Medsurg 1 (CH 5) - Neurological Disorders PT 1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
LOC assessments
- Alert --> able to concentrate, spontaneous eye movements
- Lethargic --> responsive to voice unable to concentrate/awake
- obtuned --> responsive to touch, AOx1-2
- stuporous --> responsive to sternal rub, unable to awake
- coma --> unable to arise for a long time period
mental status assessments
- appearence
- behavior
- speech
- thought process
- mood
- cognitive ability
behavior observations
- posture/gait
- facial expressions
- eyes
- affect
mental status vs LOC assessments
- LOC = glassglow coma scale, determining state of arrousal
- mental status = direct relationshiop, LOC assumes mental status level. affect of a person
Glassglow coma scale assessments
determines LOC based on 3 subclasses (eyes, speech, motor)
- lowest score = 3 (deep coma state)
- highest score = 15 (fully alert state)
- <8 score = high comatose risk
glassglow coma scale EYE grading
EYES: grading 4-1
- 4 = sponatneous
- 3 = to speech
- 2 = to pain
- 1 = nonresponsive
glassglow coma scale SPEECH grading
SPEECH: grading 5-1
- 5 = AO
- 4 = confused
- 3 = inappropriate responses
- 2 = incomprehensable
- 1 = non-responsive
glassglow coma scale MOTOR grading
MOTOR: grading 6-1
- 6 = obeys commands
- 5 = localized pain to commands
- 4 = withdraws from pain to
- 3 = decorticate
- 2 = decerebrate (mental status is reverting back to fetal responses EMERGENCY)
- 1 = non-responsive
Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE)
mental status assessment grading out of 30 based on 5 subclasses
- lower the score = severe impaired mental state
- orientation (AOx0-4)
- registration (immediate memory)
- attention/calculation
- recall (short-term memory)
- language and visual skills
national institute of health stroke scale (NIHSS)
mental status assessment to determine neurlogical function for suspected stroke
- determines severity
- LOC
- facial drooping
- arm/leg strength
- speech/language abilities
- AO grading
altered LOC causes
- traumatic brain injuries
- stroke
- infections (MENINGITIS/ENCEPHELITIS)
- metabolic disturbance
- overdose
nursing priorities for altered LOC assessments
- ENSURE AIRWAY
- neuro checks frequently
- determine baseline altered LOC/mental status
- baseline vitals
- safety assessments
CT scan education
- series of X-ray images on different angles/areas of the body. shows cross-sectional imaging of body
- lay fat on a table
- doughnut shaped machine scans body/rotates around you
- takes 10-15MIN
nursing priorities for CT scans
- reduce anxiety
- educate to remain as still as possible
- education radiation risk
primary use for CT scans
- trauma injuries
- bone fractures
- tumors/growths
- heart disease
- vascular disease
- biopsy
- infections
MRI pt education
magnetic scanning of the body,
- can be very claustraphorbic for some people/LOUD
- must not have any metal at all
- takes 45MIN-1HR
primary use for MRI
- aneurysm
- MS
- stroke
- spinal disorders
- tumors
- blood vessel issues
- join/tendon anxiety
nursing priorities for MRIs
- minimize anxiety
- assess for any metal in or on body
- educate to remain as still as possible
- assess problems addressed on MRI
X-RAY pt education
quick/painless procedure uses X-Rays to look at dense images in the body (AKA: bones, growths, swallowed items, poop)
- takes 10-15MIN
primary use for X-RAYs
- bone fractures
- orthoitis/osteoporosis
- infections
- growths/cancer
- swallowed items
- digestive tract issues
nursing priorities for X-RAYs
- minimize pt anxiety
- educate importance or procedure
- educate risk of radiation exposure
ultrasound pt education
use of a small remote uses high frequency sound waves to look at imagines of the body
- use of gel/lube is applied to skin to get clearer image of inside body and protect the skin
- takes 30MIN-1HR
primary use for ultrasounds
- gallbladder issues
- lumps/growths
- pregnancy
- genital/prostate issues
- biopsies
- blood flow issues
- joint inflammation
PET scan pt education
use of radioactive drugs/dye is inserted into the blood stream in order to show scans of organ/tissue functioning
- tracker can be ingested or via IV
- takes 1 1/2 - 2HRs
primary use for PET scans
- cancer
- heart disease
- CAD
- alzhiemers (pinpoint origin)
- seizures (pinpoint origin)
- epilepsy (pinpoint origin)
- parkinsons
- stroke
nursing priorities for PET scans
- do not eat 4-6hrs before procedure
- assess swallowing/aspiration risk
- assess IV patency
- allergy assessments
- pt positioning: supine (lying on their back) with arms above their head
ICP education
increased intracranial pressure (normal limits = 0 - 10)
- buildup of pressure in the skull damaging the brain
- 15> upper limits (very dangerous)
CAUSES:
- stroke (ischemia)
- increased edema
- decreased cerebral perfusion
- brain tissue death
causes of ICP
- trauma to head
- metabollic reasons
epilepsy education
reacurring seizures <24HRs APART commonly caused by chronic underlying conditions
CAUSES:
- cerebral vascular disease
- childhood fevers
- MENINGITIS
- brain tumor
- head trauma
- HYPOGLYCEMIA (metabollic changes)
- hypoxemia
epilepsy s/s
- loss of consciousness
- muscle stiffness/jerking
- staring spells
- confusion
- unusal sensory changes (touch, auditory, smell, visual)
nursing priorities for epilepsy
- safety assessment's
- maintain airway
- pos-seizure education
- determine underlying triggers for episodes
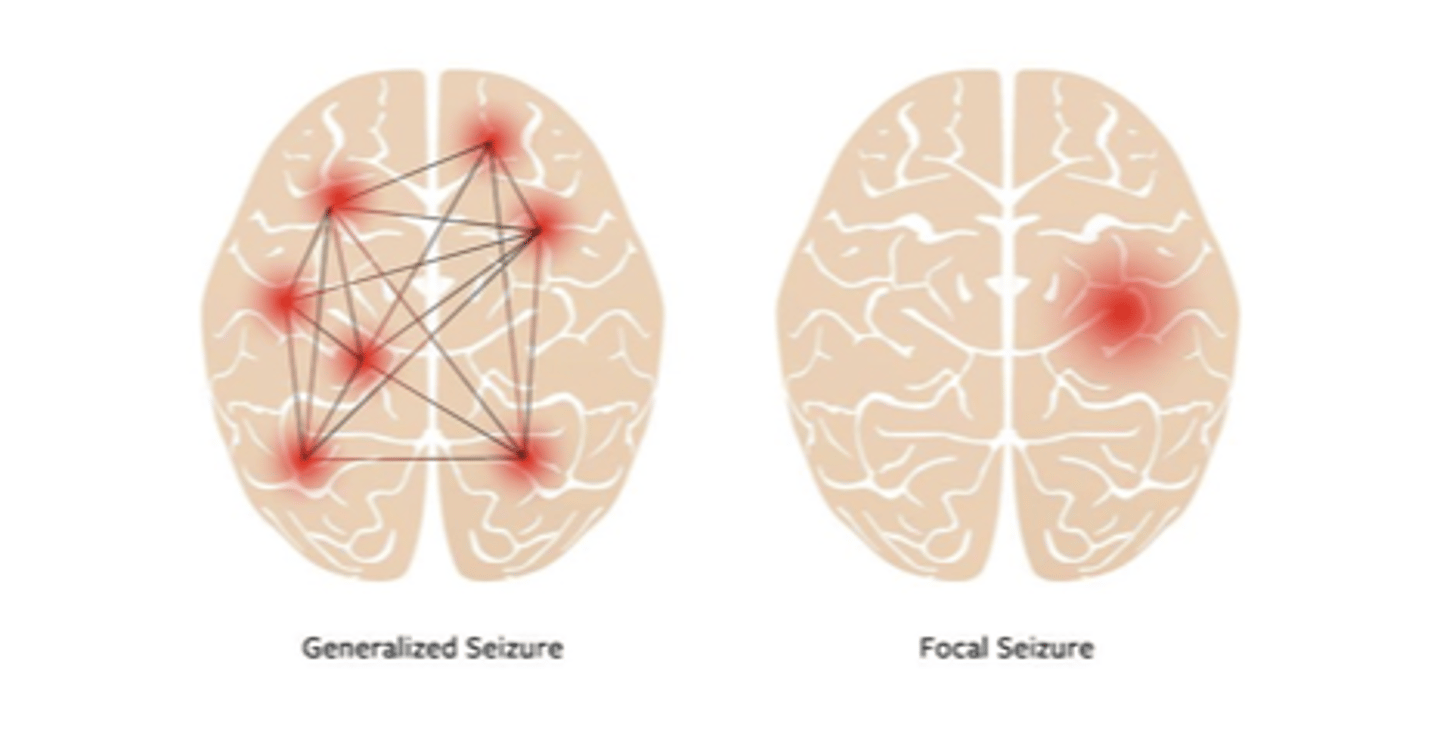
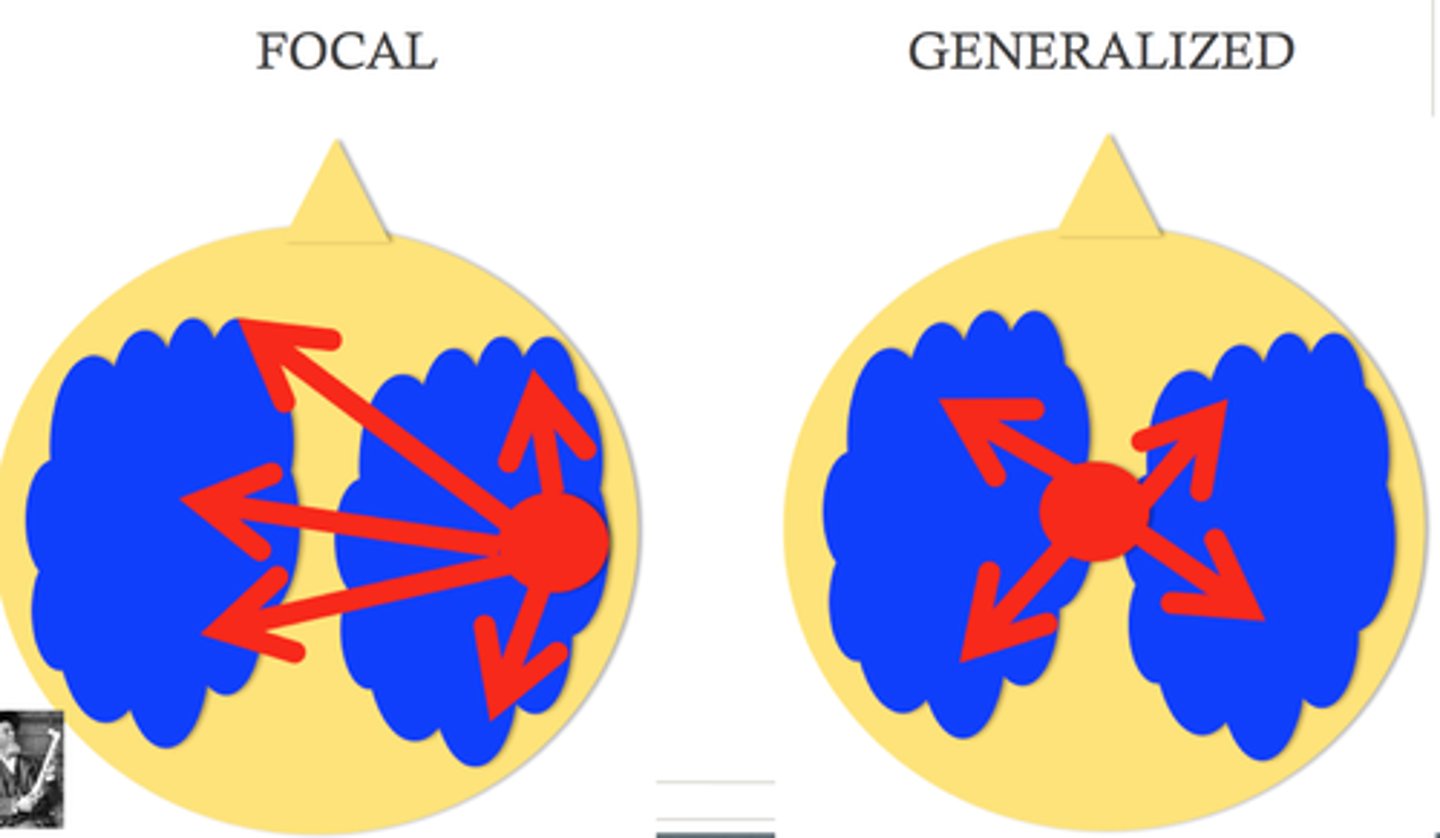
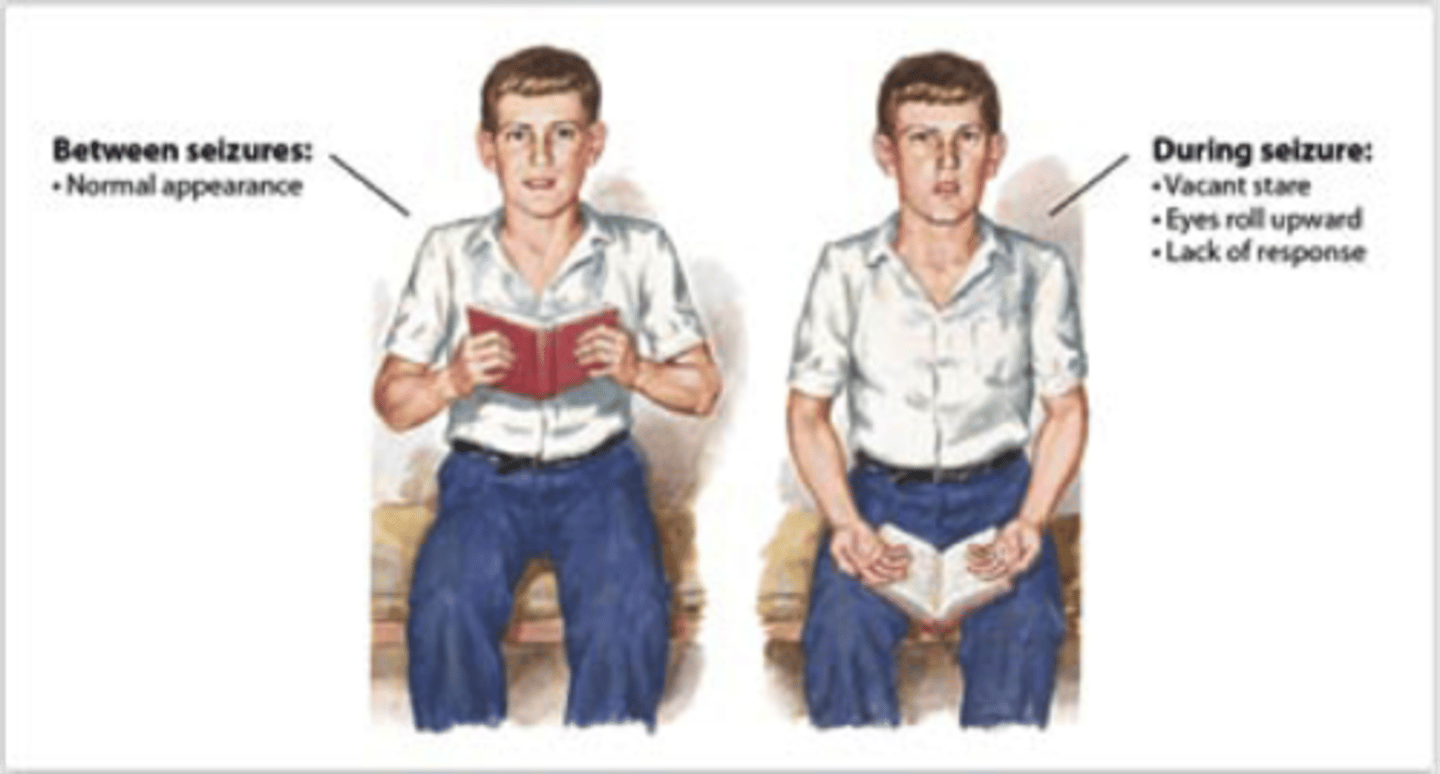
focal seizure classification
potential onset symptoms --> start on one side of brain (symptoms SOMETIMES affect awareness)
- focal-aware seizures
- Focal-impaired awareness seizures
focal-aware seizures s/s
- person is conscious/appears awake
- specific body part twitching
- fear/anxiety
- sensory changes
focal-impaired awareness seizures s/s
- alerted conciousness, appears awake but is not responsive
- confusion
- sensory changes
- difficultly responding
- memory loss
- repetitive movements
- lip-smacking

generalized seizure classification
starts on both sides of the brain, loss of consciousness, severe symptoms typical of what people expect seizures to look like --> (ALWAYS LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS)
- lasts >2min
- > 5min = status epilipticus
- recovery phase lasts hrs, sleepiness = hrs
types:
- tonic clonic seizure
- abscence seizure
- myoclonic seizure
- atonic seizure
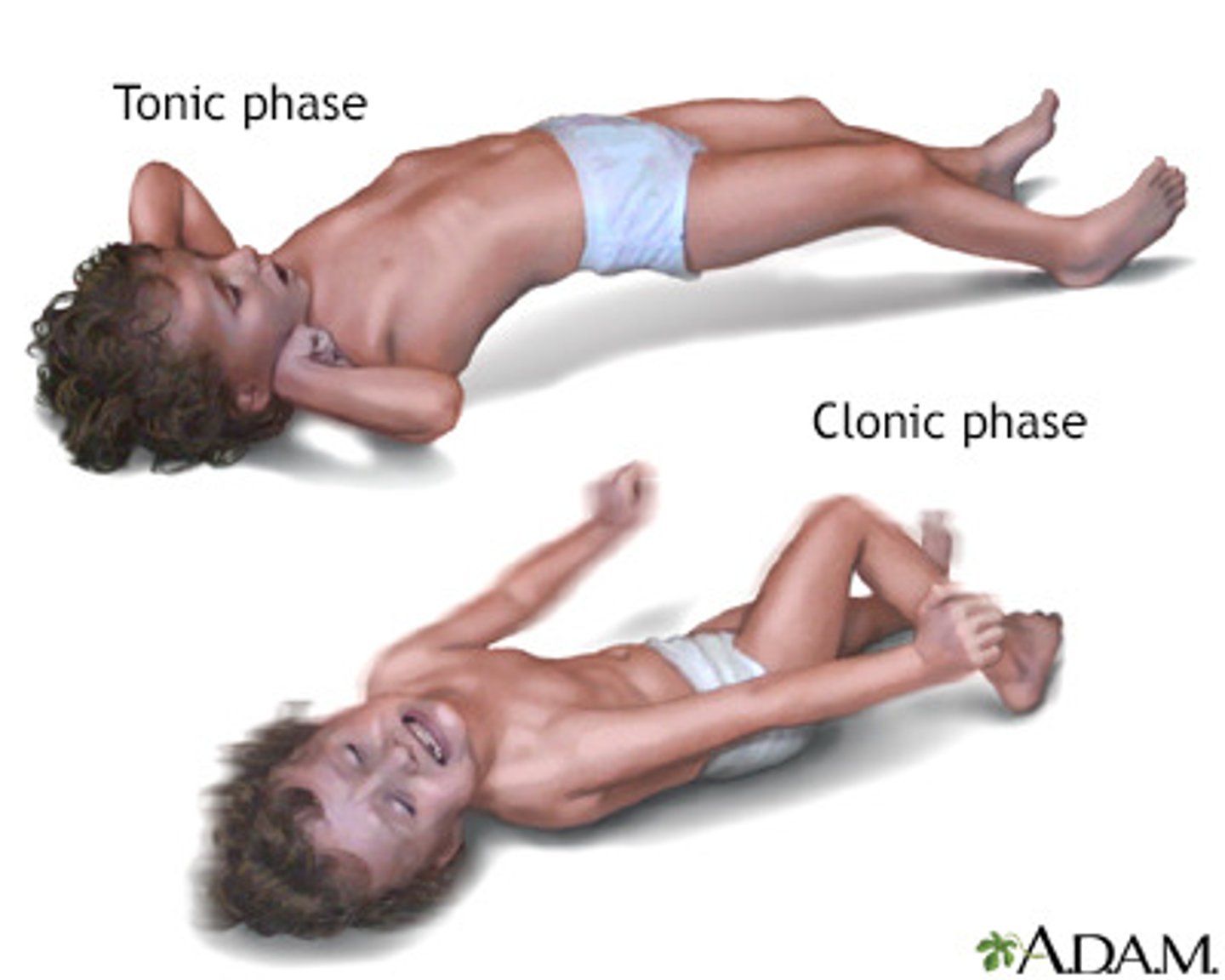
tonic clonic seizures s/s
- stiffening and jerking movements
- loss of consciousness
- moaning/painful sounds
- frophing at the mouth
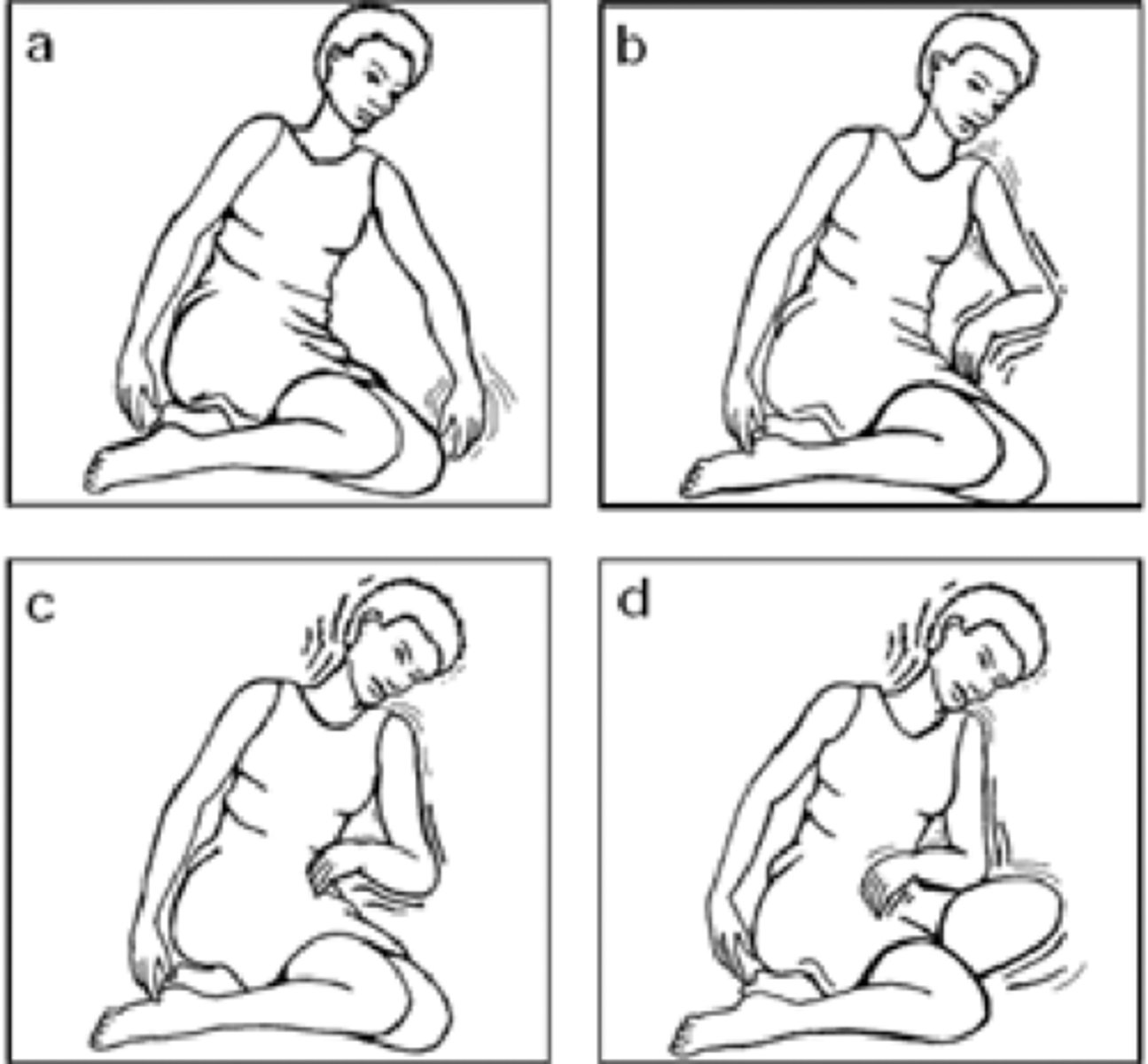
absence seizures s/s
- brief staring spells
- rapid facial movements/blinking
- short/onset symptoms
myoclonic seizures s/s
- sudden uncontrolled muscle jerking
- can occur in clusters
- frequent falls
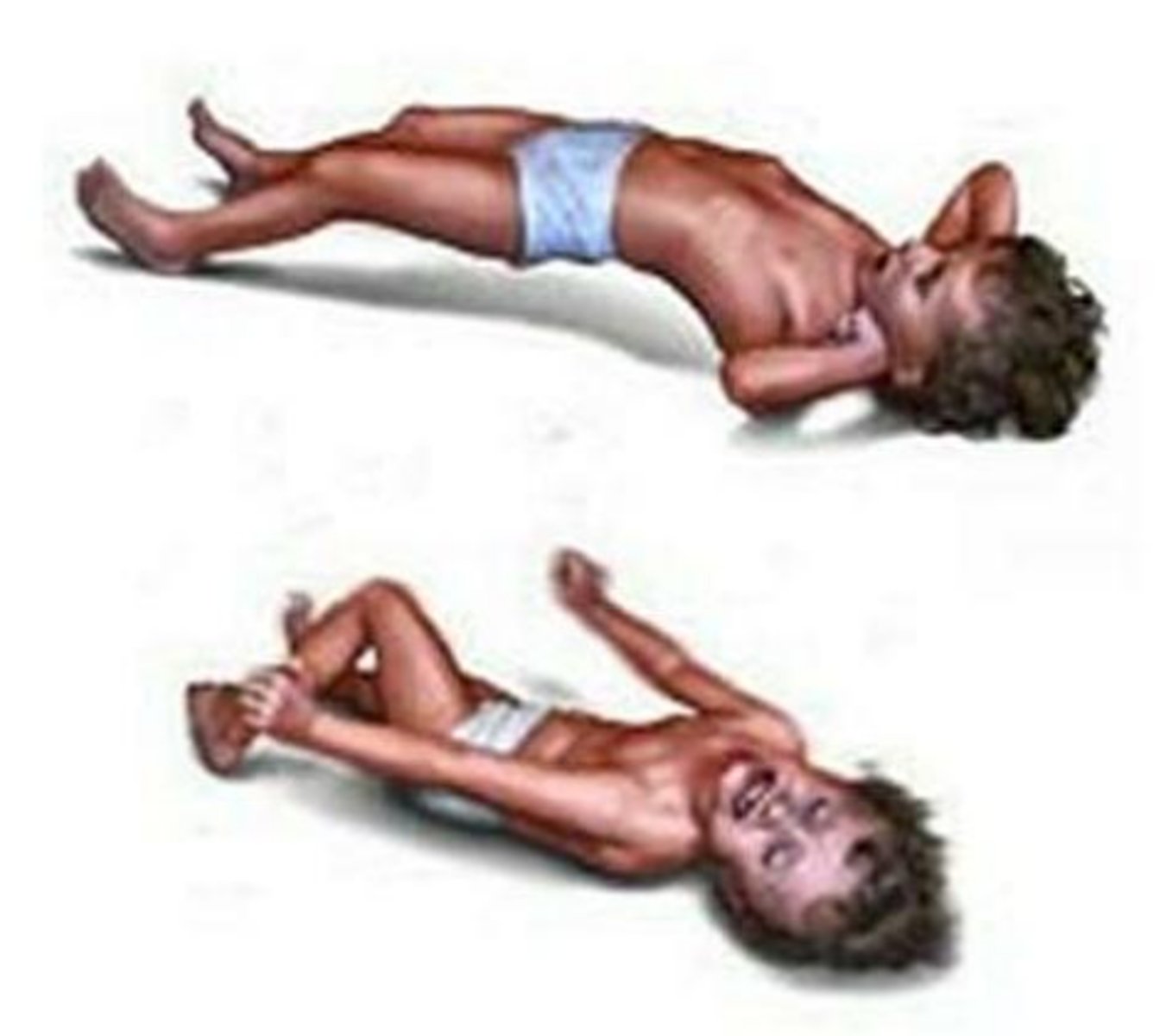
atonic seizures s/s
- sudden brief shocks of muscle jerks
- unable to move
- sudden falls/droping objects

nursing priorities for seizures
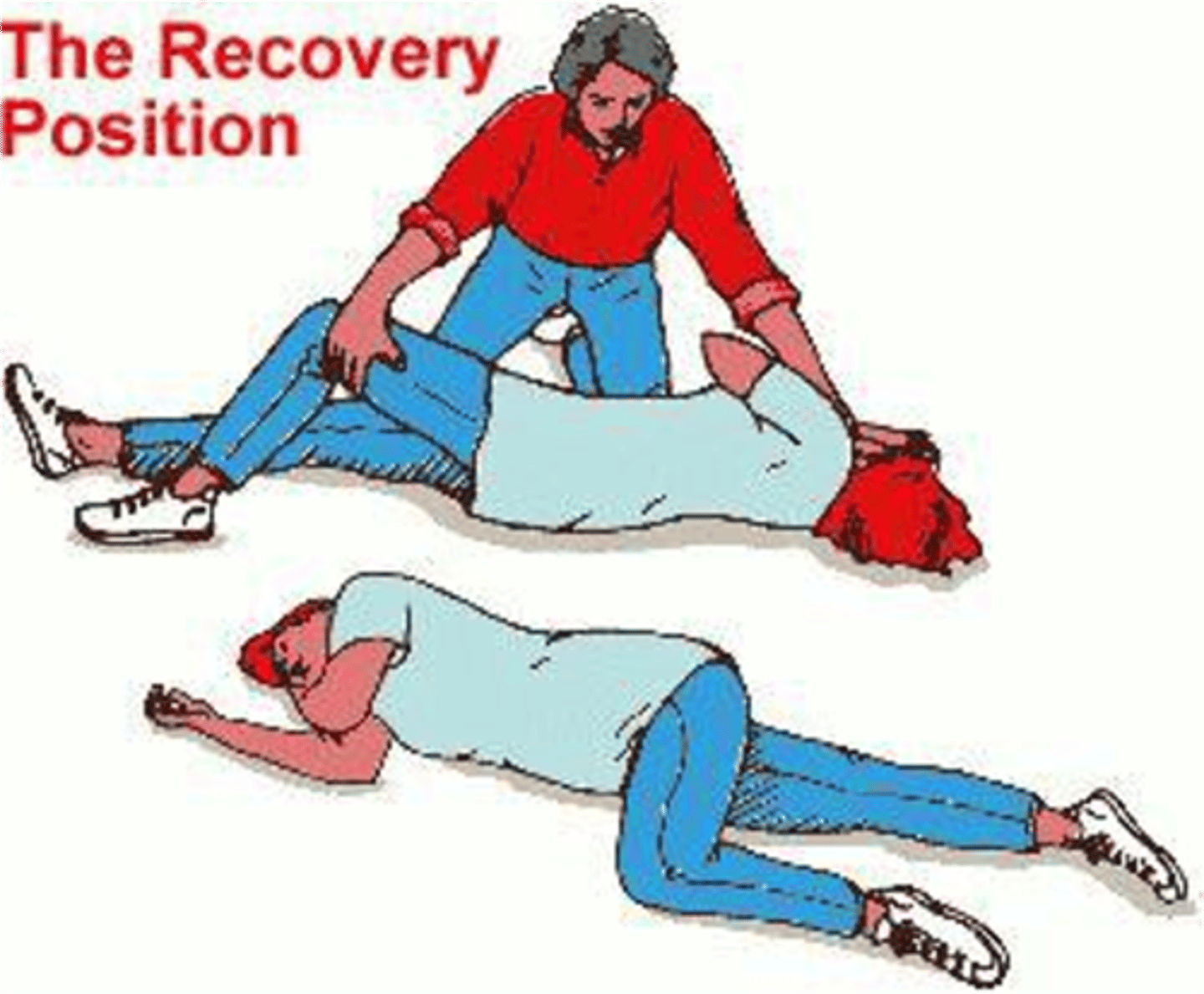
RECOVERY POSITION: promotes drainage + ensures airway
- bend the arm nearest you, raising it above head.
- other arm goes across their chest
- Bend your knee farthest from you
- mouth pointing downward
- clear surroundings
- Prepare to administer O2
- respiratory assessments post-seizure
- documentation
seizure education
uncontrolled neurological impulses causing a change in LOC, memory, behavior, and feelings
CAUSES:
- cerebral vascular disease
- Childhood fevers
- MENINGITIS
- brain tumor
- head trauma
- HYPOGLYCEMIA (metabolic changes)
- hypoxemia
status epilipticus education
continuous seizure state >5MIN --> MEDICAL EMERGENCY
- PRIORITIZE stopping the seizure
- WHY STOP? =
status epileptics nursing priorities
- ABCs --> MAINTAIN AIRWAY
stopping the seizure:
- IV vavlium/ativan
- IV phenytonin
- pt positioning promoting drainage
- anticipate invasive airway methods
diagnostic priorities for seizure care
- EEG 24HRS WITHIN SEIZURE + repeat
- MRI/CT/PET scan/MRA
- labs ruling out metabolic issues
EEG education
Multiple electronic wires are connected over the entire head via gel/pads to look at electrical activity in the brain
- takes 1HR
- must remain completely still
- flashing lights/buzzers = risk seizure precautions
EEG pre procedure care
- shampoo/wash hair before
- NO caffeine 24- 48hrs
- withhold non-compatible meds 24- 48hrs before
Medications not compatible w/ EEGs:
- vaccines
- Profanolol (general anesthesia)
- IV benedryl
- hormone meds
phenytoin priority care
- CNS effects w/ toxicity = ataxia, hystammus, blurry vision
- gingivitis in children
- SJ syndrome monitoring
- therapuetic range 10-20mcg
- IV care = 50mg MAX dose/ 25mg MAX dose in elderly
primary headaches
no underlying condition/cause
- migraines
- tension
- cluster
secondary headaches
arise from underlying structural, systemic, or infectious causes and may be life-threatening
(INFECTIOUS MOST COMMON)
- neck
- sinus
- TMJ
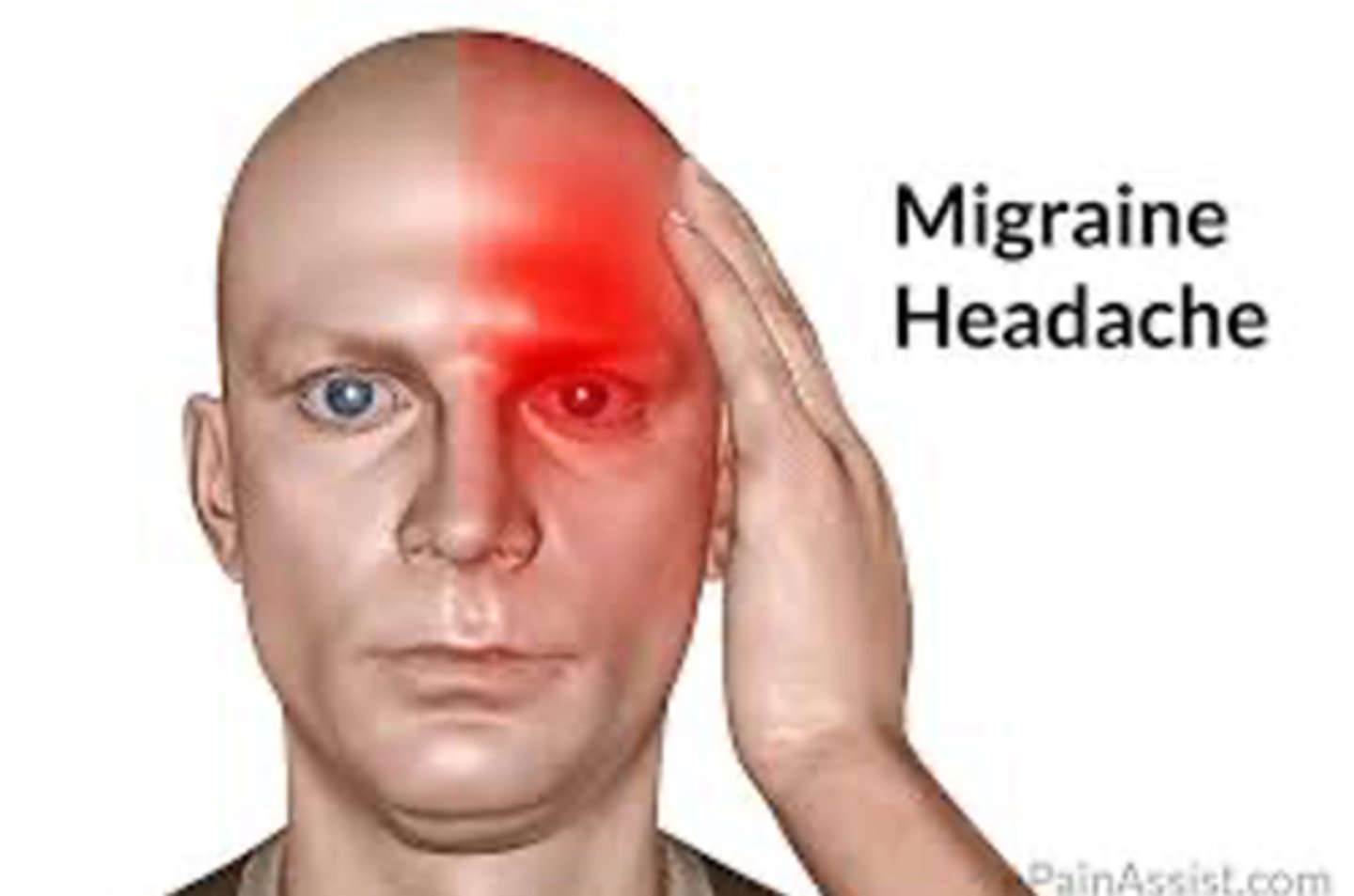
migraines
an intense constant headache surrounding the entire head
manifestations:
- N/V
- sensitivity to light/noise
- head throbbing
- dizziness
- neck pain/stiffness
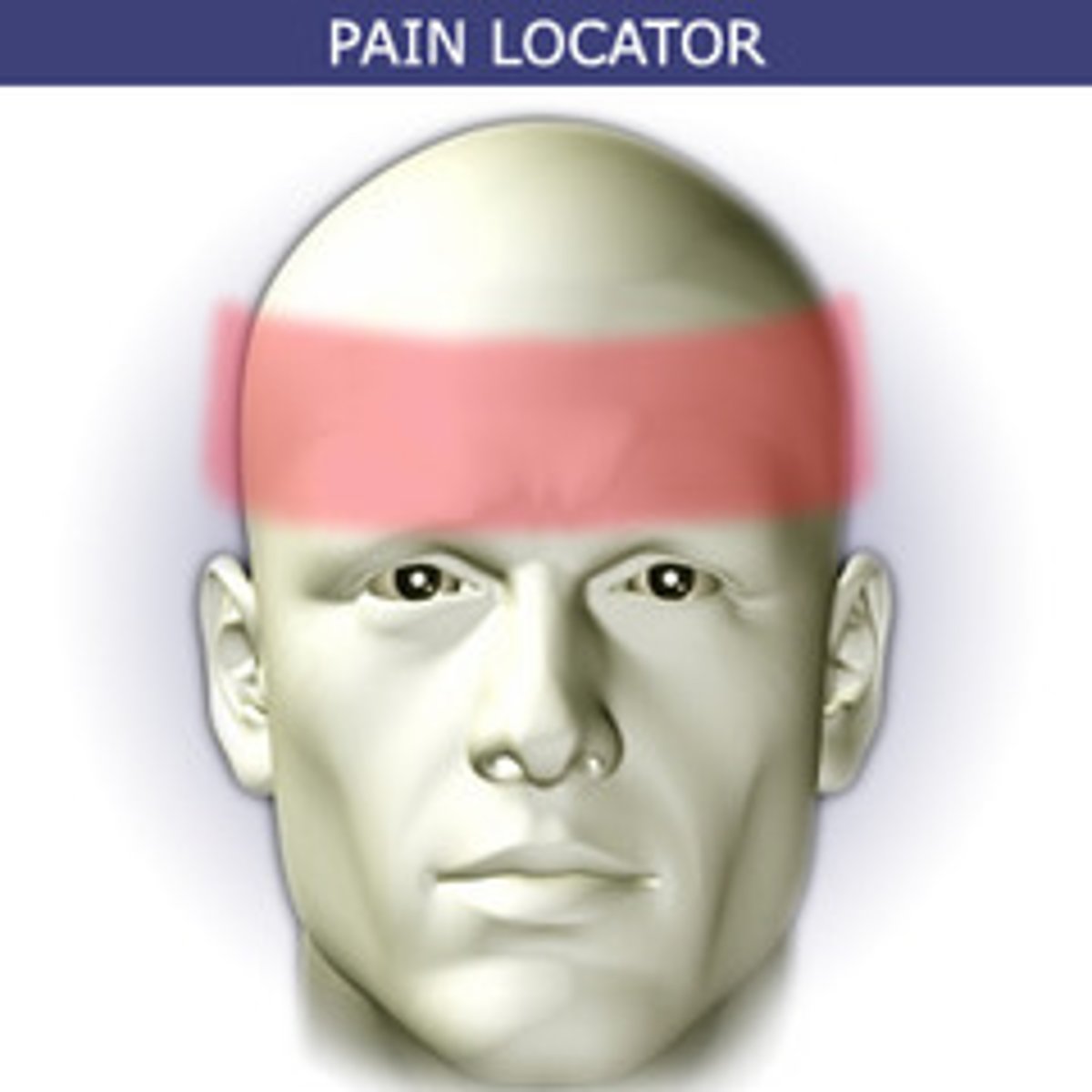
tension headaches
dull aching pain, band of tightness across the head
manifestations:
- dull aching pain
- tightness in forehead/temples
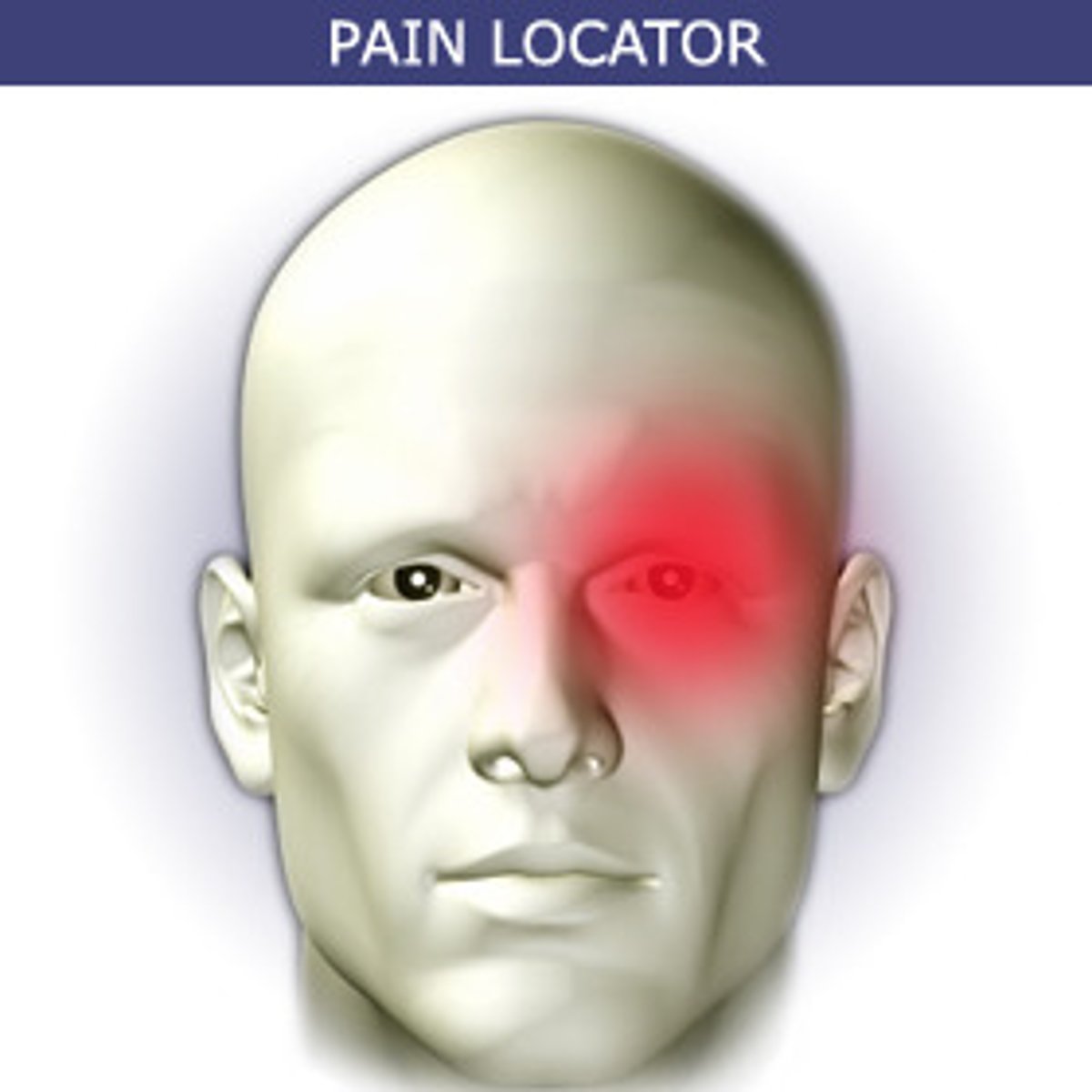
cluster headaches
sharp headache in one side of head affecting the eye
manifestations:
- watering of eye
- N/V
-facial flushing
- onset symptoms
- sensitivity to light/sound
- can be treated with "triptin medications" and high flow oxygen
primary/secondary headache nursing care
- low stimulating environment
- medication therapy
- reduce light and sound triggers
- cool compress for head
- prioritize determining triggers for headaches
SECONDARY: prioritize determining cause of the headache
TMJ headache
pain is at temples, in front of ears
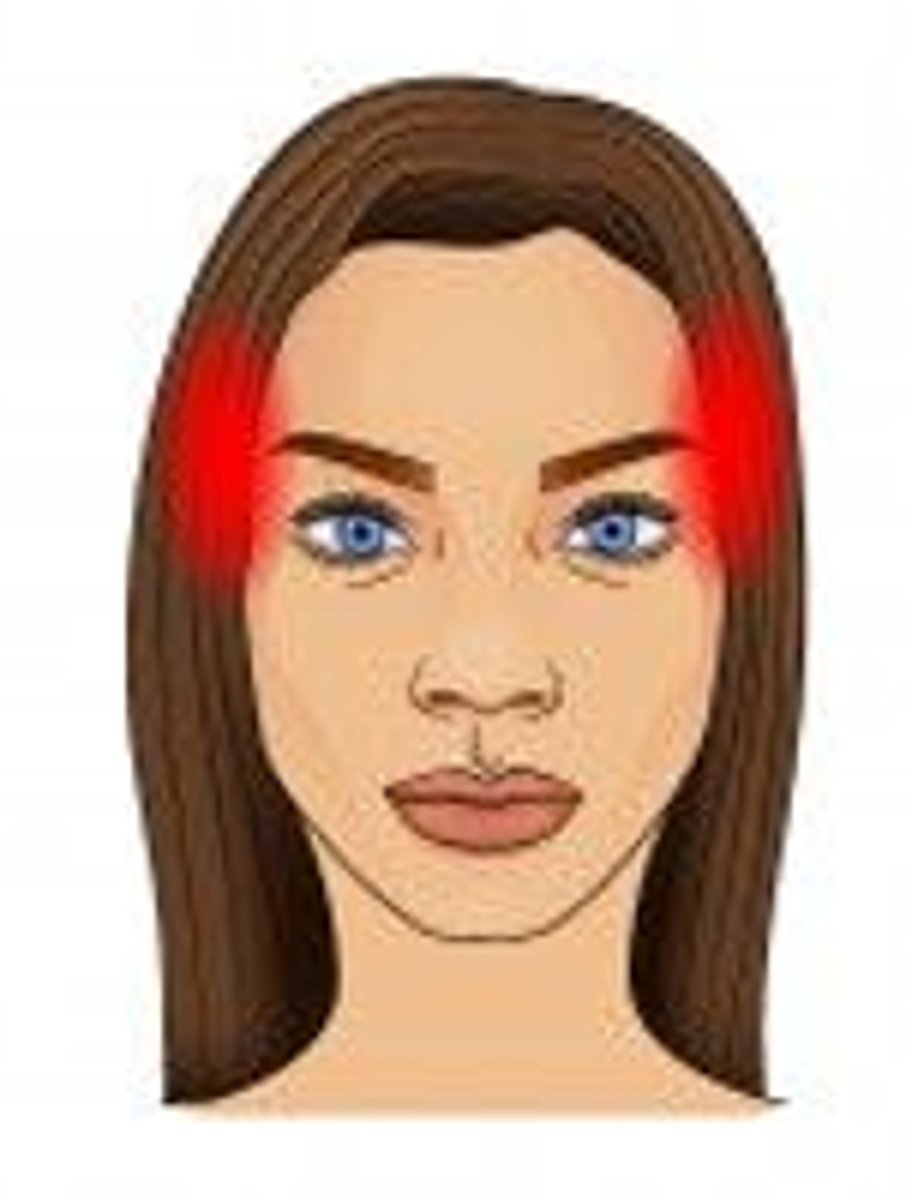

sinus headache
pain is usually behind the forehead and/or cheekbones
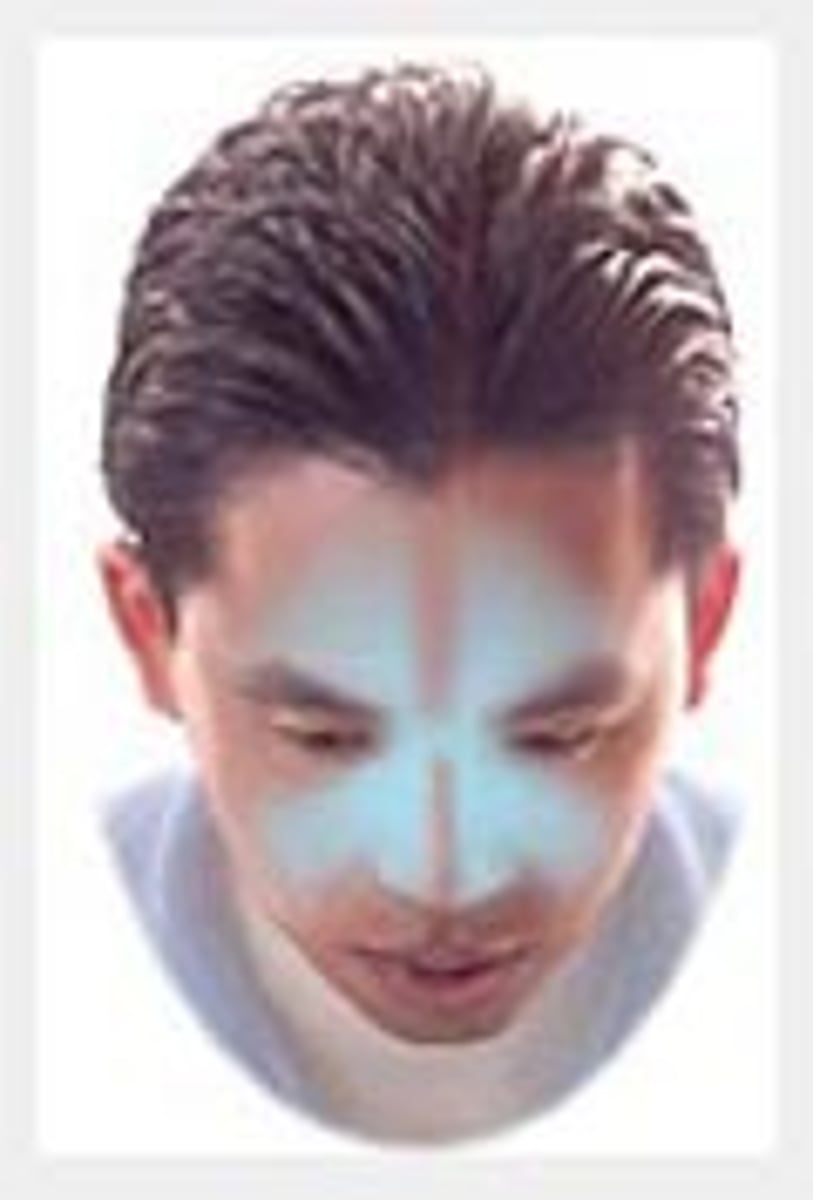

neck headache
Pain is at the top and/or back of head
