Lecture 4 -- Forelimb Anatomy and Elbow Joint
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What are the two main bones of the antebrachial region?
Radius and Ulna.
Which bone is the longer and what is its function?
Ulna
Provides leverage in the forelimb
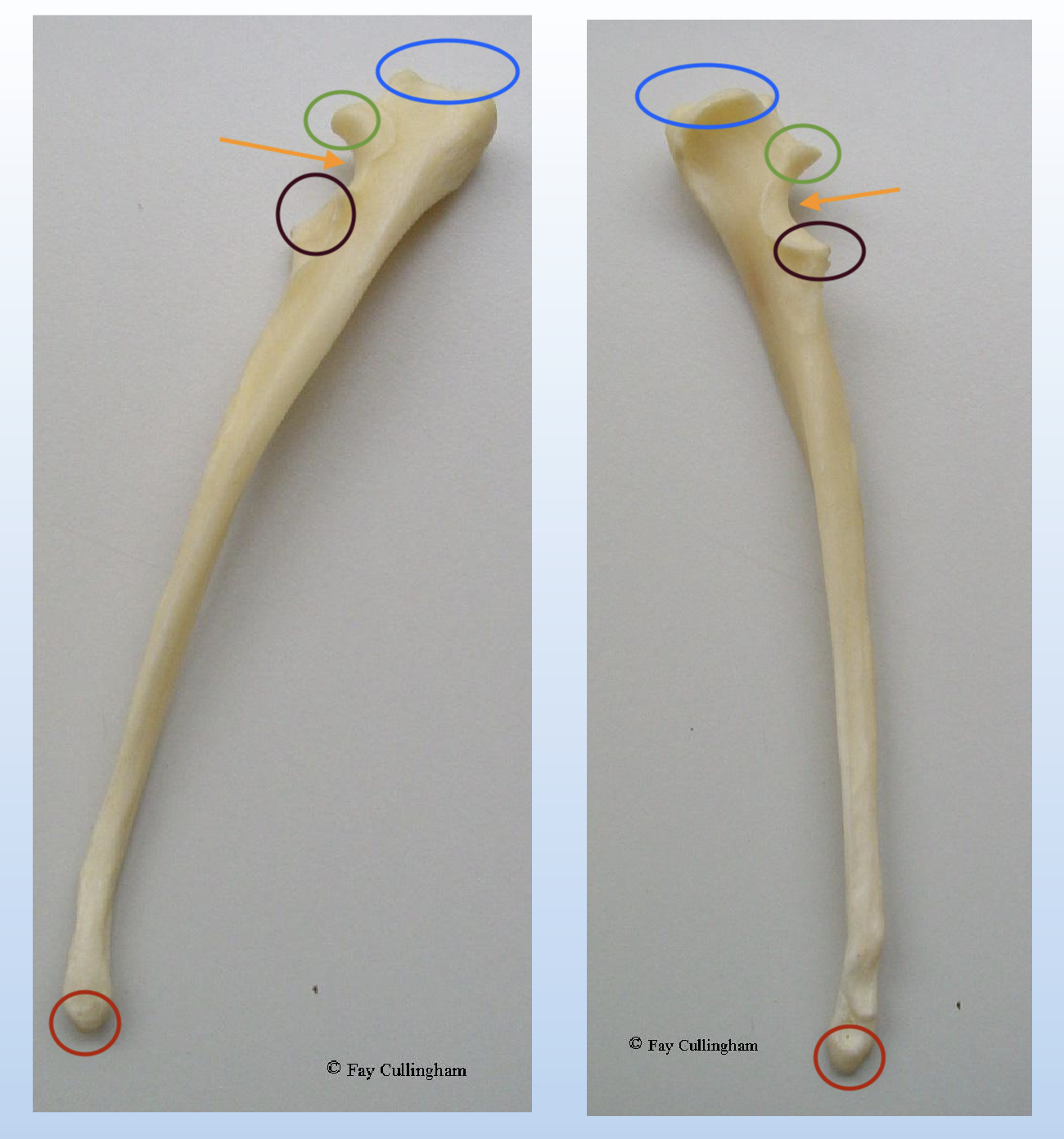
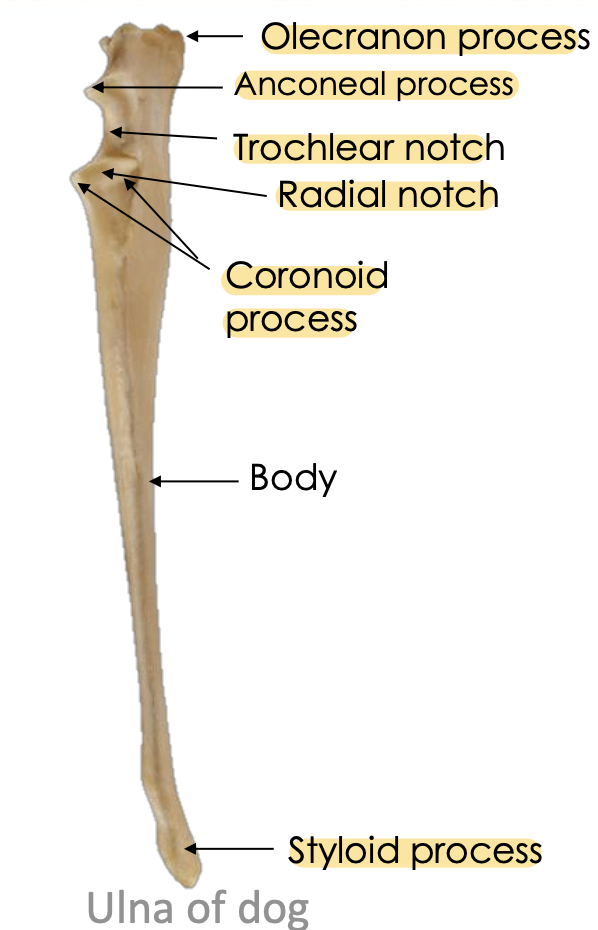
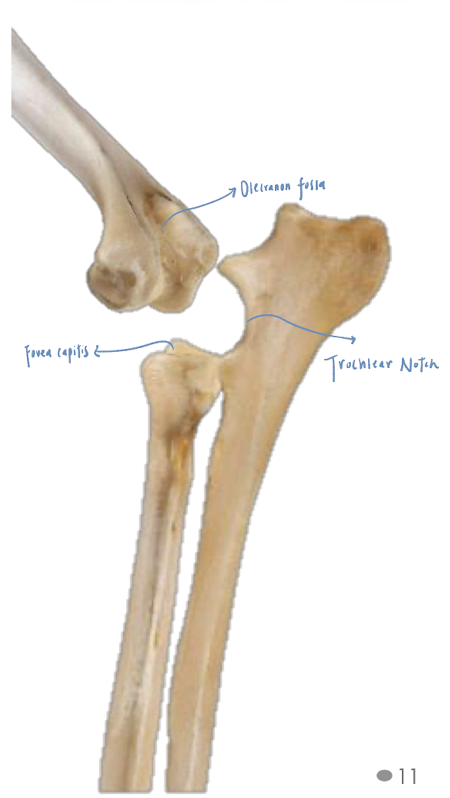
Name the above structure and identify its key structure.
Which part of humerus that anconeal process of the ulna fits into?
Olecranon fossa of humerus
What is the styloid process of the ulnar attached to?
Ulnar notch of ulnar
Which ligament is the styloid process of the ulna attached to?
Lateral collateral ligament of the elbow
How many ossification centre of ulna?
4
Olecranon process, Anconeal process, Body and distal epiphyses
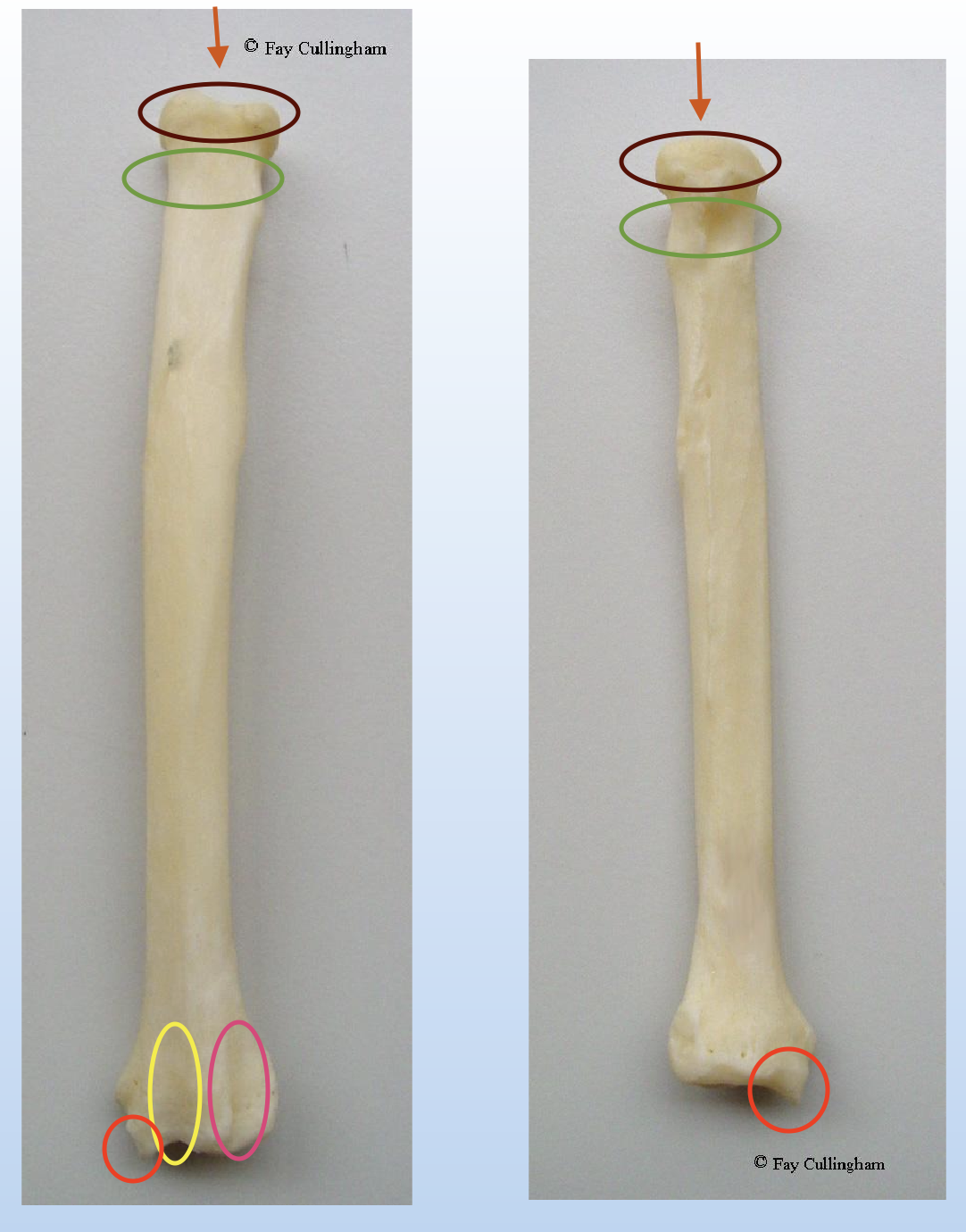
What is this? What aspect is shown in these pictures?
Name the structure of it.
Left: Cranial aspect
Right: Caudal aspect
Yellow: Groove for common digital extensor
Pink: Groove for extensor carpi radialis
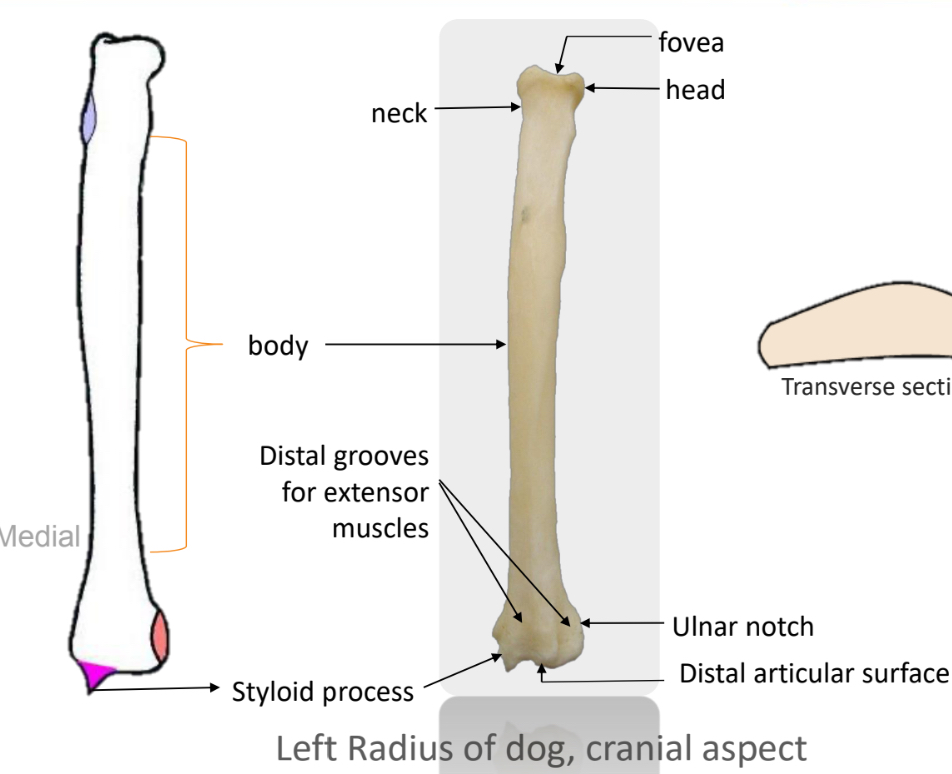
What is the function of radius?
Weight-bearing bone of the forelimb
What is the head of the radius articulate with?
Radial notch of the ulna
What structure stabilises the proximal articulation between the radius and ulna? How does it attached the radius to ulna?
Annular ligament. It runs from the lateral to medial coronoid process.
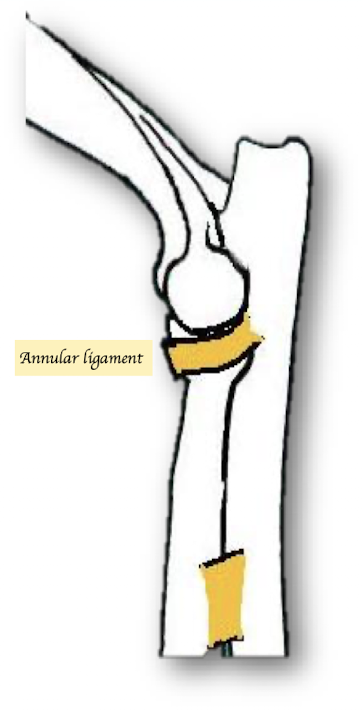
What is the function of the annular ligament?
Allows for rotation between the radius and ulna.
What separates the ulna and radius in the forelimb?
Interosseous space.
What structure stabilises the distal articulation between the radius and ulna?
Interosseous ligament
How does the alignment of the radius and ulna differ in cats compared to dogs?
Cats have more interosseous space allowing for greater movement and rotation.
What is key structure of ulna and radius of cat that differ with dogs
Squared olecranon
Diameter of radius and ulna is similar
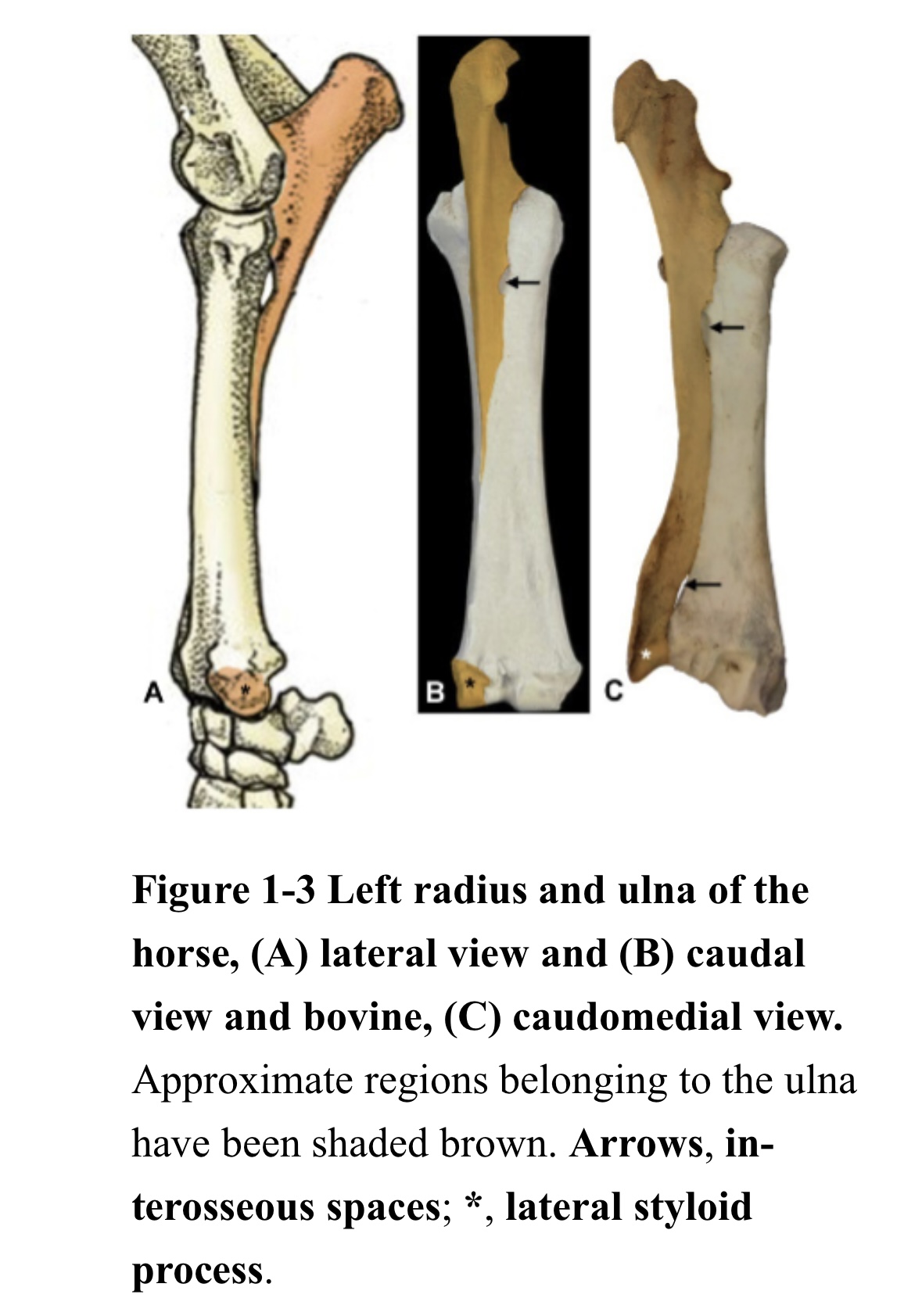
What is key structure of ulna and radius of horses that differ with dogs
Proximal ulna present + Fuse to radius
Body of ulna absent → Greatly reduce in size → Do not extend up to radius
Distal ulna present + Fuse to radius → Medial styloid process + Lateral styloid process
Small interosseous space → No rotation
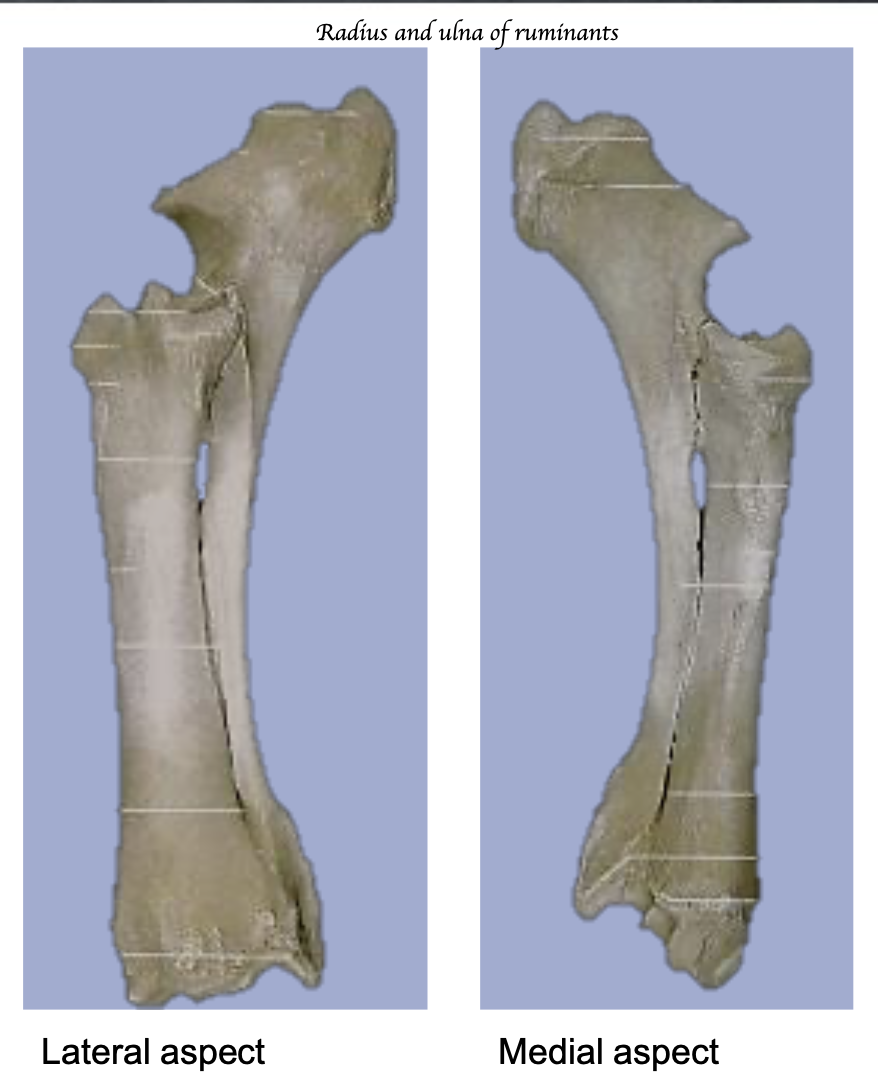
What is key structure of ulna and radius of ruminants that differ with dogs
2 complete bones
Fuse as animal ages
No rotation
What is key structure of ulna and radius of pigs that differ with dogs
2 complete separate bone
Ulna same diameter as radius
No interosseous space → No rotation
How many ossification centre of radius?
3
Proximal epiphyses, body and distal epiphyses
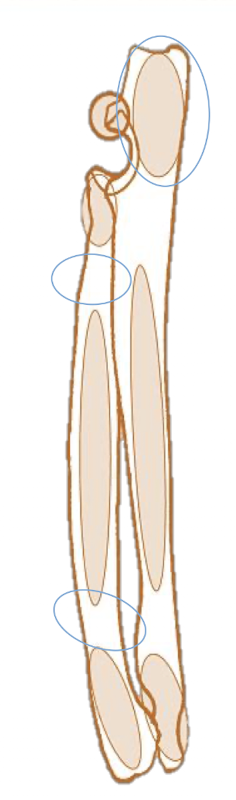
What are the palpation landmarks of the radius and ulna?
Ulna: Olecranon process + Lateral styloid process
Radius: Medial styloid process
How did the radius and ulna evolve? How does this evolution affect the proximal and distal positions of the ulna at birth in medial and lateral projections?
Toes rotate cranially → Elbow rotate caudally → Radius and ulna rotate around each other
Proximal: Ulna is positioned medially to the radius
Distal: Ulna is positioned lateral to the radius
How is the elbow joint formed?
Trochlea articulates with trochlear notch of ulna + fovea capitis of radius
+ Capitulum articulates only with fovea capitis of radius
What type of joint is the elbow?
Synovial joint.
What types of ligaments provide stability to the elbow joint?
Collateral ligaments x4 (Humerus - Radius and ulna)
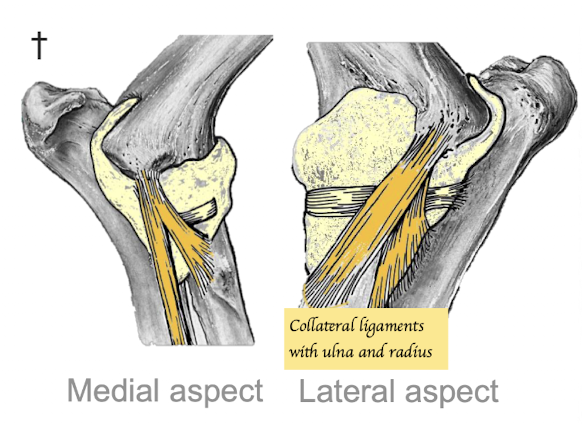
Apart from collateral ligaments, what are the bony structures provide stability to the elbow joint?
Anconeal process of ulna fits into the olecranon fossa of humerus → Prevent hyperextension of joint → More stability of elbow joint
Elbow extensors insert onto olecranon
What are the main extensors of the elbow joint?
Triceps muscle.
How many heads are there in triceps muscles? What are they originated and inserted to? Which nerve innervate the triceps nerves?
Long head:
→ O Caudal border scapula
→ I: Olecranon process
Lateral head:
→ O: Lateral aspect humerus
→ I: Olecranon process of ulnar
Medial head:
→ O: Medial aspect humerus
→ I: Olecranon process of ulnar
Accessory head
Nerve: Radial nerve (Motor + Sensory)
What muscle primarily acts as a flexor of the elbow joint?
Biceps brachii muscle + Brachialis
What is a common site for primary bone tumors in forelimb dogs?
Distal radius.
What are biceps brachii muscles originated and inserted to? Which nerve innervate the biceps brachii nerves?
O: Supraglenoid tubercle
Pass through inter-tubercular groove
I: Radius and ulnar tuberosity
N: Musculocutaneous nerve
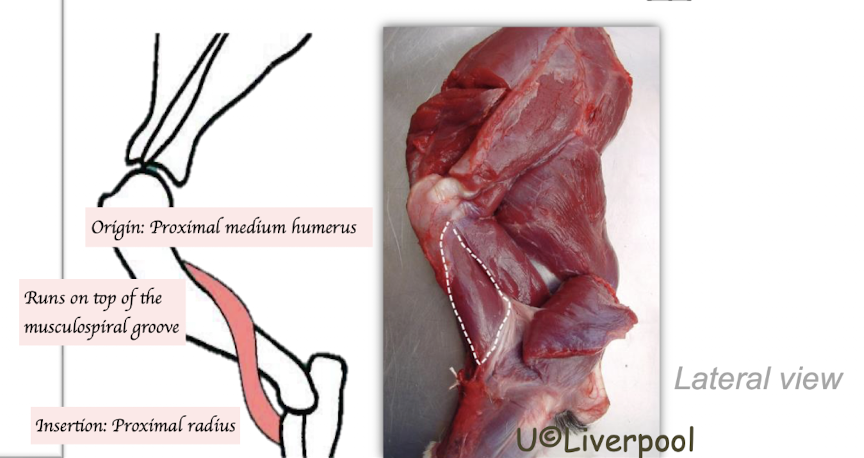
What is brachialis originated and inserted to? Which nerve innervate the brachialis muscle nerves?
O: Caudal aspect of humerus
Follow the musculospiral groove
I: Proximal radius
N: Musculocutaneous nerve
Which are the muscles that are responsible for pronation and supination? What are they originated and inserted to? Which nerve innervate these muscle?
Pronator teres muscle
O: Medial epicondyle
I: Proximal radius
Nerve: Median nerve
Supinator muscle
O: Lateral epicondyle
I: Proximal radius
Nerve: Radial nerve
Describe the branches of forelimb arterial supply. Where do they run around?
Aorta → Subclavian artery (1st rib) → Axillary artery (Axilla) → Brachial artery (Brachium) →
1. Median artery (Medial aspect of antebrachium) → Radial + Superficial palmar arch
Superficial branchial artery (Cranial aspect of antebrachium)
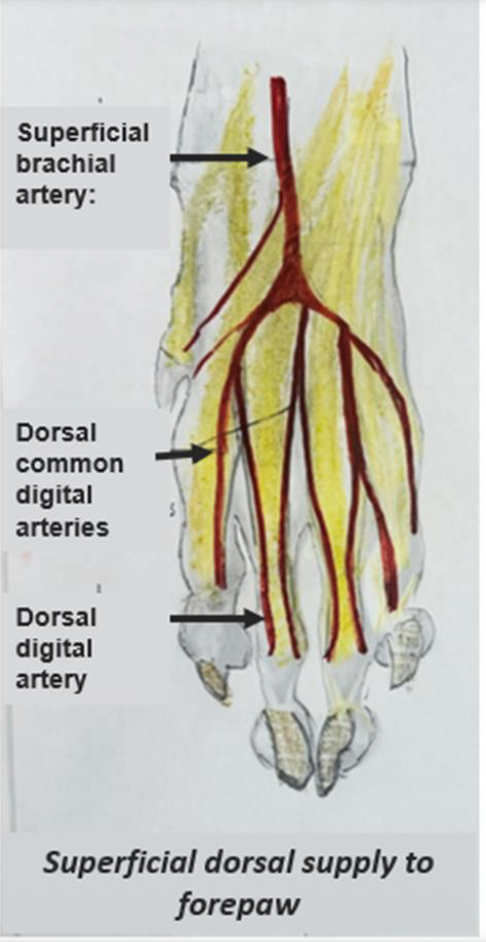
Dorsal blood supply is mainly superficial.→ Which artery supplies the superficial part of the palm, and which supplies the deep part?
Superficial brachial artery → Dorsal common digital arteries → Dorsal digital arteries→ Abaxial + axial
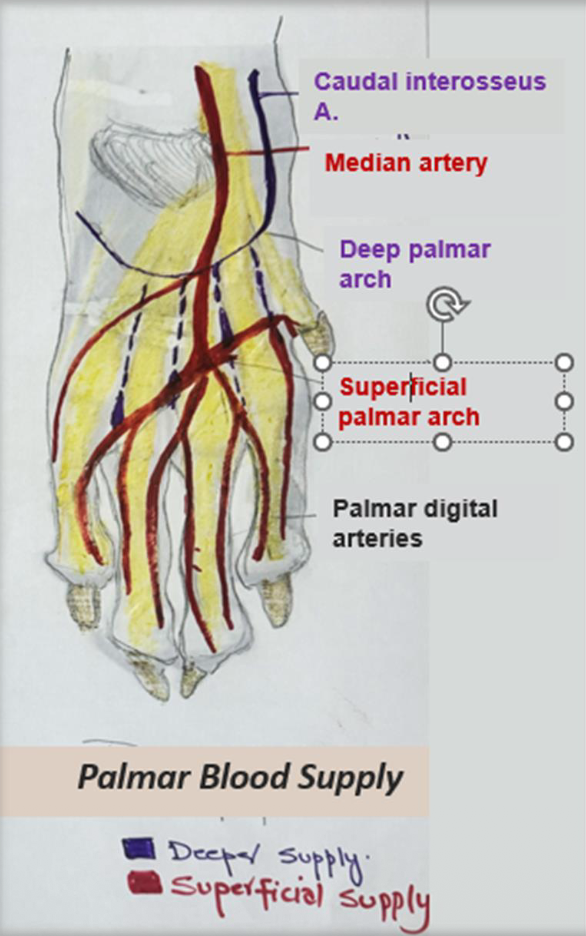
The palmar blood supply is divided into superficial and deep parts. Which artery supplies the superficial part of the palm, and which supplies the deep part?
Superficial Supply:
Median artery → Superficial palmar arch
Deep Supply:
Caudal interosseous artery → Deep palmar arch
At the Metacarpophalangeal Joint, these arches give rise to palmar common digital arteries → palmar digital arteries supplying the individual digits → Abxial + Axial
There are superficial system and deep system for venous blood drainage of forelimb. Describe the blood flow for both superficial and deep system.
Superficial system:
Cephalic vein (Runs at the antebrachial region → Jugular vein → Brachiocephalic trunk → Vena cava
Deep system:
Runs side by side with the artery