patterns of global climate change
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
biosphere
All life on earth
hydrosphere
all water on earth
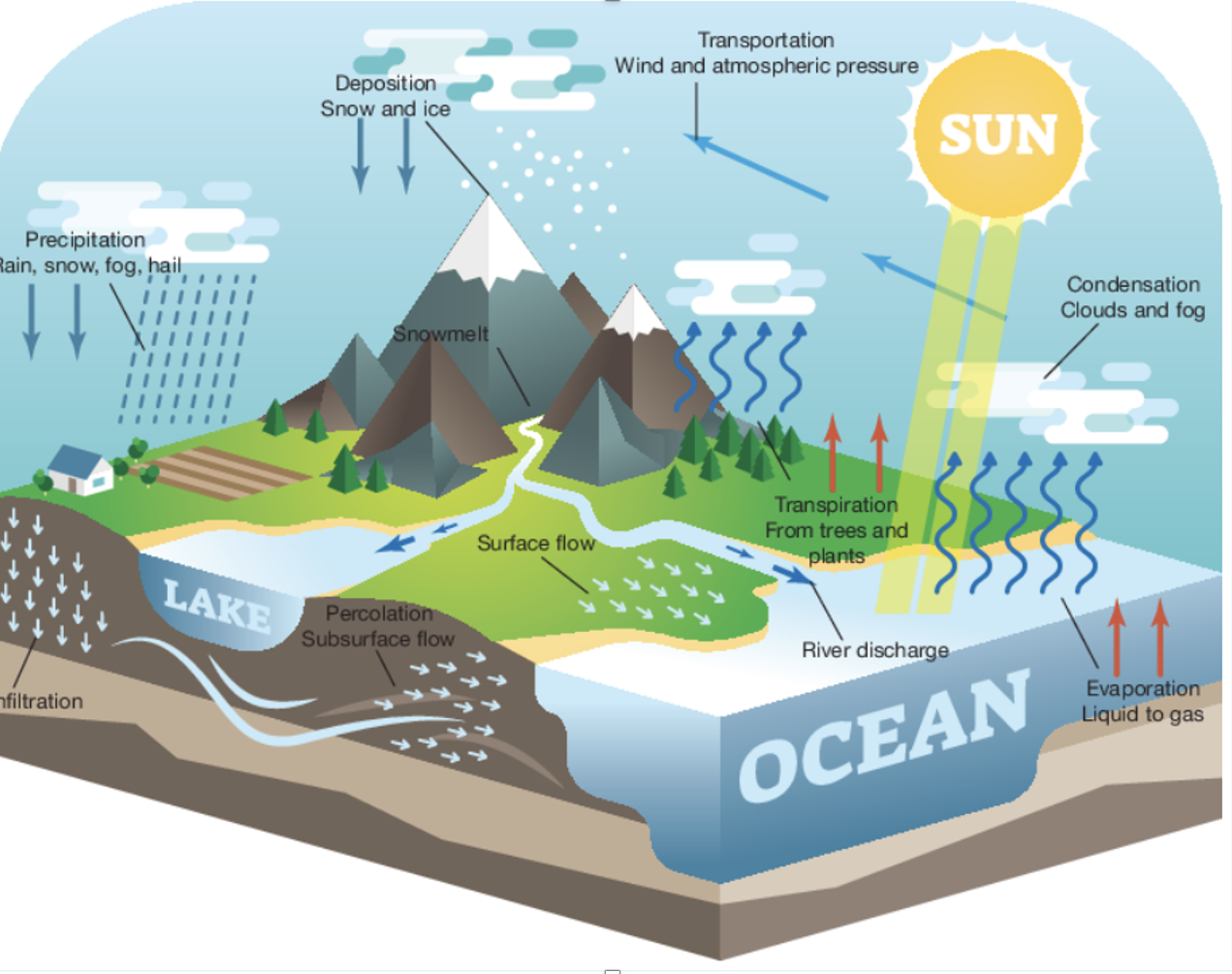
water cycle
movement of water through earths spheres
lithosphere
earths crust: rocks, dirt
atmosphere
layer of gases surrounding earth. divided into troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere
carbon cycle
how carbon moves through the biosphere. Carbo is present in hydrosphere (dissolved CO2), lithosphere (fossil fuels and rocks), atmosphere (methane or CO2) and living things (proteins, carbohydrates, lipids)
photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
cellular respiration
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + ATP
nitrogen cycle
How nitrogen moves through the biosphere. Nitrogen is important because cells use it to make DNA, proteins and chlorophyll
phosphorous cycle
how phosphorous moves from the lithosphere to the hydrosphere and through food chains
human impact on cycles
main detrimental factors include deforestation, mining, CFCs, population increase, industrial wastes, travel
Deforestation
more CO2 due to less photosynthesis, increased desertification, negative impact on cycles
Mining
land clearance, waste materails
CFCs
damage ozone layer, greenhouse gas that traps more heat than CO2
Population increase
deforestation, more livestock → more methane
industrial waste
sulfur dioxide and nitrous oxides can react with water vapour to form acid rain
travel
most travel options release CO2
climate patterns
regular patterns of seasons, weather, temperature and rainfall.
earths tilt
23.5 degrees, affects length of daylight in an area.
land vs water heat absorption
during the day land absorbs heat faster than water. At night, land loses heat faster than water. Ocean temps are more stable.
land features
temp is lower the higher above sea level you are. Sandy soil, fresh snow reflect heat, dark soils and vegetated areas absorb heat.
ocean currents
warm water near equator sinks and cools while moving towards poles, cold water from poles rises and warms while moving toward equator. Increased CO2 warms ocean, causing change in currents
wind
temp differences between tropics and poles cause convection currents that create wind.
La Nina
stronger trade winds move warm water from the east further to the west than normal. This causes an increase in rainfall in Australia
El Nino
winds weaken and reverse, sending water and wind east. This causes warmer, drier weather in australia
greenhouse effect
gases trap heat in atmosphere