Earth
4.8(4)
4.8(4)
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
1
New cards
constructive force
any natural process that builds up Earth's surface

2
New cards
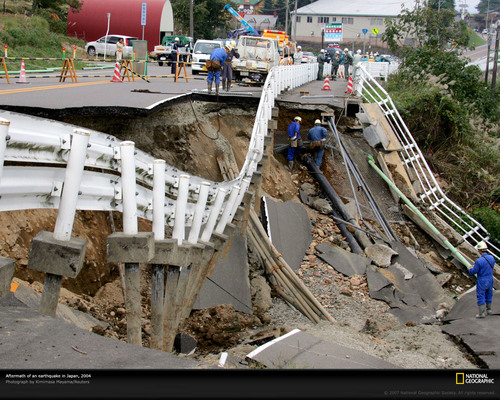
destructive forces
Any natural process that tears down or wears away Earth's surface.

3
New cards
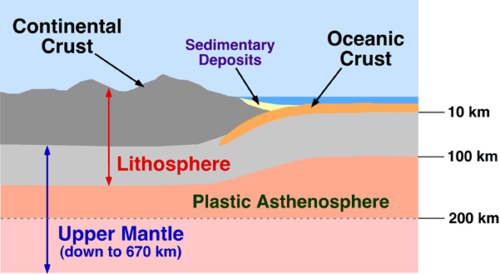
lithosphere
the rigid outer part of the earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
4
New cards
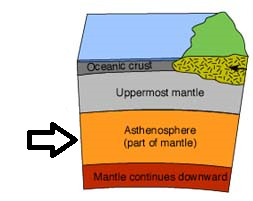
asthenosphere
The soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move
5
New cards
crust
Earth's outermost layer.
6
New cards
mantle
the layer of the earth between the crust and the core
7
New cards
core
The central part of the earth below the mantle

8
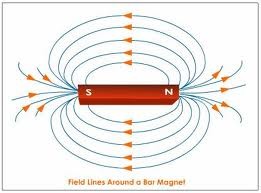
New cards
magnetic field
a region around a magnetic material or a moving electric charge within which the force of magnetism acts
9
New cards
plate tectonics
The theory that pieces of Earth's lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle

10
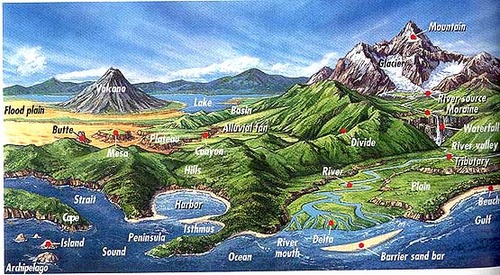
New cards
landforms
features that make up the earth's surface such as a plain, mountain, or valley
11
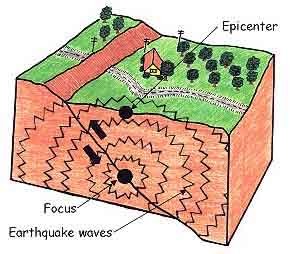
New cards
earthquake
the shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface
12
New cards
volcano
a vent or fissure in the Earth's surface through which magma and gases are expelled

13
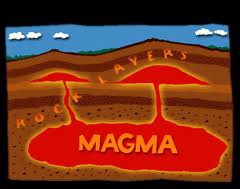
New cards
magma
molten rock beneath the earth's surface
14
New cards
lava
liquid magma that reaches the surface

15
New cards
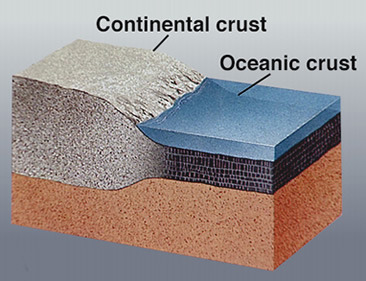
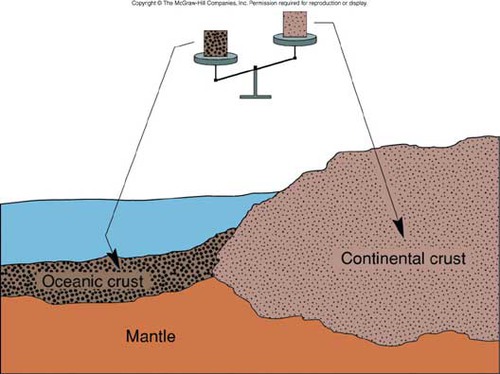
oceanic crust
earths crust located under the ocean
16
New cards
continental crust
The portion of the earth's crust that primarily contains granite, is less dense than oceanic crust, and is 20-50 km thick
17
New cards
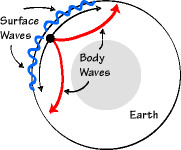
surface waves
seismic waves that travel along the Earth's surface
18
New cards
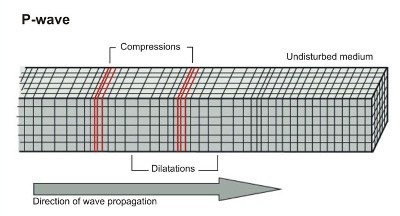
primary waves
waves that travel outward from an Earthquake's focus and cause particles in rocks to move back and forth in the same direction the wave is moving
19
New cards
secondary waves
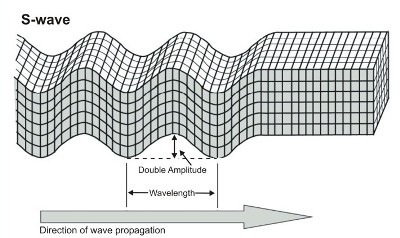
waves that travel outward from an earthquake's focus and move through Earth by causing particles in rocks to vibrate at right angles to the direction of the wave
20
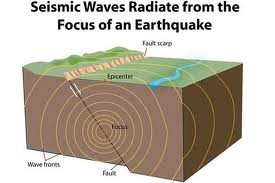
New cards
seismic
relating to or caused by an earthquake
21
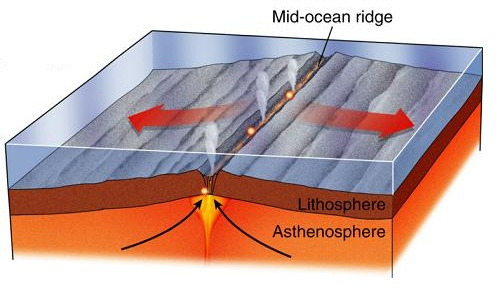
New cards
mid-ocean ridge
An undersea mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced; a divergent plate boundary.
22
New cards
seafloor spreading
The process that creates new sea floor as plates move away from each other at the mid-ocean ridges

23
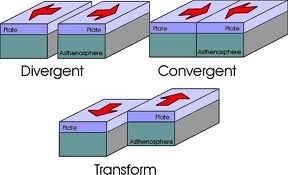
New cards
plate boundaries
the edges of tectonic plates
24
New cards
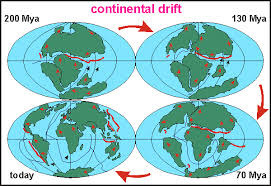
continental drift
the hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth's surface
25
New cards
divergent
going in different directions

26
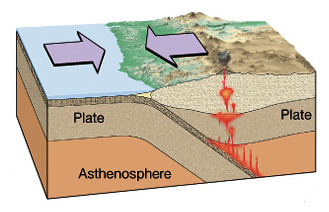
New cards
convergent
coming together
27
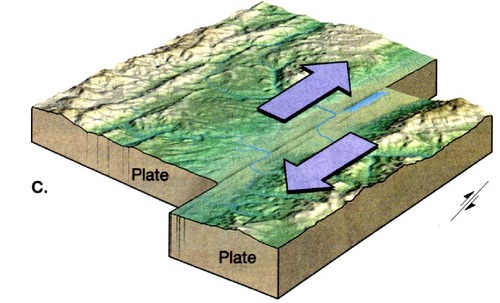
New cards
transform boundary
a plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions
28
New cards
subduction
one plate going under another plate

29
New cards
crystallization
The process by which atoms are arranged to form a material with a crystal structure

30
New cards
decay
to break down or wear away

31
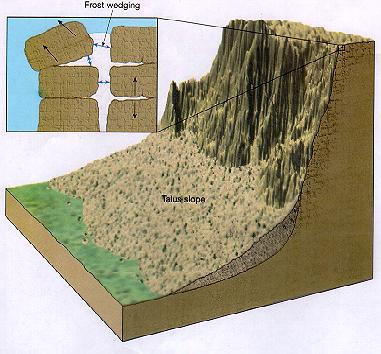
New cards
weathering
The breaking down of rocks and other materials on the Earth's surface.
32
New cards
clay
the finest soil, made up of particles that are less than 0.002 mm in diameter.

33
New cards
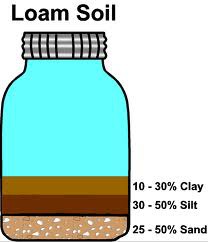
loam
A mixture of gravel, sand, silt, clay, and organic matter
34
New cards
humus
material formed from decaying leaves and other organic matter

35
New cards
sand
the coarsest soil, with particles 0.05,2.0 mm in diameter.

36
New cards
silt
A mixture of rich soil and tiny rocks

37
New cards
mineral
a naturally occurring, inorganic solid that has a crystal structure and a definite chemical composition

38
New cards
sedimentary
A type of rock that forms when particles from other rocks or the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together

39
New cards
igneous
a type of rock that forms from the cooling of molten rock at or below the surface

40
New cards
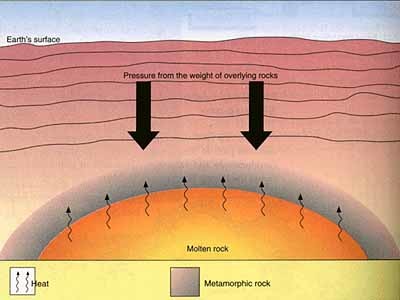
metamorphic
A type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
41
New cards
pedosphere
The outermost layer of the Earth that is composed of soil.

42
New cards
vegetative cover
grasses, trees, shrubs, and any other plants that help to hold the soil in place

43
New cards
agriculture
farming

44
New cards
contour plowing
plowing fields along the curves of a slope to prevent soil loss

45
New cards
conservation plowing
farmers disturb the soil and its plant cover as little as possible

46
New cards
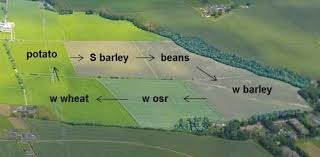
crop rotation
The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year, to avoid exhausting the soil.
47
New cards
vector
carrier (of disease, for example)

48
New cards
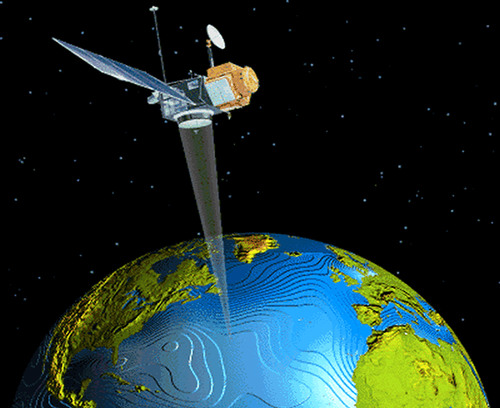
remote sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods.
49
New cards
erosion
Processes by which rock, sand, and soil are broken down and carried away (i.e. weathering, glaciation)

50
New cards
stewardship
Looking after something so it can be passed on to the next generation
