Pectoral Guirdle
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Pectoral Girdle
The shoulder girdle made of the clavicles and scapulae; connects the upper limb to the trunk and supports shoulder movement.
It provides attachment points for muscles and facilitates a wide range of motion in the arms.
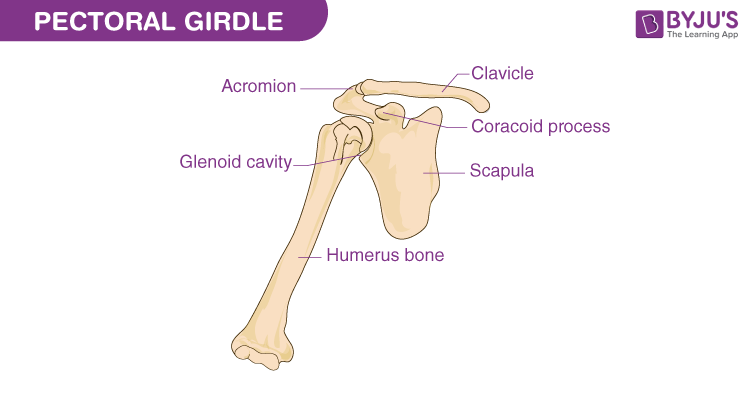
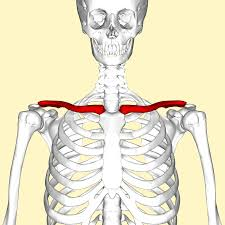
Clavicle
S-shaped collarbone connecting the sternum to the scapula; holds the scapula in place and helps support the shoulder. It acts as a strut to stabilize the shoulder and allows for movement of the arm.
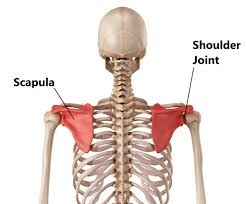
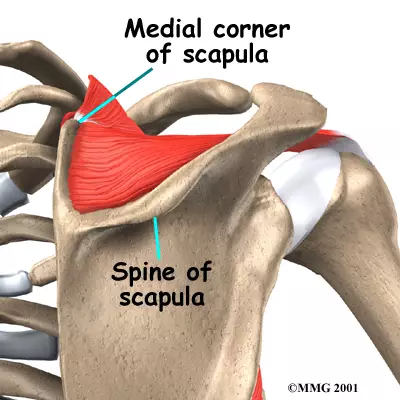
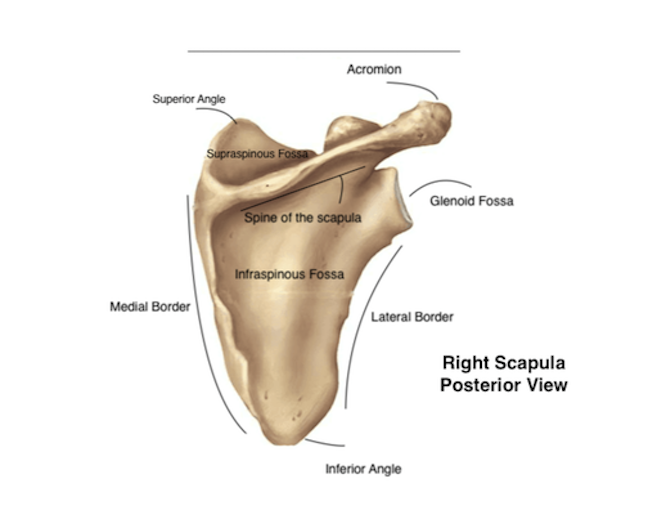
Scapula
Flat, triangular shoulder blade on the back of the rib cage; connects arm to body and gives muscles a place to attach.
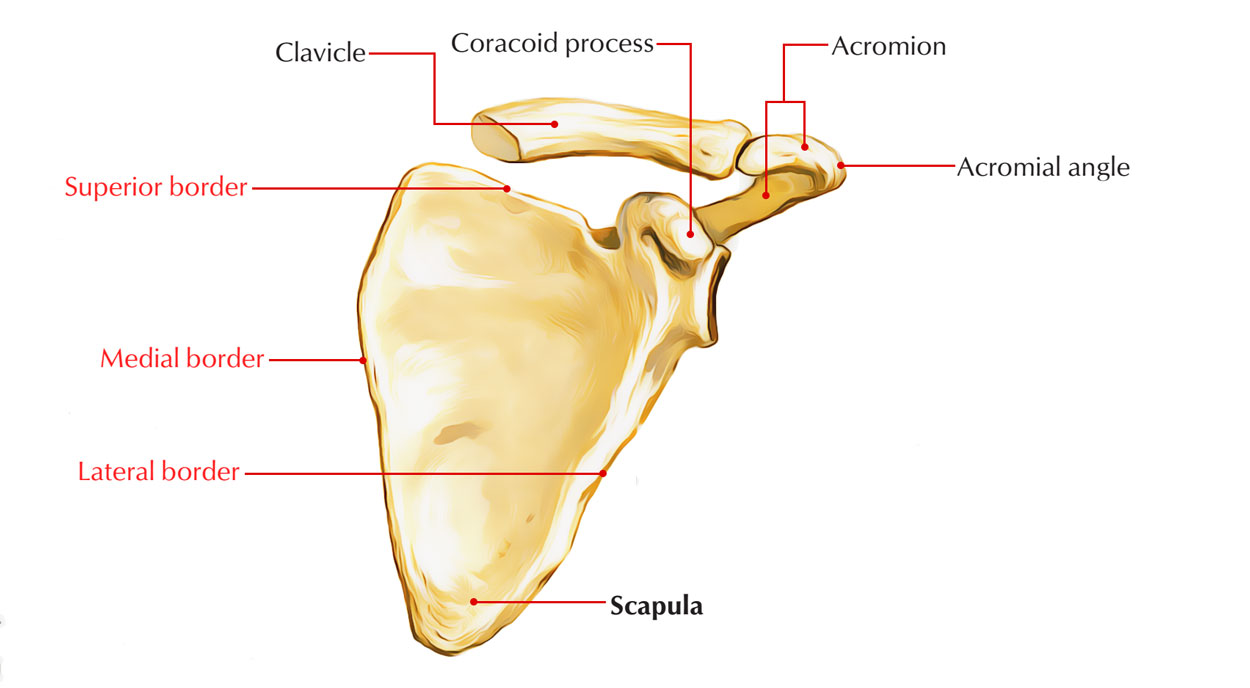
Acromion (process)
Projection on the top of the scapula; articulates with the clavicle to form the top of the shoulder.
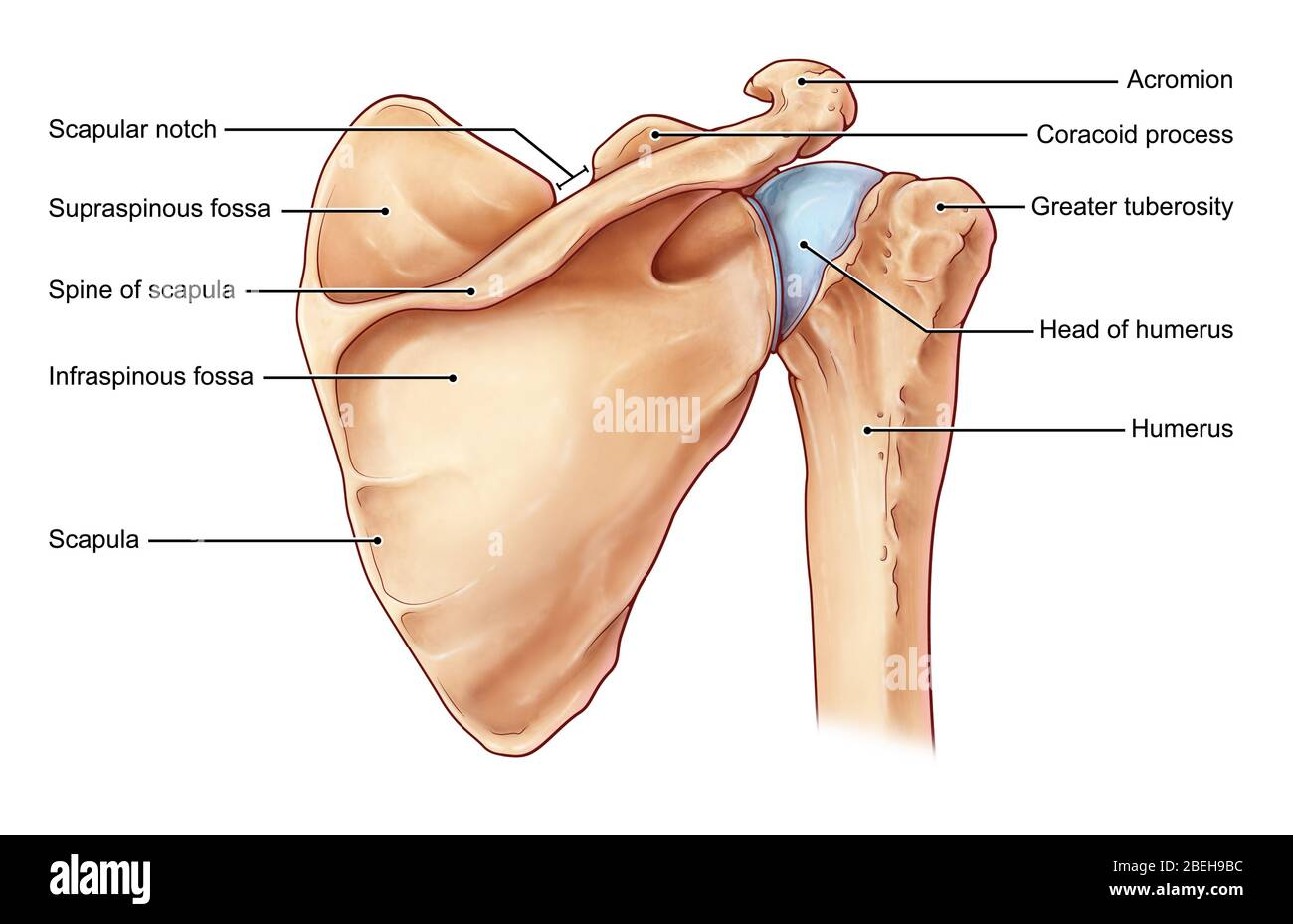
Glenoid cavity (fossa)
Shallow depression on the scapula; holds the head of the humerus to form the shoulder joint.

Spine (of scapula)
Raised ridge on the back of the scapula; separates the two fossae and is a muscle attachment site.
It also provides stability to the shoulder joint.
Borders (superior, lateral, medial)
The three edges of the scapula; give the scapula shape and serve as muscle attachment sites.
The superior border is the shortest, the medial border is the longest, and the lateral border is the thickest.
Infraspinous fossa
Depression below the scapular spine (posterior side); muscle attachment site for infraspinatus.
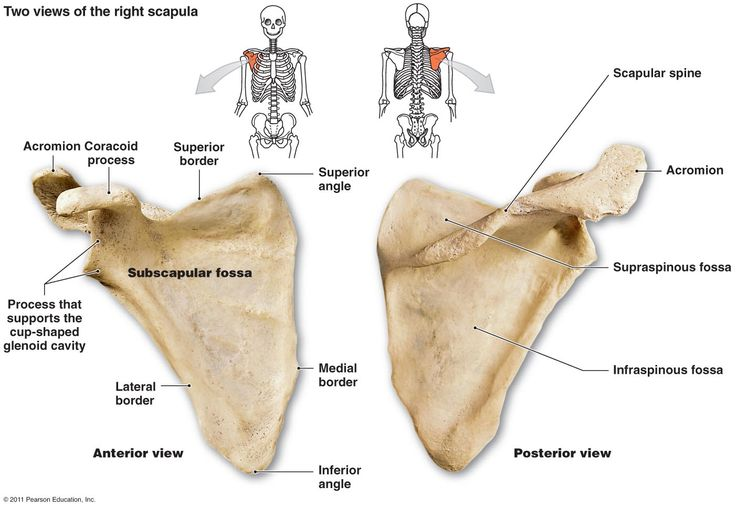
Supraspinous fossa
Depression above the scapular spine; muscle attachment site for supraspinatus.
Subscapular fossa
Large depression on the front (anterior) surface of scapula; muscle attachment site for subscapularis.
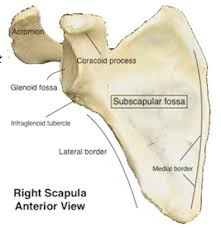
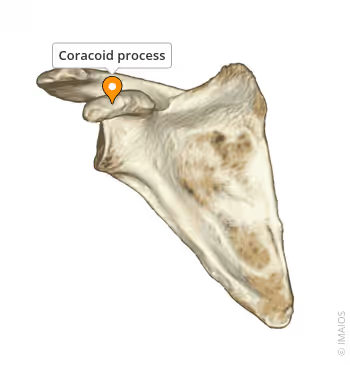
Coracoid process
Curved projection on the front of the scapula; attachment site for muscles and ligaments.