CELL COMMUNICATION QUIZ
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What are the four types of signaling?
Autocrine, Juxtacrine, Paracrine, Endocrine
What is Autocrine signaling?
Cell communication from a cell to itself, within the same cell. Ex) Cancer cells
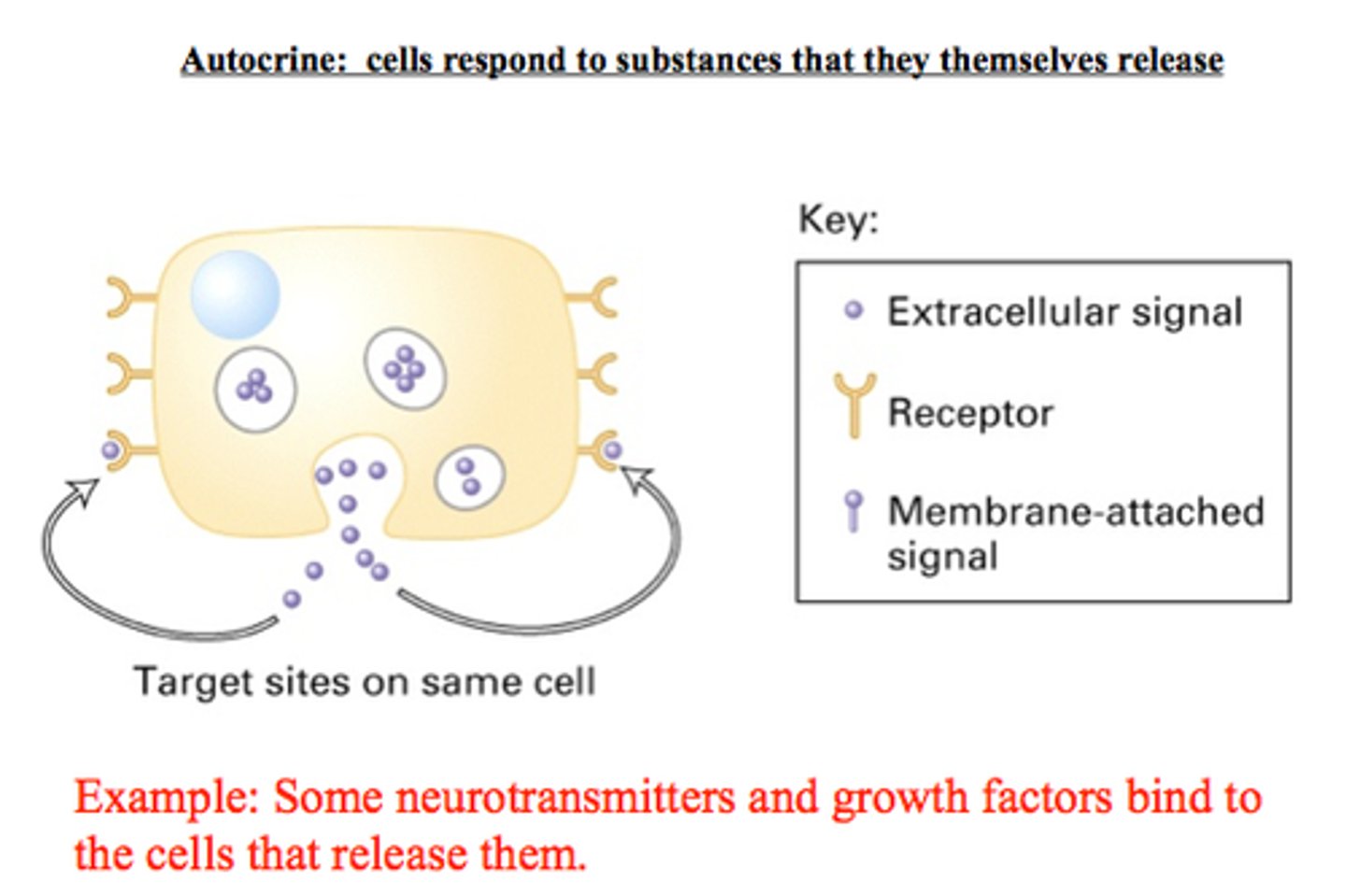
What is Juxtacrine signaling?
When a cell that is directly adjacent or next to the other cell. Ex) Plasmodesmata
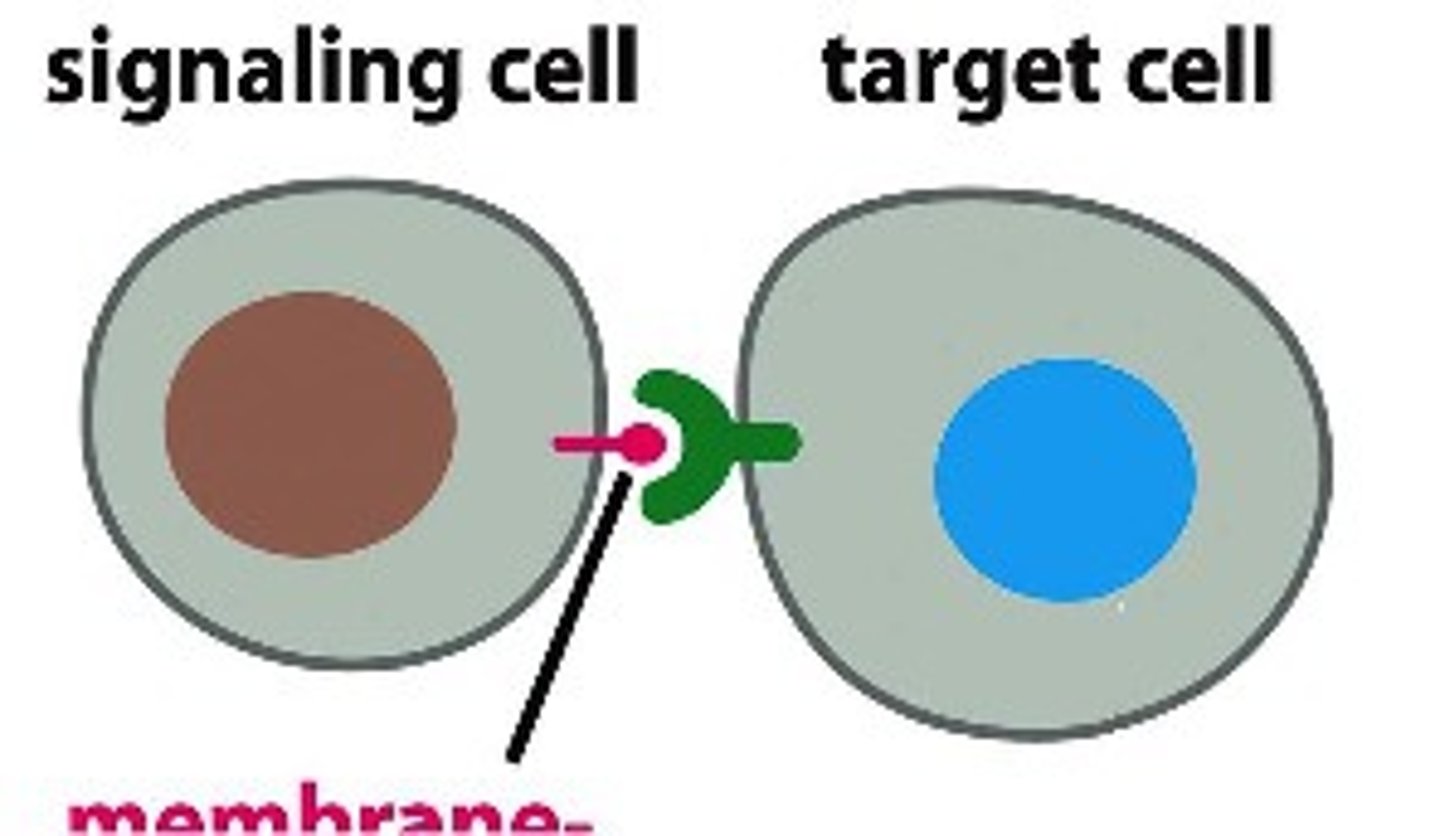
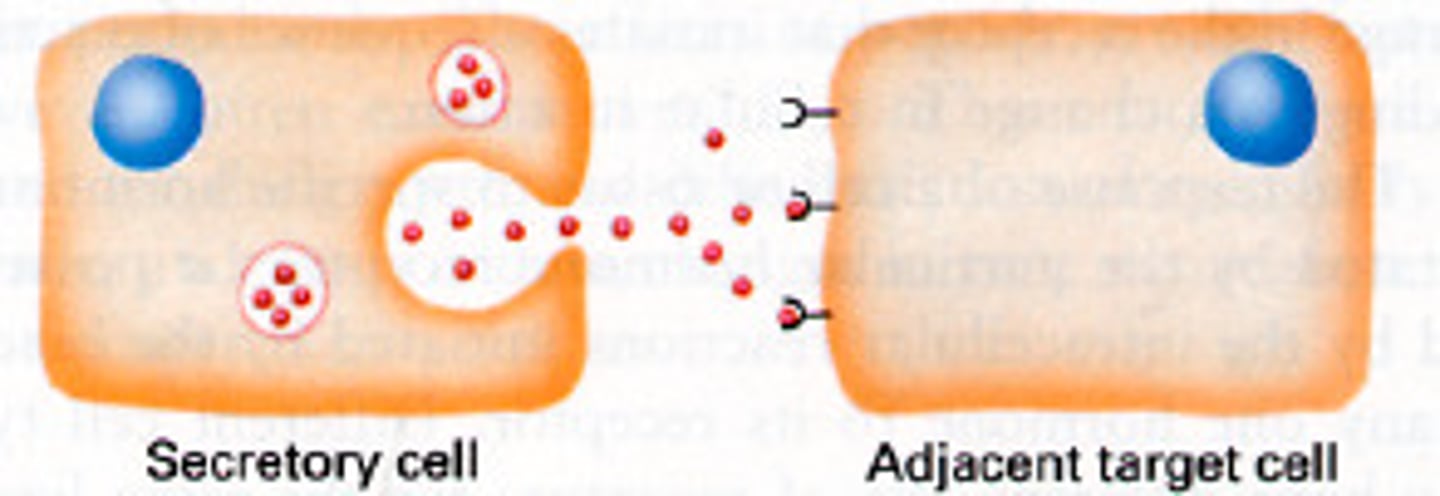
What is Paracrine Signaling?
When the hormone released from a cell acts on a neighboring cell or a nearby cell Ex) Neurotransmitters or a nerve cell
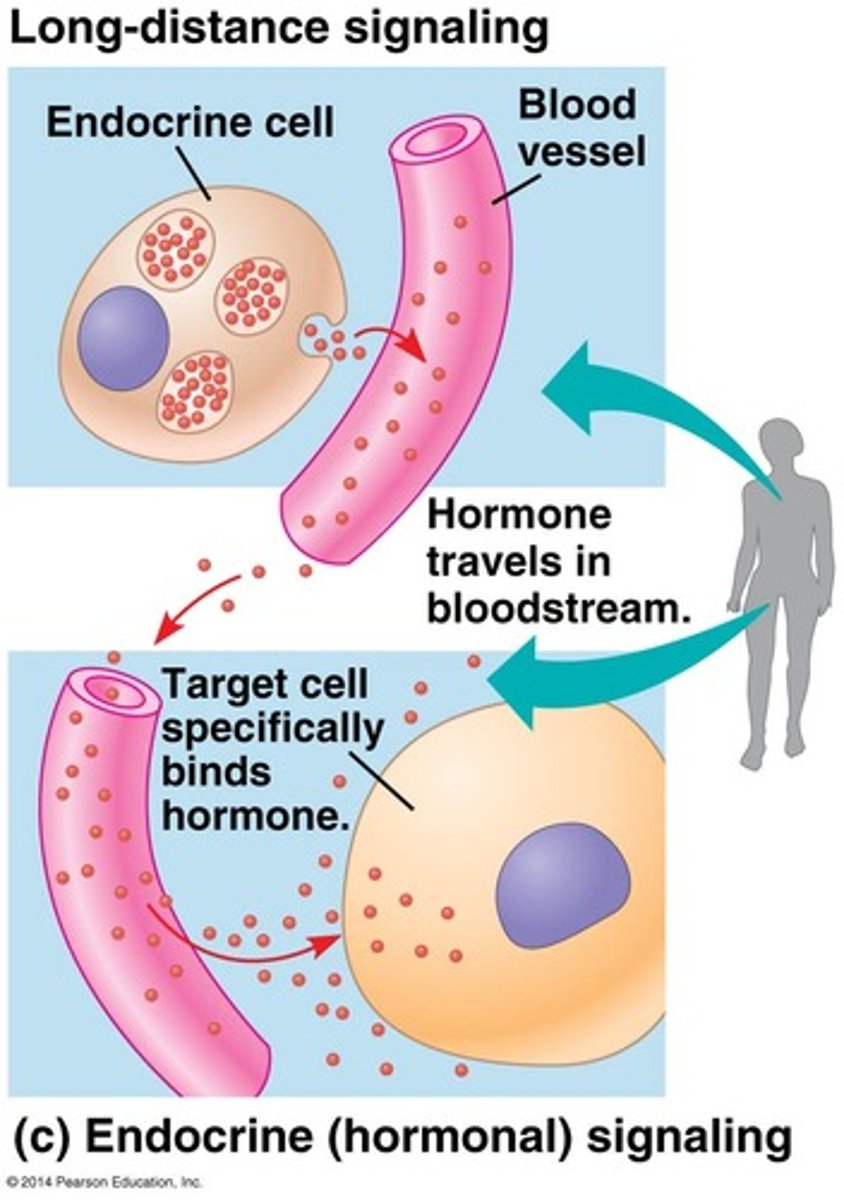
What is Endocrine signaling?
Cells secrete hormones into the bloodstream to signal distant cells. The ligand has to travel a far distance. EX) Hormones
Describe how the shape of the ligand (signaling molecule) and the shape of the receptor are related.
A ligand binds to a receptor protein. The binding is highly specific. Ex) Lock and key, Puzzle Piece
Do all ligands for cellular communication have the same chemical structure (shape)?
No, they need to all be different because they could be misunderstood, or they could be sent a wrong signal therefore they must have different shapes
Quorum Sensing
Used by bacteria to interact with members of the same species as well as members of other species that are close by. Can be used to determine the population density of their species in a local area.
Morphogens
Produced in embryos from a central source early in development. They diffuse throughout the tissue creating a concentration gradient that provides a spatial reference for developing cells.
Pheromones
A hormone, a chemical signals released by an animal that communicate information and affect the behavior of other animals of the same species.
Neurotransmitters
Ligands that are released from the axon of one nerve cell to teh dendrite of another nerve cell
What are some methods that could be used to stop a signal transmission from cell to cell?
-Make a drug that prevents production of the ligand
- Make a molecule that blocks the receptor site of the ligand of the cell
-Make a chemical that changes the ligand shape so that it can't fit into the receptor
-Block secondary receptors
What are some methods that could be used to enhance signal transmission from cell to cell?
-Make a drug that increases production of the ligand or increases production of the receptor protein in cells
-Produce more of the ligand into the organism to increase its overall concentration (signal)
The examples of cellular communication used in this activity vary from bacteria to plants to vertebrates. However, the mechanisms of cellular communication are similar among varied species. Explain how scientists might use cellular communication systems to show evolutionary relatedness between species.
Scientists could look at the chemical structure of the ligands or the receptor proteins to see which species have the most similar structures in their communication systems
Some hormones such as estrogen and testosterone are lipids and are therefore nonpolar. Explain why a receptor protein would not be needed for this type of ligand to activate a response in a cell
Since the hormones are nonpolar they can diffuse through the cell membrane without a protein channel
What are some stiumuli that might cause a cell to release a ligand and begin communication between cells?
Signals from hormones, stress, senses like smell or taste, light levels, temperature, or age of the cell
What is a signal transduction pathway?
A series of steps by which a signal on a cells surface is converted into a specific cellular response
What is transduction?
A transition of the signal into the response
What are some responses that could occur due to a signal being received by a cell?
A gene is activated, a protein is manufactured, enzyme is activated, a cell divides or dies
Once a response is achieved in a cell, what would need to occur to stop the response?
The relay protein would need to be deactivated (at base, the ligand would need to develop from the receptor)
What event sets off a phosphorylation cascade inside of a cell?
A ligand causes a receptor protein to activate a relay protein
Phosphorylation
A process that adds a phosphate group onto a protein to "activate" it, that is to change its shape enough that it can function properly. Using a lot of ATP
What class of enzymes performs phosphorylation?
Protein Kinases
What does amplification mean in terms of signal transduction pathway?
More molecules, than the original ligand are being involved
What advantage would there be to an organism if the signal transudction pathway had several amplification steps?
A single (or low count of) ligand molecules can lead to a magnified response by the cell
What would occur in the cell if the activated protein kinase enzymes continued to be activated for a long period of time?
ATP molecules would become used up
What needs to occur in the cell to deactivate the protein kinase enzymes?
Depolarization and deactivation of the relay protein
Although a signal transudction pathways vary among species, there are several common elements. Explain how a biologist might use details about signal transduction pathways used in different species as evidence for evolutionary relatedness.
Species with common signal pathways are more closely related then those with dissimilar pathways. Signal pathways appear to be ancient
What event begins the process of producing a cellular response?
A ligand binds to a receptor protein
What activates or opens the transport protein channel that allows the secondary messengers to enter the cell?
An active relay protein
What is the role of cell communication in a single-celled organism?
In single celled organisms, signal transduction pathways influence how the cell responds to the environment. For example, Quorum sensing in bacteria, bacteria cells get close to each other and release chemical signals, then go into neighboring cells with results in glowing
What is the role of cell communication in a multicellular organism?
Signal transduction pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function of the organism as a whole. For example, Fight or Flight response. Epinephrine is released, which leads to a chemical signal binds to a protein and so on
What is the signficance of the similarities in signal transduciton pathways between single celled and multicellular organisms?
Suggests that ancestral signaling molecules evolved in prokaryotes and were modified later in eukaryotes
A signal transduction pathway occurs when...
-A chemical messenger binds to a cell receptor
- The signal is tranferred into the cell
-A cellular response is produced
Earl W. Sutherland
Discovered how the hormone epinephrine acts on cells and suggested that cells receiving signals went through process called reception, transduction, and response
Most receptors for hormones are on the...
nucleur membrane
What are the three main types of membrane receptors?
-G protein coupled receptors
- Receptor tyrosine kinases
-Ligand Gated Ion channels
Facts on G-proteins
-G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR's) are the largest family of cell surface receptors
-The G protein acts as an on/off switch: If GDP is bound to the G protein, the G protein is inactive
-When the G protein and the receptor aren't connected they're off
Facts on Tyrosine Kinases
-Receptors Tyrosine Kinases (RTK's) are membrane receptors that attack phosphates to tyrosines
-An RTK can trigger multiple signal transduction pathways at once
-Abnormal functioning of RTK's is associated with many types of cancers
Facts on Ligand Gated Ion Channel
-Act as a gate when the receptor changes shape
-When a signal molecule binds as a ligand to the receptor, the gate allows specific ions such as NA and Ca, through a channel in the receptor
Intracellular Receptors
Proteins found in the cytosol or nucleus of target cells. Small or hydrophobic chemical receptors.
What is Adenylyl cyclase?
An enzyme that converts ATP to cyclic AMP in response to a signal
What is cAMP
cAMP is on eof the most widely used secondary messengers that target protein kinase. cAMPs binds to the regulatory subunits of protein kinase A and adds a phosphate group from ATP, which activates the catalytic subunit
Second Messengers are small, nonprotein, water soluble molecules or ions that...
spread throughout a cell by diffusion and are always inside the membrane
The two most common secondary messengers are...
cAMP and Calcium ions
Calcium is an important second messenger because...
cells can regulate its concentration
Protein Kinase
An enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein, thus phosphorylating the protein.