Anatomy Axial Skeleton Practical Terms
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Coronal suture
Parietal bone
sagittal suture
lamboid suture
occipital bone
frontal bone
supraorbital foramen
nasal bone
frontal process of maxilla
lacrimal bone
perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
Maxilla
vomer bone
anterior nasal spine
infraorbital foramen
cribriform plate
crista galli
optic foramen
sella turcica bone
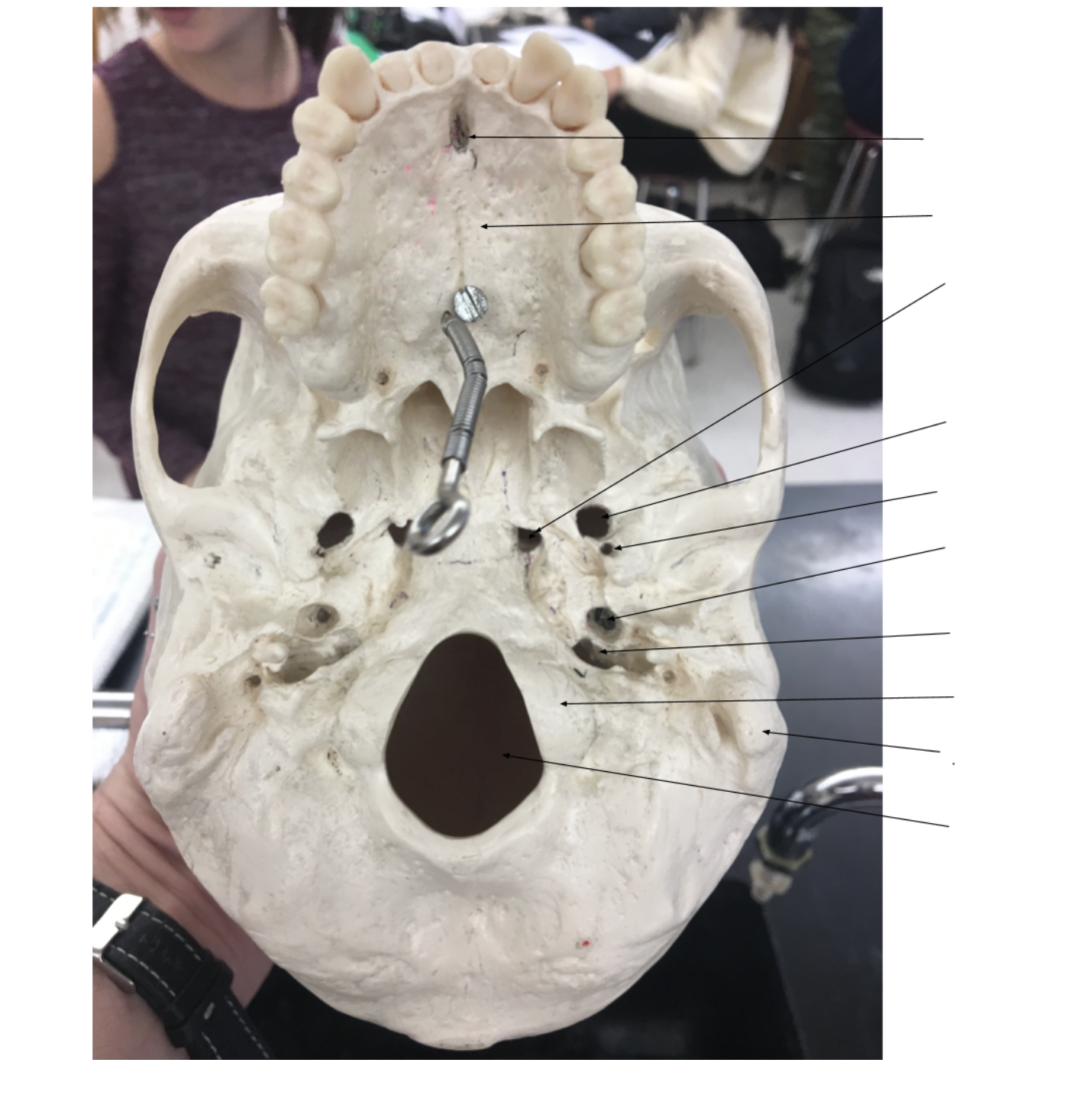
incisive foramen/incisive canals
palatine process
foramen lacerum
foramen ovale
foramen spinosum
carotid foramen
jugular foramen
occipital condyle
Mastoid process
foramen magnum
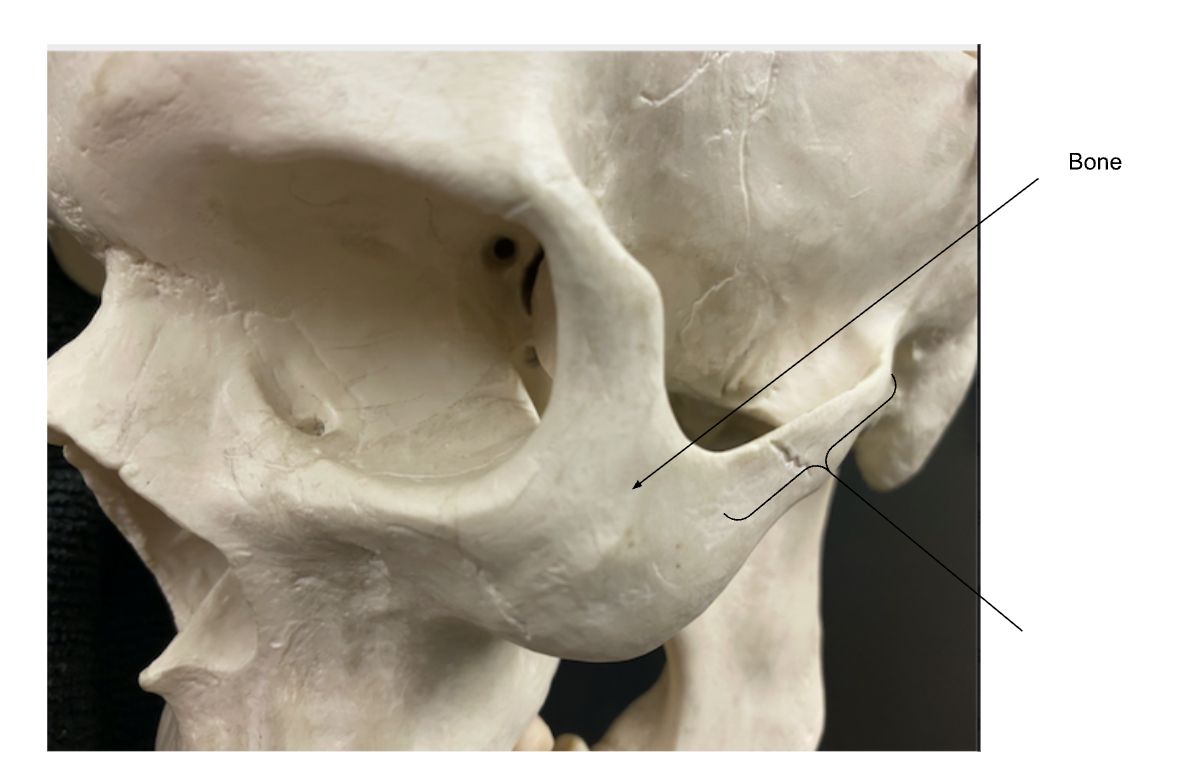
Zygomatic bone
Zygomatic arch
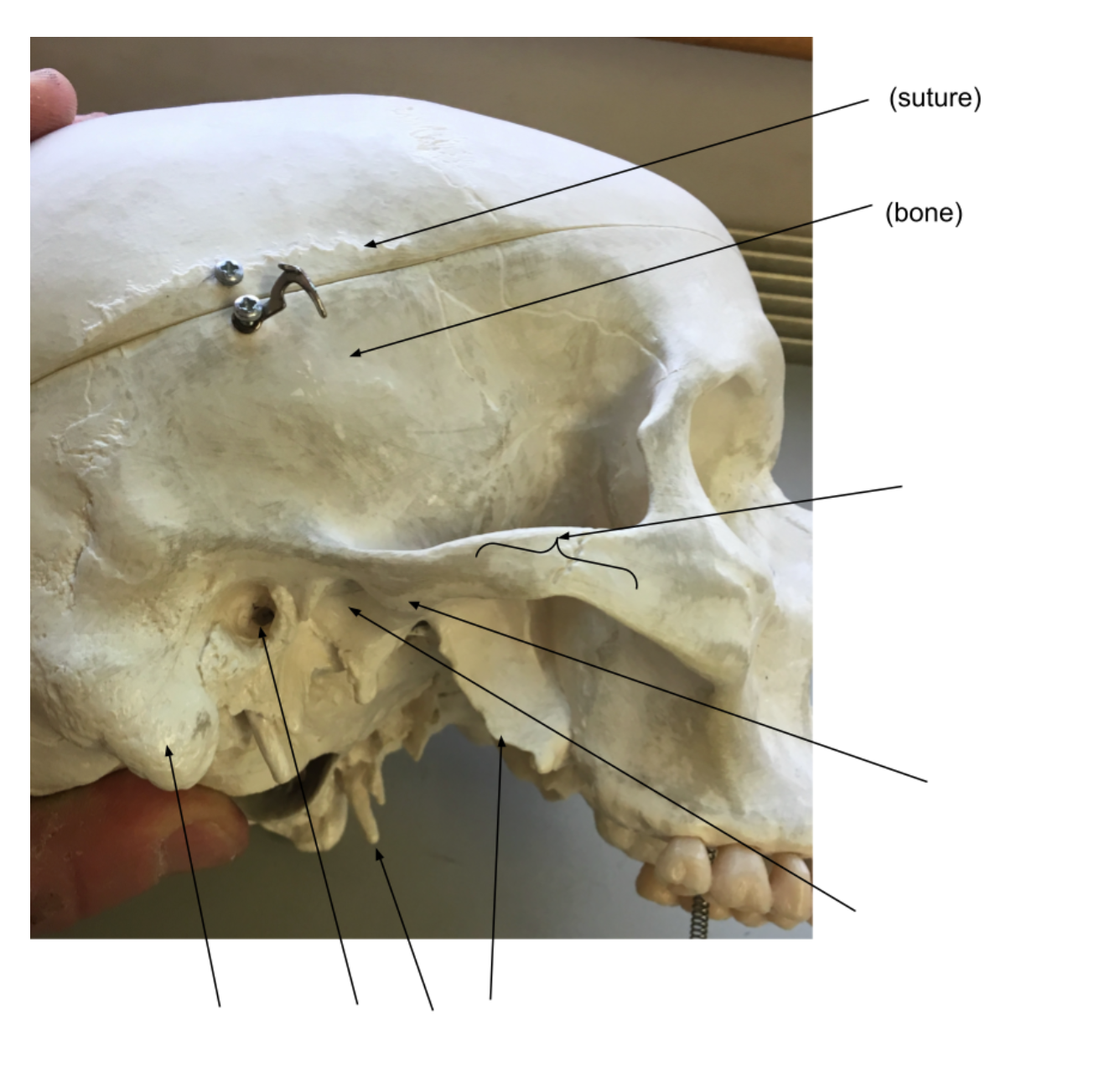
squamous suture
temporal bone
zygomatic arch
articular tubercle
mandibular fossa
pterygoid process
styloid process
external auditory meatus
mastoid process
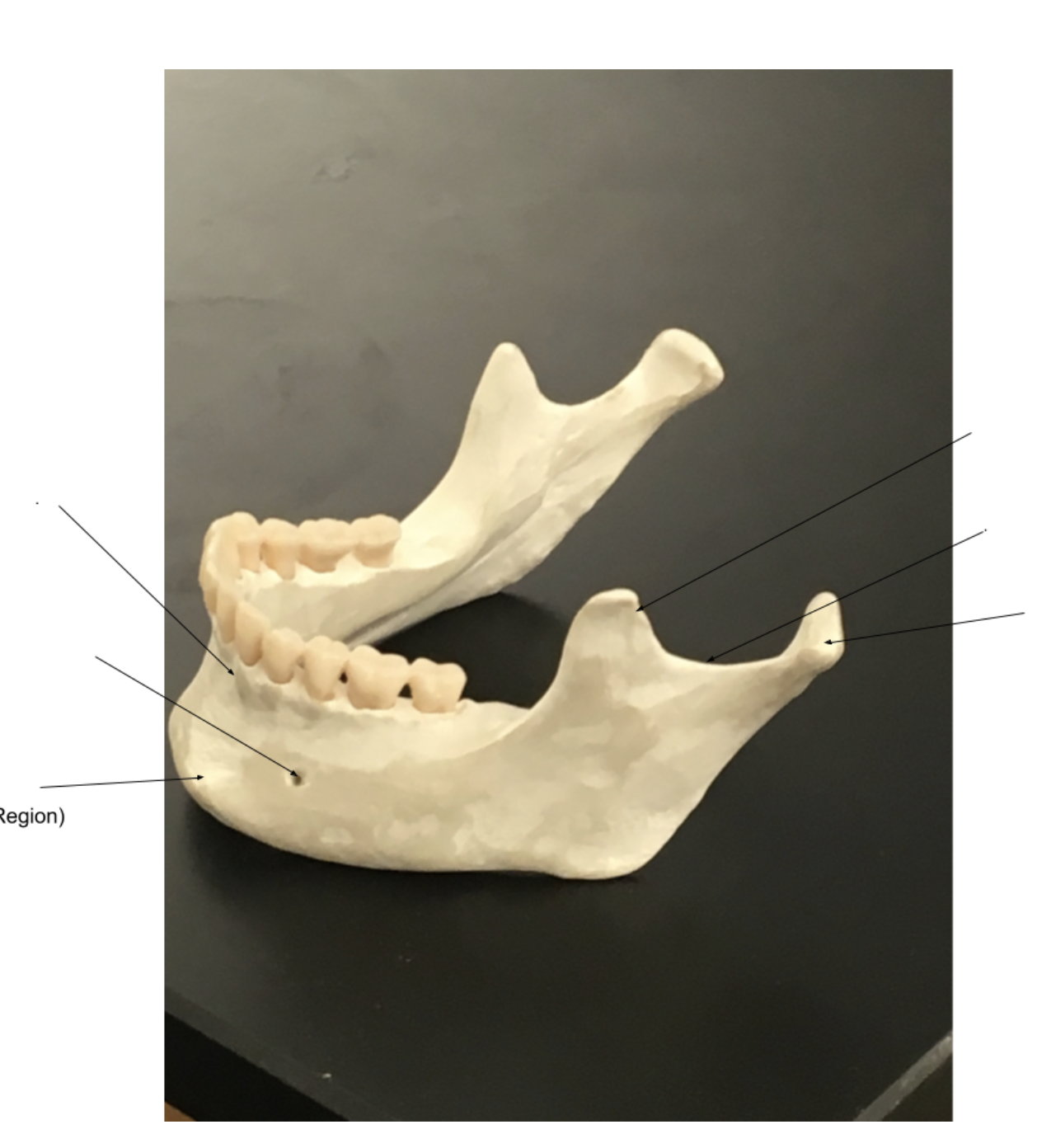
Left:
Right:
left
inferior alveolar process
mental foramen
mental protuberance
right
coronoid process
mandibular notch
mandibular condyle
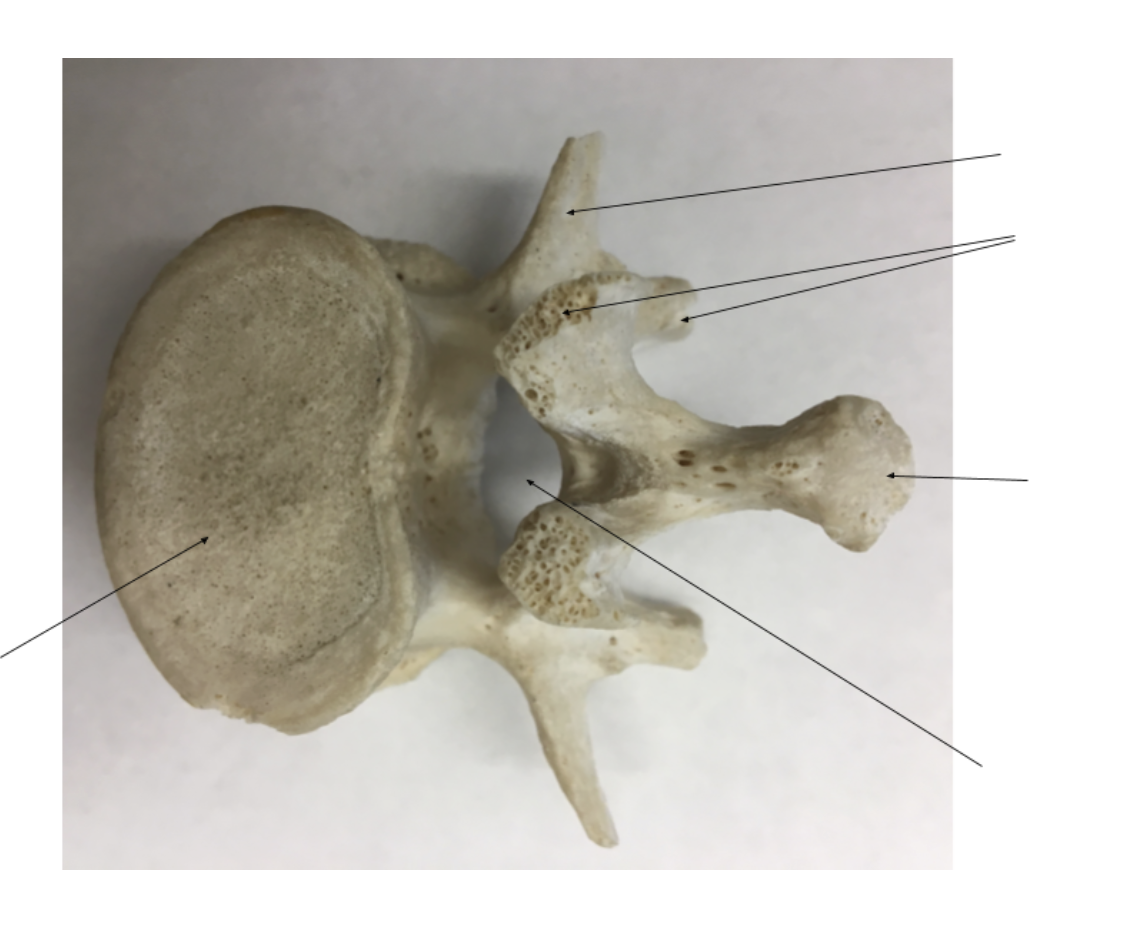
Left:
Right:
left
vertebrae body
right
transverse processes
articulating processes
spinous process
vertebral foramen
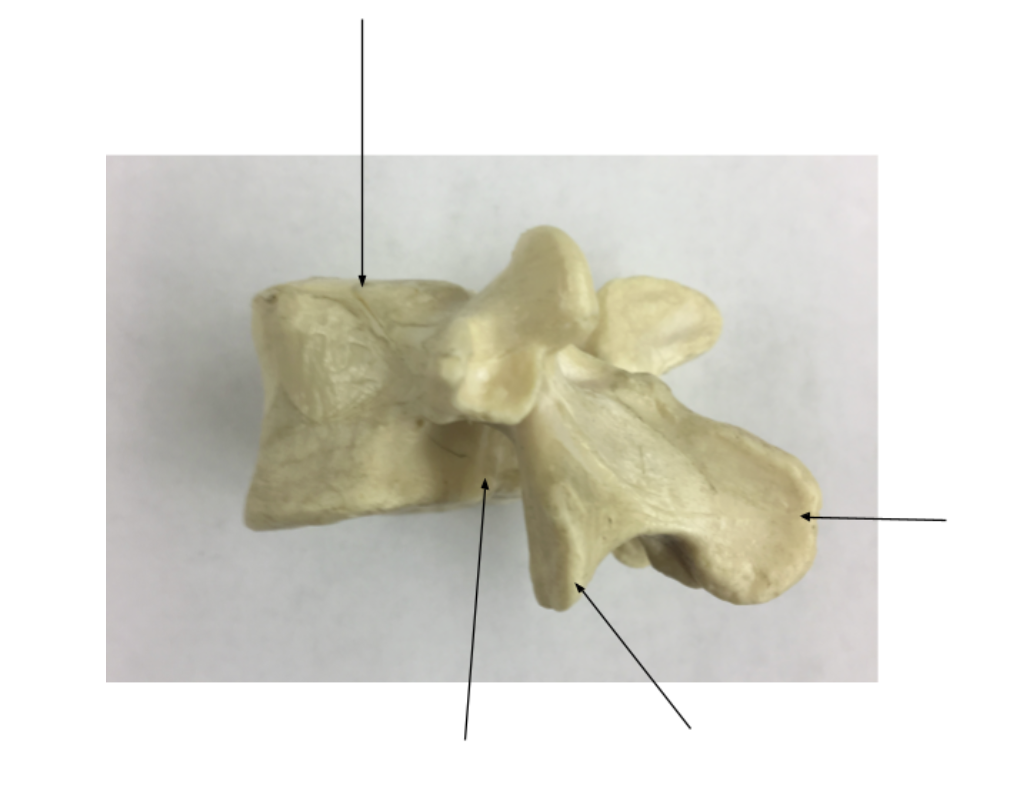
vertebral body
spinous process
articulating process
vertebral foramen
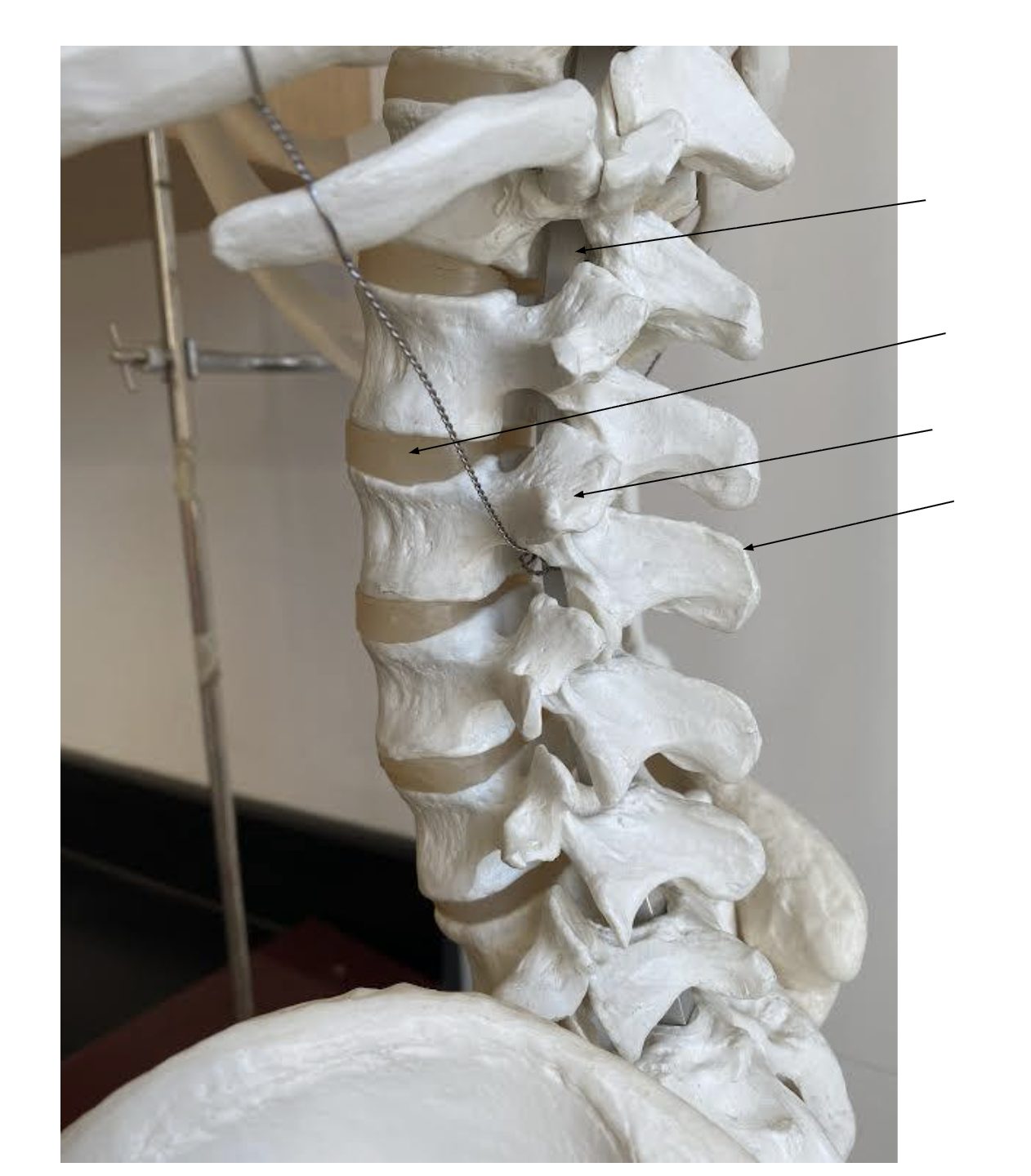
intervertebral foramen
intervertebral disc
transverse process
spinous process

left:
right:
left
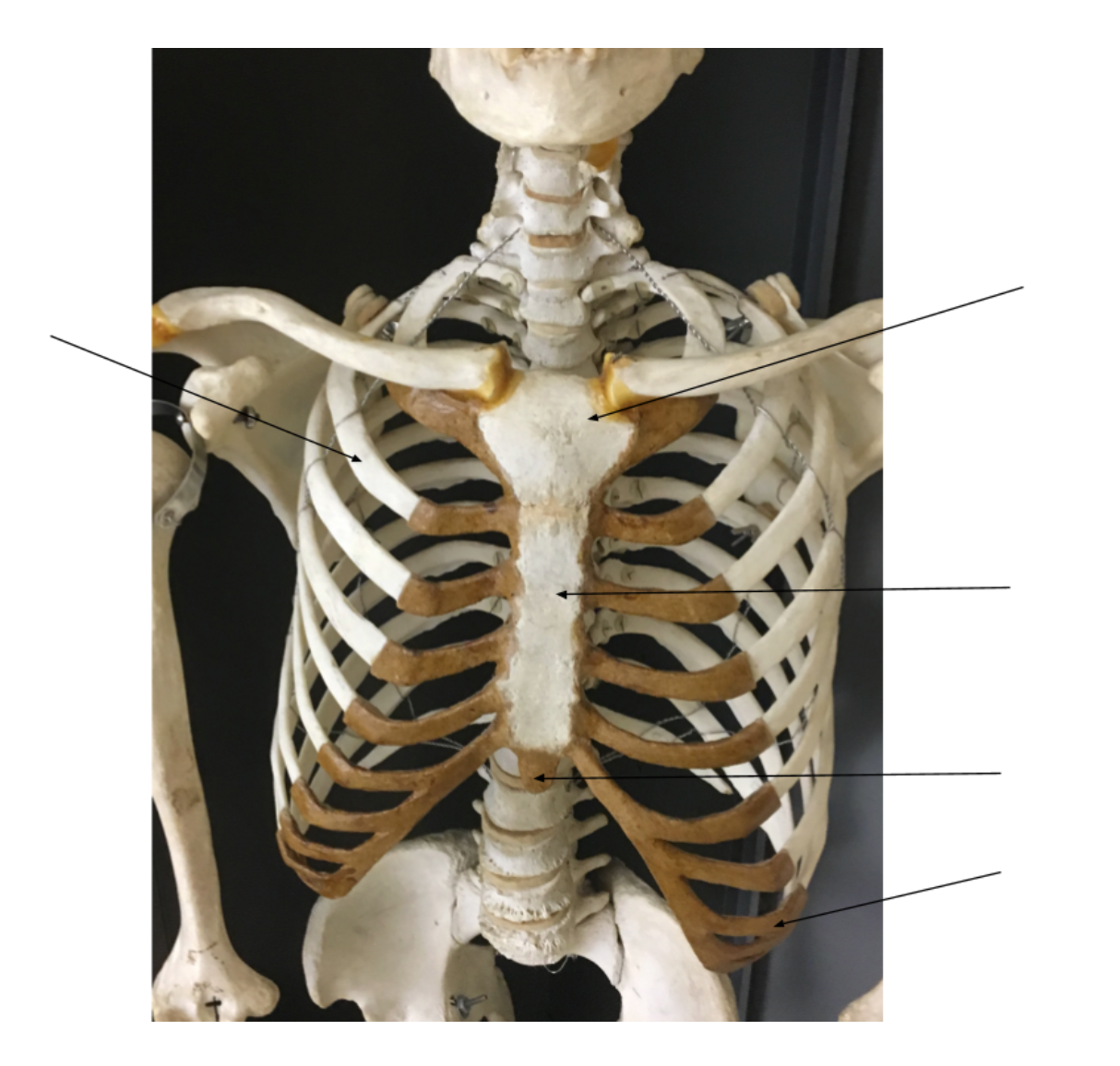
floating ribs
right
cervical vertebrae
thoracic vertebrae
lumbar vertebrae
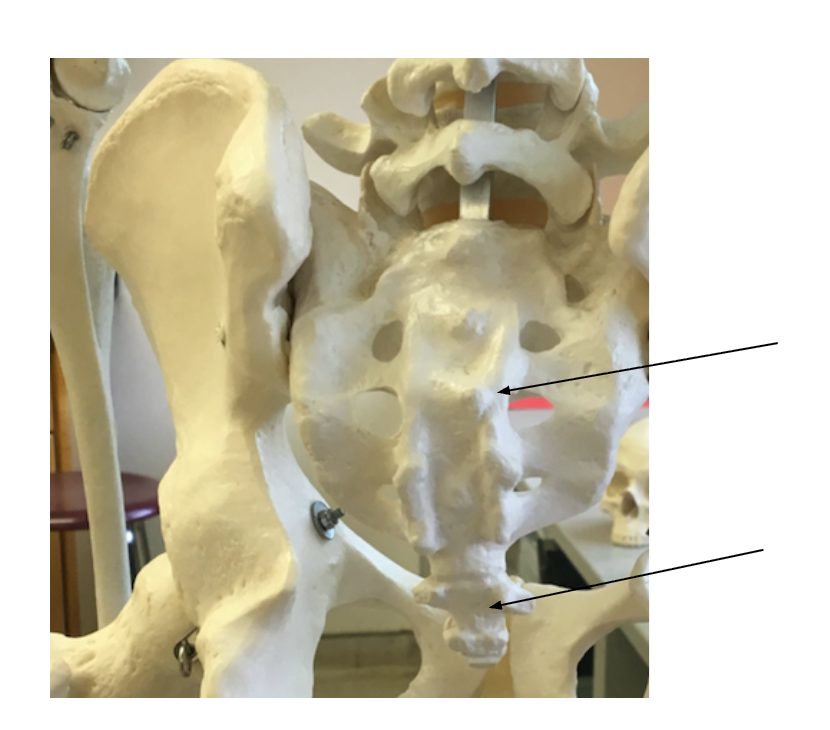
sacrum
coccyx
left
right
left
true ribs
right
manubrium
sternum body
xiphoid process
false ribs
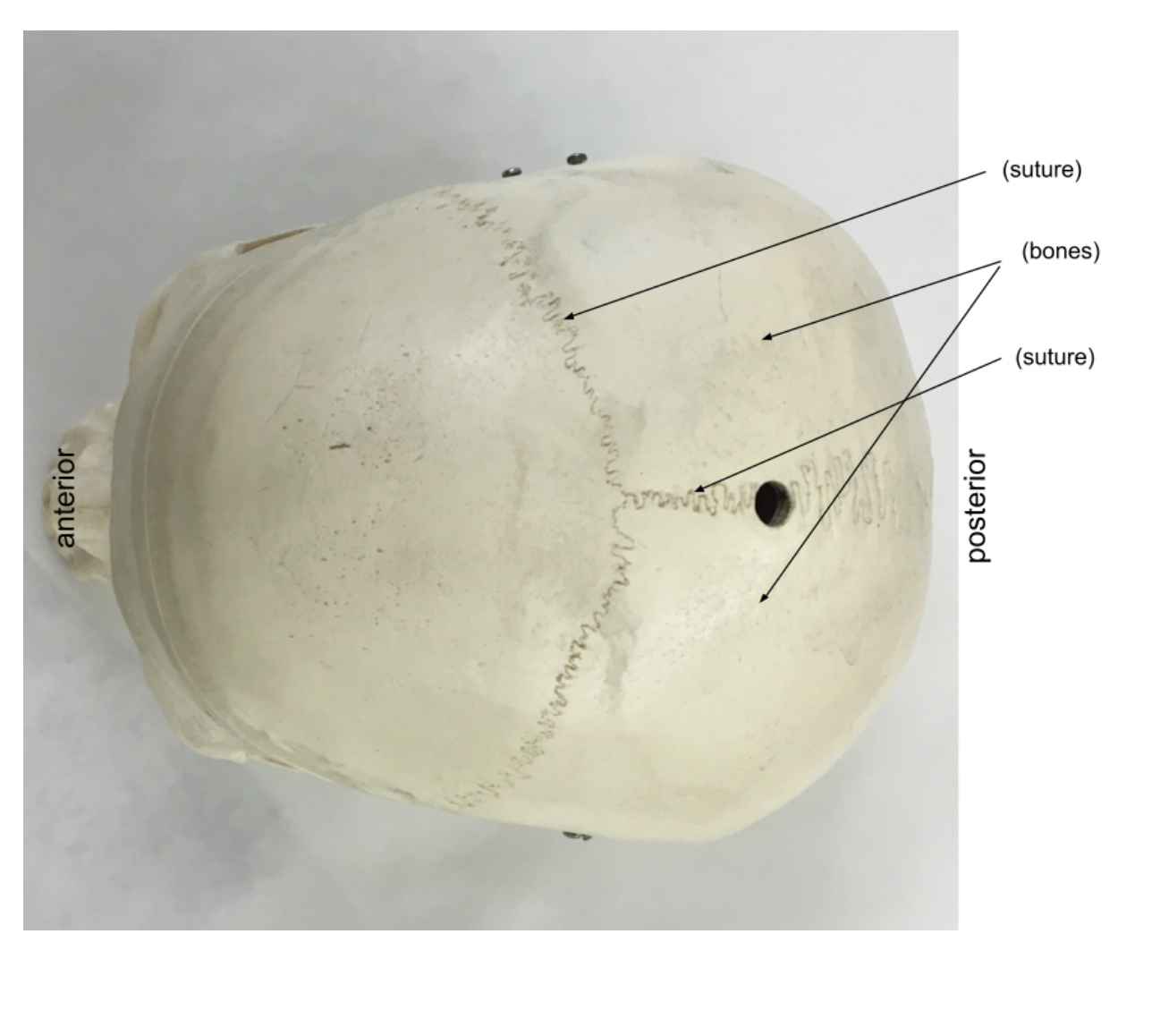
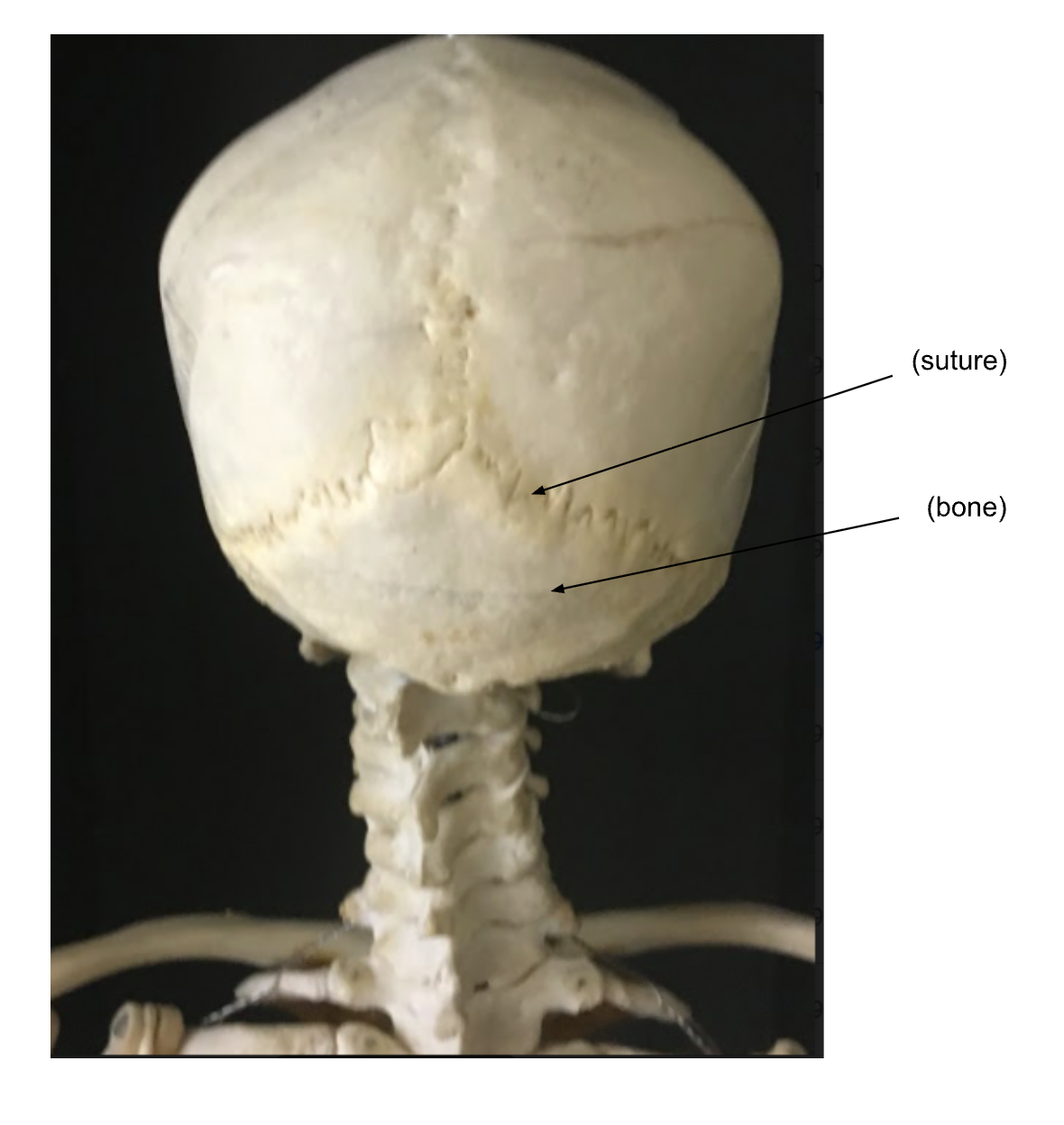
A. Cranial Sutures -
Joints made of strong, fibrous tissue hold the bones of your skull together.
Sutures:
Coronal Suture, Lambdoidal Suture, Sagittal Suture Squamosal Suture
B. Cranium -
the part of the skull that encloses the brain
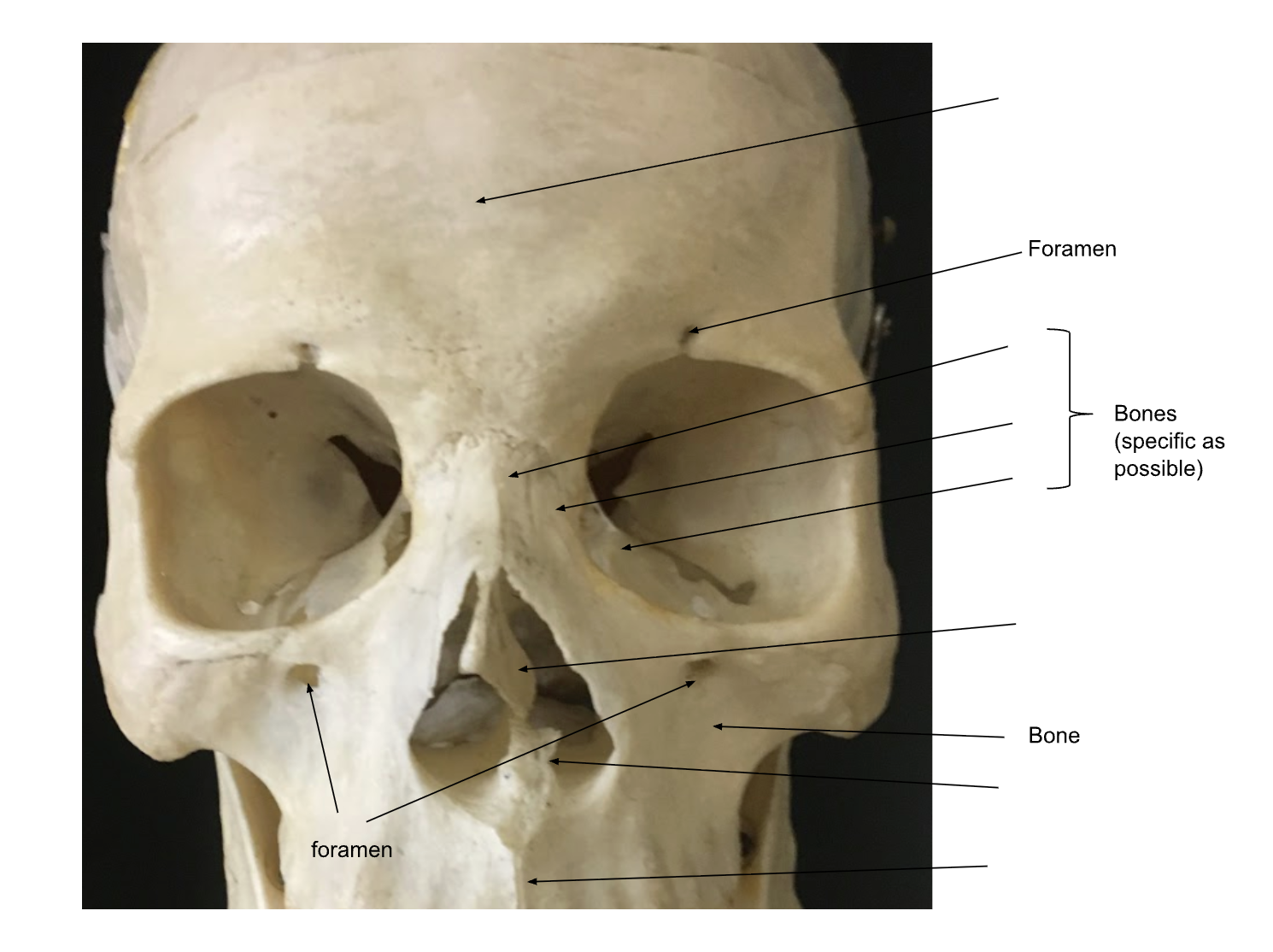
1. Frontal Bone -
forms the anterior and superior portions of the skull.
Supraorbital foramen -
a path for vessels and nerves from the orbit to the superficial region of the forehead
2. Parietal Bone (x2) -
form the sides and roof of the cranium
3. Occipital Bone -
major part of the posterior wall and base of the skull
a. Foramen Magnum -
a passage of the central nervous system through the skull connecting the brain with the spinal cord.
b. Occipital Condyles -
articulate with the superior articular facets of the atlas (C1 vertebrae) and form a hinge joint allowing flexion and extension of the head.
4. Temporal Bones (x2) -
forms lower lateral walls of the skull
5. Sphenoid Bone -
forms the base of the cranium, behind the eye and below the front part of
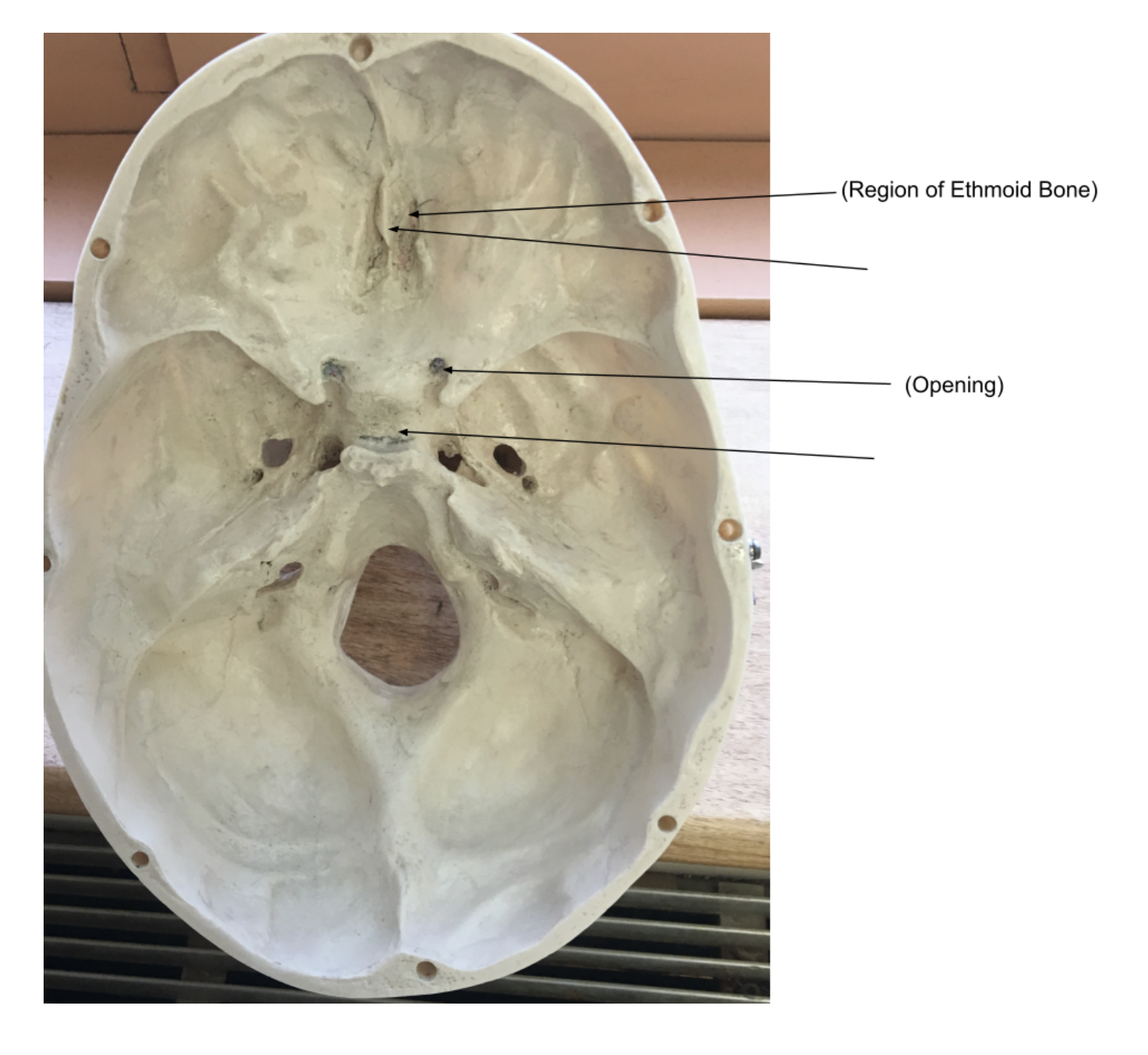
6. Ethmoid Bone -
a small, cube-shaped bone in the center of the skull that helps form the eye sockets, nasal cavity, and sinuses:
C. Facial Bones -
bones that make up the face and are located between the cranium and the mandible
1. Maxilla -
bones that form the upper jaw, the roof of the mouth, and parts of the eye socket and nose:
a. Superior Alveolar process -
the thick, curved ridge of bone that forms the socket for upper teeth
Infraorbital foramen -
small holes in the maxilla, located below the eye socket and to the left and right of the nose.
Frontal process -
thin, long, superior projection found along the side of the nose forming part of its lateral boundary
Anterior nasal spine -
projects anteriorly in the midline, inferior to nasal cavity
Lacrimal bones -
two small bones of the maxilla are roughly the size of the little fingernail and situated at the anterior portion of the medial wall of each orbit.
Lacrimal fossa
opening in the lacrimal bone that provides drainage for the lacrimal gland (produce tears)
a U-shaped groove in the mandible found between the coronoid process anteriorly and the condylar process posteriorly.
bony projections that connect vertebrae together, forming joints that help stabilize the spine
wing-like projections of bone extending laterally from each
side of the vertebrae body that allow back muscles and ligaments to attach to the vertebral column
the bony framework of the thoracic cavity that surrounds and protects vital organs including heart and lungs.