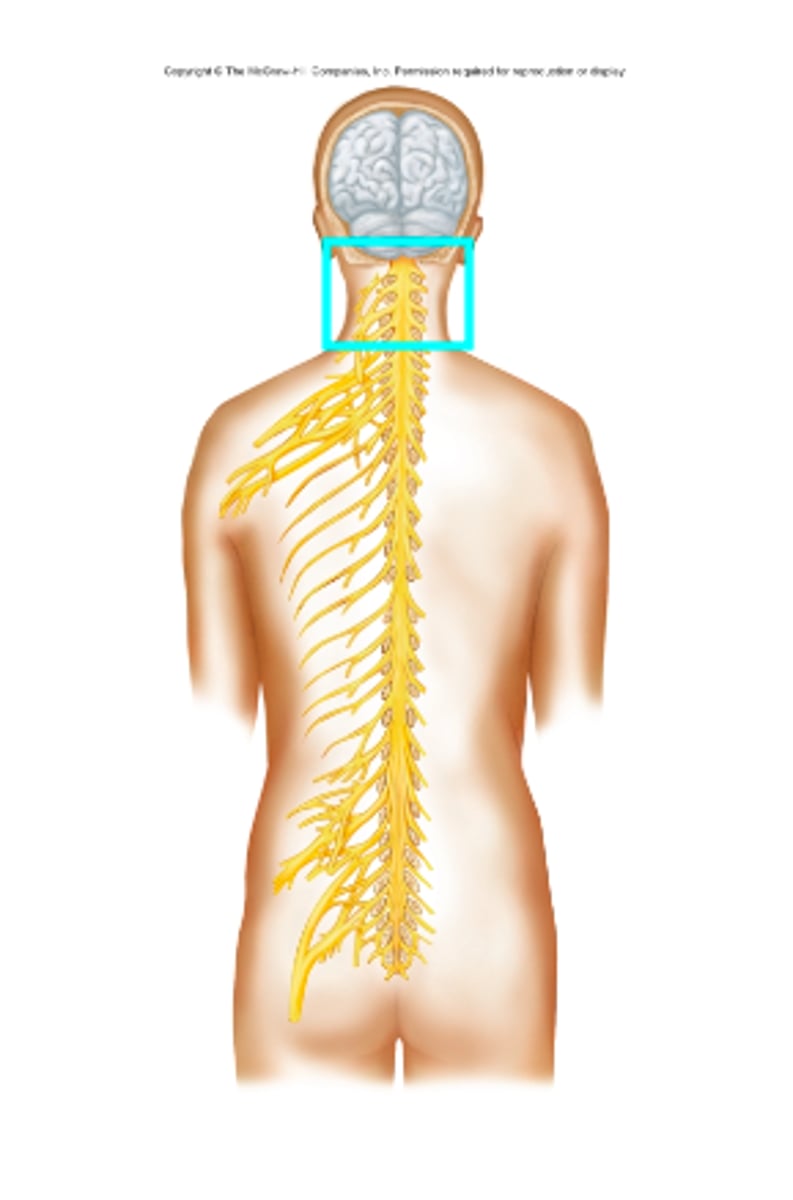
Brachial plexus
What nerve plexus is the blue box surrounding?
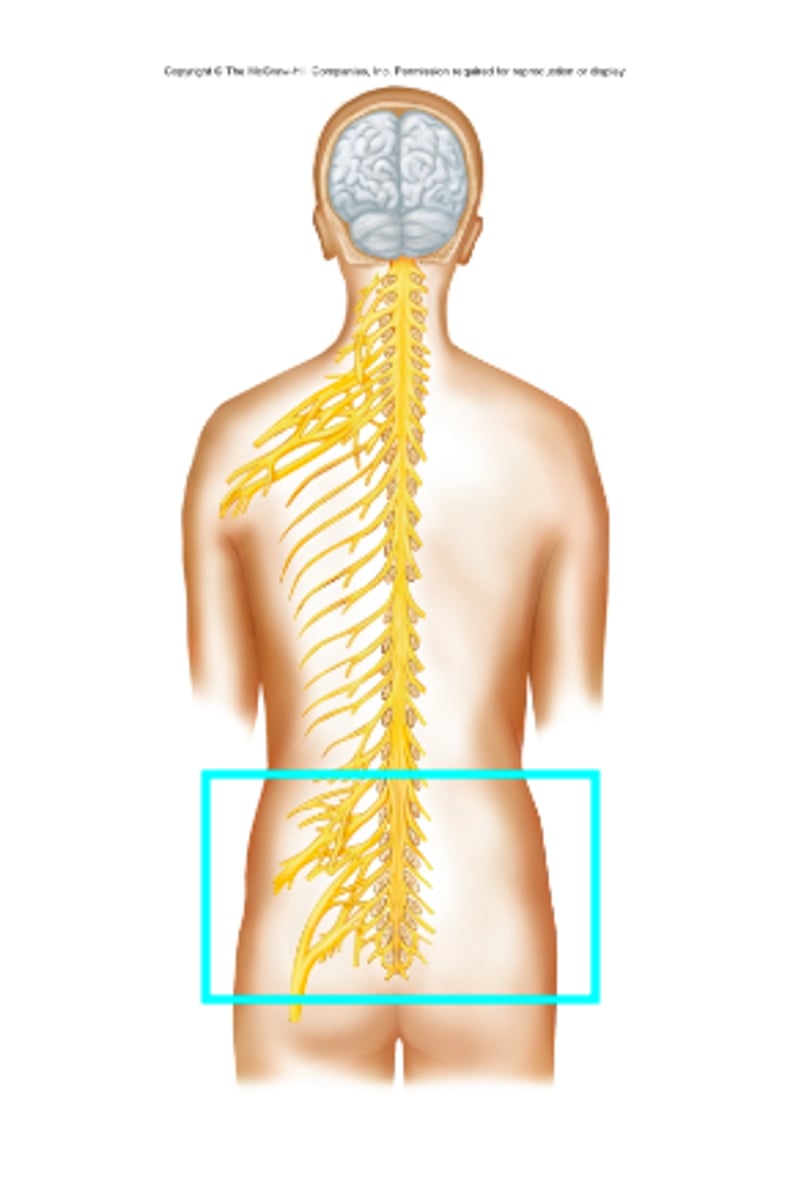
Lumbosacral plexus
What nerve plexus is the blue box surrounding?
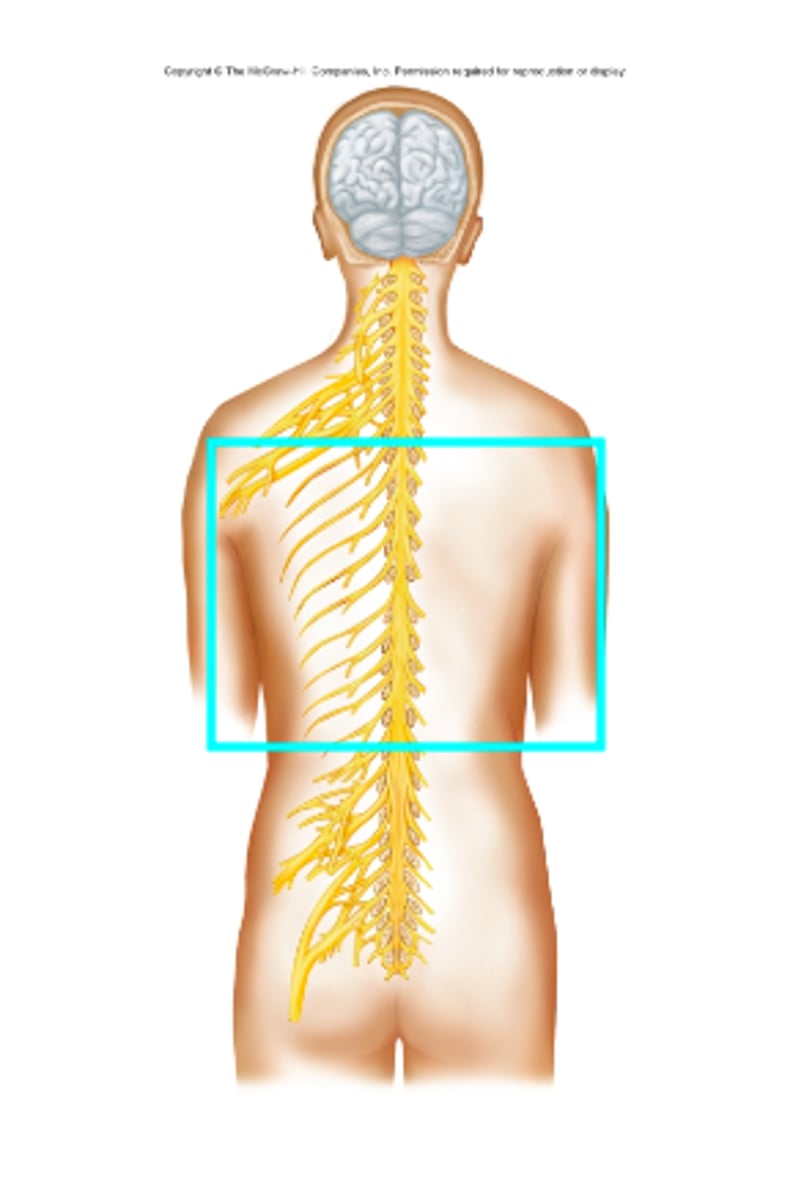
intercostal (thoracic) nerves
What nerves is the blue box surrounding?
Cervical plexus
Which nerve plexus' fibers supply muscles and skin of the neck?
Brachial plexus
Which nerve plexus' fibers supply the shoulders (neck to armpit), muscles of the arms and forearms, and skin of the hands?
Lumbosacral plexus
Which nerve plexus' fibers are associated with the lower abdominal wall, external genitalia, buttocks, thighs, legs, and feet?
Intercostal nerves
Which nerves supply motor impulses to the intercostal muscles and the upper abdominal wall muscles as well as receive sensory impulses from the skin of the thorax and abdomen?
Tactile (Meissner's) corpuscle
Which sensory structure is the blue arrow pointing at?
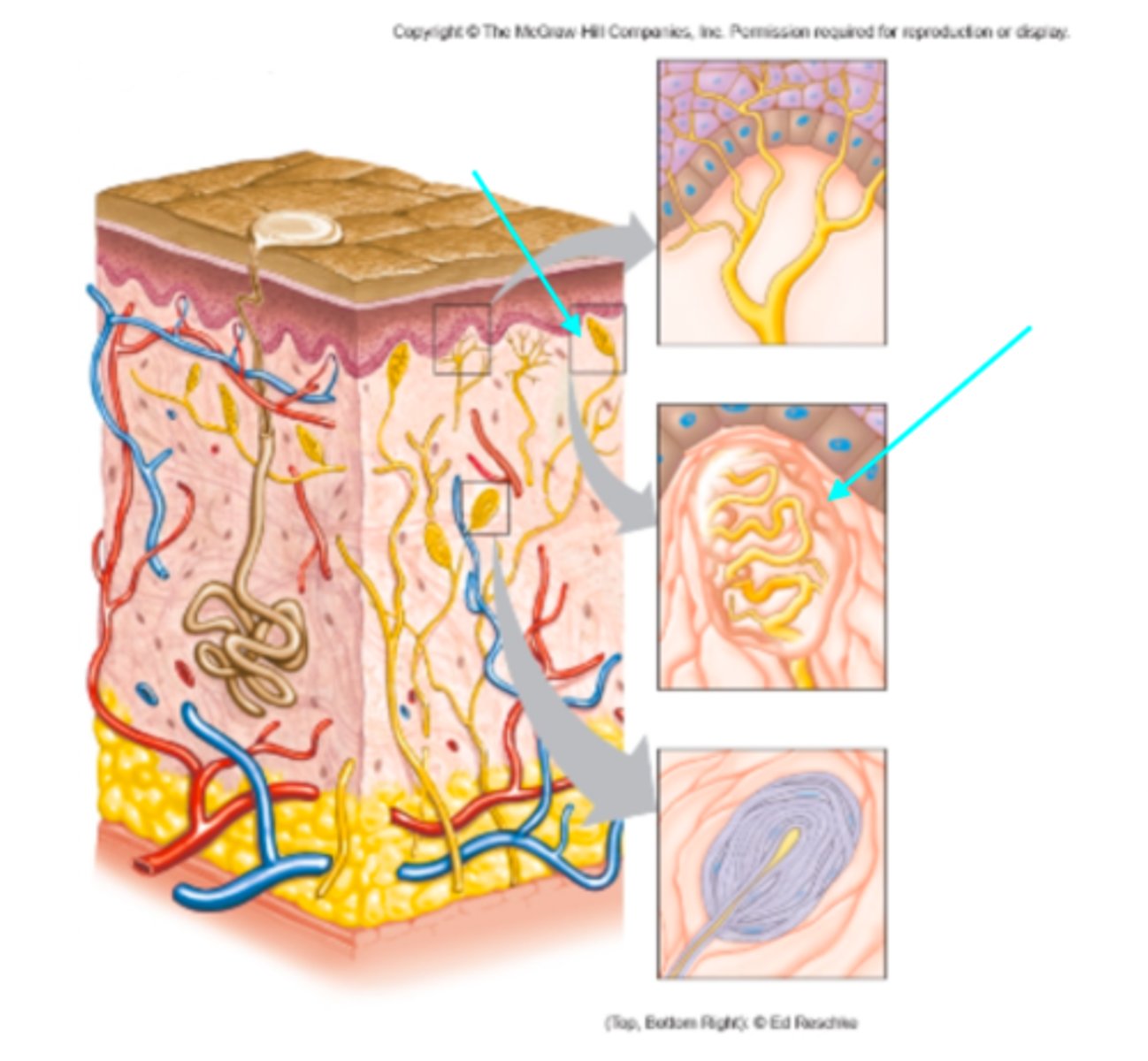
Lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscle
Which sensory structure is the blue arrow pointing at?
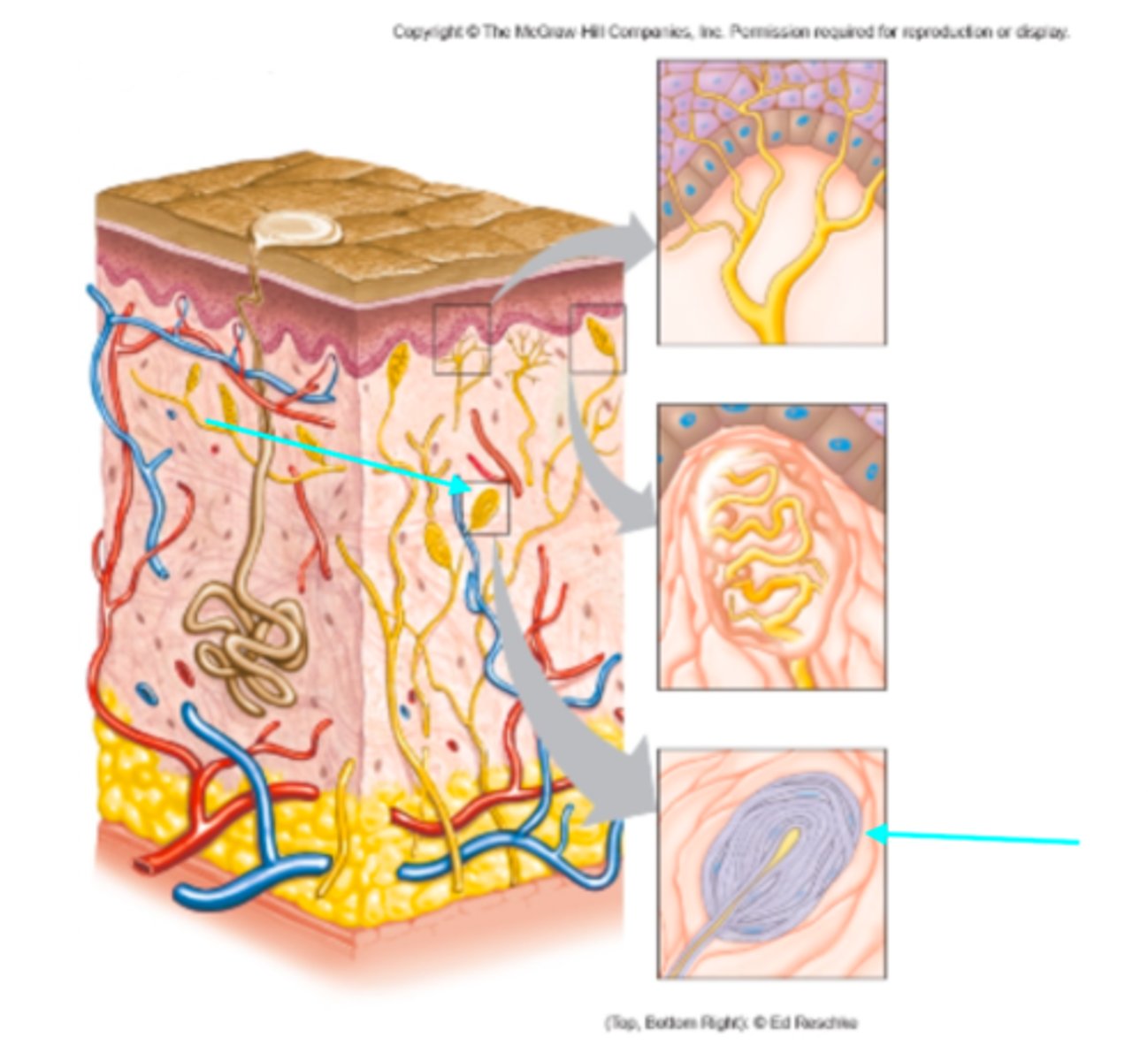
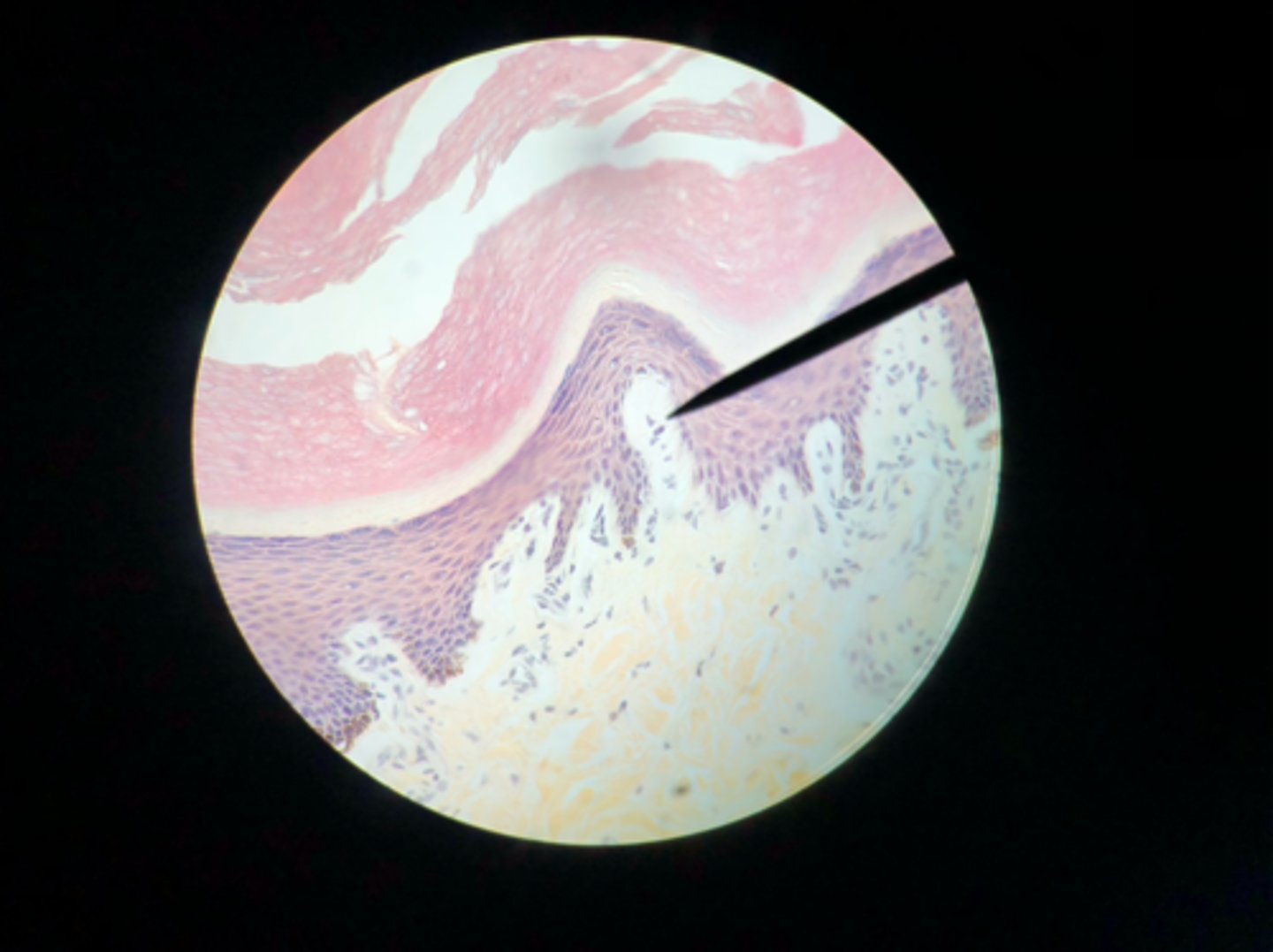
Tactile corpuscle
What sensory structure is a receptor for touch?
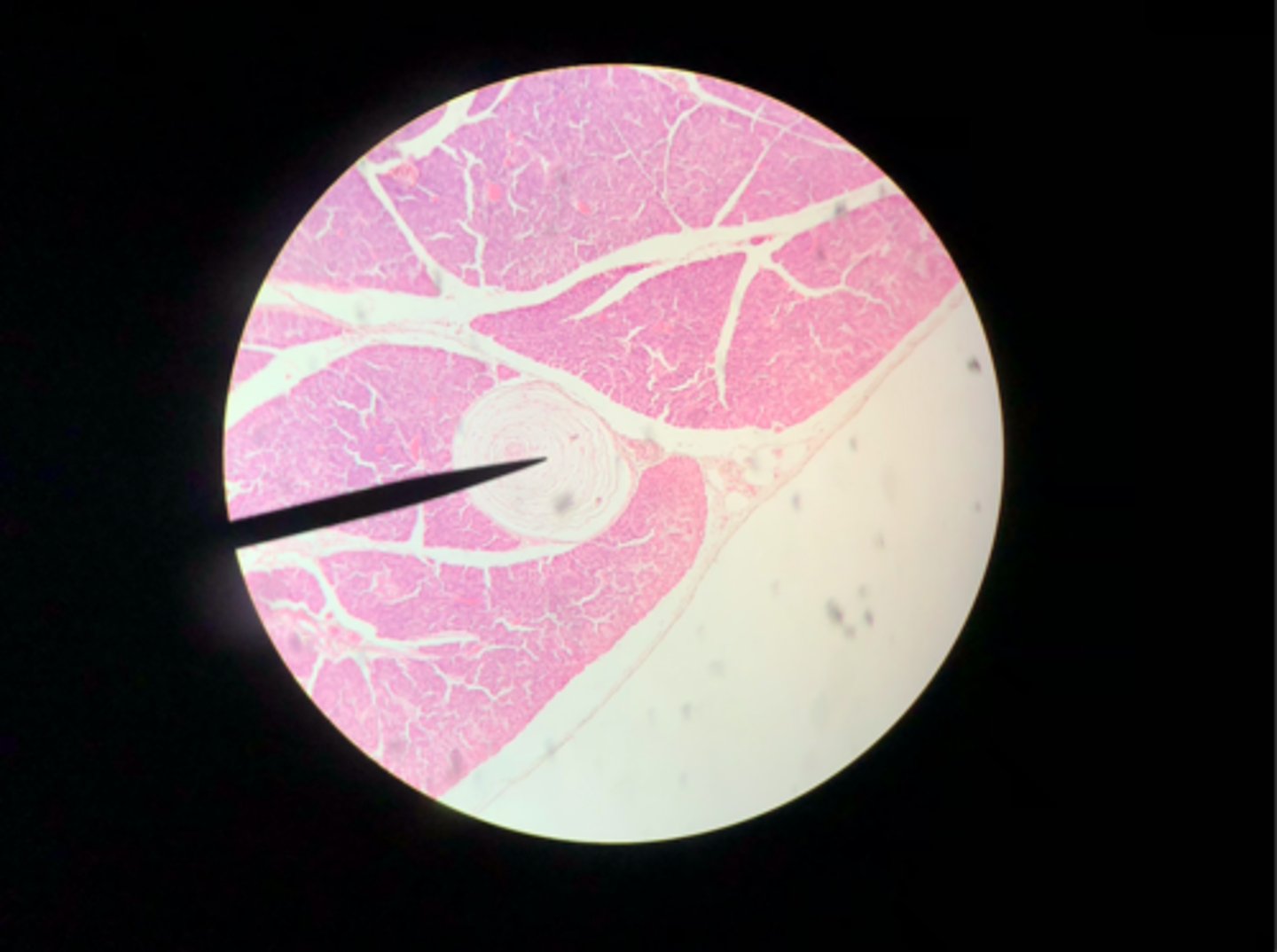
Lamellated corpuscle
What sensory structure is a receptor for pressure?
Tactile (Meissner's) corpuscle
What sensory structure is the pointer placed on?
Lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscle
What sensory structure is the pointer placed on?
The distribution of touch receptors across the body is not uniform, and it varies considerably. We noticed that there are more touch receptors in areas that deal with fine touch such as the finger tips compared to the upper arm region which does not have much use for numerous touch receptors.
The distribution of receptors is more concentrated in areas that need to identify smaller signals. These receptors are closer together and can both be stimulated. In areas where we do not need to detect fine signals of touch, receptors are more spread out. If receptors are closer together, it is easier to identify two separate touches. It is difficult to differentiate between a single touch and two separate touches if the receptors are further away.
Describe and compare the distribution of touch receptors on various regions of the body, and how this distribution affects our ability to identify a single touch from two separate (simultaneous) touches
Sensory adaptation
This is the decreased action potential generation as a result of continuous stimulation of the receptor. The action potential generation may cease completely.
Touch receptors, tactile corpuscles, that are continuously stimulated decrease action potential generation. This causes you to not "feel" or "feel" less of those senses of touch because they are not leading to stimulation as often.
Discuss sensory adaptation as it applies to the sense of touch
With our data, we saw that the forearm area was more sensitive to both warm and cold senses compared to the lower leg. This shows that the distribution of thermoreceptors included a higher concentration on the forearm compared to the lower leg.
Regarding temperature, we tested the locations of the forearm and the anterior lower leg. Describe and compare the distribution of warm and cold receptors on various regions of the body.
Sometimes, we would feel the probe touch our skin without a sensation of temperature. This is because thermoreceptors had adapted, so only the tactile corpuscles were responding. The thermoreceptors would undergo continuous stimulation, causing a decrease in action potential generation. This led to a lack of feeling of temperature.
Discuss sensory adaptation as it applies to thermoreceptors.
The body surface has receptors to detect pain caused more by tissue damage. Viscera, however, respond more to displacement and the moving around of organs. These are two different types of pain.
Explain why the sense of pain varies between the body surface and viscera
Referred pain is the rejection error when pain in internal organs is projected elsewhere, often on the surface of the body. This is due to the sharing of a common nerve pathway (between organs and the skin) as it travels to the CNS, carrying impulses from both. Pain located at a specific position in the body is transferred through a shared pathway with other neurons.
Describe the phenomenon of referred pain
Enkephalins and endorphins act at the two synapses where moderation of signals in the CNS is possible. Both of these chemicals help reduce the transmission of pain signals by decreasing the number of impulses that leave the synapse.
Describe how pain impulses can be affected by enkephalins and endorphins
Ethmoid bone
What bone is this?
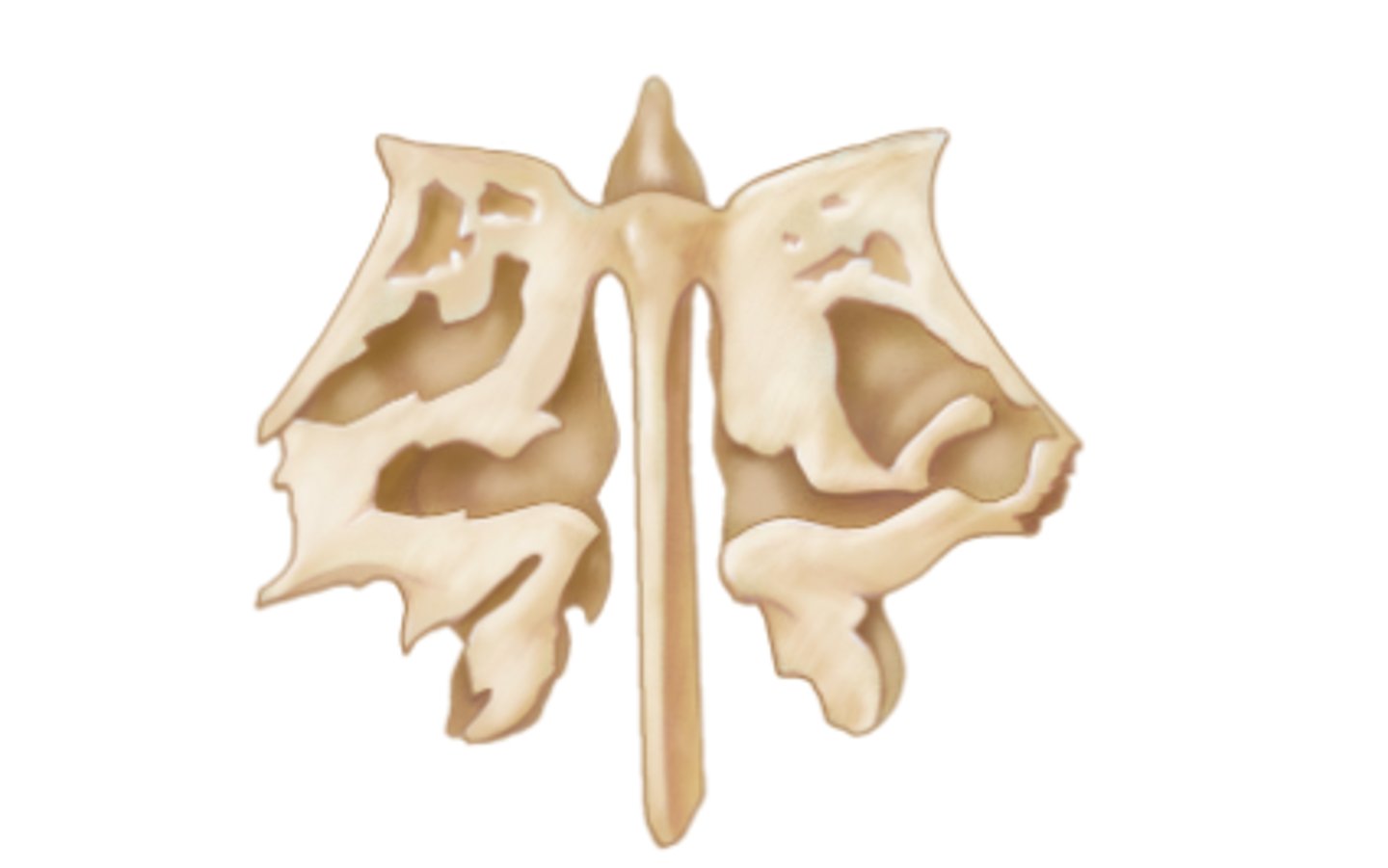
The ethmoid bone has cribriform plates which contain numerous fibers of the olfactory nerve that allow the nasal cavity to detect smells.
What is the ethmoid bone's relationship to the olfactory nerve?
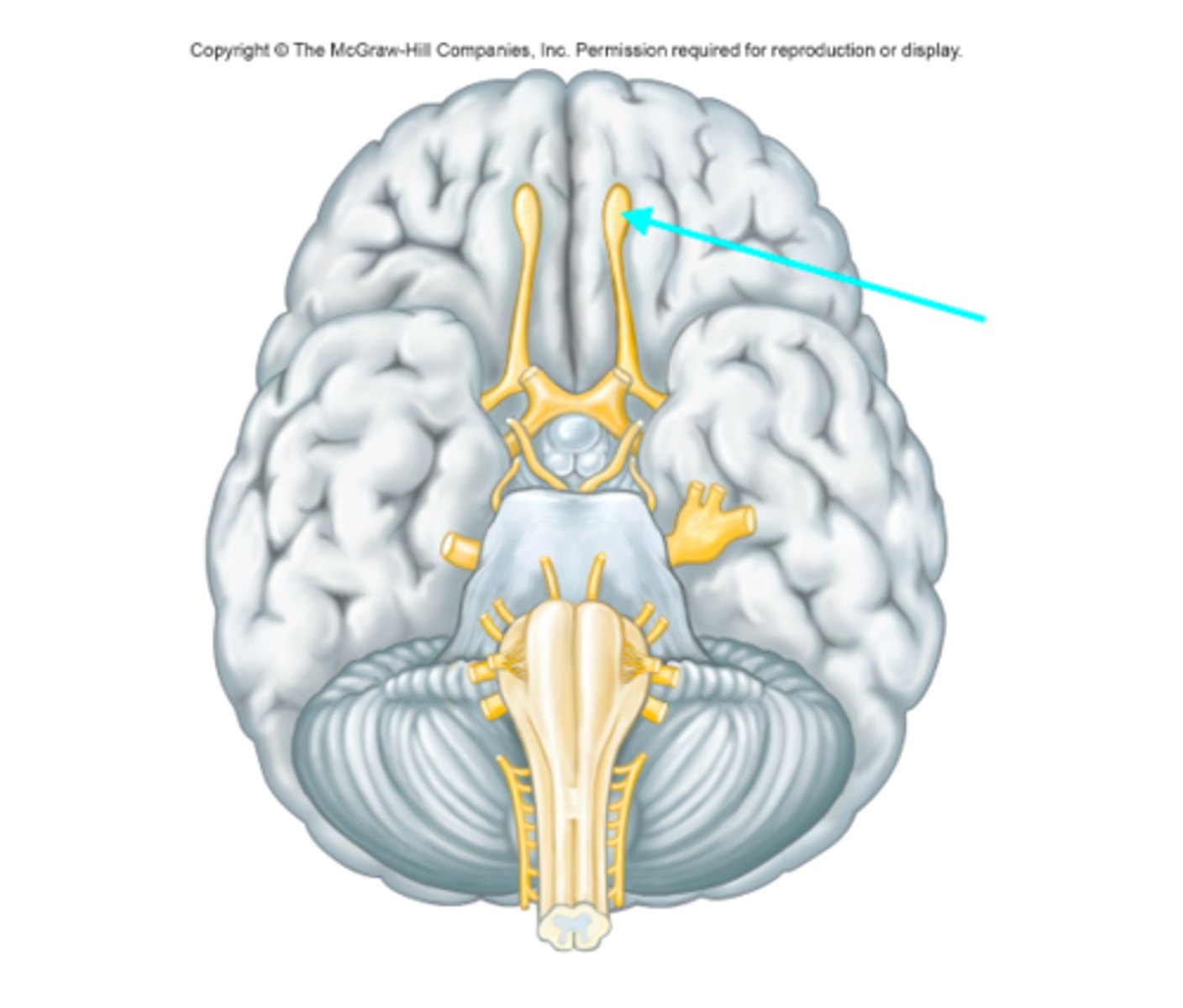
Olfactory nerve (Cranial nerve I)
What cranial nerve is the blue arrow pointing at?
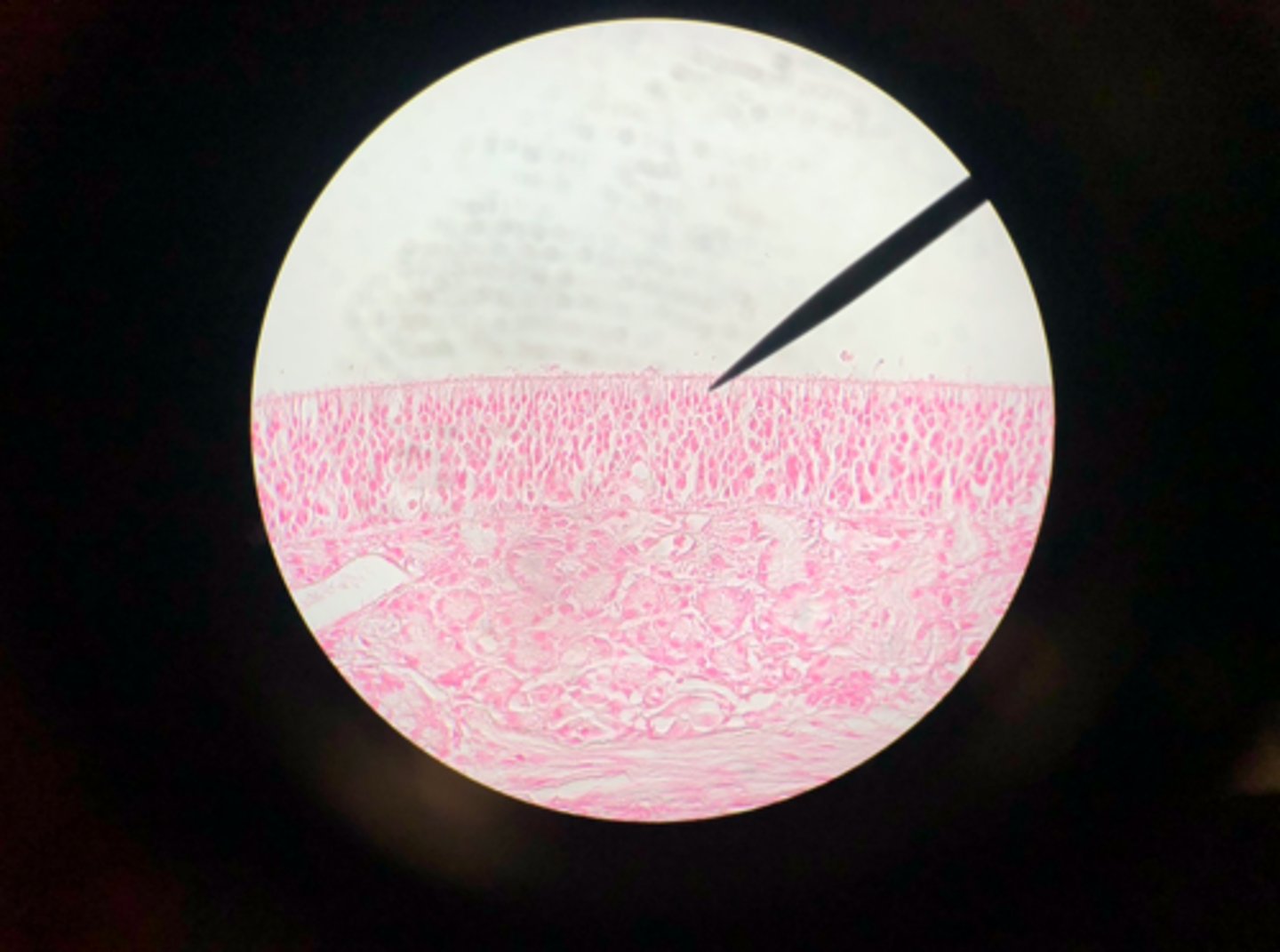
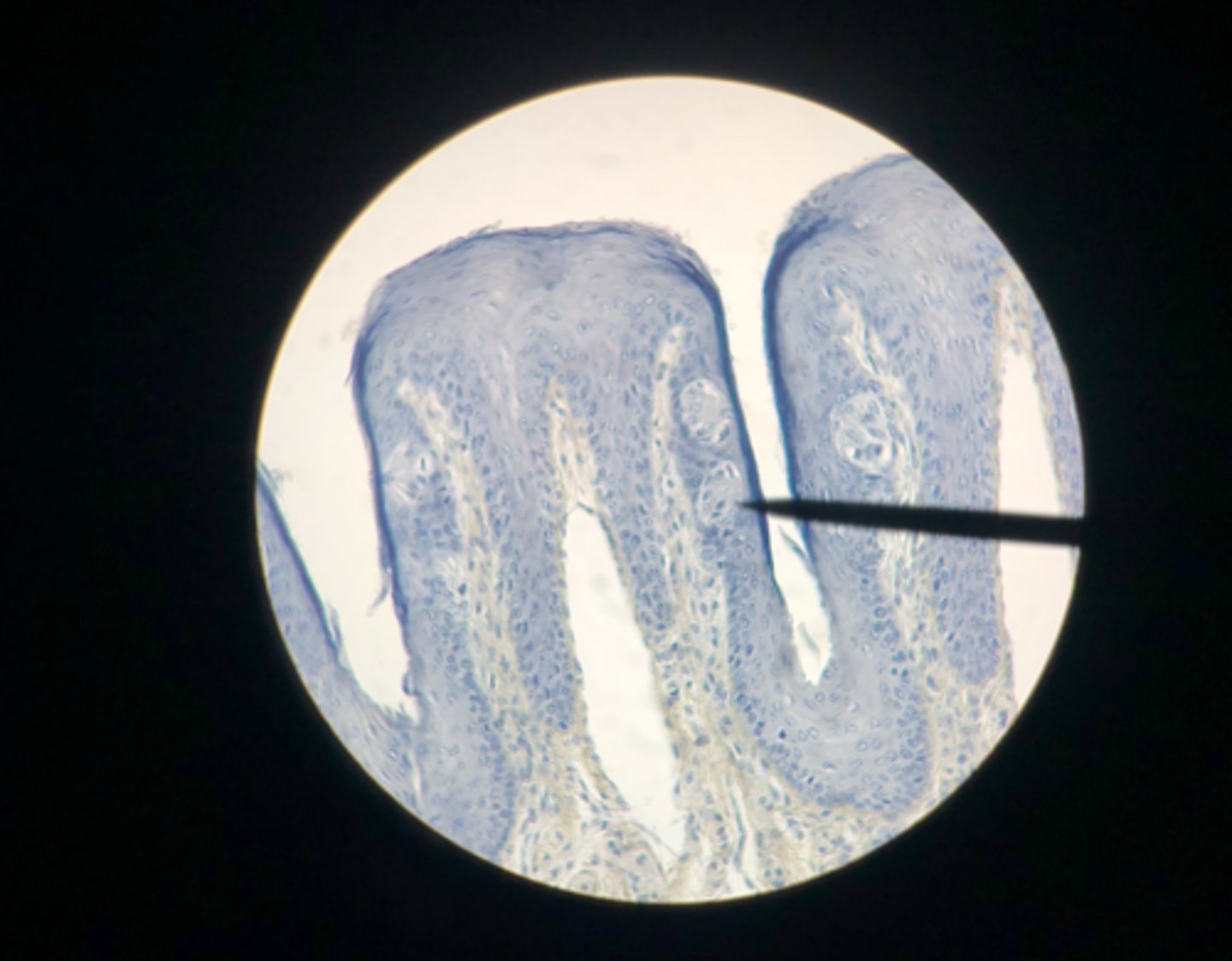
Olfactory epithelium
What tissue is depicted on the microscope slide?
If a specific sense of smell continuously stimulates the nerve fibers responsible for its detection, the amount of action potentials generated will decrease. This continuous stimulation of the receptor may completely cease generation of the potential
Discuss sensory adaptations as it applies to the sense of smell
-osmia
Root word for the sense of smell
dys-
Prefix for distorted
a(n)-
Prefix for absence
hypo-
Prefix for diminished
-geusia
Root word for the sense of taste
hyper-
Prefix for heightened
The diminished sense of smell
What is hyposmia?
The absence of the sense of smell
What is anosmia?
The heightened sense of taste
What is hypergeusia?
The distorted sense of taste
What is dysguesia?
They can be caused by the environment, such as chemicals, toxins, or medications. They can also be caused by the injury to the nerves themselves or the nerve pathways as a result of something like a head injury or stroke
What are possible causes for hyposmia, anosmia, hypergeusia, and dysgeusia?
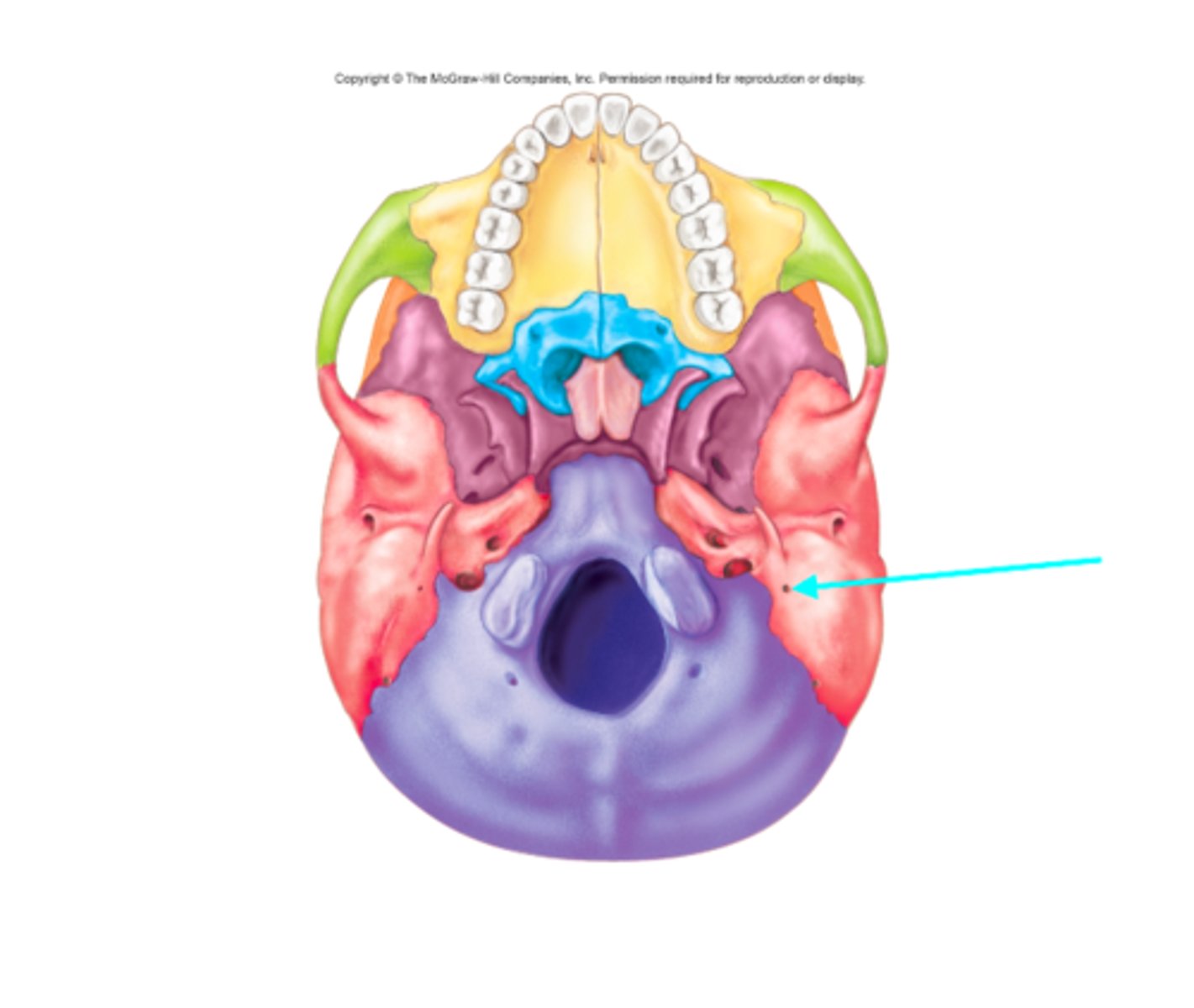
Stylomastoid foramen
What feature is the blue arrow pointing at?
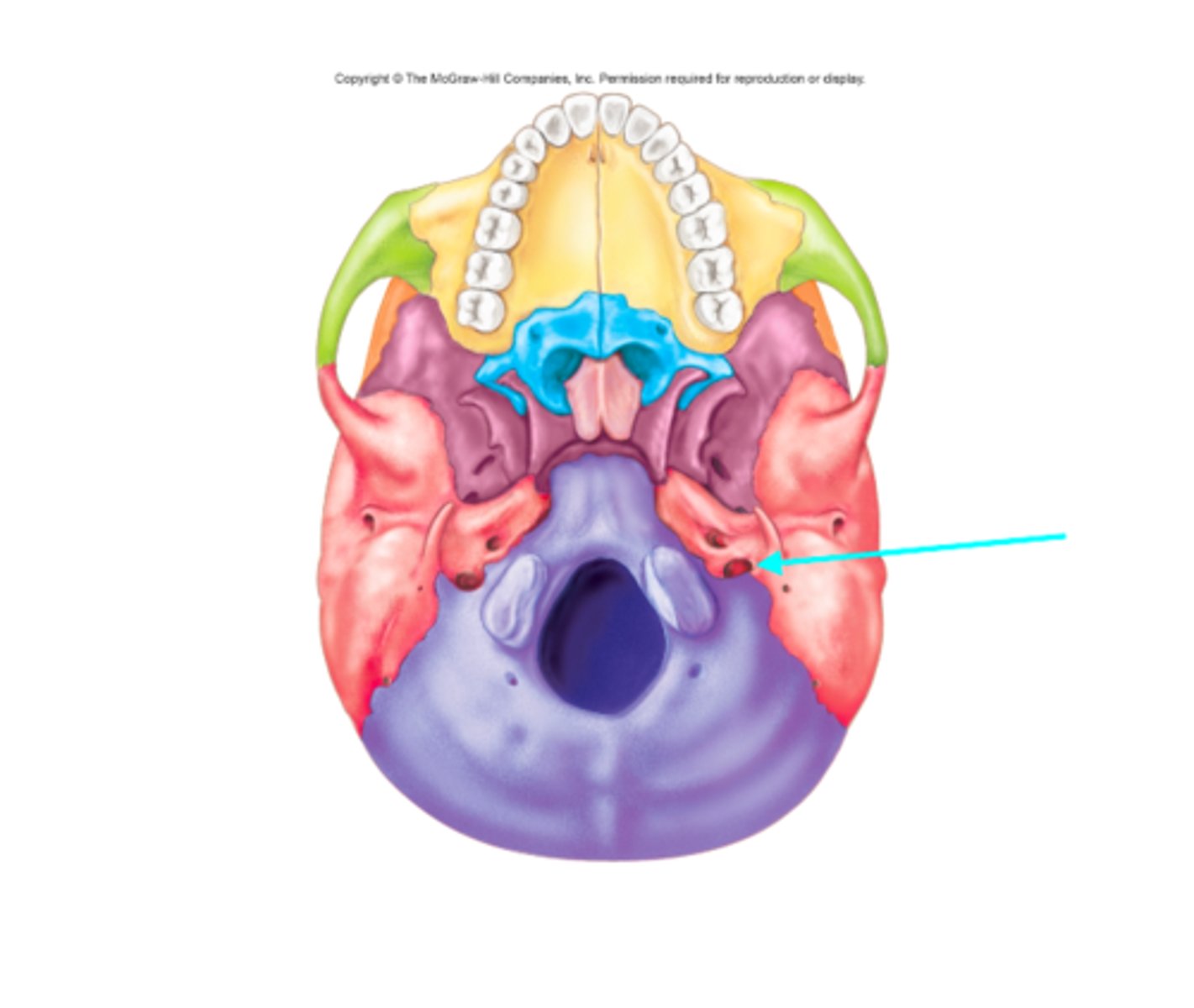
Jugular foramen
What feature is the blue arrow pointing at?
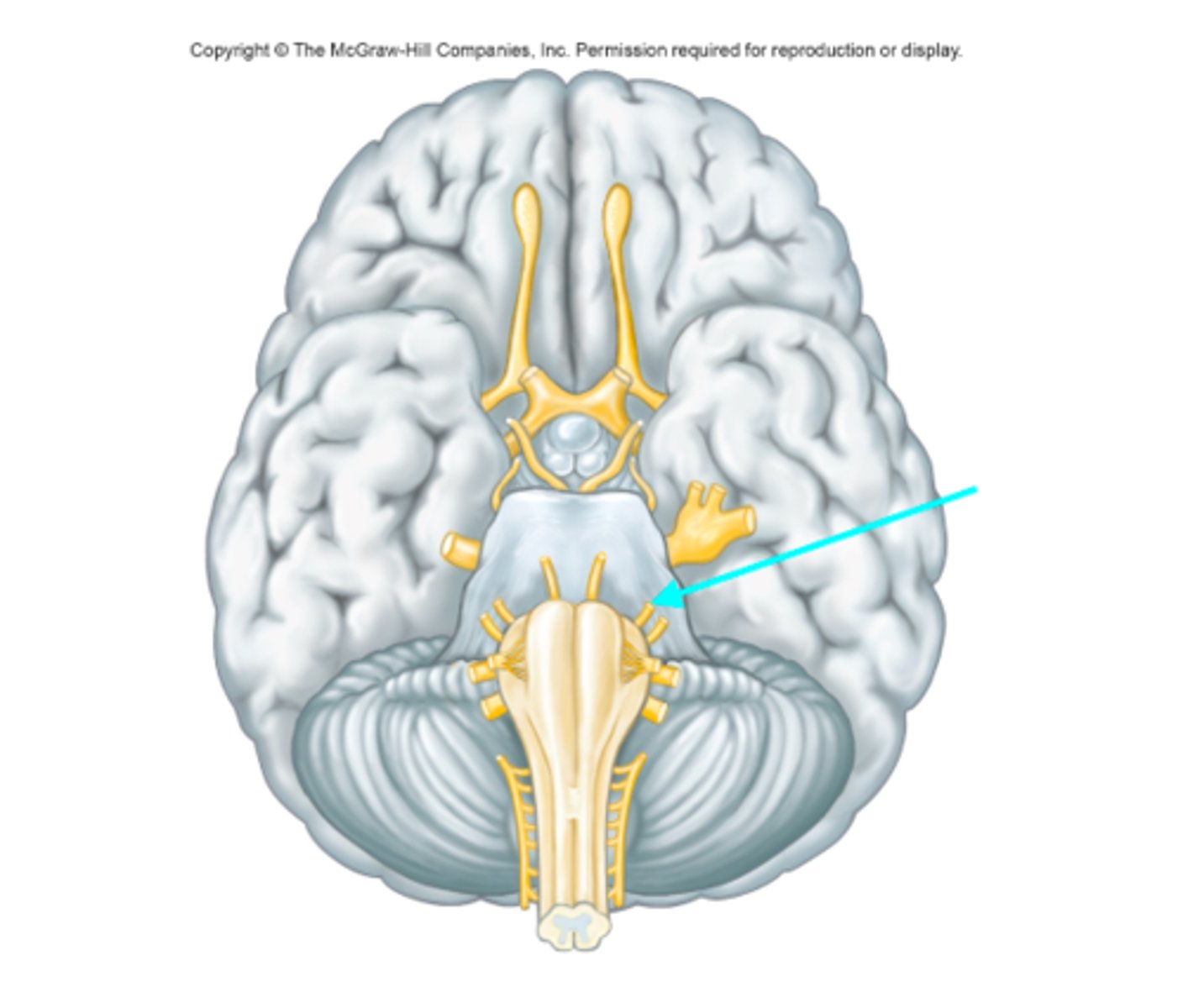
Facial nerve (Cranial nerve VII)
Which cranial nerve is the blue arrow pointing at?
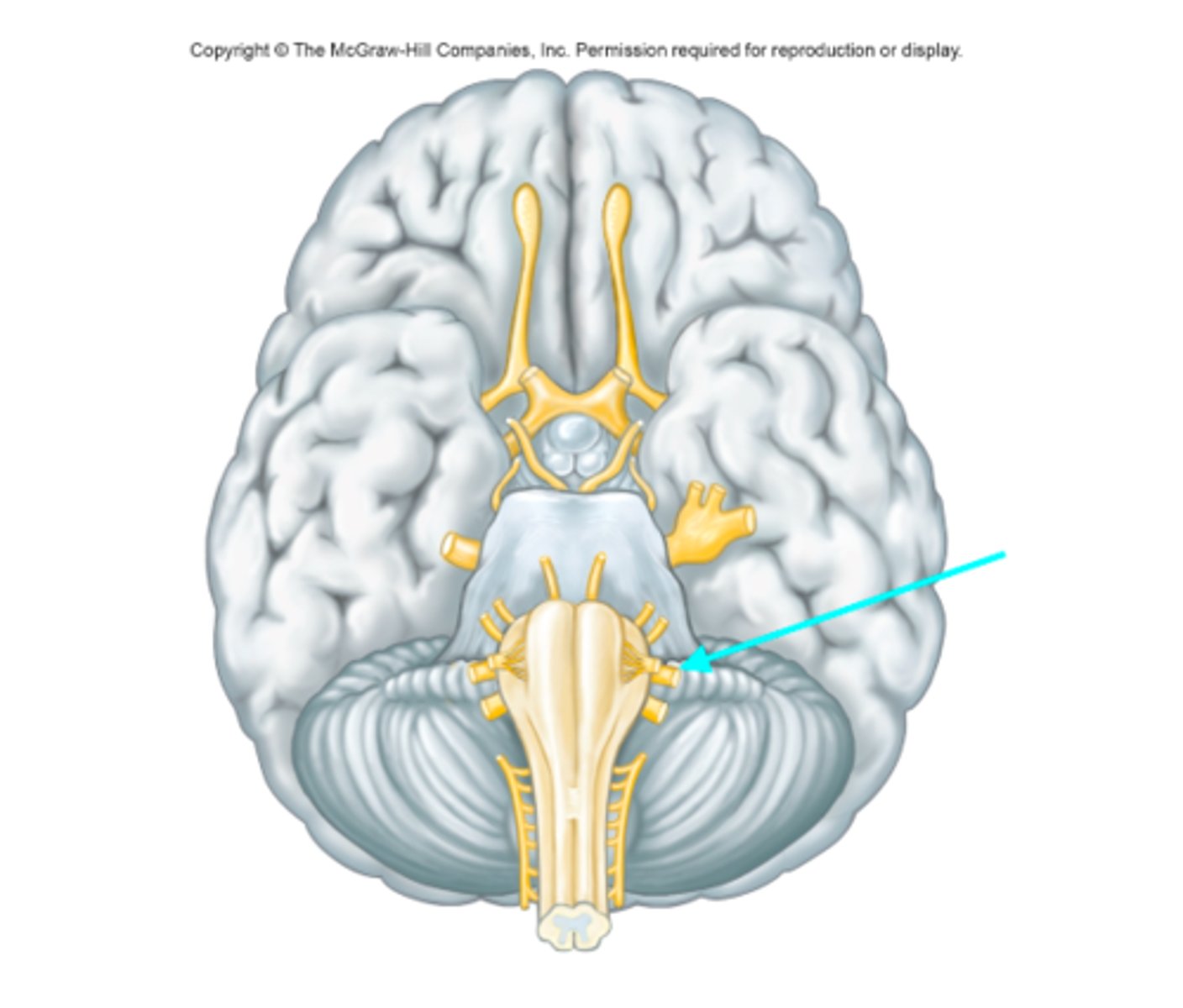
Glossopharyngeal nerve (Cranial nerve IX)
Which cranial nerve is the blue arrow pointing at?
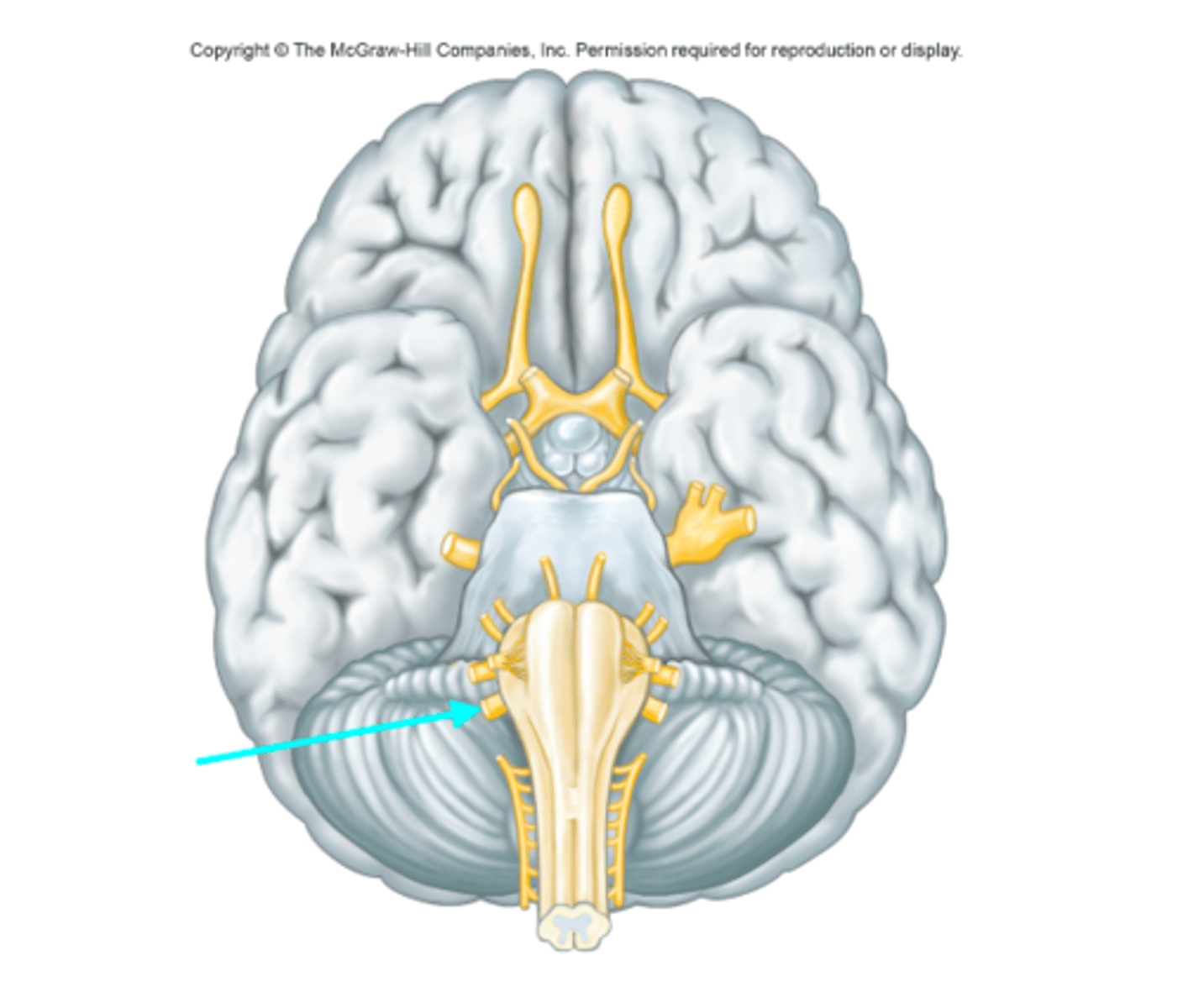
Vagus nerve (Cranial nerve X)
Which cranial nerve is the blue arrow pointing at?
Stylomastoid foramen
Which opening in the skull does the facial nerve (CN VII) pass through?
Jugular foramen
Which opening in the skull does the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) pass through?
Jugular foramen
Which opening in the skull does the vagus nerve (CN X) pass through?
Taste bud
What structure is the pointer placed on?
Tip of the tongue
- I felt it on the outer front edges of my tongue
Where are the sweet receptors located on the tongue? Sucrose was used in the experiment
They are widely distributed
- I felt it on the sides of my tongue
Where are the salt receptors located on the tongue? NaCl was used in the experiment
The margins of the tongue
- I felt it on the back and tip of my tongue
Where are the sour receptors located on the tongue? Acetic acid was used in the experiment
The back of the tongue
- I felt it on the back of my tongue
Where are the bitter receptors located on the tongue? Quinine sulfate was used in the experiment
Undetermined
- I felt it on the back of my tongue
Where are the umami receptors located on the tongue? Monosodium glutamate was used in the experiment
10%
What percent of the population cannot tase quinine sulfate?
Chemoreceptors
These receptors respond to a change in chemical concentration; smell and taste, internal organs
Mechanoreceptors
These receptors detect changes that deform the receptor; physical contact, muscle tension, blood pressure, lung inflation, balance, vibrations
Nocicpetors
These receptors respond to tissue damage, excess stimulation, pain
Thermoreceptors
These receptors respond to changes in temperature
Chemoreceptors
What general category of receptors are used in the sense of taste?
Chemoreceptors
What general category of receptors are used in the sense of smell?
Nociceptors
What general category of receptors are used in the sense of pain?
Thermoreceptors
What general category of receptors are used in the sense of temperature?
Mechanoreceptors
What general category of receptors are used in the sense of touch?
A person with synesthesia perceives one sense as originating from another sense (flowers smelling blue is an example). This is a genetic condition and the person is born with it, but they are not likely to be born with other disorders.
Describe how a person with synesthesia perceives his/her surroundings and explain the cause of synesthesia