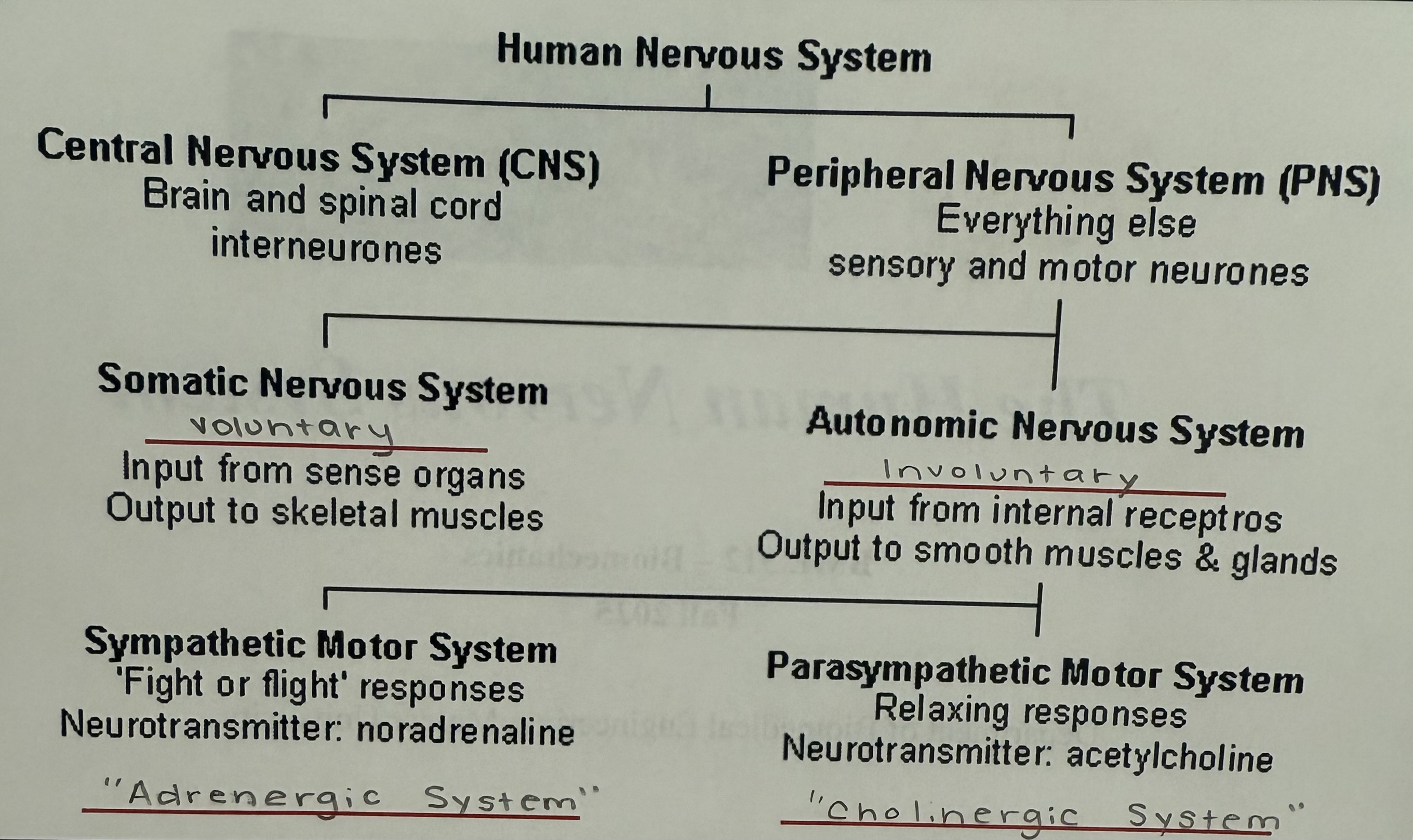
Human Nervous System - EXAM 3
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
consists of around …..
a hundred billion neurons (nerve cells)
parts of the nervous system
centeral nervous system (CNS)
peripheral nervous system
parts of the central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
the cranial of the central nervous system
part of the peripheral nervous system
spinal nerves
peripheral nervous system (PNS) info
connect the CNS system to the sense organs
like organs for vision, hearing, smell, ant etc.
responsible for the body funtion which are not under conscious control
heartbeat
digestive system
The PNS is divided into…?
sympathetic
parasympathic
What is unique about the part of the PNS?
the two systems are opposing actions and check on each other to provide a balance
The nervous system uses…?
electrical impulse (travel along the length of the neuron
How fast are these impulses?
travel at up to 250 miles per hour
unlike the endocrine system which takes many hours
human nervous system breakdown
main types neurons of peripheral nervous system
sensory
motor
sensory neurons
send message to the brain
motor neurons
deliver messages to glands and muscles
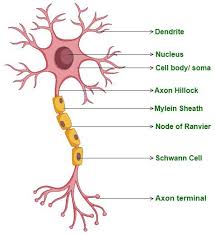
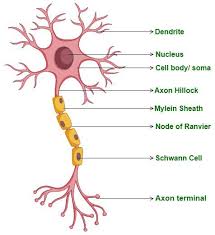
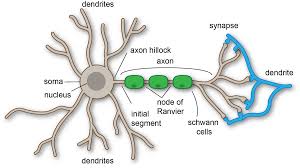
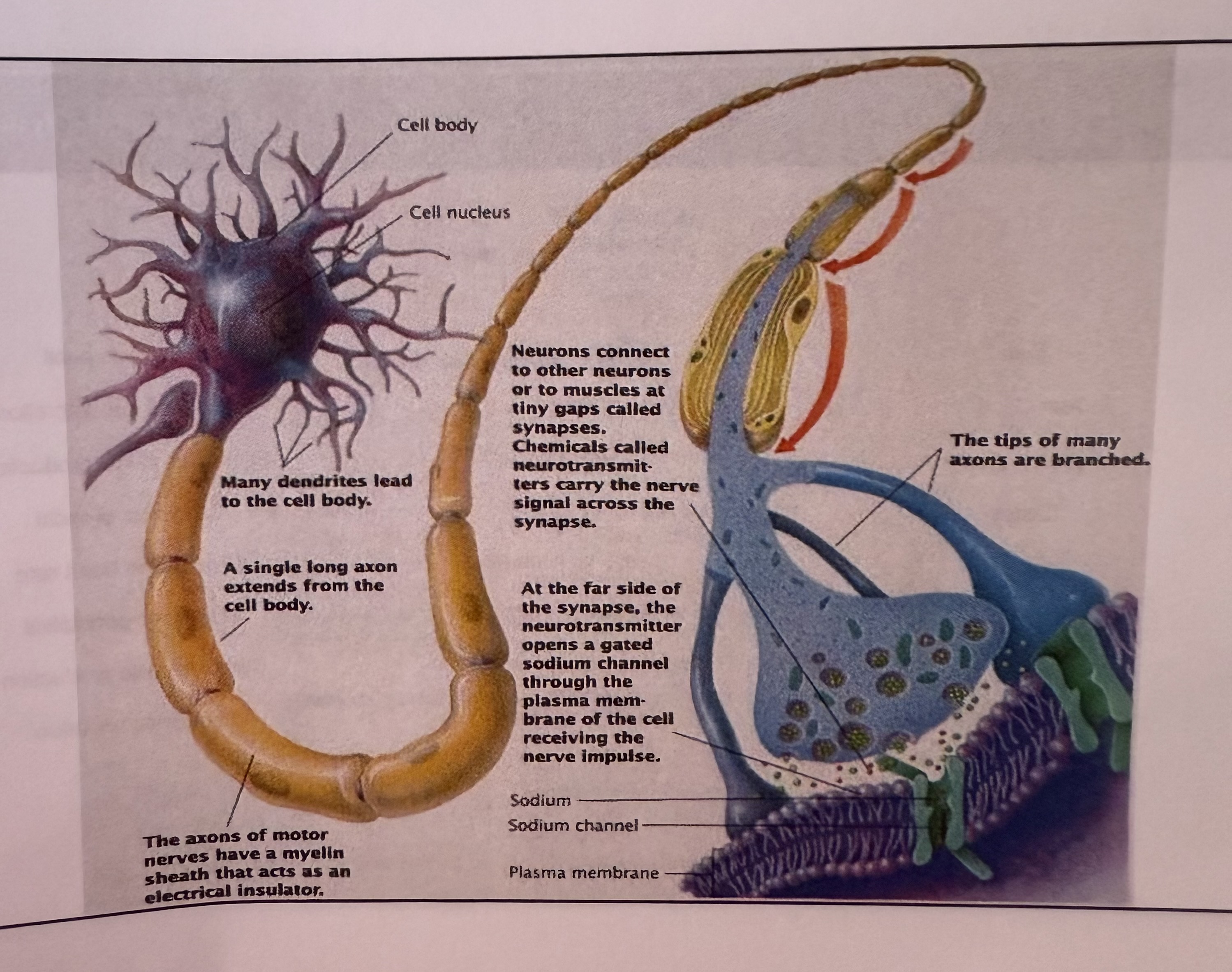
cell body
largest part of neuron
contains the nucleus and much of the cyptoplasm
most of the metabolic activity of the cell
including ATP generation
synthesis of protein
cytoplasm
area between the nucleus and the cell membrane
ATP
adenine triphosphate compound
stores energy
dendrites
short branch extensions spreading out from the cell body
receive stimulus
carry impulse from the environment or from other neuron and carry them toward the cell
action potentials
stimulus
axon
a long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body
each neuron as ONE
ends in axon terminals
axon terminals
a series of swellings
How many dendrites and axons on a neuron?
hundreds of dendrites
usually ONE axon
myelin sheath
a lipid layer that covers the axon of most neurons
insulates and speeds up transmission of action potentials through the axon
Schwann cells
produce the myelin
surround the axon
in PNS
nodes of ranvier
gaps/nodes in the myeline sheath along the length of the axon
functions of sensory neurons
afferent
carry impulses from the senses organs to the brain and spinal cord
receptors detect external or internal changes and send information to the CNS in the from of impulses
functions of motor neurons
efferent
carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles or glands
muscles and glands are 2 types of effectors
in response to impulses, muscles ________ and glands secrete
contract; secrete
functions of interneuron
connect sensory and motor neurons
carry impulses between them
entirely within the CNS
dendrites
nucleus
cell body
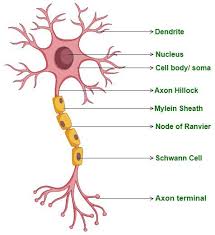
myelin sheath
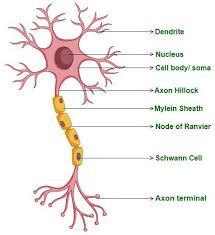
axon
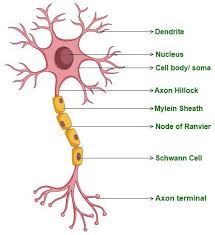
node of ranvier
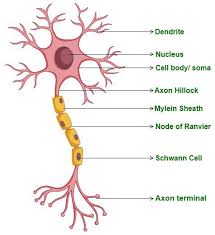
synapses
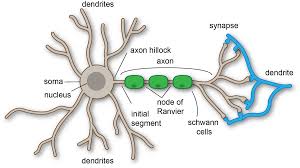
axon terminals
active transport
creates a concentration gradient across the cell membrane for sodium ions (Na+) and potassium ions (K+)
K+ ions are actively pumped INTO the cell while the Na+ ions are actively pumped OUT of the cell by the sodium-potassium pumps
K+ diffuses out of the cell rather slowly but nonetheless faster than Na+ can diffuse in
diffusion process
the unequal diffusion results in a net positive charge outside and excess of negative charge inside the membrane
a nerve cell has _____________ potential across its cell ____________ because of a _______ in the number of _______ and ________ charged ions on each side of the cell membrane
electrical
membrane
difference
positively
negatively
What is the electrical potential due to?
protein in the neurons knowen as sodium-postassium pumps that move sodium ions OUT of the cell and direct
What happens to the cytoplasm after active transport?
neurons contain more K+ ions and fewer Na+ ions than the surrounding medium
What does the cytoplasm also contain?
many negative charge protein molecules and ions
K+ ions can move out across the membrane _______ ______ than Na+ ions can enter in the cell
more easily
Do negatively charged protein molecules and ions move in and out of the cell?
NO; they do not move in and out of the cell
resting potential
charge difference of the leakage of positively charged ions out of the cell is a negative charge on the inside of the neuron’s cell membrane
the nueron is said to be ________ (_________ charged on the inside of the cell membrane and __________ charged on the outside). A nueron maintain this polarization until it is __________
polarized
negatively
positively
stimulated
stimulus
change in the environment that may be of sufficient strength to initiate an impulse
process diagram
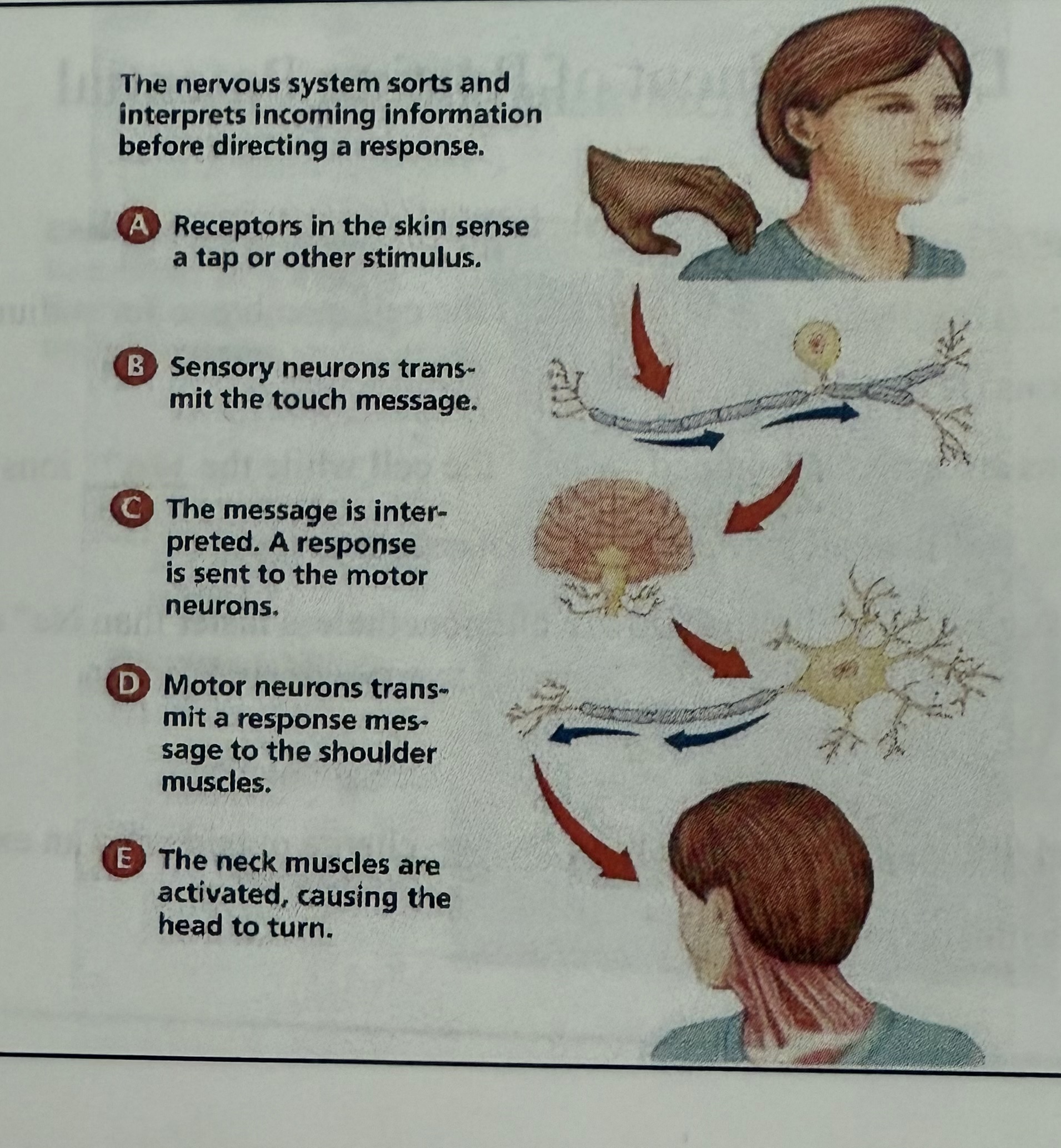
diagram 1
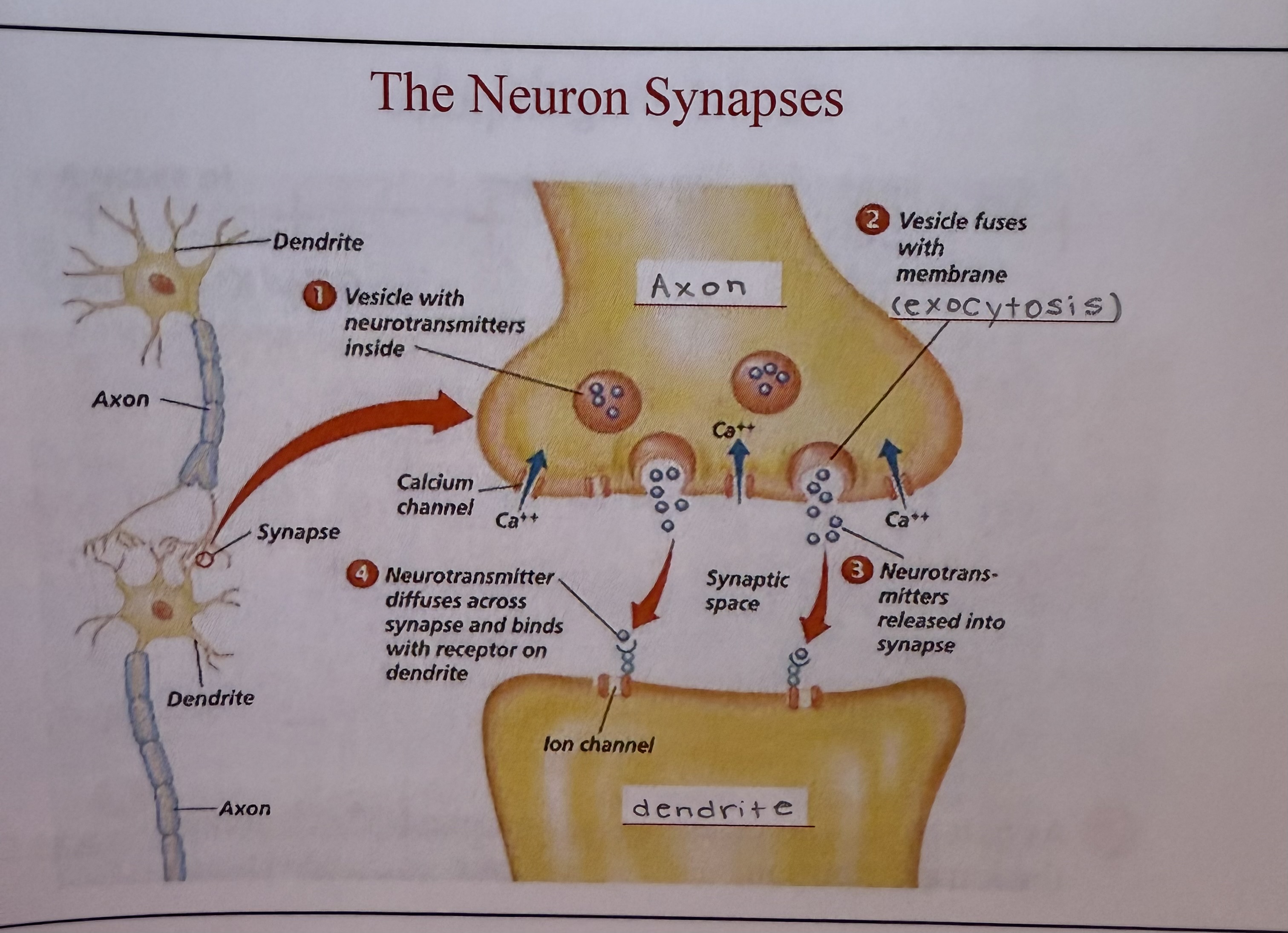
diagram 2
sympathetic motor system
adrenergic system
parasympathetic motor system
cholinergic system
synaptic space
gaps between the neurons
electrical signal has to jump across in order to continue
neurotransmitter
an electrical impulse is passed by a chemical signal called ____________