Actin filaments
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Monomer
ATP-actin (G-actin)
*assembles into filaments
Associated motor protein
myosin
Broad function
motility, contractility (muscle)
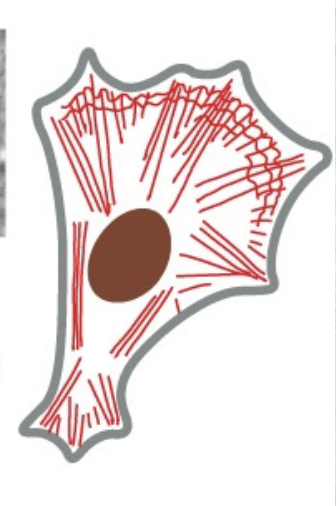
placement of actin w/in a cell → form outline

Actin monomer
disassembly, ADP-G-actin = (-) end
assembly, ATP-G-actin = (+) end
How does the interconversion of the nucleotide state affect assembly/disassembly of actin subunits?
ATP-G-actin binds to the plus end (growing nearly x10 faster than the minus end)
ATP hydrolysis can’t keep up with the plus end/lags behind, but catches up with additions of ADP-F-actin on the minus end (bound less tightly and eventually released)
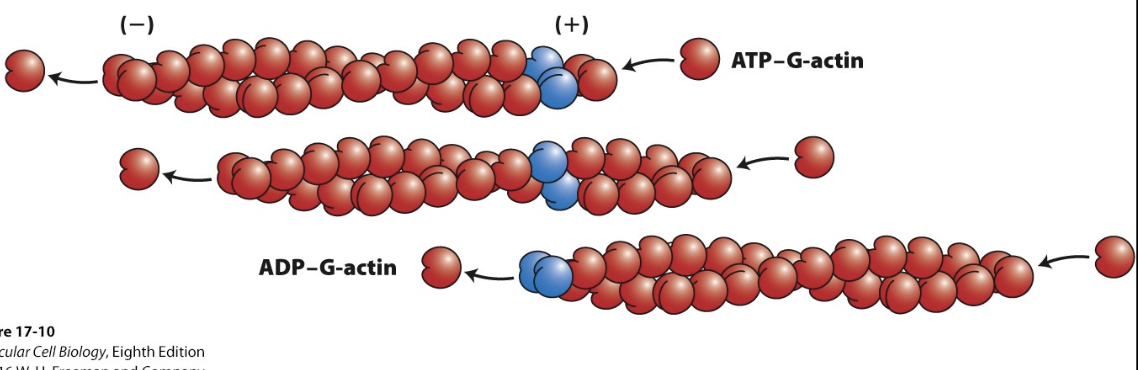
movement of actin → treadmills backward (from + to - end)
*subunits add predominately to filament + ends
What would happen if a mutation prevented actin’s ability to bind ATP?
there would be no assembly and disassembly would occur until it reaches the critical concentration
What would happen if a mutation prevented actin’s ability to hydrolyze ATP?
the filament would assemble (G-actin → F-actin), there would be no disassembly
*filaments will continue to grow
Profilin
binds to free subunits to assist w/ association to growing filaments
*promotes actin assembly and controls assembly @ the plasma membrane
Thymyosin
binds to free subunits to prevent their association to filaments
Cap Z
blocks gain/loss of actin @ + end
*allows elongation/dissociation @ - end
Arp 2/3
nucleates assembly to connect filaments together in a branching formation
Tropomodulin
blocks gain/loss of actin @ the - end
*allows elongation/dissociation @ the + end
Cofilin
promotes depolymerization in established filaments
*cleaves actin by twisting adjacent F-actin monomers in the filament
What properties do all myosin types share?
*associated motor protein
20 different types
structure → common head and specific tail domains
2 heavy chains (w/ ATP binding sites)
2 copies of each 2 light chains
What makes the types of myosin different?
some move towards the (+) end → I, II, IV
some move towards the (-) end → (only VI)
Myosin II
only myosin capable of producing contractile force
forms bipolar filaments → can pull actin in 2 directions @ once (others only move in 1 direction towards a pole)
Cross bridge cycle
a myosin head w/o a bound nucleotide is locked tightly onto an actin filament (rigor configuration)
ATP binds to the cleft on the back of the head → conformation change of actin-binding site
reduces the affinity of the head for actin allowing it to move along the filament
the cleft closes around the ATP → causing the head to cock back
ATP hydrolysis occurs, but the ADP and Pi remain bound to the actin
weak binding of the myosin head to a new site on the actin causes release of Pi and tight binding of the head to actin
release triggers power stroke → generates force, the head loses its bound ADP (starts new cycle)
@ the end, the myosin head again locks tightly to actin in rigor conformation
How does ATP hydrolysis lead to mechanical movement w/in a sarcomere?
the ADP and Pi remain bound to actin
weak binding of the myosin head to a new site on actin → release of Pi and tight binding of head to actin
release triggers power stroke/force-generating change
head loses bound ADP and locks tightly to actin in rigor conformation (starts over)
Skeletal muscle
Ca2+ binds to troponin, moving tropomyosin and uncovering actin → allows myosin to bind → mechanical action
Smooth muscle
Ca2+ binds to calmodulin → activates/binds to myosin light chain kinase → phosphorylation of MLC → contraction
How are smooth and skeletal muscles similar?
contractions are triggered by an increase in cytosolic Ca2+
What happens during asthma attacks?
phosphorylation of MLC kinase by PKA inhibits MLC kinase activation by Ca2+/calmodulin
Why is albuterol useful for treating asthma attacks?
PKA adds inhibitory phosphate onto MLC kinase → prevents association w/ Ca2+/calmodulin
no association = no activation of MLC kinase
no phosphorylation of MLC = no filaments and no association w/ actin to cause contraction of smooth muscle cells
What does a migrating cell need to move in specific directions?
must use extracellular cues to establish which portion of the cell acts as the front/back ends
GTPase proteins (cellular migration)
cdc42, Rac, Rho
Cdc42
establishes filopodia and polarity/directionality in the cell @ the leading edge
Rac
changes extend and establish the front/leading edge of the cell
Rho
changes contract the rear end of the cell towards the middle
*keeps polarity in the front
How are Rac and Rho related?
they mutually inhibit one another
are either highly expressed/constitutively active in invasive cancers
Scratch assays
detect the rate of migration of cells growth in a dish
Compared to healthy cells, what would you expect to see in a scratch assay of cancerous cells?
increased wound closure/migration
Process of cellular migration
1) Arp2/3-dependent mechanism extends one or more lamellipodia @ leading edge
2) lamellipodia adhere to substratum by formation of focal adhesions → integrin connect actin and ECM proteins (fibronectin, collagen)
3) actin-myosin II-dependent contraction @ rear end propels bulk of cytoplasm forward
4) deadhesion and endocytic recycling @ back of cell → trailing edge stays attached to substratum until tail detaches; membrane/integrins @ rear of cell and transports to front for reuse in making new adhesions
Actin assembly
can produce force for movement
When does the power stroke occur?
during the release of Pi
Microtubules
polymers of tubulin, basis of mitotic spindle
Microfilaments
composed of actin, contribute to shape/organization of plasma membrane (eukaryotic cells)
IFs
only type of cytoskeletal filament not used as tracks by motor proteins