Lesson 2: Errors
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Error
Denotes uncertainty and difference between two natural values.
less representative
Result of a greater error
Types of errors
Systematic error
Random error
Gross error
Systematic error
Result of variation of a measurement of the true value. Affects accuracy and also known as determinate error. Can be detected and eliminated.
Instrumental
Method
Personal
Instrumental - systematic error
Anything that is used and applied in the analysis. Calibration eliminates most systematic errors.
Calibration
Eliminates most systematic errors.
Method - systematic error
Anything related to the method. May be the behavior of the reagent. Is the MOST DIFFICULT to determine and correct.
Personal - systematic error
Something that is inherent on the analyst. Also known as operative errors and may be skill based or a mistake.
CRM
Certified reference materials (uncertainty). Controls or standards do check the quality and metrological traceability of products.
Independent analysis
Asks other chemist to analyze.
Round robin experiment
Different people at different laboratories analyze identical sample.
Blank determination
Contains the reagents and solvents use din determination but no analyte. May be from sample size and can replicate.
method
Reagent
Field
Method - blank determination
Taken through all steps
Reagent - blank determination
Not subjected to all sample
Field - blank determination
Exposed to the sampling site.
Random error
Simply there. No identified cause and gives the ultimate limitation. Affects precision and is indeterminate but can be minimized.
Gross error
Product of human errors. Often large and called outliers, has no alternatives.
Statistics
Way to test or identify outliers
False negative
Indicated as correct but is actually incorrect
False positive
Indicated as incorrect but is actually correct.
Outlier
An observation that lies outside the overall pattern.
Grubb’s test
Compares the deviation of the suspect value from the sample mean. ISO (International Organization for Standardization) recommended.
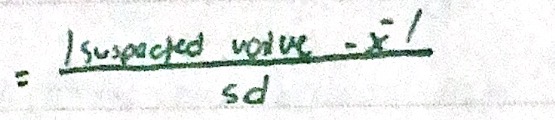
Dixon’s test
Also known as Q-test. Assess a suspect of measurement by comparison of data. If level of confidence is not given, assume 95%. Outliers are not included in the mean calculation.
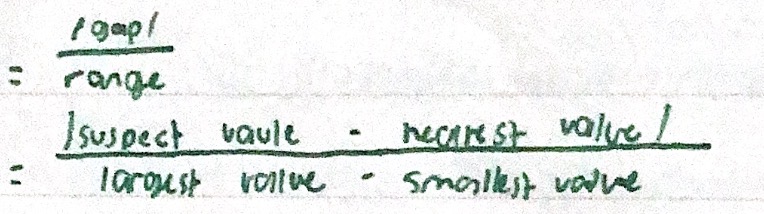
Accuracy
Indicates the closeness of measurement to the true or accepted value. Has mean and median under.
Mean
Arithmetic average
Median
Middle value when arranged
Absolute error - expressing accuracy
Difference between measured value and true value. E= xi - xt
Relative error - expressing accuracy
Absolute error divided by the true value. Er = ((xi-xt)/xt) •100%
Precision
Arrangement among several results obtained in the same way.
Types of precision
Instrument
Intra-assay
Indeterminate
Interlaboratory
Instrument - precision
Injection precision. Reproducibility observed.
Intra-assay - precision
Analyzing aliquots several times a day by the same analyst.
Indeterminate - precision
Ruggedness, same with intra-assay but different people and same laboratory.
Interlaboratory - precision
Most general measure of reproducibility.
Bigger random error
Result when variability is increased
Repeatability
Same all
Reproducibility
Nearness of results
Standard deviation - expressing precision
Measure spread or distribution around the mean of a data set.

Relative standard deviation (RSD) - expressing precision
Standard deviation by mean, often used to compare precision of results.
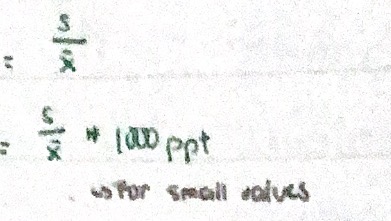
Coefficient of variation - expressing precision
Relative standard deviation expressed as percentage.
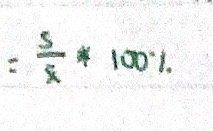
Variance - expressing precision
Square of standard deviation. Useful measure of the scatter particularly for random errors.
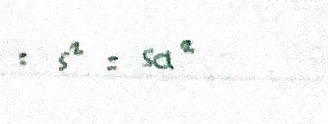
Standard deviation of the mean - expressing precision
Referred to as the standard error.
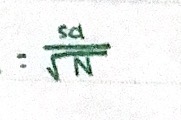
Uncertainty
Measurement without level of certainty.
Absolute uncertainty
Margin of uncertainty associated with a measurement. Nakalimutan q formula omai
Relative uncertainty
Comparing the size of the absolute uncertainty to the size of its associated movement. = (absolute uncertainty/magnitude of measurement) • 100%