Low unemployment and low inflation rates
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Unemployment
The situation when people are willing and able to work and actively seeking employment but are unable to find work
Unemployment rate
Measures the percentage rate of the labour force that is unemployed. Calculated by the formula: (total unemployed/total labour force) x 100
The labour force
People of working age who are in employment (including self employment) plus those who are seeking work, that is, those who are available for work at current wage rates
Underemployment
Underutilization of the labour resources in the economy, which limits the economys productivity and efficiency
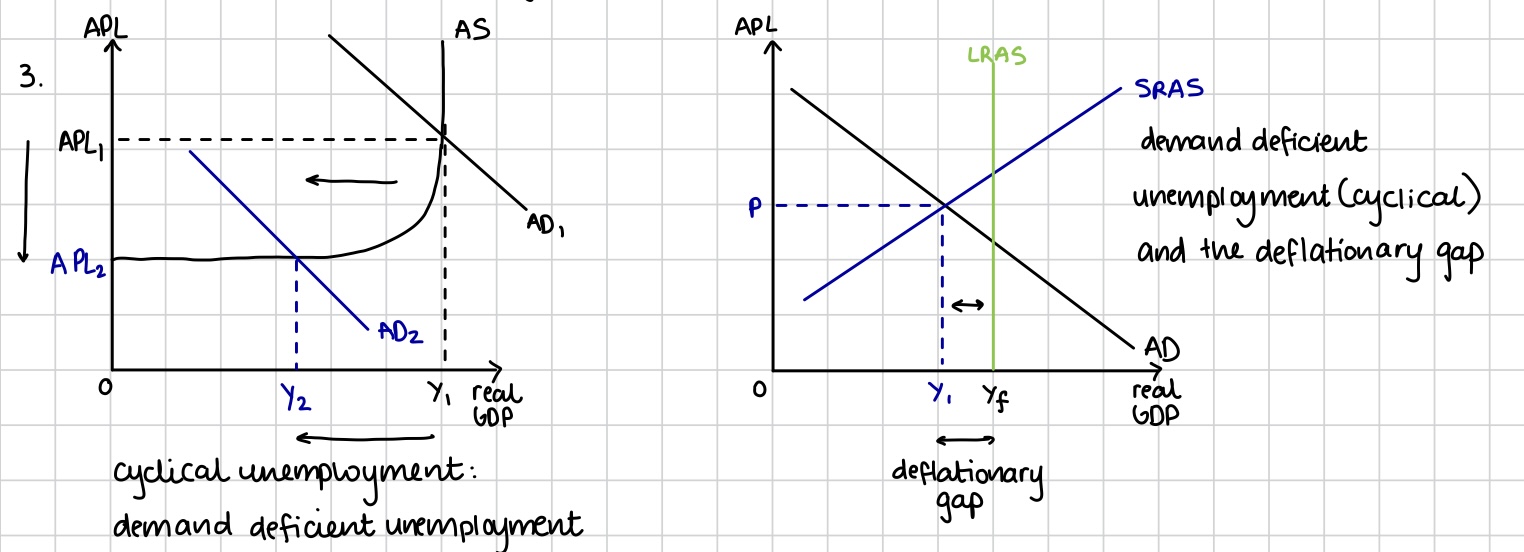
Cyclical unemployment or demand deficient underemployment
Unemployment caused by a lack of demand for goods and services in the economy, downturn in the business cycle. Shown using a AD-AS diagram that shows a deflationary gap
Structural employment
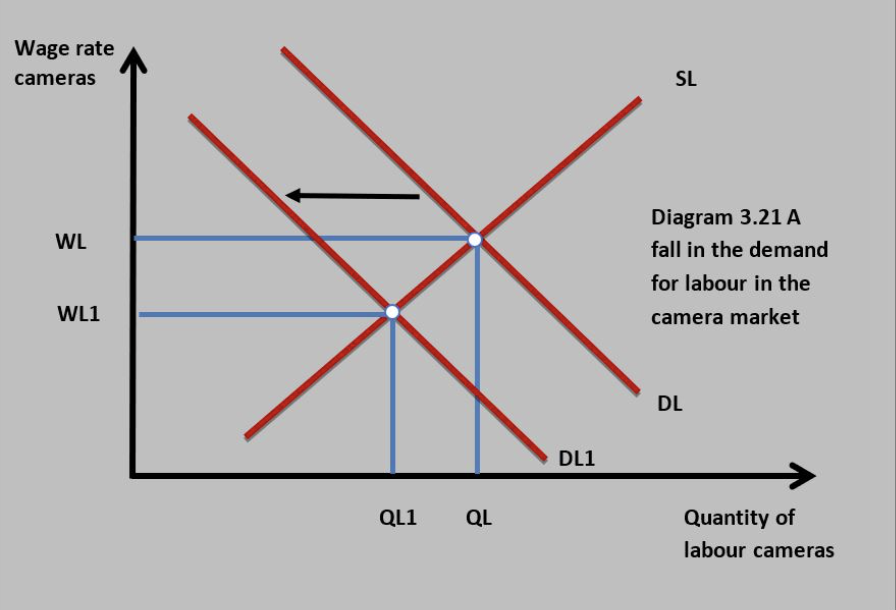
Exists when the demand for labour is less than the supply of labour in a particular industry. Due to skills mismatch between jobs available in the economy and the skills of workers or also due to changes in geographical locations
Seasonal unemployment
Unemployment caused by regular and periodical changes in the derived demand for labour at different times of the year. Seasonal peaks and troughs in production and sales of products. Eg ice cream reatilers during winter. Harmful to individuals and households in low income.
Frictional unemployment
Cause or type of unemployment that exists when people are temporarily unemployed while they actively search for a new job or are waiting to start a new job. Delay a the labour market is unable to immediately match people with the supply of appropriate jobs
Natural rate of unemployment
Level of unemployment at the full employment equilibrium level of national output, comprising frictional, season, and structural unemployment
Costs of unemployment
Stress, low self esteem, poverty, family breakdowns. Crime and antisocial behaviours, indebtedness, social deprivation. Loss of GDP, loss of tax revenues, increased cost of unemployed benefits, loss of income for individuals, greater disparities in the distribution of wealth and income
Inflation
Sustained rise in the general price level in an economy over time, that is, prices in the economy are, on average, rising over time
Price stability
Occurs when the general price level of prices remains largely constant due to a low and stable rate of inflation in the economy
Hyperinflation
Extortionately high and uncontrollable rates of inflation that causes serious macroeconomic problems
Money supply
Amount of money in circulation within the economy at a particular point in time, as determined by the CB. The money supply comprises legal tender (banknotes and coins), loans, credit, bank deposits and CB reserves
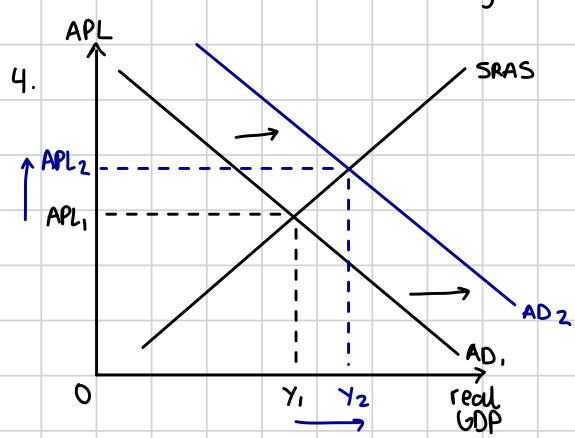
Demand pull inflation
Inflation caused by higher levels of AD in the economy, which drives up the general price level. Result from a change in the factors of AD
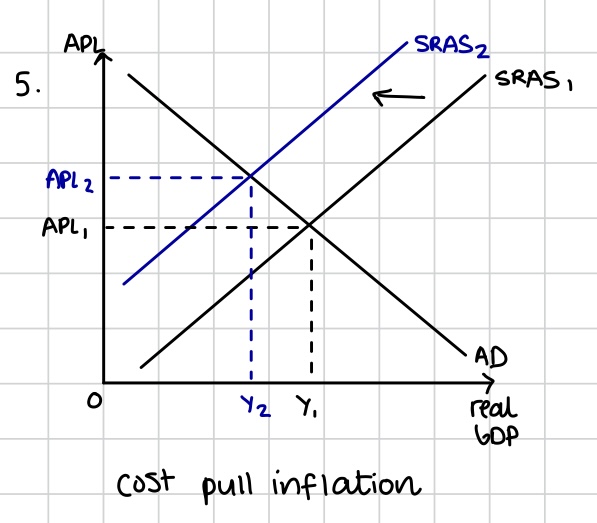
Cost push inflation
Inflation caused by higher costs of production, such as higher labour costs or skyrocketing rents. It is shown by a leftwards shift of the AS curve, forcing up the average prices. Resulting from increases in costs of production or supply shocks
The costs of inflation
REUSER (Redistributive effects, Export competitiveness, Uncertainty, Savings, Economic growth, Resource allocation)
Deflation
Persistent fall in the APL in an economy over time, that is, lower prices in general
Supply side deflation
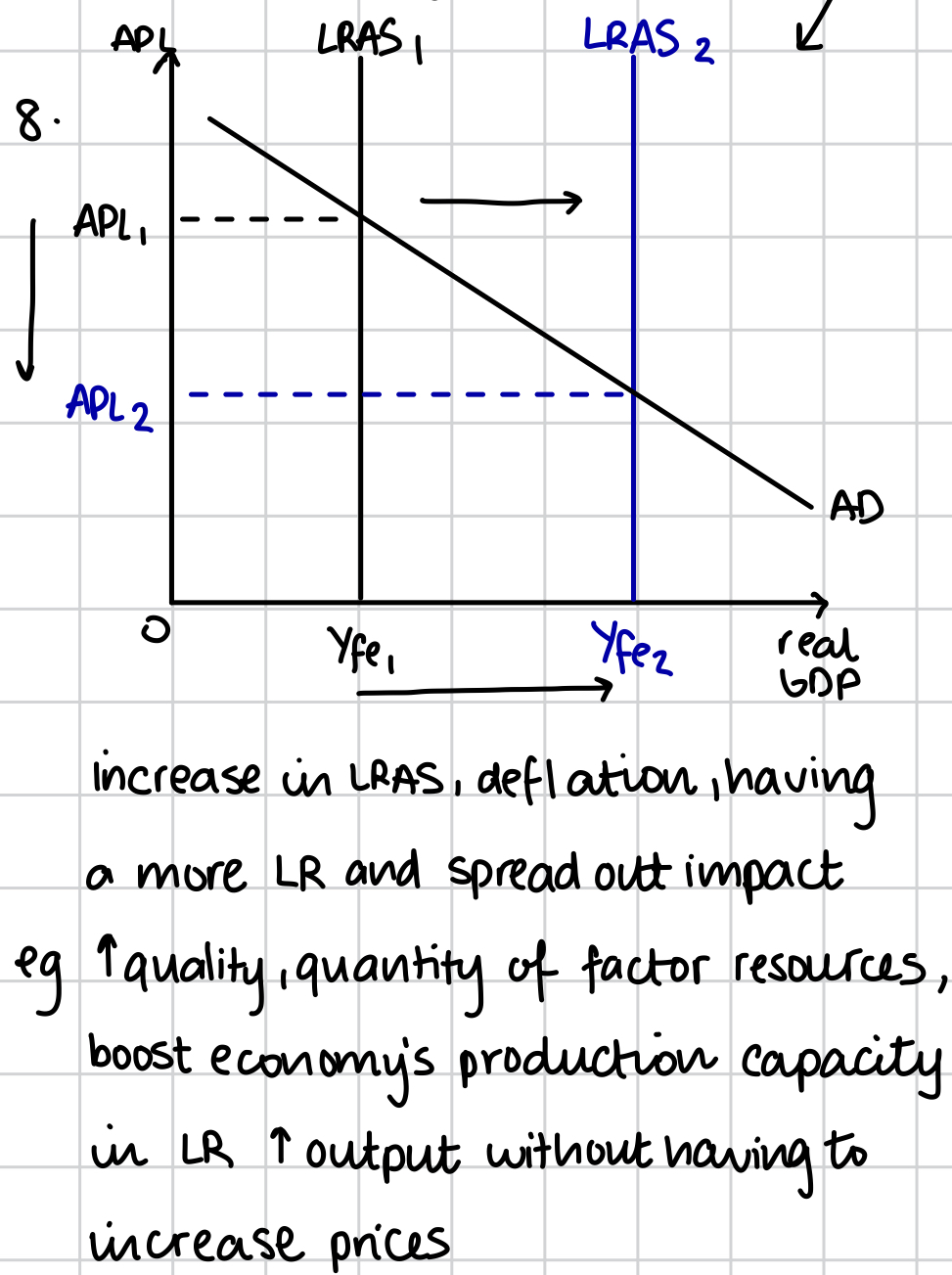
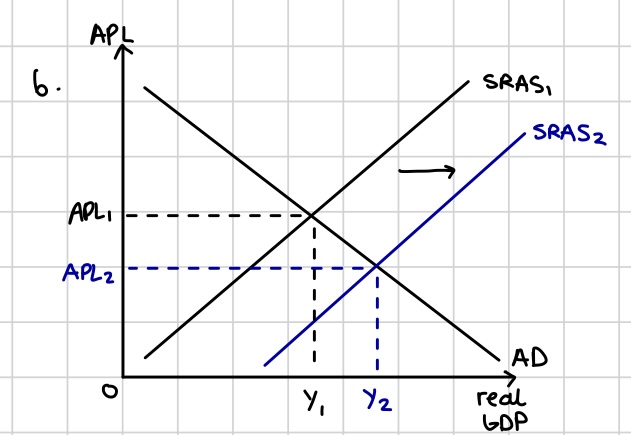
Generally unharmful deflation as the economy is able to produce more without an increase in the general price level, shown by an outwards shift of the SRAS curve, “Good deflation” as higher levels of GDP associated
Demand side deflation
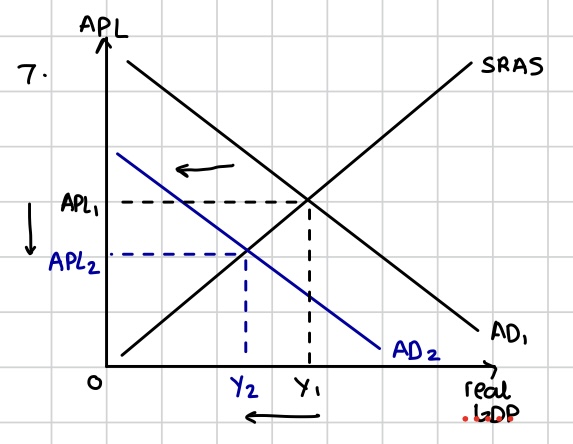
Generally harmful deflation due to a decline in AD for goods and services in the economy, shown by an inwards shift of the AD curve and hence a fall in real GDP. Occurs in a recession and “bad deflation.”
Costs on deflation
R U CUPID (Redistributive effects, Uncertainty, Consumption being deferred, Unemployment and bankruptcies, Policy ineffectiveness, Inefficient resource allocation, Debt)
Deflationary spiral
Circular process of downward pressure on the general price level caused by a weak economy, which leads to lower wages and confidence levels that in turn causes prices to fall further
Claimant account
Measure of the number of people who are out of work, actively seeking employment but claiming unemployment benefits
Difficulties in measuring unemployment
Hidden unemployment (employed people who are excluded from the measure of unemployment owing to the chosen definition of unemployment), underemployment (people who want full-time jobs but are only able to get part-time jobs), voluntary employment and disparities (such as regional, gender, age and ethnic disparities).
Consumer price index (CPI)
A weighted index of average consumer prices of goods and services over time, used to measure inflation (or changes in the cost of living) for the average household in the economy
Increase in AD or demand pull inflation
Reduced interest rates raise the level of consumption and investment.
A rise in house prices makes consumers feel wealthier and raises consumption.
High levels of business and consumer confidence stimulate consumption spending and investment.
Expansionary fiscal policy by the government is trying to stimulate economic growth
Reason for cost push inflation
If the cost of any of the factors of production increases, the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left.
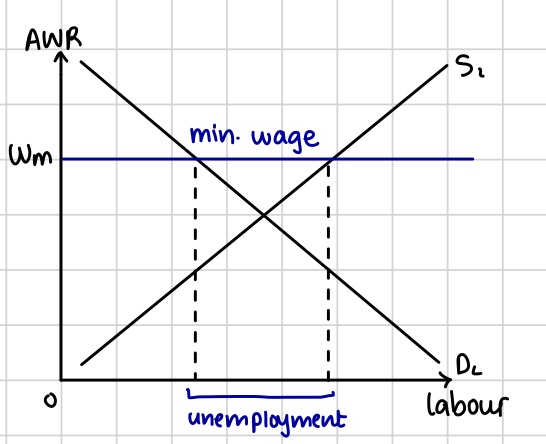
Labour market with minimum wage
Shows disequilibrium unemployment
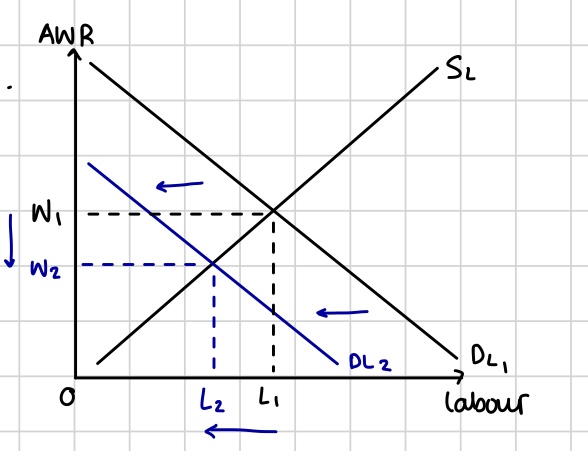
Impact of structural change on D for labour
Supply side deflation long run
Having more LR and spread out effect