Final Exam A&P
1/488
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
489 Terms
respiration
the exchange of gas between an organism and its environment
inspiration
bringing oxygen to the body’s cells by breathing in
expiration
eliminating carbon dioxide from the body’s cells by breathing out
diaphragm
the primary muscle for inhalation; dome-shaped muscle located below the lungs at the base of the rib cage, separating the thorax from the abdomen
does 90% of the work required for breathing (inhale, contracted. exhale, relaxed)
phrenic nerve
the spinal nerve that innervates the diaphragm
(P1)(V1) = (P2)(V2)
What is Boyle’s Law?
inversely
Volume and pressure are (directly/inversely) related.
P = F/A
What is Pascal’s Law?
thorax
the area of the body between the neck and the abdomen; the chest; contains the heart, major blood vessels, and lungs; supported by the ribs, breastbone, and spine
clavicle
the scientific name for the collar bone; bone that connects your arm to your body
sternum
long flat bone that forms the center front of the chest wall; aka breastbone; attached to the collarbone and where the ribs attach
intubation
a medical procedure that involves inserting a tube (called an endotracheal tube) into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway
costal
Latin: pertaining to the ribs or the upper sides of the body
osteophytes
abnormal bony projections that can affect swallowing
respiration
Energy for speech comes from ______________.
intercostal muscles
a group of muscles located between the ribs; play a crucial role in breathing by expanding and contracting the chest cavity and raising the rib cage; have both external and internal muscle groups
seven
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
cervical vertebrae
the top seven vertebrae; found in neck area supporting the head and neck (pharynx and larynx); the vertebrae most studied by SLPs
pharynx
muscular tubes located in the neck that connects the nasal cavity, oral cavity, and larynx to the esophagus (throat); serves as a passageway for air, food, and water to the throat
larynx
the area of the throat containing the vocal cords and used for breathing, swallowing, and talking
twelve
How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
thoracic vertebrae
the middle twelve vertebrae found in the middle of your back; support the upper body’s weight and stabilize rib cage
five
How many lumbar vertebrae are there?
lumbar vertebrae
the bottom five vertebrae; found in the lower back and glutes; the largest movable bones in the spine; support upper body’s weight and allow for movement
spinous process
a bony projection that extends posteriorly from the back of each vertebra, forming the spinal ridge
rib cage
group of bones that protect your lungs and heart; sternum serves as focal point; atttach to sternum via cartilaginous chondral
speech and swallowing
Breathing affects ____________ and _____________, both of which are treated by SLPs.
true ribs
ribs 1-7, each independently connected to the sternum
false ribs
ribs 8-10, which each connect to each other with cartilage before jointly connecting to the sternum
floating ribs
ribs 11-12, which do not connect to the sternum
trachea
windpipe, is a tube-like structure that forms part of the respiratory system; extends from the larynx to the bronchi (connects voice box to your lungs)
bronchi
main airways leading to the lungs
vertebral foramen
hole in each vertebrae through which the spinal tract passes through
costal cartilage
the chondral cartilage that connects the ribs and the sternum
xiphoid process
the pointed tip at the bottom of the sternum
manubrium
the circular “head” at the top of the sternum
nasal pharynx
pharynx that is connected to the nasal cavity
oral pharynx
pharynx that is connected to the oral cavity
laryngeal pharynx
pharynx that is connected to the larynx
process
term for a part of a bone that projects out; usually a bump or ridge that is an attachment point for muscles or tendons; allows for leverage and articulation with other bones
girdle
a bony ring that supports the outer limbs where they connect to the body; ex: pectoral and pelvic
pleura
thin, serous membranes that line the lungs and the interior of the chest cavity; protects and cushion the lungs; helps prevent injury and allows lungs to move smoothly
esophagus
a muscular tube that connects the pharynx to the stomach; vital in the digestive system
bronchi
tube that connects to the trachea and goes into the lungs
carina
a C-shaped ridge of cartilage at the bottom of the trachea that separates the left and right bronchi; prevents food, drink, and other foreign particles that got past the vocal folds from getting into the lungs by being one of the two muscles that can trigger the cough reflex
vocal folds
two muscular bands inside your voice box that produce the sound of your voice by vibrating together; also help prevent food, drink, and other foreign particles from going down the trachea and into the lungs by being one of the two muscles that can trigger the cough reflex
vocal folds and carina
What are the two muscles capable of triggering the cough reflex in reaction to foreign particles attempting to enter the trachea and the lungs?
crichopharyngus muscle
tight closed muscle at the top of the esophagus that controls the flow of food and liquid between the throat and the esophagus; responsible for the noise that comes with a burp
laryngectomy
surgical removal of the larynx (voice box), such as after larynx cancer or blunt trauma to the larynx, by creating a permanent hole in the neck through which the patient can talk and breath
thyroid cartilage
cartilage that makes up a shield-shaped structure in the front of the larynx to protects the vocal cords; the most prominent bit makes up the Adam’s apple
trachial ring
cartilage rings in the trachea that keep trachea open and firmly in place
right upper lobe, right middle lobe, right lower lobe
What are the three lobes of the right lung?
three
How many lobes are there in the right lung?
left upper lobe and left lower lobe
What are the two lobes of the left lung?
two
How many lobes are there in the left lobe?
Neither. Both lungs are the same size, just divided into lobes differently.
Which lung is smaller?
alveolus
one of the millions tiny air sacs found at the end of the lobes of the lungs; allow for rapid gaseous exchange and the inflating of the lungs
bronchial tree
a network of airways within the lungs that carries air from the trachea (windpipe) to the alveoli (air sacs) along five different lobes
right lower lobe, because the right lobes are more vertical and so gravity pulls it to the RLL
Which lung lobe is the most likely to get liquid trapped within it and why?
aspiration
when something other than air gets into the airway and passes below the vocal folds; at risk for the substance entering the lungs; can be caused by swallowing disorders
pneumonia
respiratory infection from liquid in the lungs
pleural effusion
a condition where excess fluid accumulates in the pleural space; can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, etc.
pleural space
the thin area between the lungs and the chest wall
diaphragm, external intercostal, internal intercostal, sternocleidomastoid, scalene, trapezius, abdominal muscles
What are the seven muscles of respiration?
sternocleidomastoid
each of a pair of long muscles that connect the sternum, clavicle, and mastoid process of the temporal bone; helps turn and nod the head; becomes active during forced inspiration to lift the chest wall and allow increase ventilation
parietal pleura
pleura found between the ribcage and the lungs
visceral pleura
pleura found between the heart and the lungs
negative
The air pressure inside the pleural space is always (negative/positive).
quiet inspiration
inspiration when body is at rest; diaphragm is the only muscle active
forced inspiration
inspiration when body is active or recovering from being active; uses both the diaphragm and the accessory muscles to increase inspiration maximally
scalene
a group of three muscles located in the neck; rotates and tilt the neck, elevates the upper ribs during deep breaths, and supports the weight of the head and neck
trapezius
muscles located on the upper back that enlarge the upper chest during deep breaths
abdominal muscles
group of muscles located in the front and sides of the abdomen; support body and help lengthen the diaphragm to help with respiration
expand
When the diaphragm contracts, the lungs (deflate/expand).
the volume increases and the pressure decreases
What happens to the volume and the pressure when the lungs expand?
inverse
Air pressure and volume have a(n) (direct/inverse) relationship.
deflate
When the diaphragm relaxes, the lungs (deflate/expand).
760 mmHg
What is the value of atmospheric pressure?
763 mmHg
What is the value of positive pressure?
757 mmHg
What is the value of negative pressure?
the volume decreases and the pressure increases
What happens to the volume and the pressure when the lungs deflate?
positive pressure
During exhalation or when not breathing, the air pressure within the lungs is (negative pressure/positive pressure).
negative pressure
During inhalation, the air pressure within the lungs is (negative pressure/positive pressure).
gas exchange (O2 and CO2)
What is the goal of respiration?
oxygenate the blood and heart
What does the gas exchange of respiration accomplish?
ventilation
the actual movement of air in the conducting respiratory passageways; both inhalation and exhalation (air inhaled/time)
quiet inspiration
inspiration when body is at rest and calm
active inspiration
aka forced inspiration; inspiration when body is not at rest, either active or recovering from being active (increased heartbeat and inhalation)
passive expiration
expiration when body is at rest; driven by elasticity of muscles and gravity
active expiration
aka forced expiration; expiration when body is not at rest; quickened heartbeat or shortness of breath; driven by muscular activity forcing exhalation
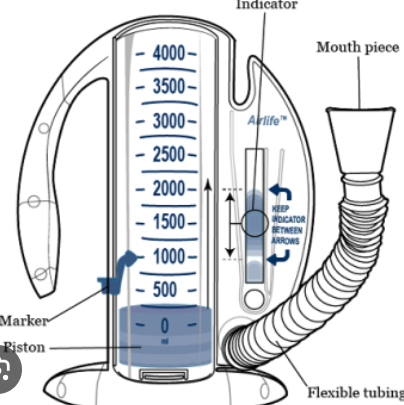
spirometer
measuring tool that measures volume of air and the flow of air during respiration
manometer
measuring tool that measures pressure of exhalation air force
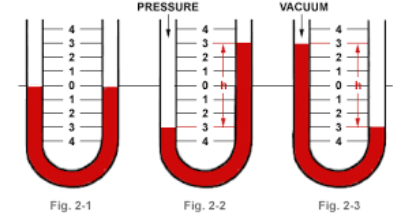
water manometer
simple manometer used by many SLPS in which patient blows through a straw into a glass of water to measure their exhalation air flow
perfusion
the movement of blood through the tissues and organs, particularly in the lungs
diffusion
the process of exchanging gases in the lungs through the movement of molecules from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure to achieve balance
voiceless sounds
sounds produced without the use of vocal folds; open vocal folds, sound based on breath; ex: /s/, /f/, /p/
voiced sounds
sounds produced by an action by the vocal folds; closed or partially closed vocal folds + airflow from lungs = vibration of vocal folds; ex: /z/, /v/, /b/
phonation
the shaping of vocal production into speech; the sounds heard; occurs within the larynx
respiration
What provides energy for phonation?
vocal folds
layers of tissue and muscle that vibrate as air passes between them, producing phonation