Science Test All Combined
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
this is all kaelyn and alan they sweated it
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Which of these celestial objects wouldn't lie near/on Earth's orbital plane?
Polaris
3 multiple choice options
Earth completes one full revolution around The Sun every one _________.
year
3 multiple choice options
Polaris is another term for the ________________.
North Star
3 multiple choice options
Why is the Scorpius constellation unable to be seen in January?
The Sun and Scorpius are in the same direction from Earth.
3 multiple choice options
What's Earth's axis?
The imaginary point/line Earth rotates around.
3 multiple choice options
What is Earth's orbital plane?
A flat surface stretches past Earth's orbit and continues forever.
3 multiple choice options
What is one reason circumpolar stars are visible all year round?
They are located near the celestial poles, and due to Earth's rotation, they never dip below the horizon.
3 multiple choice options
Earth's rotation is a process that causes _________________.
all of the above
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following statements does NOT describe the behavior of a celestial object?
A communications satellite revolving around Earth.
3 multiple choice options
What object(s) does Earth revolve around?
The Sun.
3 multiple choice options
Which of these most closely describes the shape of an ellipse?
A thin oval.
3 multiple choice options
Our ability to observe the sun travel across the sky because we are standing on a moving object is an example of...
a cause and effect relationship.
3 multiple choice options
Earth rotates on its axis approximately once every _________.
day
3 multiple choice options
Why are seasonal stars only visible during certain times of the year?
Their visibility depends on Earth's position relative to the Sun.
3 multiple choice options
Why are circumpolar stars that reside below the South Pole not visible in Earth's northern hemisphere?
They are blocked by Earth.
3 multiple choice options
The overall pattern of the Sun rising toward the East and setting toward the west _______________.
never changes
3 multiple choice options
The action of spinning on the axis is ____________.
rotation
3 multiple choice options
Why do stars seem to change their positions overtime?
Because Earth rotates on it's axis, making it seem as if they move.
3 multiple choice options
What are the two constellations on the Earth's orbital plane?
Orion and Scorpious.
3 multiple choice options
Circumpolar stars can be seen year-round.
True
1 multiple choice option
Why can Aussies not see Polaris?
Because it's blocked by the Earth.
3 multiple choice options
What is an axis of rotation?
An imaginary line passing through an object's center of mass around which the object rotates.
3 multiple choice options
Why do the Sun, Moon, and stars appear to rise in the east and set in the west?
Because of the way Earth rotates, it makes it seem in perspective that the celestial bodies are moving.
3 multiple choice options
Is a day the same length universally?
No: This is because of the difference in daylight hours each region gets.
1 multiple choice option
Why does the Earth spin?
Intertia.
3 multiple choice options
Why has the Earth's spin slowed?
It's slowed because the Moon's rotation, which moves the waves, tries to stop Earth's rotation.
3 multiple choice options
What will eventually happen to the Moon?
It will eventually drift away from Earth.
3 multiple choice options
What direction does Earth rotate?
Counterclockwise (west to east).
1 multiple choice option
Why is Earth closer from the Sun in the winter and farther in the summer?
Because Earth's orbit path isn't circular and elliptical path of Earth is sometimes closer to the Sun in the summer.
3 multiple choice options
The USA is in the ______________ Hemisphere.
Northern
1 multiple choice option
What happens to the Sun during the winter?
It rises later in the morning and sets earlier in the evening.
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following is determined by your location on Earth?
All of the above.
3 multiple choice options
What is a system?
A set of connected parts that form a complex whole.
3 multiple choice options
Which statement is true regarding the December Solstice?
The Southern Hemisphere is experiencing summer.
3 multiple choice options
What happens when sunlight hits Earth's surface near the equator?
Sunlight transfers a large amount of energy to each spot it hits.
3 multiple choice options
What change(s) might occur in the sun with the changes in seasons?
All of the above.
3 multiple choice options
If you were to shine a flashlight on a piece of paper, at which angle would you expect to have a more concentrated amount of light?
90 degrees.
3 multiple choice options
In which month in the northern hemisphere might you expect to see the sun arc high in the sky and remain there for about 15 hours?
June.
3 multiple choice options
Earth's axis is not perpendicular to its orbital plane, which means that...
Different latitudes receive different amounts of sunlight throughout the year.
3 multiple choice options
Which of these marks the first day of spring in the northern hemisphere and the first day of autumn in the southern hemisphere?
March Equinox.
3 multiple choice options
How does Earth's shape affect the way that sunlight hits it?
Sunlight always hits different parts of Earth at different angles.
3 multiple choice options
Which of these best describes a seasonal pattern?
Leaves falling off trees in autumn for 10 years.
3 multiple choice options
At which latitude north and south are the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn located?
23.5 degrees.
3 multiple choice options
Which statement is NOT true regarding the September Equinox?
Sunlight hits the Tropic of Capricorn at a perpendicular angle.
3 multiple choice options
Which month marks the start of winter in the Southern Hemisphere?
June.
3 multiple choice options
Which of these statements is NOT true regarding an equinox?
Places on the equator experience sunlight at a 23.5° angle.
3 multiple choice options
In this image, at which location(s) does light hit the Earth's surface at a non-perpendicular angle?
Northern latitudes.
3 multiple choice options
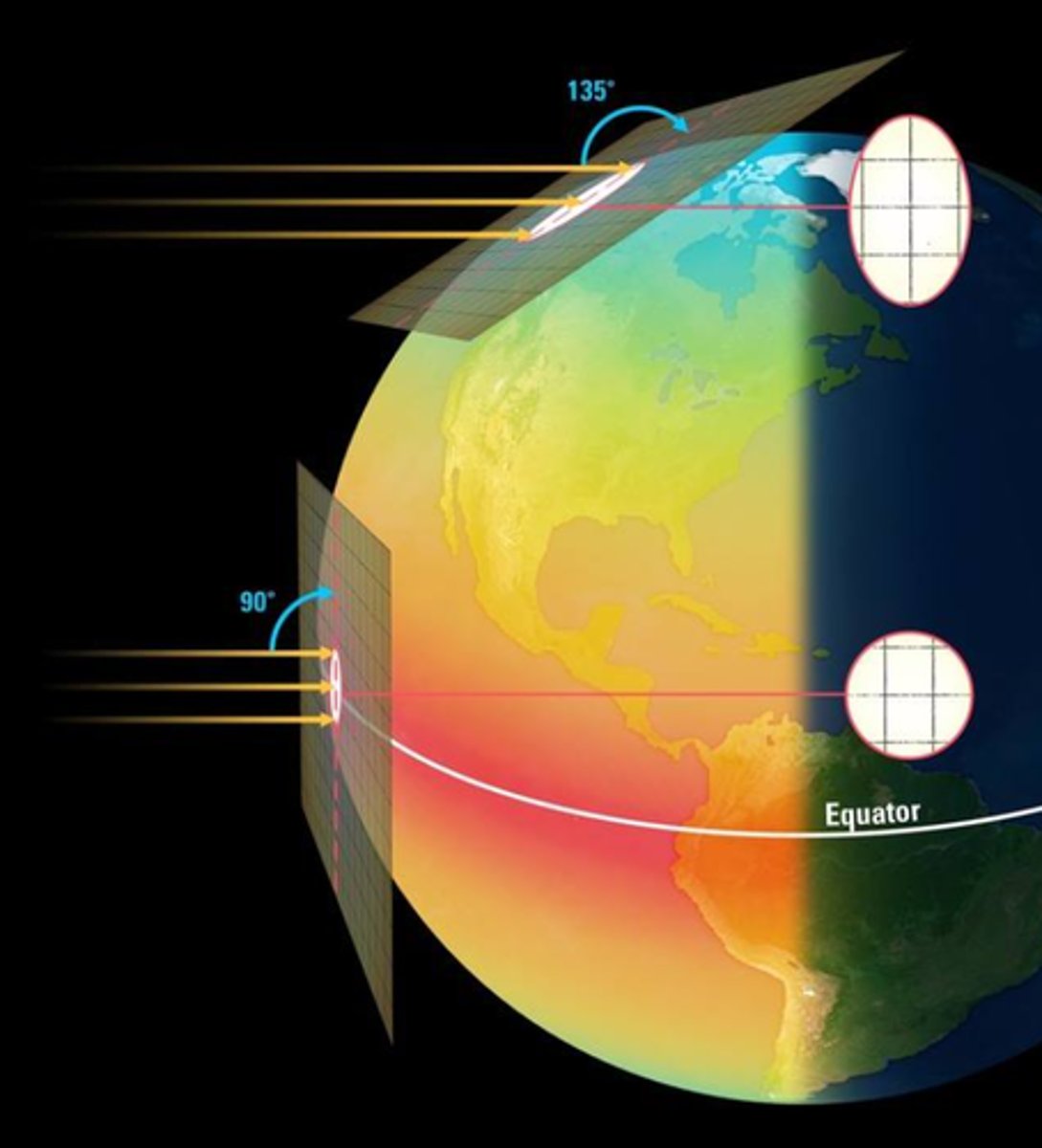
During which month is the Sun more likely to directly hit one of the tropics?
December.
3 multiple choice options
When does the June Solstice occur?
When the Sun hits the Tropic of Cancer perpendicularly.
3 multiple choice options
When does the first day of summer happen for the Northern Hemisphere?
June Solstice.
3 multiple choice options
When does the first day of winter happen for the Northern Hemisphere?
December Solstice.
3 multiple choice options
When do solstices occur?
When the Earth is tilted to the maximum away/from the Sun.
3 multiple choice options
When do equinoxes occur?
When the Earth's axis isn't pertaining to any side from the Sun.
3 multiple choice options
When does the first day of autumn happen for the Northern Hemisphere?
September Equinox.
3 multiple choice options
____________ have the longest days/nights.
Solstices
___________ have equal day and night hours.
Equinoxes
How much is Earth's axis tilted to Polaris?
23.5 degrees.
3 multiple choice options
Which of these statements is NOT true of lunar phases?
They change with the seasons.
3 multiple choice options
What were the two main criteria that the Apollo 11 astronauts had for their moon mission?
To land on the Moon and safely return to Earth.
3 multiple choice options
The phase between a full moon and a third quarter moon is called a ___________________.
waning gibbous moon
3 multiple choice options
What is a lunar phase?
The shape of the lit area of the Moon as seen from Earth.
3 multiple choice options
At any moment, the Sun shines on how much of the Moon?
Half of the Moon.
3 multiple choice options
What is a crescent moon?
When the Moon's shape is smaller than a semicircle, but not completely dark.
3 multiple choice options
Which of these describes one purpose of scientific models?
They make important aspects easier to observe.
3 multiple choice options
Why is the Moon visible from Earth?
Sunlight that hits the moon is reflected off its surface.
3 multiple choice options
Where is the Moon located during a new Moon?
Directly between Earth and the Sun.
3 multiple choice options
The first time a human walked on the surface of another celestial body was when Commander Neil Armstrong ______________________.
stepped onto the surface of the Moon
3 multiple choice options
What are two patterns that the moon seems to have that most other celestial objects do not?
Changing shape and varied rising and setting times.
3 multiple choice options
Each of the four main phases of the moon each take place over the course of about ________________________.
seven days
3 multiple choice options
Which of these accurately describes the Moon's behavior in the Northern Hemisphere?
It appears to grow from the right then shrink to the left.
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following was one of the criteria for the Apollo 11 moon landing?
They needed sunlight to hit the Moon at a very specific angle.
3 multiple choice options
The Moon seems to change from a full Moon to crescent shapes back to a full moon over the course of ______________________.
about a month
3 multiple choice options
What determines how the different moon phases appear from Earth?
The relative positions of the celestial objects in the Earth-Sun-moon system.
3 multiple choice options
Why are consistent patterns useful to scientists who study the movement of celestial bodies?
Consistent patterns are easily modeled.
3 multiple choice options
What would be one simple way to model the pattern of how the moon changes in the Earth-sun-moon system?
Rotate around a bare light bulb while holding a ball in front of your body.
3 multiple choice options
______________ is the term for a Moon that's getting bigger.
Waxing
1 multiple choice option
______________ is the term for a Moon that's getting smaller.
Waning
1 multiple choice option
During NASA's Apollo 11 mission they had to land when the Moon was in it's _________________________ phase.
waxing cresent
3 multiple choice options
How long did NASA (Apollo 11) power their engine to stay on course?
151 seconds.
3 multiple choice options
How often does the Moon's orbit intersect Earth's orbital plane?
Twice a month.
3 multiple choice options
What is a corona?
The Sun's glowing ring caused by the Moon during a solar eclipse.
3 multiple choice options
When is a lunar eclipse likely to occur?
When Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon.
3 multiple choice options
Which of these statements does NOT accurately describe a solar eclipse?
The moon's light is visible from Earth.
3 multiple choice options
What is one reason a total solar eclipse does not last very long?
The perfect size match of the Sun and the Moon means Sun is only blocked for a short time.
3 multiple choice options
Which of these statements is accurate about the Moon's orbit?
It is tilted compared to Earth's orbital plane.
3 multiple choice options
Why is the penumbra of a shadow lighter than its umbra?
A penumbra receives some light from a given light source.
3 multiple choice options
What is an eclipse?
An event in which the shadow of one celestial object falls on another celestial object
3 multiple choice options
Due to Earth's spherical shape, its umbra casts a shadow in the shape of a __________.
cone
3 multiple choice options
How many times larger or smaller is the Sun's diameter compared to the Moon's diameter?
400 times larger.
3 multiple choice options
Where or when can viewers on Earth experience a partial solar eclipse?
When they are in the Moon's penumbra.
3 multiple choice options
During which phase of the Moon are solar eclipses visible?
New moon phase.
3 multiple choice options
Which of these statements does NOT accurately describe what happens during a lunar eclipse?
A new Moon passes through Earth's orbital plane.
3 multiple choice options
What event is said to occur when the Moon moves completely into Earth's umbra?
A total lunar eclipse.
3 multiple choice options
What is one reason the Sun and the Moon appear to be the same size when viewed from Earth?
The Sun is larger in size than the Moon, but farther away from Earth.
3 multiple choice options
Which of these accurately describes an umbra?
An umbra is the darker, center part of a shadow.
3 multiple choice options
What is one effect that a partial lunar eclipse has on the appearance of the Moon?
The part of the Moon that is not in the umbra remains bright.
3 multiple choice options
During which of the following is an eclipse likely to occur?
When Earth, the Sun, and the moon all lie on the same plane.
3 multiple choice options
What makes Jupiter easier to see than Mars?
It is larger than Mars, so it appears to be brighter
3 multiple choice options
What is an astronomical unit (AU)?
A unit of measurement that is about the distance of the Earth to the Sun
3 multiple choice options
A solar system is a system...
made up of a star and all the objects around it.
3 multiple choice options