Economic Growth
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
How does short-term growth occur?
Changes to any of the components of AD will cause short-term economic growth
This is illustrated on an AD/AS diagram by a rightwards shift in AD
What does short-term economic growth look like on an AD/AS diagram?
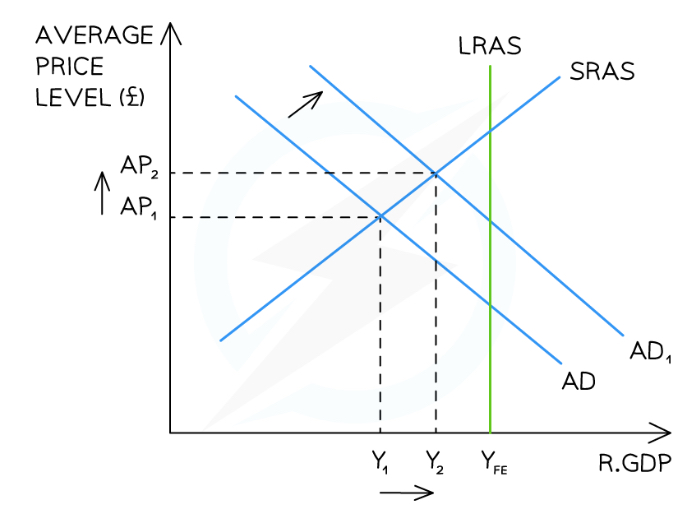
What is the analysis of short-term growth on an AD/AS diagram?
An increase in consumption, investment, government spending or net exports has caused a shift in AD fromAD→AD1
The current real output has increased from Y1→Y2 which represents an increase in real GDP
An increase in real GDP = economic growth
This short-term growth has led to an increase in average prices from AP1→AP2
What does short-term economic growth look like on a PPC?
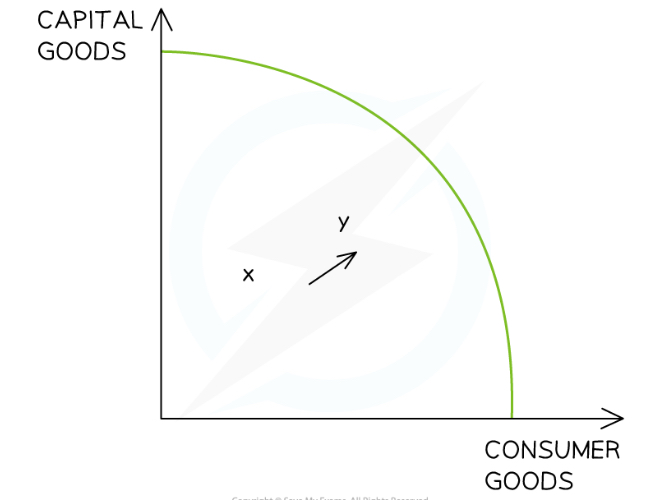
What is the analysis of short-term economic growth on a PPC?
An increase in production has caused a shift in production combinations from X→Y
The current real output has increased moving closer to the maximum possible output of the economy
This represents an increase in real GDP
An increase in real GDP = economic growth
What causes long-term growth?
Caused by any improvements to the determinants of LRAS
This is illustrated on an AD/AS diagram by a rightward shift in the LRAS
What does long-term economic growth look like on an AD/AS diagram?
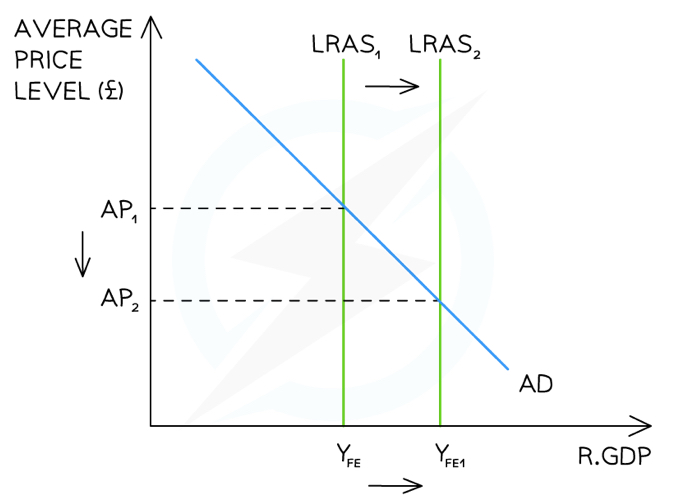
What is the analysis of long-term economic growth on an AD/AS diagram?
A change to the quantity/quality of the factors of production has increased potential output of the economy from YFE→YFE1
E.g. More rigorous competition policy creates a higher number of firms in each industry leading to greater aggregate supply in the economy
This shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right LRAS1→LRAS2 resulting in economic growth
The final impact on price levels depends on the shape of the long-run aggregate supply curve (Keynesian or Classical)
What does long-term economic growth look like using a PPC diagram?
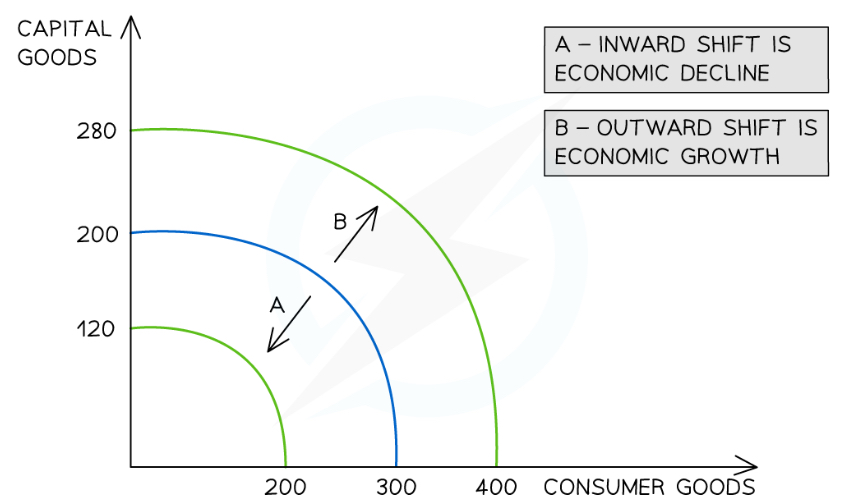
What is the analysis of the long-term economic growth on a PPC diagram?
Economic growth occurs when there is an increase in the productive potential of an economy
This is demonstrated by an outward shift of the entire curve
More consumer goods and more capital goods can now be produced using all of the available resources
This shift is caused by an increase in the quality or quantity of the available factors of production
How do you calculate economic growth rates?
Economic growth is measured by calculating the change in the real GDP between two time periods (usually quarterly or annually)
The growth rate is expressed as a percentage
Several steps can be included in the calculation of an economic growth rate
Calculate nominal GDP from a set of data for two time periods
Calculate the real GDP for each time period using the GDP deflator
Calculate the percentage change in real GDP between the two time periods
What is impacted by economic growth?
Living standards
The environment
Income distribution
What are the benefits of economic growth on living standards?
Increased incomes lead to better standards of living
Increased employmentresolves some of the negative social impacts of unemployment
What are the costs of economic growth on living standards?
Rising aggregate demand causes demand pull inflation and the purchasing power of people on fixed incomes may fall
Increased income usually leads to greater consumption of demerit goods
Greater output often requires more time from workers and can decrease leisure time and well-being
What are the benefits of economic growth on the environment?
Improvement in the quality/quantity of environmentally friendly technologies
What are the costs of economic growth on the environment?
Environmental damage caused by negative externalities of production and consumption increases
Resources are depleted more rapidly
What are the benefits of economic growth on income distribution?
Decreased levels of absolute poverty
Higher levels of employment mean that there is more tax revenue for governments to redistribute on welfare payments
What are the costs of economic growth on income distribution?
Lack of equity in the distribution of income - the rich may get richer and the poor poorer