Forestry midterm 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Autotroph
producers in an ecosystem (photosynthesizers)
Biome
a very large area of earth’s surface that has a similar climate and vegetation
Biosphere
The entire planet (areas where life exists)
Community
a group of populations or organisms which live and react in a prescribed area
Decomposer
organisms that break down dead or decaying organisms
ecosystems
all of the interacting biological and physical aspects of an area
Genus
category of classification in biology that ranks between the family and the species, also contains related species (capitalized)
Heterotroph
Consumers (primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers)
includes herbivores, omnivores, and carnivores
Hybrid
result of successful interbreeding of two species
Population
individuals of a specific species in a certain area
Primary consumer
Herbivores, heterotrophs
Producers
photosynthesizers, autotrophs
Secondary Consumers
Omnivores, heterotrophs
Species
a group of individuals with similar morphologies, interbreed naturally, and produce fertile offspring (not capitalized, after genus)
Subspecies
populations which have some identifiable difference. Do not interbreed with other groups in the species due to geographical differences. (not capitalized, after species)
Taxon (pl. Taxa)
a taxonomic group of any level (species, subspecies, genus, class, etc)
Taxonomy
subdiscipline of biology concerned with classifying and naming organisms
Tertiary consumer
Carnivores, heterotroph
Angiosperm
have enclosed seeds (in a fruit)
usually having broadleaves, deciduous and evergreens
hardwoods (short fibers)
Broadleaves
tree or plant with wide, flat leaves
Cambium
Located in between the xylem and phloem.
undesignated cells which produce xylem towards the inside of the stem or trunk or phloem towards the outside
Carbohydrates
sugar molecules, it is a source of energy for plants
Conifer
Cone bearing seed plants , subset of gymnosperms
Ecological niche
favorable combinations of environmental factor ranges for a given species to grow and reproduce
Gravitropism
growth of roots or stems towards or against gravity’s direction
Gross photosynthesis
total amount of carbohydrates produced
Gymnosperm
Have exposed seeds or those which are enclosed in a cone
Conifers (usually needle or scale like leaves, also mostly evergreen)
Soft wood (long fibers)
Ginko is also a Gymnosperm despite broadleaves and seeds that look like fruits (smell bad lol)
Hardwood
Short fibered wood
usually contains many layers and grow very slowly
Heliotropism
growing towards sunlight (or other light sources)
Mycorrhizae
a fungus with a symbiotic relationship with the root systems of certain plants and trees
Net Photosynthesis
Gross photosynthesis minus the respiration
phloem
pretty much the bark, or right underneath it
in charge of transporting sap
Photosynthesis
process by which plants use water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide to produce carbohydrates and oxygen
Primary Growth
tree and plant growth which lengthens the stems and branches
Respiration
process by which plants produce energy, converting oxygen and carbohydrates for water, carbon dioxide and energy
Secondary growth
plant and tree growth outwards
adding to the width of a branch or stem
Softwood
wood from gymnosperms, longer fibers, grows faster as well
theory of tolerance
theory that species can only live and reproduce in a certain range of a given environmental (e.g. heat, rain)
Tree
A woody plant with usually a single stem at least 2m tall or if multistemed, at least one vertical stem 5cm+ in diameter at breast height
a plant that produces timber ($$$)
Tree Rings
represent growing seasons
usually years, but false rings do occur
xylem
tissue which transports water and nutrients through the center of the tree
Afforestation
establishment of a forest on land that wasn’t previously classified as forest
done by planting and deliberate seeding
Basal Area
area of a cross-section of a tree at DBH [m²]
in plots or stands is measured as Basal area per hectare (sum of all the basal areas in the hectare
Biogeoclimatic zone
an area with similar climate, soils, vegetation, and energy flows.
Result of broadly homogenous micro climates
Biome
large areas of earth’s surface with similar climate and vegetation
Boreal forests (a.k.a. taiga)
Needle leaf and evergreen trees
cold and frost resistant with adaptations for long periods of low to no light.
Largest pool of biomass on earth, summertime has massive bug booms
Canopy cover
area covered by tree crowns in a forest
must have at least 10 percent cover to consider land a forest
Climate graph
displays yearly temperature and precipitation for a given region
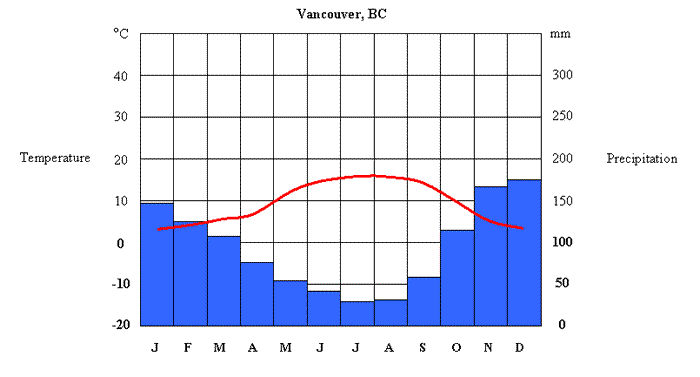
Deforestation
conversion of forest into another type of land (usage)
or degradation of canopy cover under the 10% mark
Diameter at Breast Height (DBH) [cm]
the diameter of a tree at breast height (1.3 meters off the ground)
in a plot DBH is the avg of all tree DBH in an area
*see notes for proper measurement technique
Dominant height (HD) [m]
mean of the largest trees in an area. (e.g. largest tree for every unit2)
Forest
A wooded area of land at least 0.5 hectares, with trees at least 5m in height and with at least 10% canopy cover.
Must be ab le to achieve in situ
Forest estate
all land containing a forest endowment
Forest Region
A large area with fairly uniform vegetation cover, or a dominant species or stand type
Forest plot
A polygon or circle, usually small (e.g. 300m2) where all trees are measured to estimate stand or forest level metrics
Forest stand
continuous piece of land
Formation
communities with specific vegetation structure
also used in biome subdivision
Growth Form
Type of plants present
e.g. trees, shrubs, herbs, epiphytes, lianas, bryophytes
Epiphytes
nonparasitic, but growing on trees
lianas
woody vines
bryophytes
mosses and lichens
Height (H) [m]
tree height measured from ground to highest tip
Mean Height (Hm) [m]
mean height of all trees in a plot or a stand
Merchantable volume
volume excluding stump (30 cm) and tree top (anything less than 10 cm in diameter)
Montane forest
Needleleaf trees (northern hemisphere) or broadleaf evergreen (southern hemisphere)
cold resistant, and fire and drought resistant (not all)
very diverse, occurring at all latitudes
it is an umbrella term for most high altitude forests
natural forest
a forest that has developed relatively free of human contact
Plantation
a forest managed by a company for the purpose of producing wood products.
Planted forest
A forest stand established through seeding or planting (afforestation or reforestation)
overtime will be considered primary
Primary forest
naturally regenerated forest of native species, with no clear indications of human activities
Reforestation
reestablishment of forest through planting or seeding on land previously classified as forest
stand table
a description of the number of trees in an area by diameter class
Stocking density (trees/hectare)
Number of trees in a hectare (extrapolated)
Temperate Deciduous forest
broadleaf, deciduous forest
annual leaf growth, with resistance to hit and cold temperatures
fall colours
commonly converted into agricultural or urban areas
not good with fires
Temperate rainforest
needleleaf and broadleaf trees, epiphytes, bryophytes, shrubs, ferns
layered structure, with long lifespans, shade tolerant, and gap dynamic regeneration
very valuable wood, high biodiversity, high productivity, high biomass, scarce, and high conservation priority.
total volume (Vt) (m3)
the total volume in a stand
Tree
A woody plant at least 2 meters in height
or
A woody plant with multiple stems with one at least 5 cm in diameter ad breast height (1.3m)
Tree Density (a.k.a. stocking density)
number of trees in a hectare
it is an area measurement by default
Tropical Rainforest
all forms of vegetation
competition for light, shade tolerance, layered structure, wet soil
extremely high biodiversity and biomass
lots of logging, burning, and clear cuts to make way for cattle and agriculture
Tropical seasonal forest
broadleaf deciduous trees and shrubs (they drop leaves because of dry seasons)
fire and extreme humidity tolerance, and annual leaf growth
monsoon reliant, and high biodiversity
commonly converted for agriculture
Volume
timber volume from ground to tip
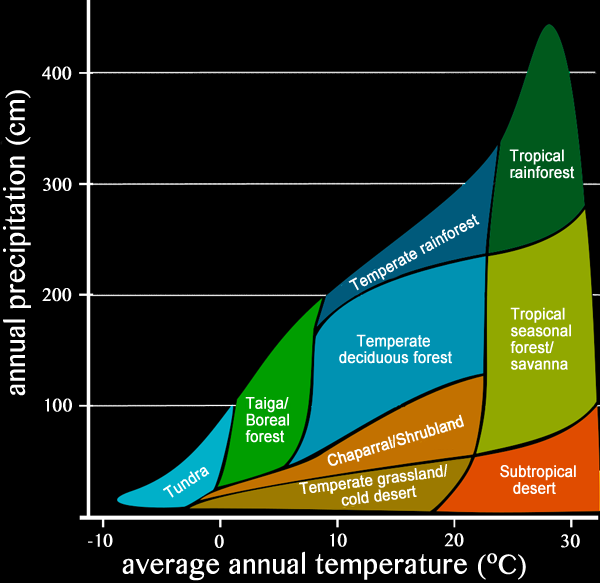
Whittaker diagram
Cellulose
crystalline, polysaccharide that provides structure in cell walls
(~40% of wood)
(pulp and fibers)
Ecosystem service
benefits people get from ecosystems
Forest Product
Any monetizable market demand obtained from the forest
classifications: Timber forest product, non-timber forest product, fuel
Forest Value
anything the forest can provide, monetizable or not
can be with specific monetizable value
or things which it is hard to place a value on
hemicellulose
amorphous weak polysaccharide that supports attachments with lignin (~30% of wood)
Lignin
rigid and durable polymer that reinforces cell walls (~30% of wood)
non-timber forest product
physical goods obtained from the forest excluding industrial wood/pulp
Polysaccharide
A chain of carbohydrate molecules
Timber forest product
Anything made primarily of recognizable wood/ wood fibers
Forest service
provision depending on a forest, without extracting goods
Cultural services
nonmaterial benefits obtained from ecosystems
Ecosystem services
benefits people obtain from ecosystems (4 catagories)
Forest zoning
optimize allocation of different areas for best use or ecosystem service
Examples:
Triad Concept
land and resource management plans
Land and Resource Management Plans
guidelines on projects for local land use in agriculture, communities, natural resources, recreation, utilities and agriculture
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
a UN led initiate to assess consequences of ecosystem change for human well-being
what needs to be done
main finding → substantial net gains in human well-being comes with ecosystem degradation
Provisioning services
Products obtained from ecosystems
Regulating services
Benefits from regulation of ecosystem processes
Supporting services
services necessary for production of all other ecosystem services
Triad concept
three main zones in forest landscape
production forest
protection forest
ecological mix