Unit 7 BTEC level 3 Business
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
business plan
a formal written document or statement about the intentions and purpose of the business
What a business Plan includes
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Market analysis
- Marketing strategies
- Financial plans
Factors that influence how a 'Developing' business develops
- Gap in the market
- Competitors
- Current trends
- Likely demand
Reasons a business may need to change its ownership
- Age, death
- Change of business operation
- A corporate buyout
- Merger
- Business failure
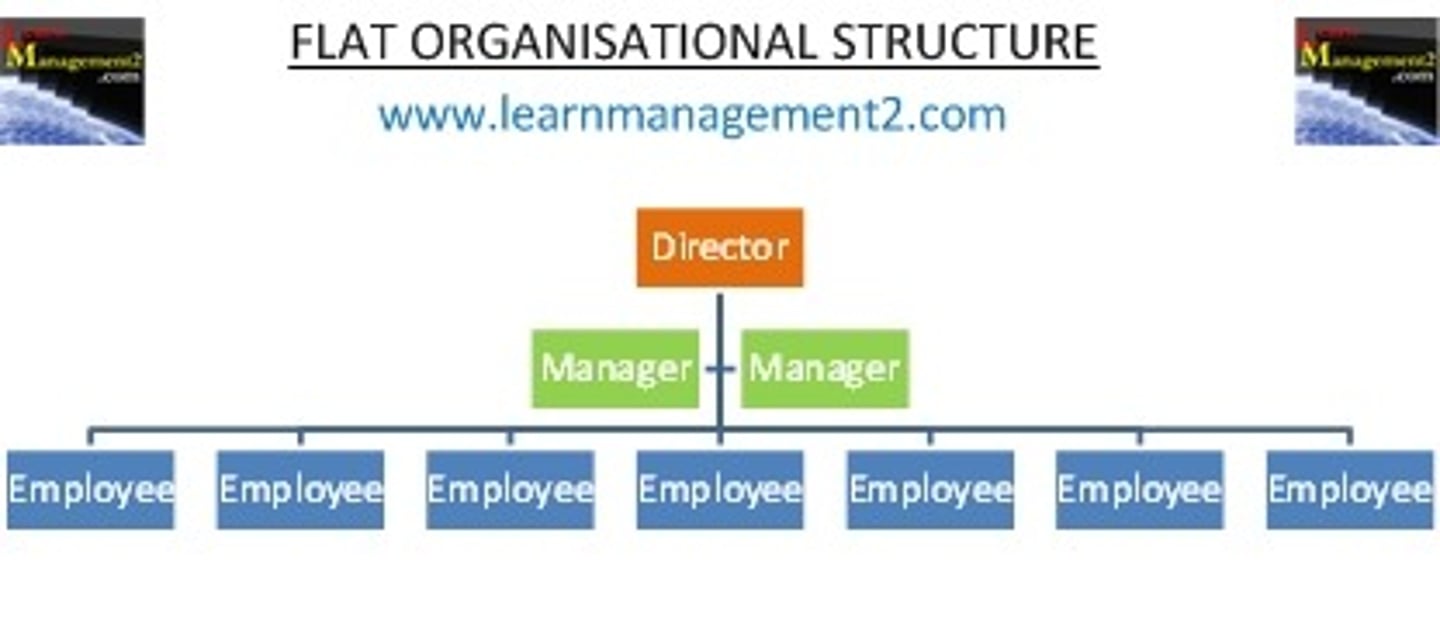
Flat Structure
Has a wide span, is horizontally dispersed, and has fewer hierarchical levels
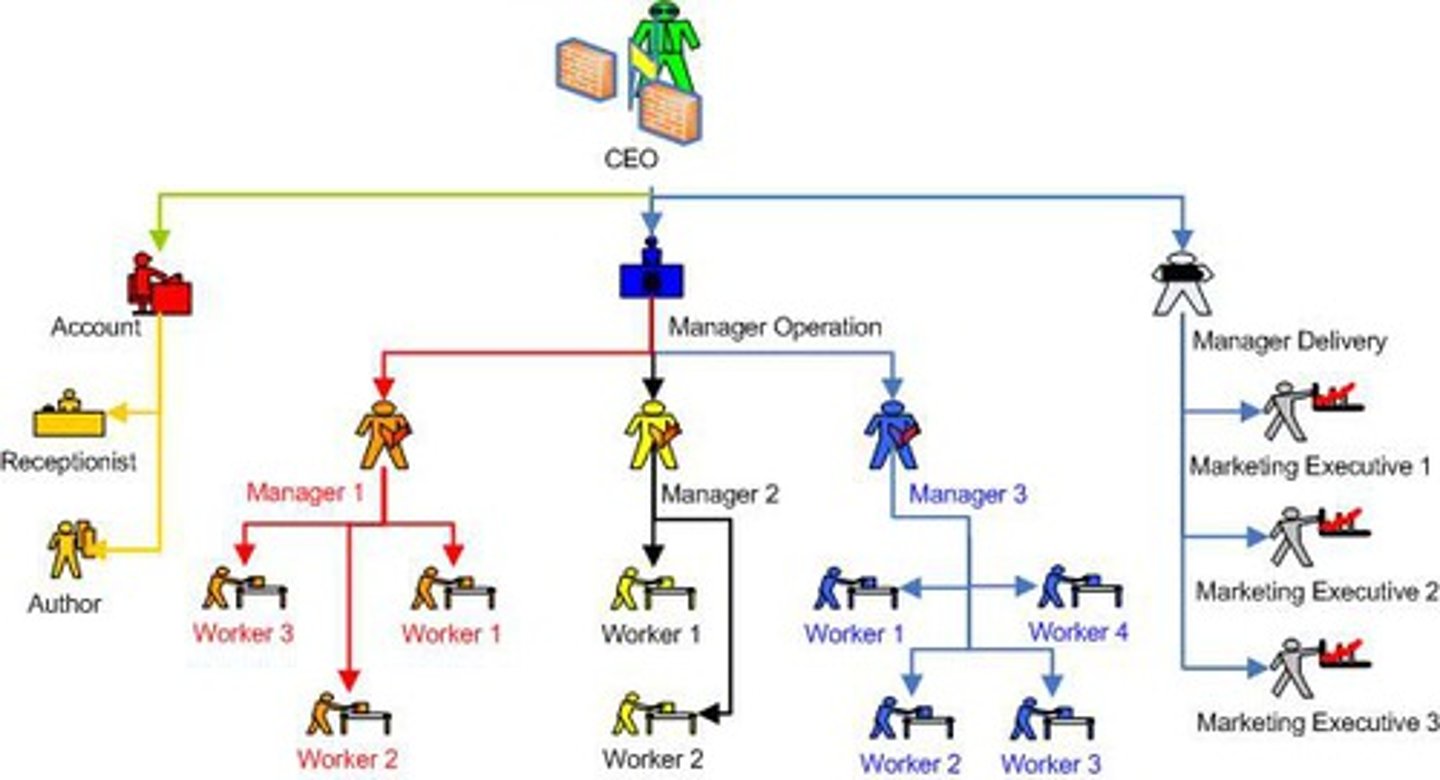
Matrix Structure
An organizational structure that simultaneously groups people and resources by function and by product.
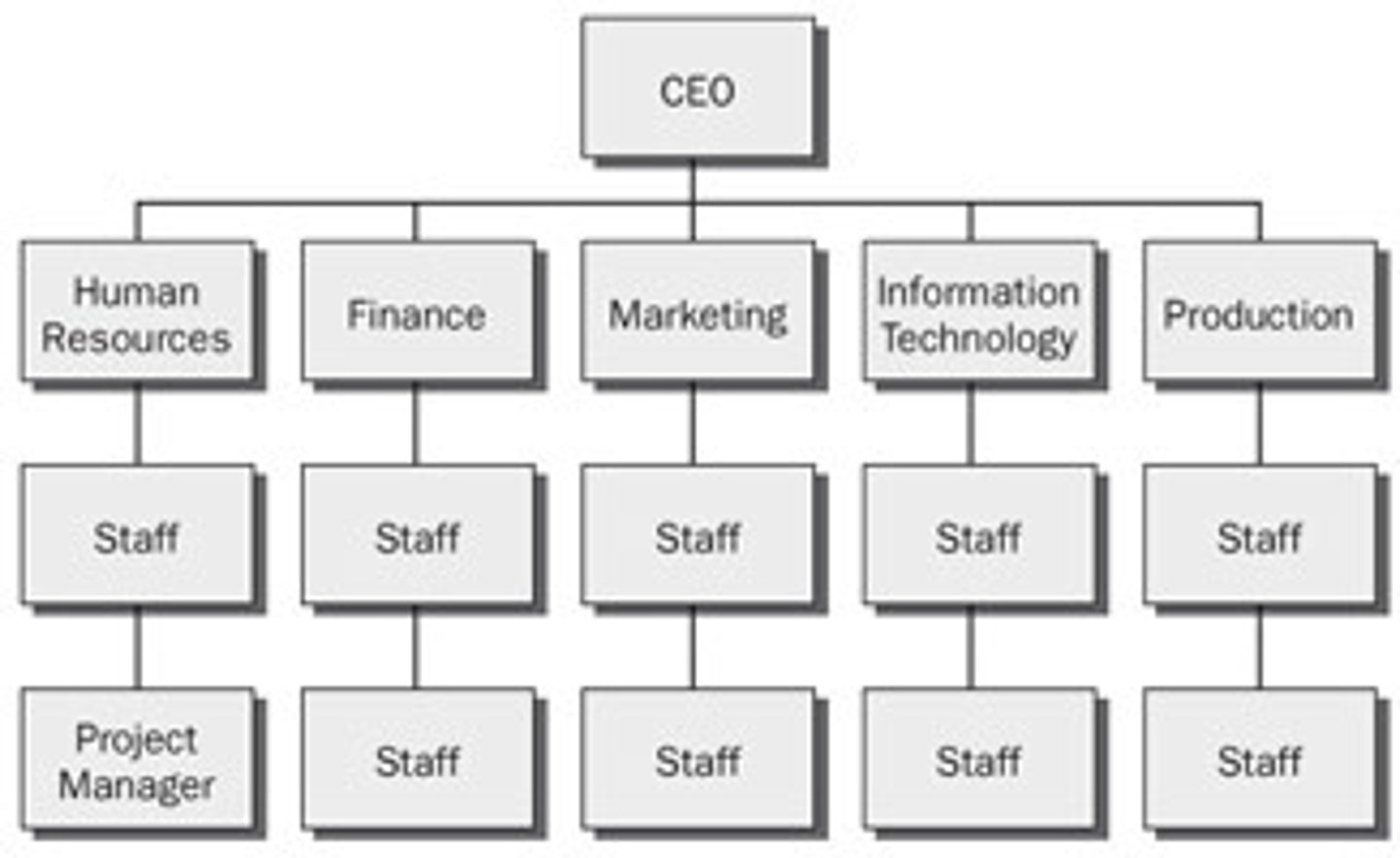
Hierarchical Structure
Shows a hierarchy of responsibilities and authority showing who is responsible for what and who has authority to make decisions regarding business operations
Secondary research sources
- Previous market research
- Trade journals
- Websites
- Books and newspapers
- Census data and public records
Security of information
Info should be kept secure in accordance with the nature and sensitivity of that information. There is a legal requirement to store info securely and there are rules dictating how info is stored and for what period of time
Legislative
It is vital businesses are up to date with the legal requirements around data storage. Data protection act 1998 is the main legislation they must follow
Regulatory and ethical issues
Businesses will need to ensure they are frequently monitoring impending changes to any legislation or regulation
Porters 5 forces
1. Existing competitive rivalry between suppliers
2. Threat of new entrants
3. Bargaining power of buyers
4. Power of suppliers
5. Threat of substitute products
5C'S
1. Customer
2. Company
3. Climate
4. Collaborators
5. Competitors
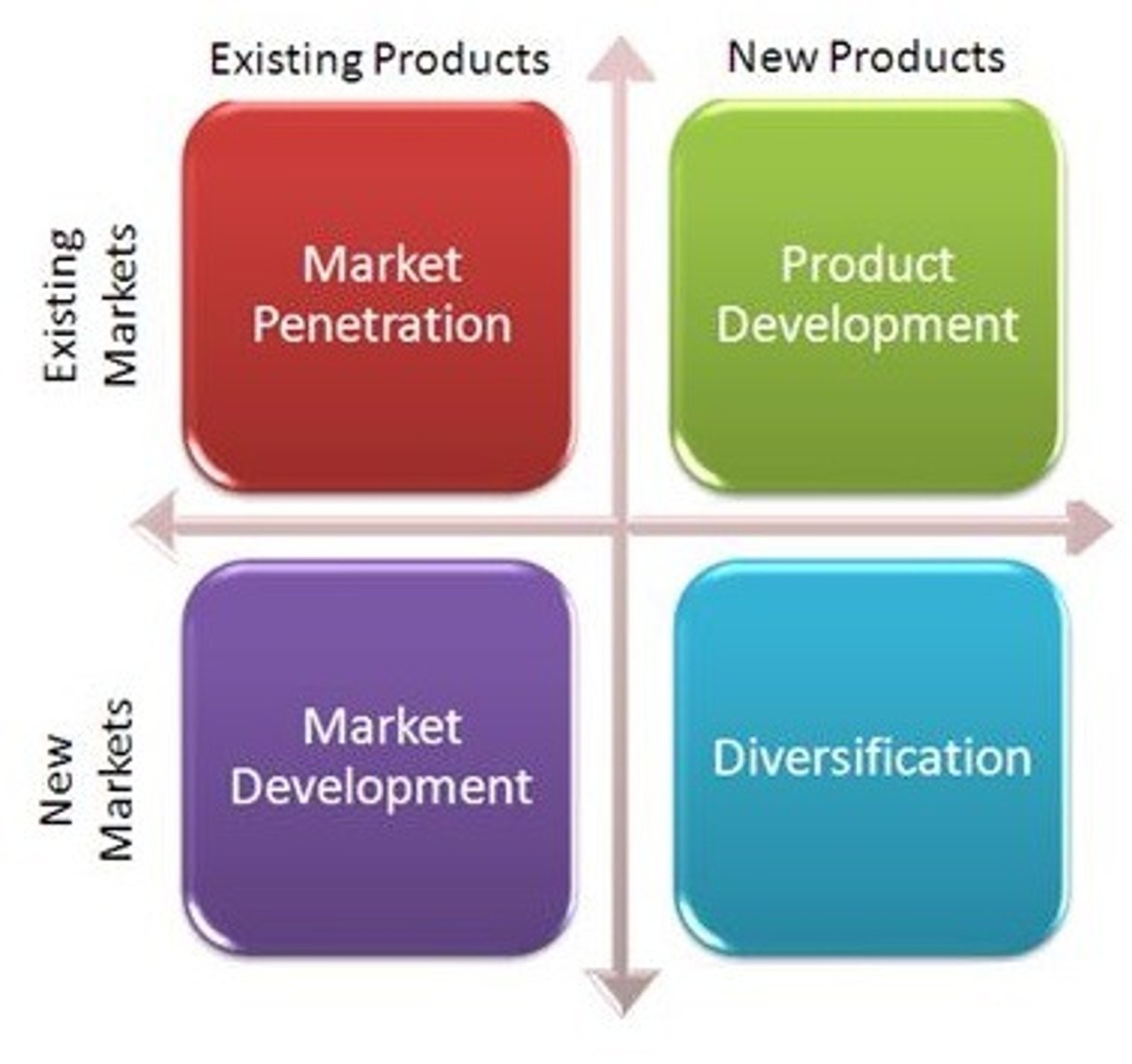
Ansoff matrix
This model is used to enable a business to make decisions about the opportunity for growth in the market place
Boston matrix
This model is used to aid the decisions making process by helping predict where a business should invest in the future.
The matrix helps with analysis concerned with market trends and considering the opportunities for increasing market share.
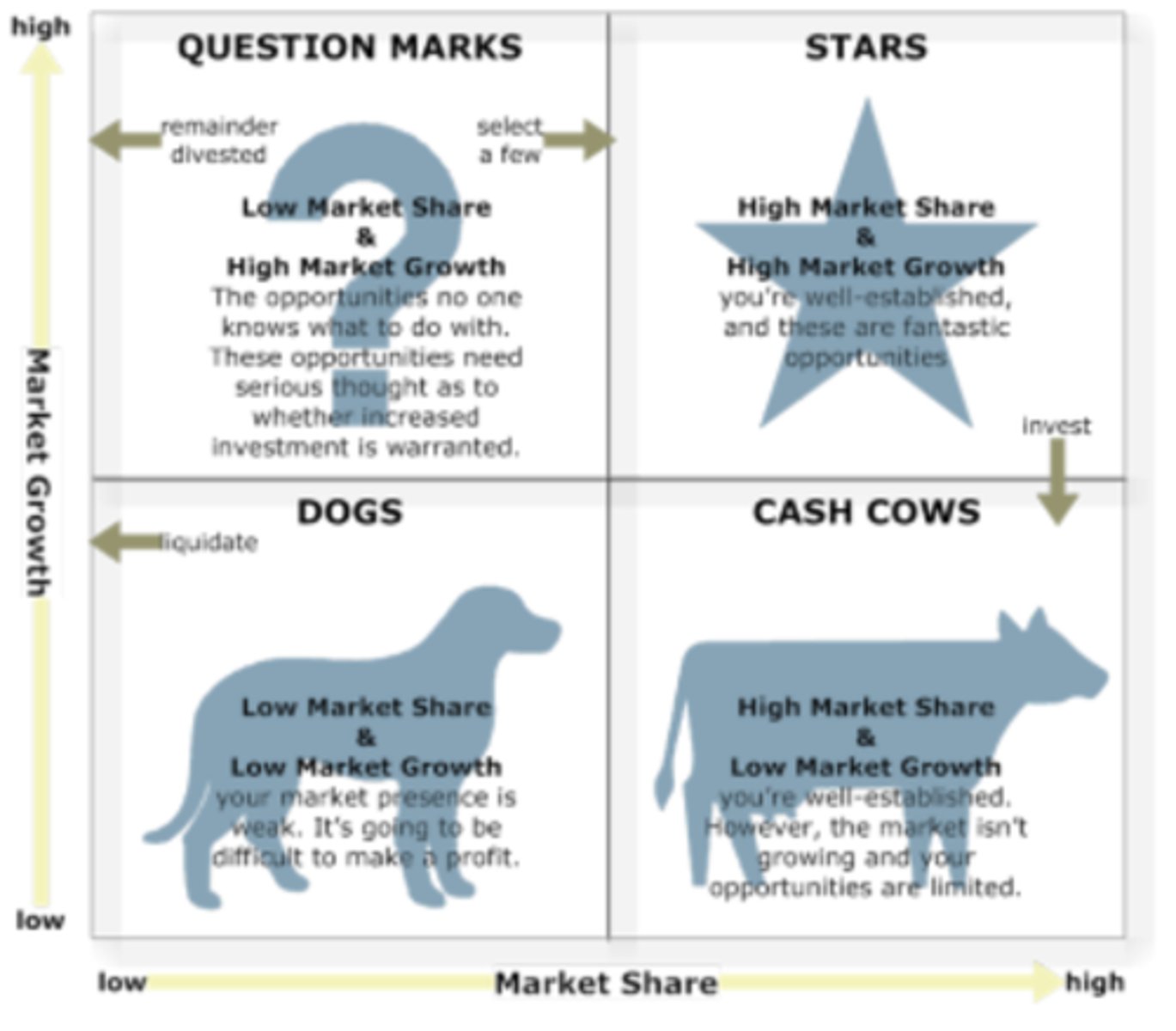
Boston matrix - cash cow
A product that has high market share but in a low growth market. They are successful, established products that won't require much investment
Boston matrix - stars
HIGH market share
HIGH market growth
needs investment to be profitable
Boston matrix - question marks
low market share, high market growth, little to no profit but could become a star or cash cows as they are in a growth market
Boston matrix - dogs
LOW market share
LOW market growth
little or no profit
frequency distribution
The number of times a set of values occur and the spread of occurrences over a range of situations
Measures of dispersion
This is the term given to the spread of the dataset and there are statistical methods for finding this out
standard deviation
Means the amount that the values vary beyond the norm.
Quartiles
Put the data in order of size, then divide the values into four equal parts
Percentiles
Percentile scores range from the 1st through 99th percentile, indicating the percentage of scores in the comparison group which are lower than the test taker's score
Correlation coefficient
a statistical index of the relationship between two things (from -1 to +1)
Economic trends
Electronic data on economic trends are available from numerous sites such as the office for national statistics
Market trends
Identify the movement of the investment market over time. These trends use financial data to forecast the direction for future investment by basing their predictions on past performance and where to place investments.
Social trends
The data collected is analysed by the ONS which provides info about the demographic of the UK population which is them compared with that of European countries and globally
7P'S
Product, price, promotion, place, people, process and physical environment
Health and safety 1974
- Safely dispose of chemicals
- Using ear defenders around loud noise
- making sure fire hazards are kept to a minimum
Data protection 1998
This act requires that personal data is not shared without the permission of the individual it relates to. Eight principles:
1. Fairly and lawfully used
2. Used for legitimate purposes
3. Adequate and up to date
4. Not kept for longer than necessary
5. Used in line with your rights
6. Secure
7. Not transferred to other countries without adequate permission
Employee rights act 1996
- Requirement to publish gender pay gaps
- National living wage
- Statutory paternal and sickness pay rates
- Protection for apprentices
- Illegal working
Consumer rights act 2015
Imposed set rules for:
- Refunds and timeframes
- Remediation options
- Replacements and repairs
- Additional items sold or provided with the item of interest
- Pre-contract info
Quality control (QC)
- How the quality of products and services are controlled through a series of consistent monitoring processes.
- In house set of procedures to check the quality is as they expect
Quality assurance (QA)
The process of planned checks which can also be designed as an in-house set of procedures.
Difference between QC and QA
QA is a component of QC procedures. The difference is that QC aims to locate incidences where quality is sub standard and requires improvement whereas QA is about maintaining confidence in the processes.
Benchmarking
The process of measuring a standard against what is expected
Quality circles
- A process for involving employees with problem solving and resolutions
- Can be really effective as it listens to the people most closely related to the issues
Self checking
This method relies on individuals to check they are meeting service standards set by the business.
ISO 9000
Provides a framework for quality processes and checks for consistency of standards across the business
TQM
Designed to involve the whole company in evaluating what works well and what it needs to improve.
Staff requirements for efficiency
Human resource:
- The types of decisions managers would make about the people they employ involves identifying skills required for each job and comparing them with existing or potential staff
Wages/salaries
Human resource:
- Businesses have to consider a number of different factors when deciding what pay to offer a job role e.g.
- The level of education/experience the role requires
- How many hours they're asking the person to work
- Should bonuses be included
Full time/part time
Human resource:
Managers need to make decisions about the arrangements for employing their staff whether fon a full time or part time basis.
Recruitment process
Human resource:
Decisions about:
- Duties that must be fulfilled
- Impact on existing staff
- Essential skills to undertake the work
- Desired skills
- Affordability for the right person for the job
- Availability of the person
Training requirements
Human resource:
Once staff have been recruited they are most likely going to need training to meet the expectations and efficiency that the business requires.
Each staff member will have different areas of training and different amounts needed
Premesis
Physical resource:
- Buy or rent a premises? depends on financial situation, forecasting, growth, flexibility requirements
Equipment required
Physical resource:
- Printer, laptop, phone, vehicle, business cards ext.
- Packaging?
big or small there is lots of equipment costs
Vehicles
Physical resource:
- Maintenance, tax, insurance, fuel to operate
IT hardware and software
Physical resource:
- All businesses require some form of dedicated hardware and software to manage their operations and this will require frequent maintenance and occasional updating.
Suppliers and cost of equipment
Physical resource:
- Sufficient funds need to be readily available to purchase the suppliers in order for the b8sines to generate revenue
Sources of finance
Financial resource:
- Hire purchase
- Donations
- Overdrafts
- Loans
- Mortgages
- Trade credit
- Share capital
- Leasing
Start up and running costs
Financial resource:
Include:
- Buying equipment
- Deposit for renting premises
- Staff wages
- Monthly bills for utilities
Cash flow forecasting
Enables a business to plan effectively for the incoming and outgoing of funds, such as revenue from sakes and payments that they need to go out on time.
Break even chart
Is a visual representation which demonstrates at what point the business is not making a profit or loss.
Fixed costs (breakeven chart)
Straight line horizontal
Variable costs (breakeven chart)
Starts at zero goes diagonal to the right
Total costs (breakeven chart)
Line starts from the fixed costs line because fc + vc = tc
Total revenue (breakeven chart)
Starts at zero - is based on revenue of the business depends how steep it'll be
Break even point (breakeven chart)
Where the total costs and total revenue cross is where the bep is
Income statement
Every transaction a business makes must be accounted for. The income statement will be used by businesses for many procedures, such as checking viability, calculating when to pay invoices, ensuring employee wages can be paid on time.
Ratio analysis
Allows for a more meaningful interpretation of published accounts by comparing one figure to another.
Liquidity ratio
(Current Assets - Inventory) / Current Liabilities
Profitability ratio
A profitability ratio measures the profitability of the business
Performance ratios
Measure how well a business turns its assets into revenue
Fixed asset turnover calculation
Revenue / value of property, plant and equipment
sales revenue per employee calculation
total sales revenue / total number of employees
Contingency plan
Provides an alternative solution or route to take based on the outcomes from analysis such as PESTEL, SWOT and other tools
Vision led
Clear image or procedures of how to deal with the situation
Plan led
Criteria or objectives are defined based on analysis of methods
Consensus led
Outcomes from discussions with other stakeholders
Legal (consideration of risk)
No control over the legal factors which are imposed on the business but they will impact on your decisions.
Reputation (consideration of risk)
The importance of building and maintaining the reputation of a business should not be underestimated.
Financial (consideration of risk)
A business must be aware of government intentions from the annual budget and reviews. The outcomes of these might include changes to the tax law.
Gross profit
Gross Profit is the amount of money left over (surplus) after the cost of sales has been removed from total sales revenue. This is not the business' final profit figure
Gross profit formula
Sales revenue - cost of goods sold
Profit/Loss for Year formula
Gross profit - expenses + other income
Income Statements
An Income Statement shows a business' income and outgoings over a shorter period of time.
Statements of Financial Position
A statement of financial position offers a snapshot of a business' financial situation, normally at the end of a financial year.
It is a summary of everything that the business owns (assets) and what it owes (liabilities), giving the business' overall value.
Non-Current Assets
A non-current asset is owned by the business and is an asset that will remain within the business for longer than one year.
Current Assets
Current assets are items owned by a business whose value can fluctuate on a regular basis (sometimes after every transaction). This includes;
Inventory
● Trade Receivables
● Prepayments
● Cash in the Bank
● Cash in Hand
Current Liabilities
A current liability is a debt owned by the business that should be paid back in under 12 months.
● Overdrafts
● Accruals (expenses paid after the period the expense relates to)
● Trade Payables
Net Assets/Liabilities
This is a highly important figure for a business as it tells them how able they are to meet short-term debts.
Working capital formula
current assets - current liabilities
Non-Current Liabilities
This is a debt that belongs to the business that is paid back over a long period of time (12+ months plus). This includes;
•Bank Loans
•Mortgages
Net Assets
Net assets is the figure that represents the total value of all assets after you have taken all liabilities into account
Net asset formula
total assets - total liabilities
Adjustments
Adjustments must be made to a Statement of Financial Position to keep the document accurate.
These adjustments include;
Depreciation
Prepayments
Accruals
Analysis of a Statement of Financial Position
Comparing figures (assets and liabilities) to understand the business' health
Comparing year on year with your own business or comparing with other businesses.
Comparing areas of the same business to measure management efficiency.
Ratio Analysis
Ratio analysis is a valuable tool for businesses to understand how profitable they are at any given time
Liquidity Ratio
The liquid capital ratio is a strict method of measuring a business' liquidity. This ratio includes the current level of inventory (stock) within the business.
Inventory is considered to be the hardest current asset to turn into cash quickly. This is also known as Acid Test.
Gross Profit Margin
This ratio looks at gross profit as a percentage of sales turnover. It shows us for every £ made in sales, how much if left as gross profit after the cost of goods has been deducted
Gross profit margin formula
Gross Profit x 100 / Revenue
Net Profit Margin
This ratio looks at net profit as a percentage of sales turnover. For every £1 made, the amount remaining after paying all expenses is net profit.
Net Profit Margin formula
Net profit / revenue x 100
Mark-Up
This ratio looks at profit as a percentage of cost of sales. It shows what percentage of cost of sales is added to reach selling price.
Mark-Up formula
Gross profit / cost of sales x 100
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)
ROCE shows the percentage return a business is achieving from the capital being used to generate that return.
It shows, for every £1 invested in the business, what % is being generated as profit.
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) formula
Net profit / capital employed x 100
Fixed Asset Turnover
This ratio informs the business of how much revenue they are generating from their fixed assets.