Biostatistics exam 3 - Adjusting for multiple comparisons
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
Family-wise error rate (FWER) equation
α = alpha
n = number of comparisons (# of tests)
• gives you the probability of committing a type I error
• Examples:
- chocolate study: 60% probability of Type I error
- astrological study: 70% probability of Type I error
• the more tests you run, the higher the probability of a Type I error

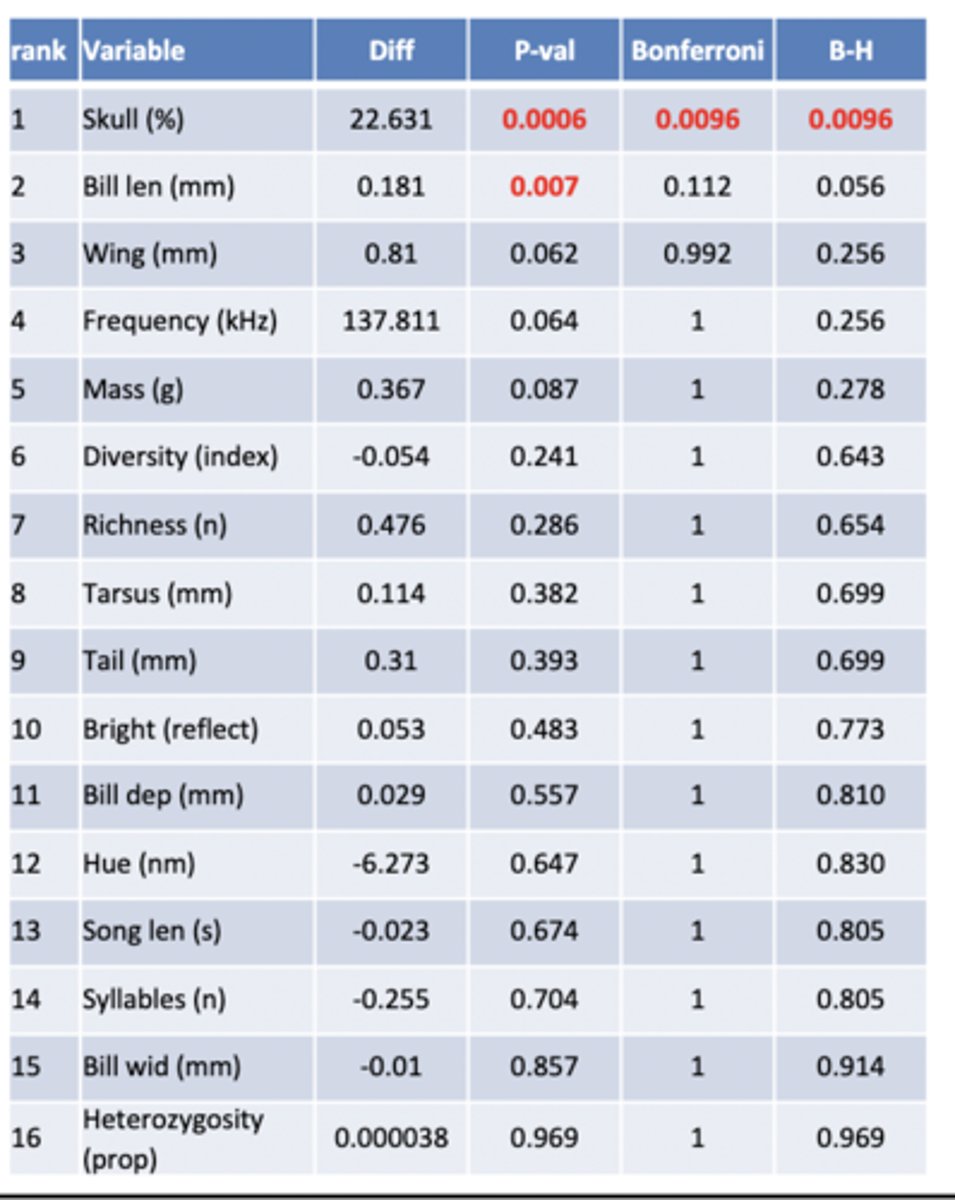
Bonferoni adjustment
• used to help adjust P-values due to multiple tests
• you run the adjustment on each other of the tests
Padj = P * k
• k = number of tests
• P = orignal p-valus
• Note: Maximun Pajd is 1
• some people say it is too harsh
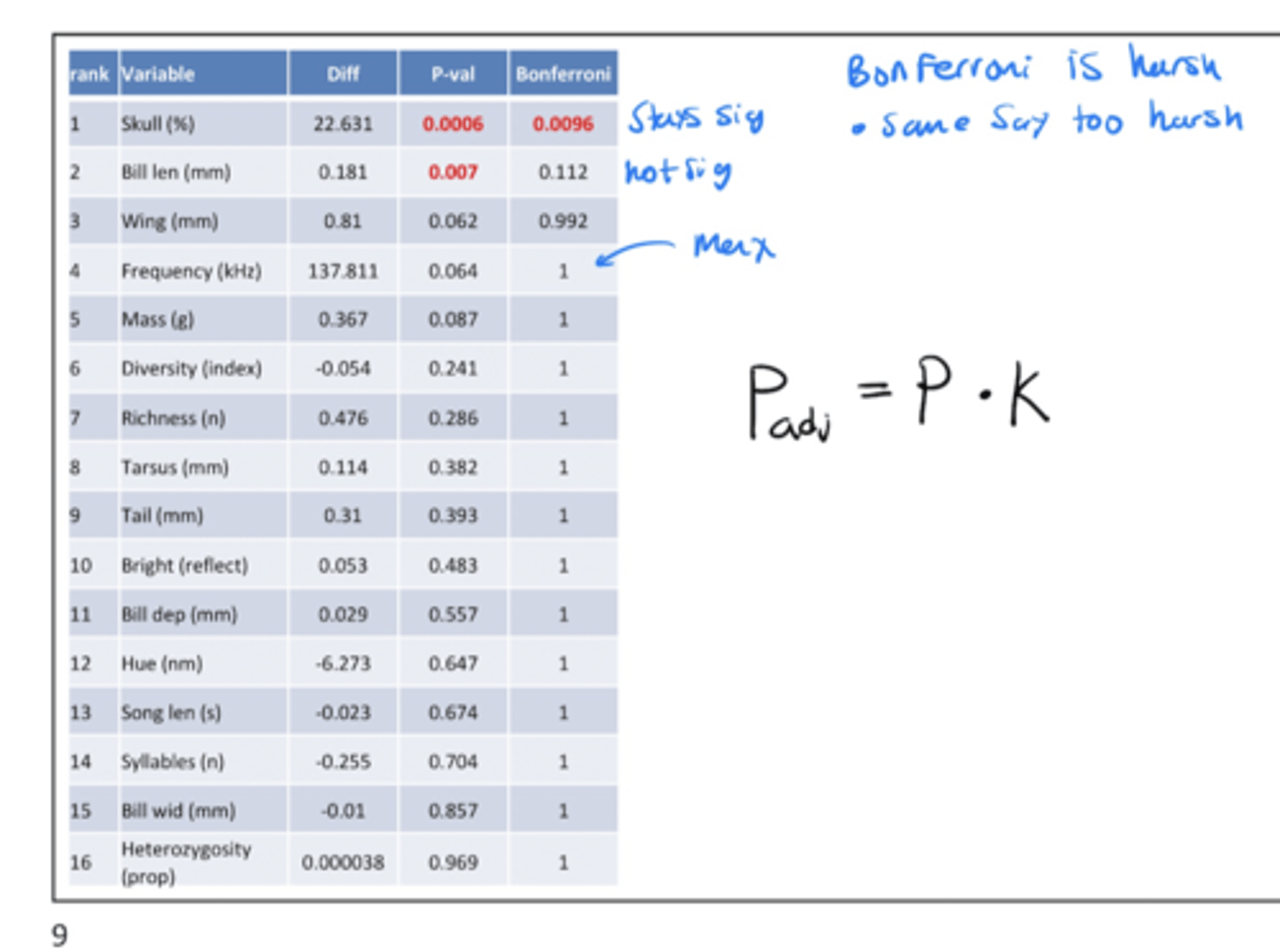
Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment
• Much more permissive and popular method
- Alias "False discovery rate"
• Sorts P-values low to high
• NOTE: the value cannot exceed BH of rank i+1
- Any adjusted P-val can't be higher than the one next to it
• k = number of tests
• i = rank of that particular test
- lowest p-val i = 1
* The highest rank will have the the same p-val from OG test bc k/i = 16/16 (in this test example)
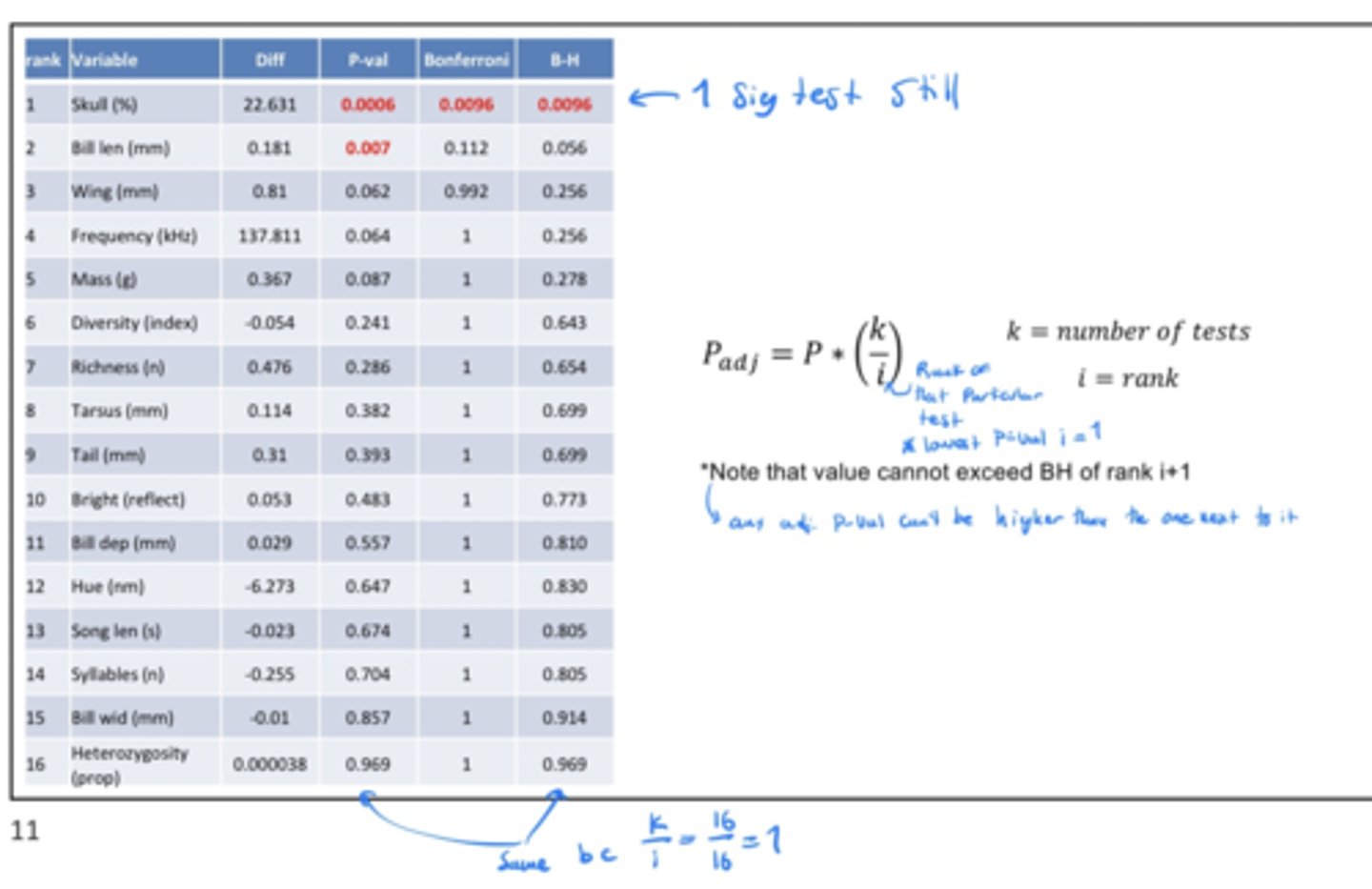
Importance of adjusting P-values
• changes biological interpretation
In this example:
• No correction
- 2 significant variables
- 3 additional variables have a P-val between 0.05 and 0.1 ("marginally significant") (so an inc. in sample size might make it significant)
• With correction
- 1 significant variable
- 1 marginally significant variable