imines and esters as electrophiles
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
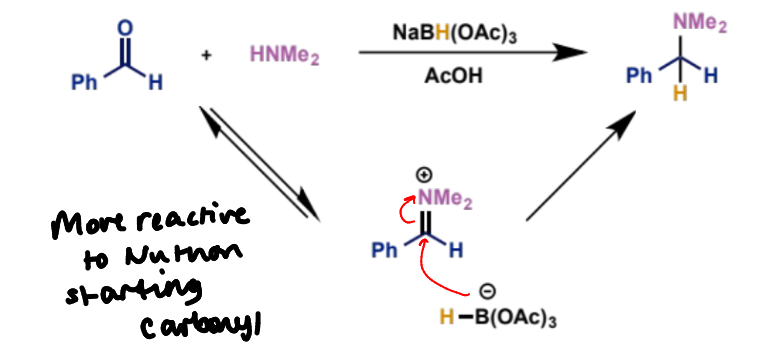
what is reductive amination
formation of substituted amines by a three-component reaction of carbonyl compounds, amines and a reducing agent
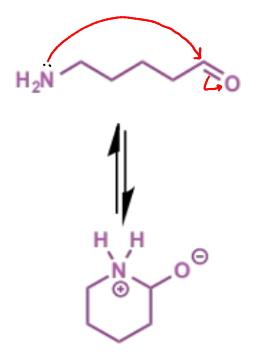
how does reductive amination work
the amine and carbonyl condense to form an iminium ion which is more electrophilic and hence reactive towards the nucleophile than the carbonyl alone
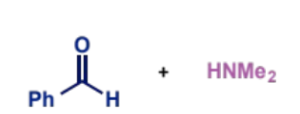
conditions
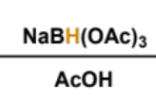
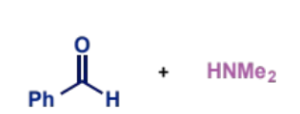
product

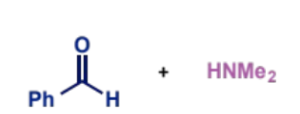
mechanism, condition + product
why this works
basis of the Mannich reaction (in terms of iminium ions)
we can harness iminium ion formation to drive carbon-carbon bond formation with enols in a three-component condensation (Mannich)
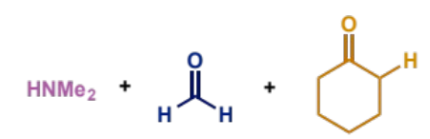
how are iminium ions generated for Mannich condensation
give specific reagent which works well
why is this done
can be formed in situ from an aldehyde and a secondary amine
formaldehyde is a particularly good aldehyde for this as it is unstable and reacts rapidly with amines
the positive iminium ion is much more reactive towards the low concentration of enol than the neutral aldehyde
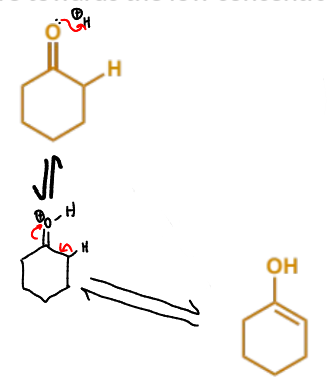
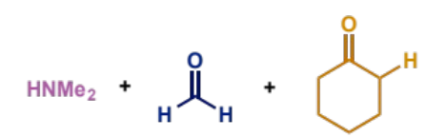
which reagent enolises? show the formation of the enol
first stage of mechanism (not enolisation)
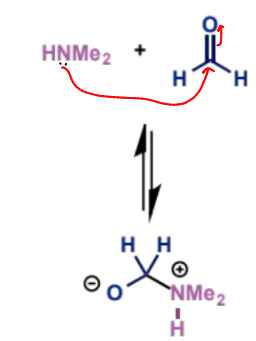
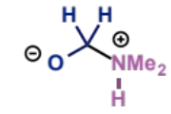
next stage of Mannich mechanism
type of product?
aminal would be 2 amines on 1 carbon, so this is a hemiaminal (hydroxy + amine group on same C)
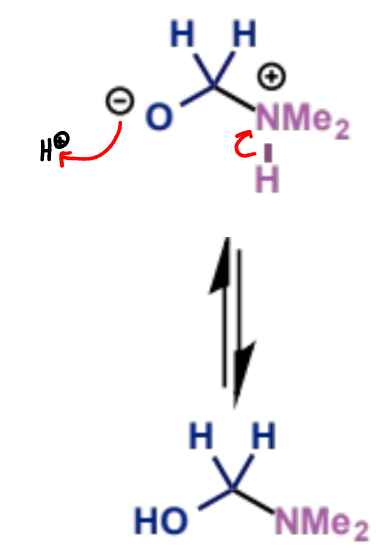
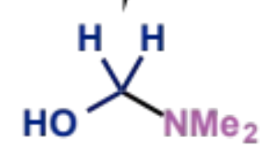
next stage of Mannich mechanism

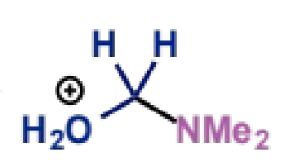
next stage of Mannich mechanism
type of product?
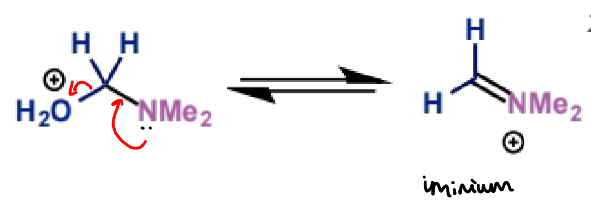
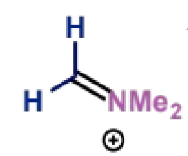
next stage of Mannich mechanism
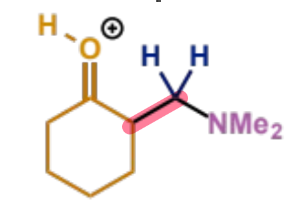
final stage of Mannich mechanism
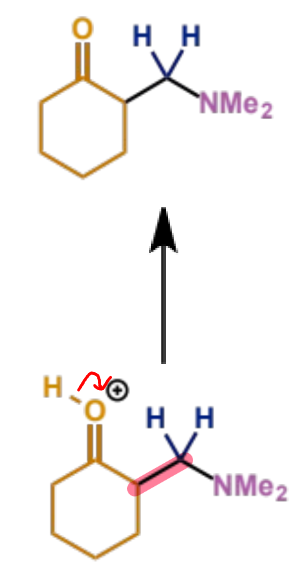
how does intramolecular Mannich condensation happen
cyclic amines can be accessed by tethering two of the components of the Mannich condensation together so that either the iminium formation or the iminium trapping by the enol (or both) are intramolecular
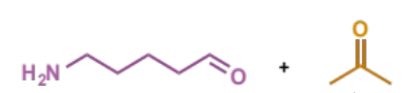
overall equation for Mannich condensation
which type of intramolecular condensation is it
iminium formation is the intramolecular part, iminium trapping by the enol will happen separately
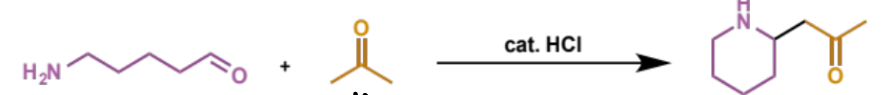
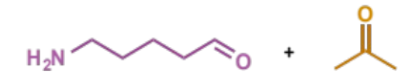
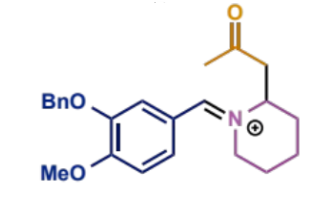
show enol formation for this Mannich condensation
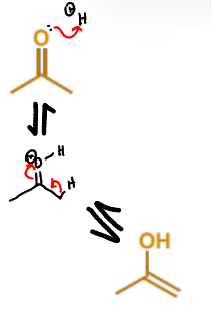
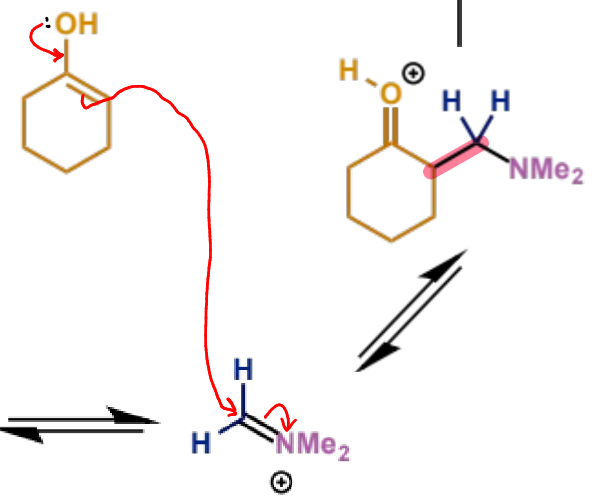
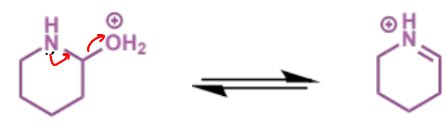
first stage of intramolecular Mannich condensation

next stage of intramolecular Mannich
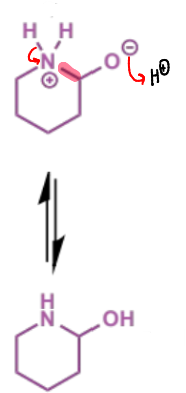
next stage of intramolecular Mannich
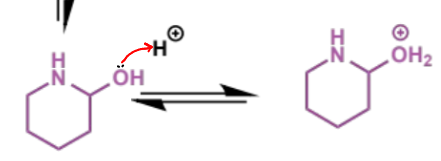
next stage of intramolecular Mannich
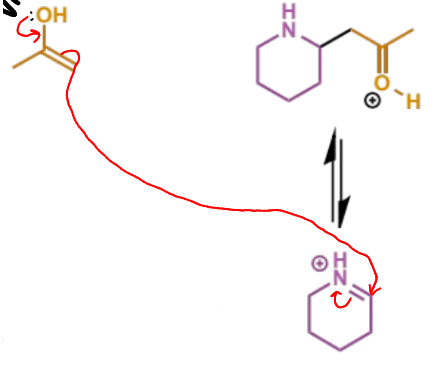
next stage of intramolecular Mannich
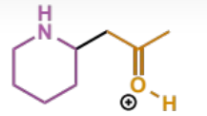
final stage of intramolecular Mannich
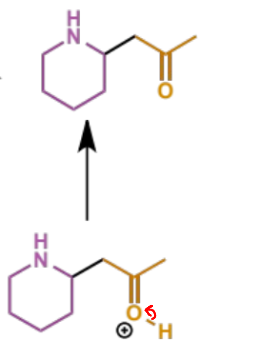
what can happen to the product of the intramolecular Mannich condensation
a second step/intramolecular condensation in which the amine and enol/carbonyl component are in the same molecule and react with the electrophilic aldehyde to form an iminium which undergoes trapping to give a second ring
intramolecular Mannich condensation overall equation
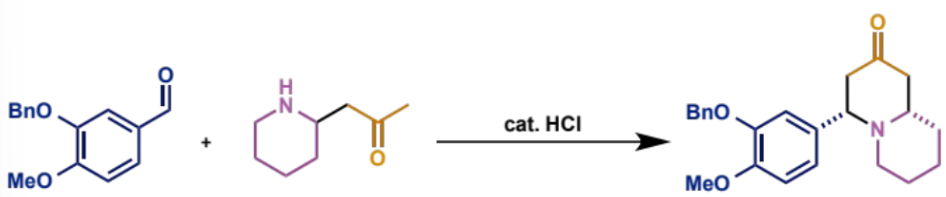
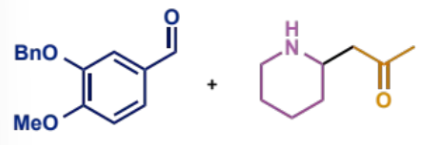
first process/stages in intramolecular Mannh


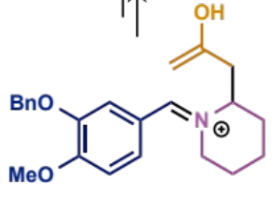
final stage of intramolecular Mannich
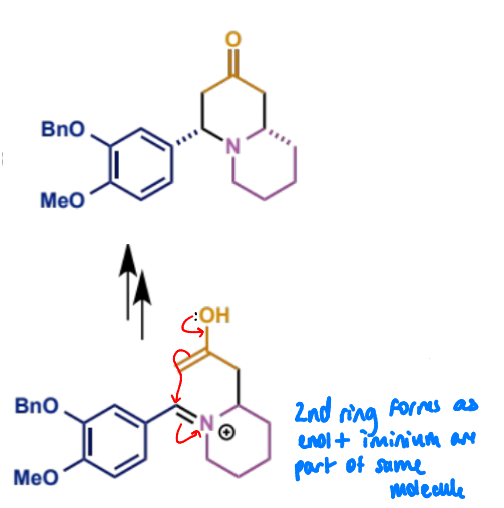
how to identify a product of a Mannich reaction
look for an amine with a 1,3-relationship to a carbonyl
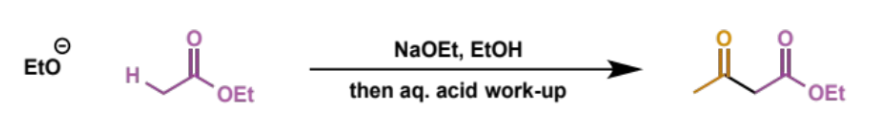
what is Claisen condensation
esters undergo self-condensation in a manner similar to the aldol reaction
base needed for Claisen condensation and why
use an alkoxide base (NOT a hydroxide) matching the ester alkoxy group to prevent trans-esterification
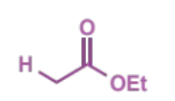
overall equation for Claisen condensation
type of product
β-ketoesters
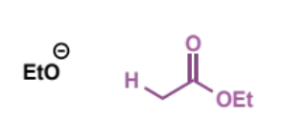
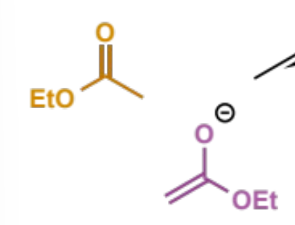
first step of mechanism
where does eqm lie?
Keq = ca. 10-9
small equilibrium population of ester enolate reacts with a second molecule of ester as the electrophile
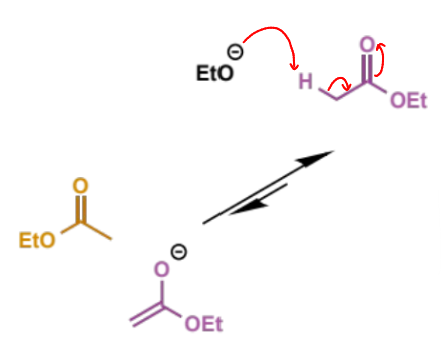
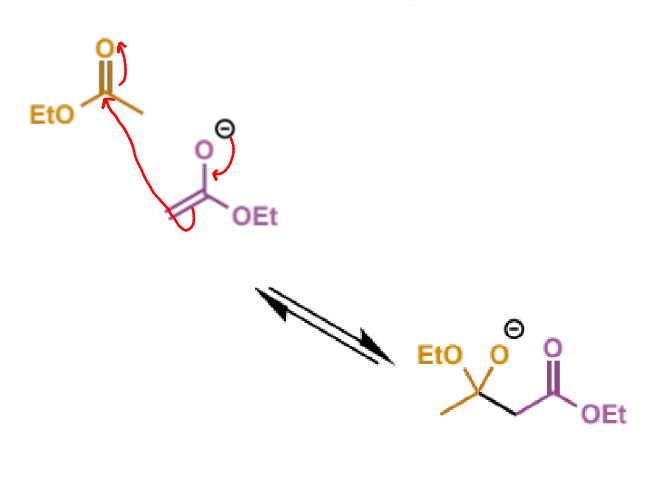
next step of Claisen
describe product
tetrahedral intermediate - wants to reform C=O
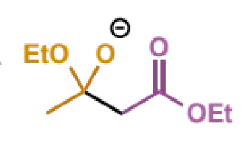
next step of Claisen


next step of Claisen
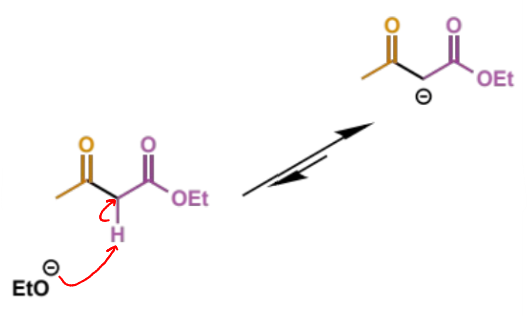
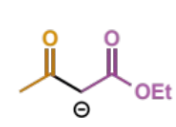
describe step
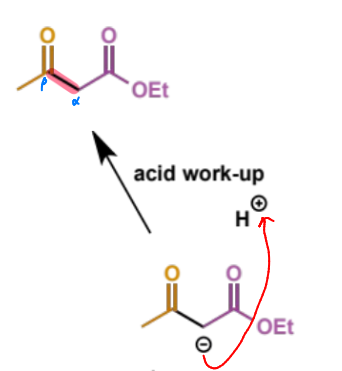
this deprotonation is the equilibrium shifting step - Keq = ca. 105
without this step the reaction does not happen as the product is thermodynamically unfavourable until this point
final step of Claisen
how do we know that the ketoester deprotonation is vital to the Claisen reaction
branched alkyl esters with only one enolisable proton do not give the Claisen product
they cannot do the deprotonation step as the carbon is tetra-substituted
what are crossed Claisen reactions
what is good about them
different esters act as nucleophile and electrophile
potentially more useful as there is a wider range of products
requirements for esters for crossed Claisen reactions
one of the esters needs to be non-enolisable so that there is only one possible nucleophile
the ester acting as the electrophile needs to be more reactive than the nucleophilic ester

overall equation (crossed Claisen condensation)
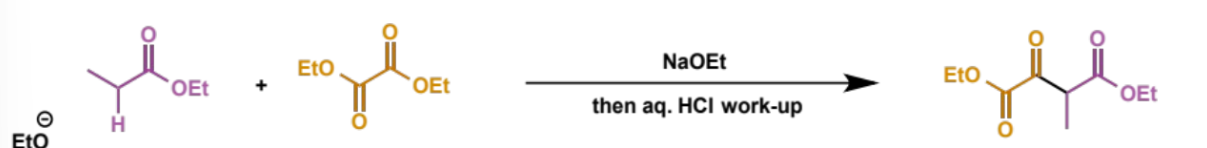

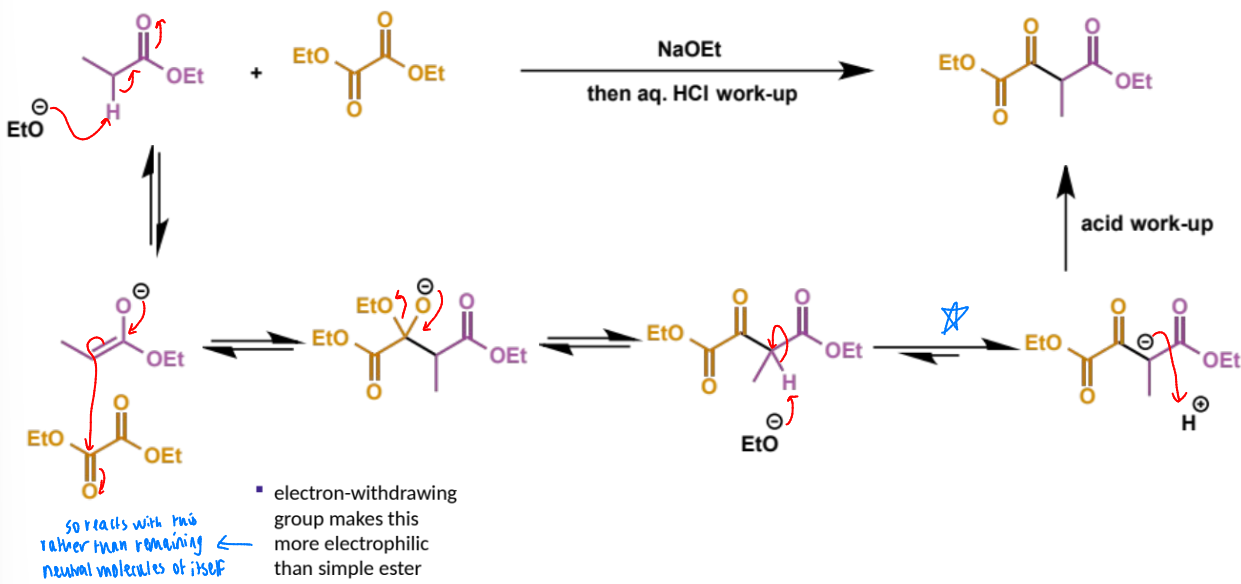
first step in crossed Claisen
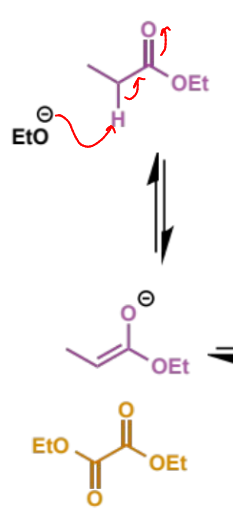
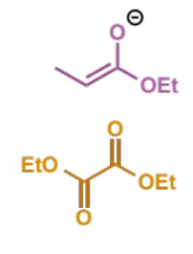
next step in crossed Claisen
why does this step happen this way
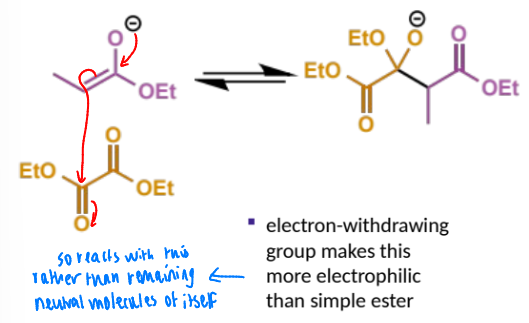
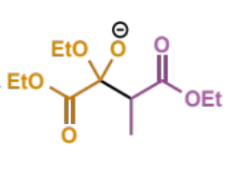
next step in crossed Claisen
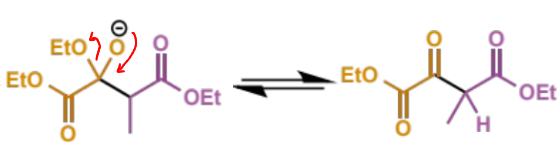
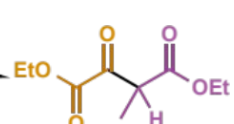
next step in crossed Claisen
describe this step
this is the eqm shifting deprotonation step
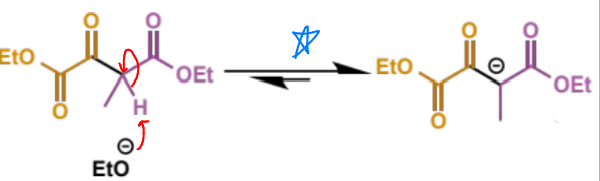

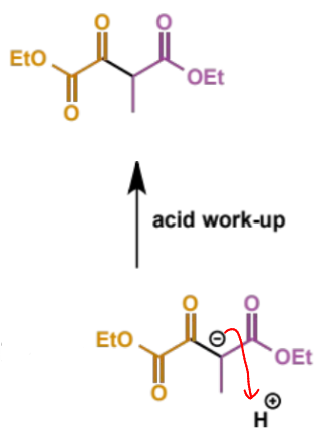
final stage of crossed Claisen

overall crossed Claisen mechanism
give 4 examples of non-enolisable, very electrophilic esters for crossed Claisen reactions

alternative nucleophile to non-enolisable esters for crossed Claisen
ketones

overall eqn for crossed Claisen
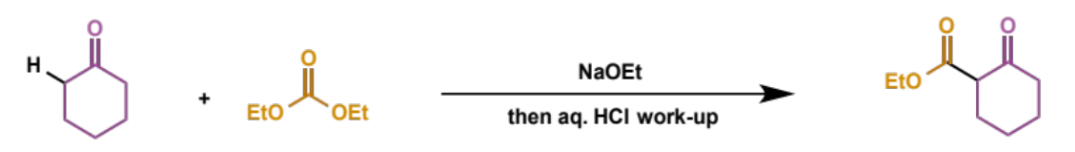

first step in crossed Claisen
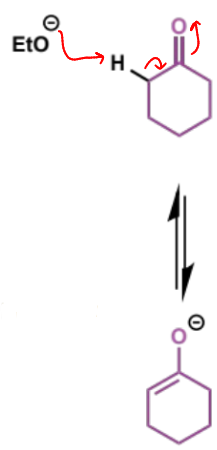
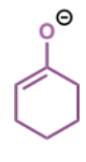
next step in crossed Claisen
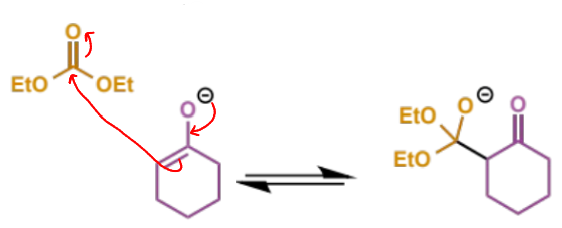
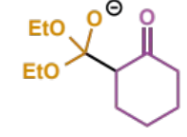
next step in crossed Claisen
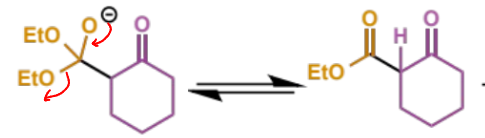
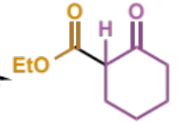
next step in crossed Claisen
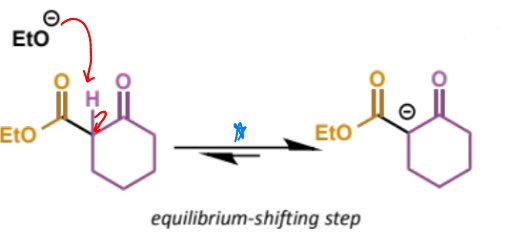
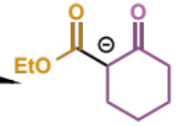
final stage in crossed Claisen


overall crossed Claisen mechanism

intramolecular Claisen
name of reaction?
forms?
what drives the reaction?
Dieckmann condensation, good way to form rings
reaction is driven by the formation of the stable enolate anion of the ketoester
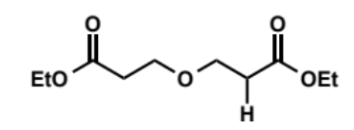
overall equation for Dieckmann condensation
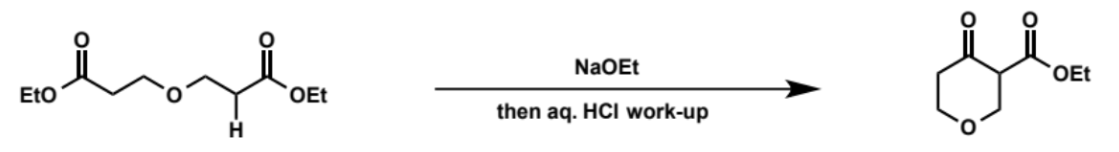
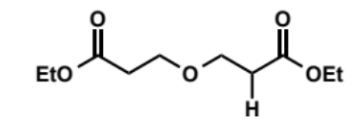
first step of Dieckmann condensation
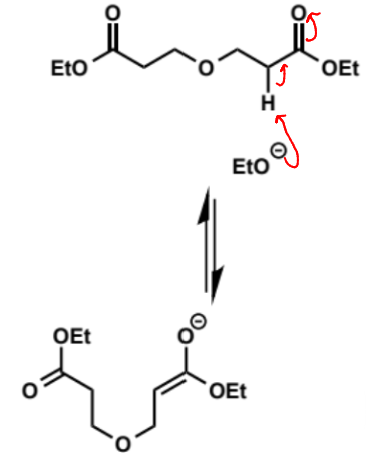
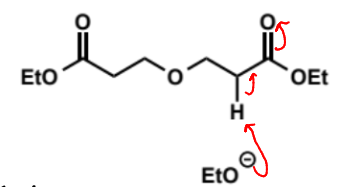
why is only one ester group shown to enolise
if eqm constant is 1 in 1 billion to form 1 enolate then it is 1 in 1018 for both esters to enolise - so safe to show only 1

next stage of Dieckmann condensation
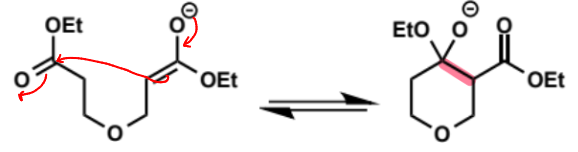
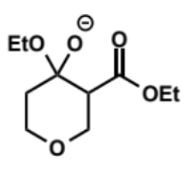
next step in Dieckmann condensation
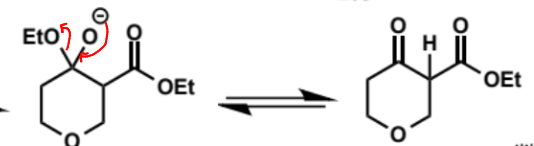
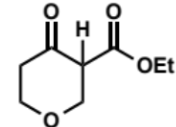
next step in Dieckmann condensation
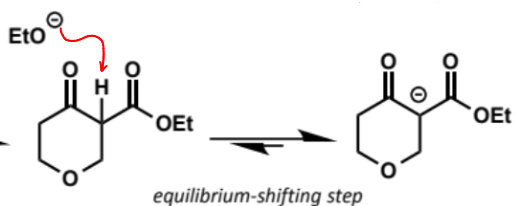
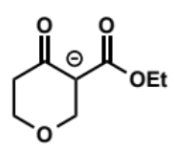
final step in Dieckmann condensation
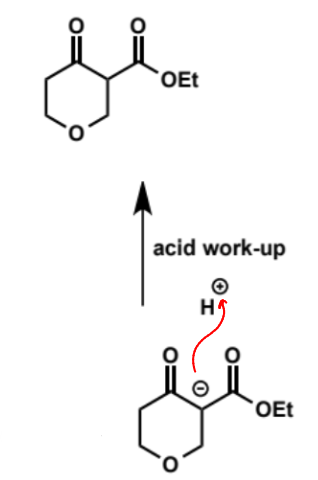

products of non-symmetrical diestere substrates for Dieckmann condensation
give overall equation
mixture of regioisomers is formed
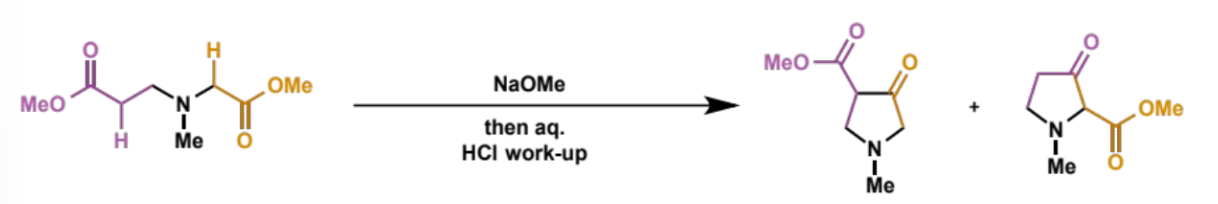
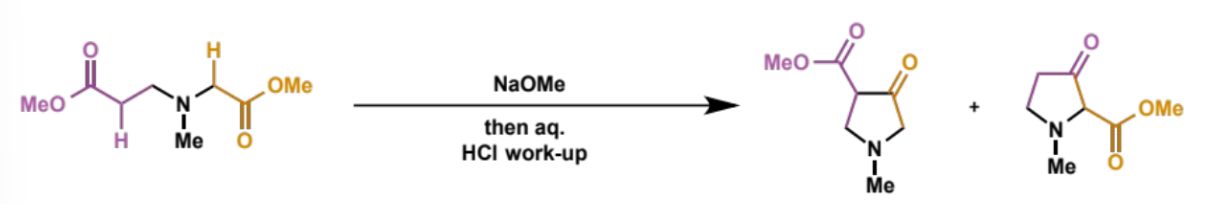
show how the different regioisomers are formed
each different ester can act either as the nucleophile (enolate) or the electrophile
