Lec 2: Quantitative/Qualitative Research
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms

what are the steps of the research process
identify research problem
review relevant literature
select appropriate research design
collect/analyze data
interpret findings/draw conclusions
disseminate results to improve nursing practice

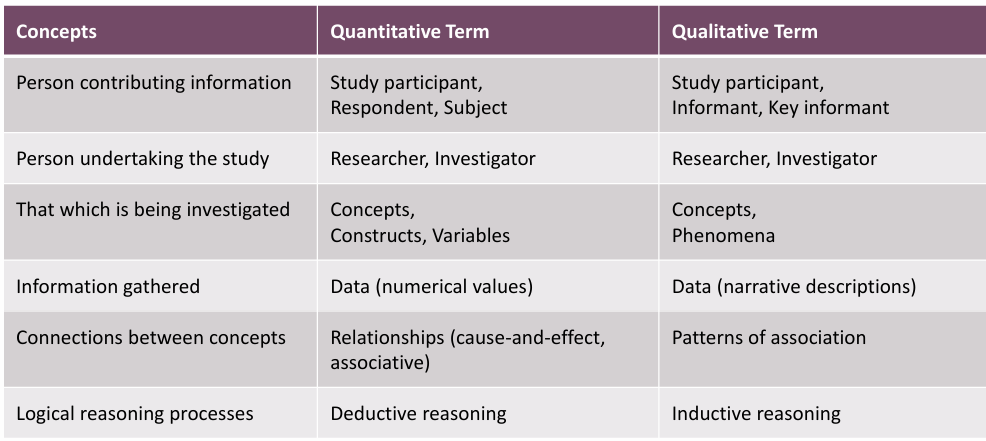
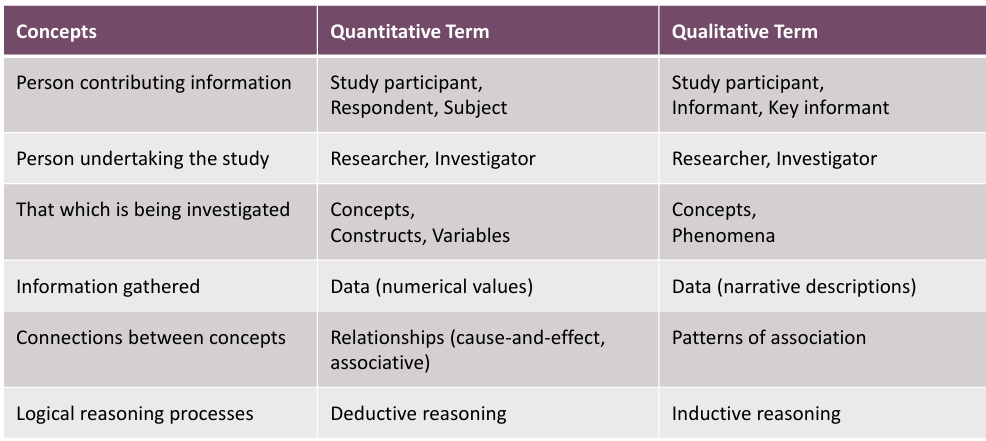
what is a person contributing research referred to as in qualitative/quantitative research
qual=study participant, informant, key informant
quant=study participant, respondent, subject
what is a person undertaking the study referred to as in qualitative/quantitative research
qual/quant=research/investigator
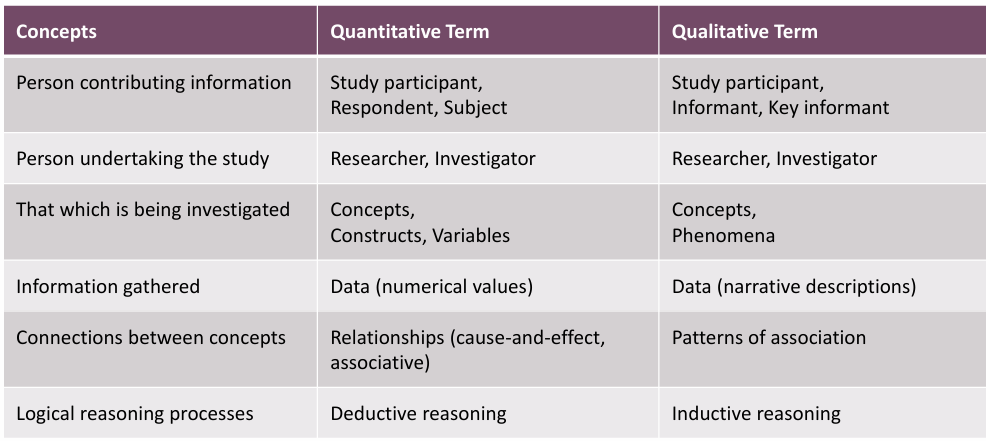
what is that being investigated in qualitative/quantitative research
qual=concepts, phenomena
quant=concepts, constructs, variables
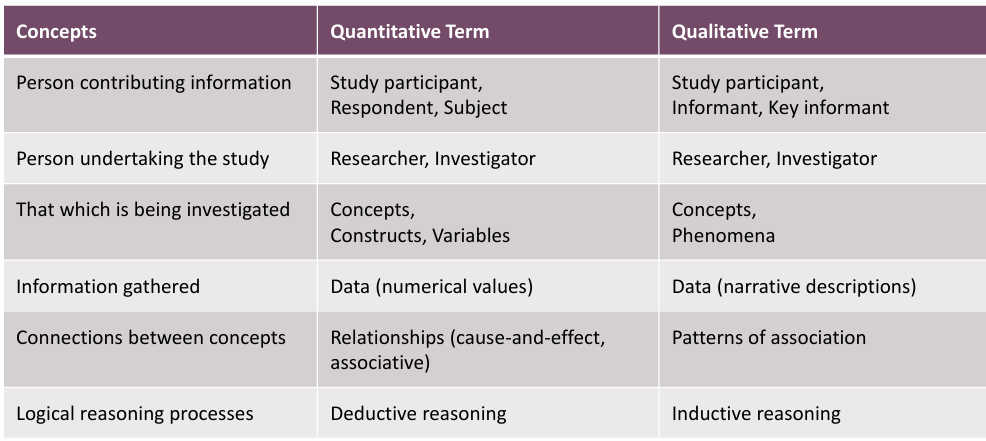

what type of information is being gathering in quantitative/qualitve research
qual= data/narrative descriptions
quant=data/numerical values

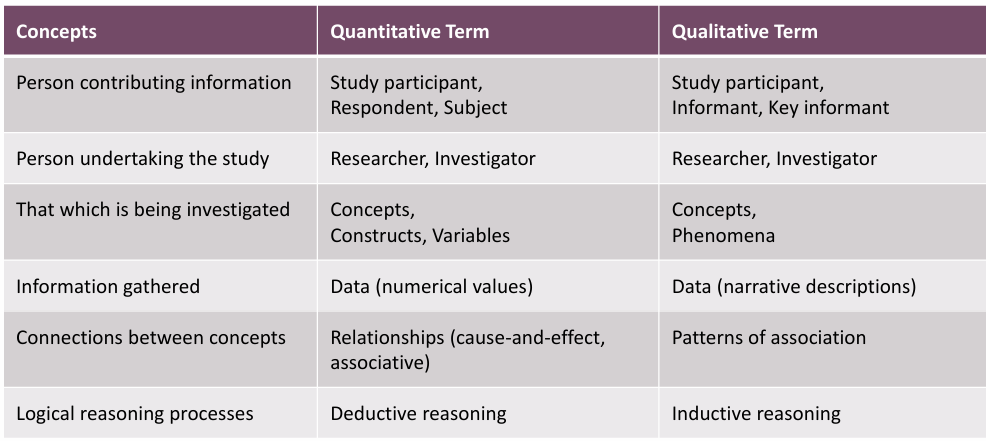
what are the connections between concepts in qualitative/quantitative research
qual=patterns of association
quant=relationships/cause-effect
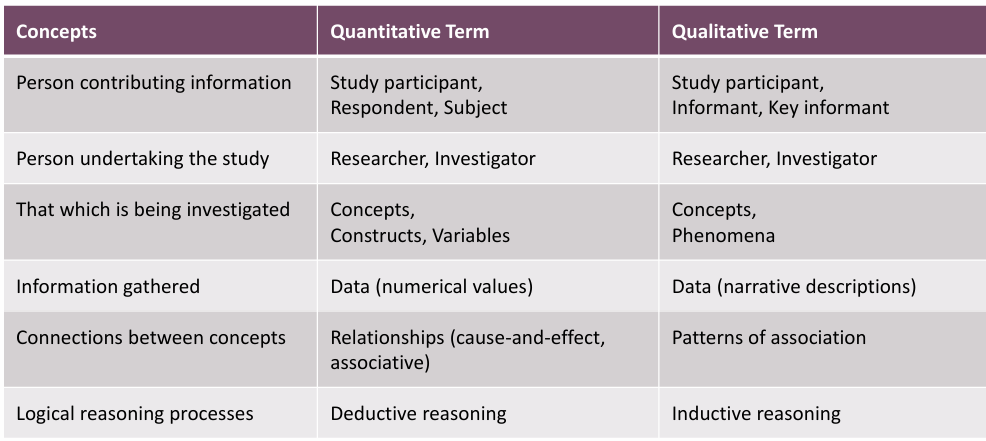
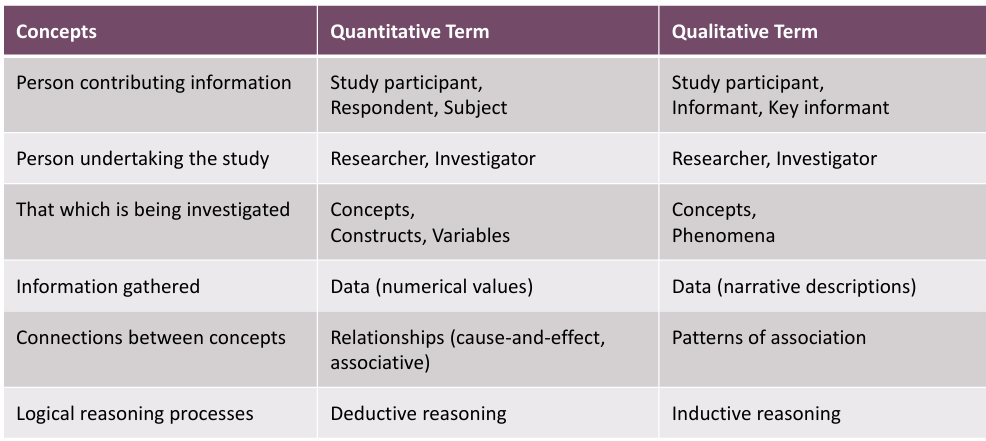
what is the name of the logical reasoning processes used in qualitiative/quantitative research
qual=inductive reasoning
quant=deductive reasoning
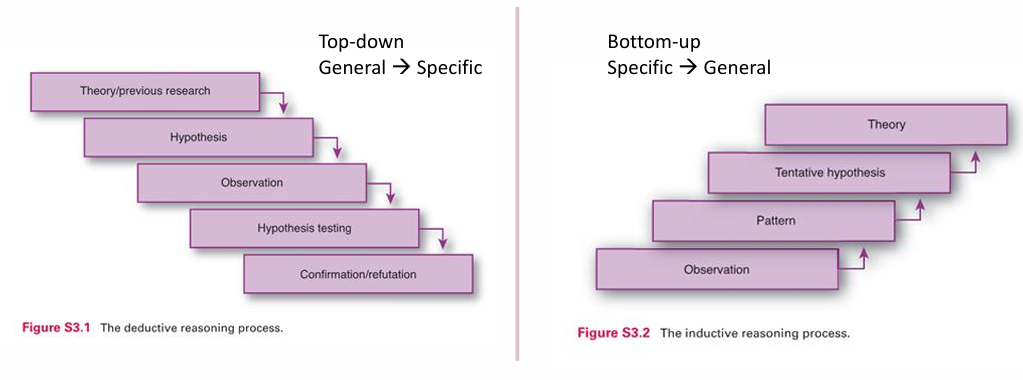
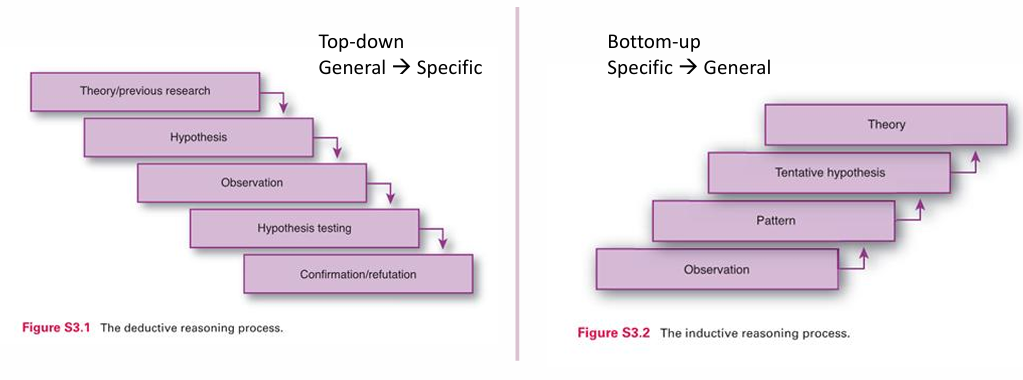
how is deductive reasoning diff from inductive (what is the process)
general => specific
theory/research
hypothesis
observation
hypothesis testing
confirmation/refutation
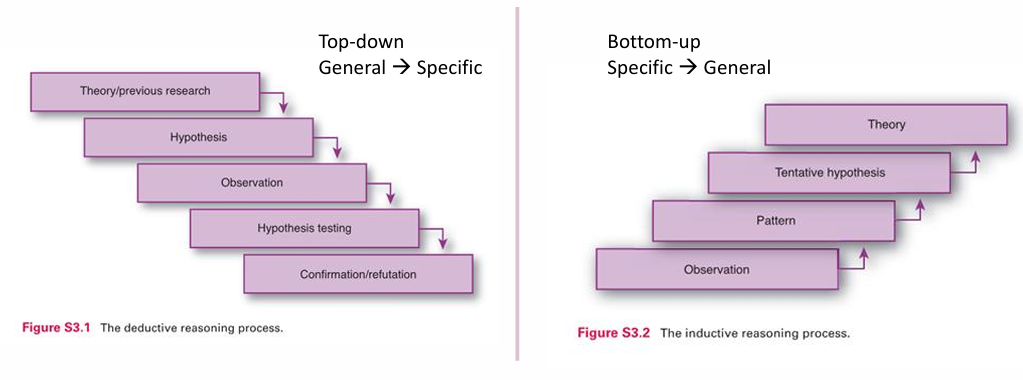
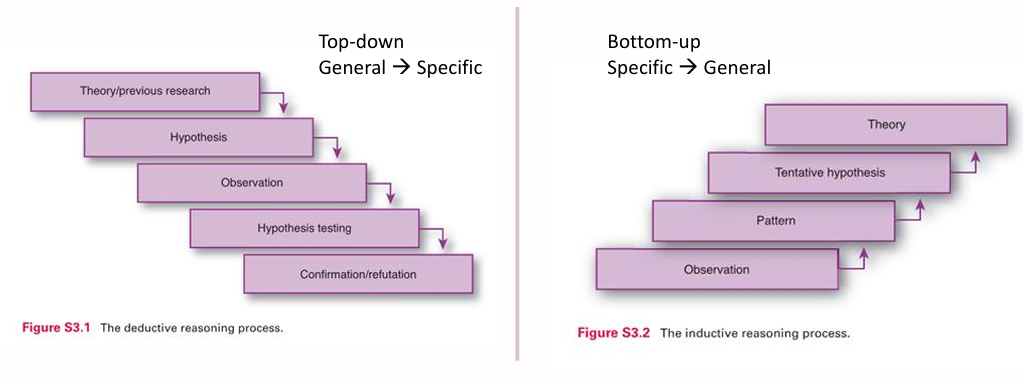
how is inductive reasoning diff from deductive (what is the process)
specific => general
observation
pattern
tentative hypothesis
theory
variable def
characteristic or quality that takes on different values (that varies from one person to the next)
building block of quantitative studies
variable examples (dont memorize)
Blood type
Height, Weight
Length of stay in hospital
Steps per day
Aerobic endurance (Distance walked in 6 minutes, 6MWD)
Quality of life
what are the diff types of variables based on measurement format
continuous ex height, weight, age in years
categorical ex marital status, age group

what are the diff types of variables based on their relationship with other variables
IV=presumed cause of a dependent variable (causal factor, risk factor, predictor, explanatory factor)
DV=presumed effect of an independent variable, the outcome that researchers want to understand, explain, or predict

quantitative relationship def
bond or connection between IVs and outcome variables
whether relationship exists/how strong
list some types of relationships that fall under quantitative relationships and their needs
cause-and-effect (causal) relationship
research implication: requires experimental or longitudinal designs to establish causality
functional (associative) relationship (ex biological sex and life expectancy)
research implication: often explored through cross-sectional, correlational studies
qualitative relationships def
study of pattern
may study patterns of association (instead of quantifying them) as a way of illuminating underlying meaning and dimensionality of phenomena of interest
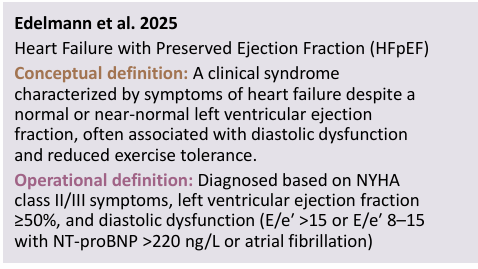
conceptual definition def
abstract or theoretical meaning of a concept being studied
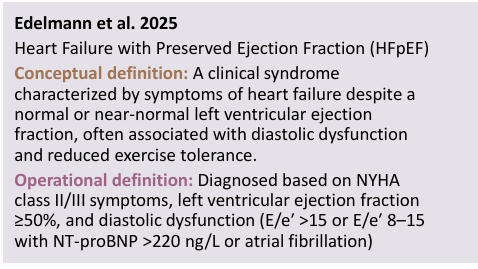
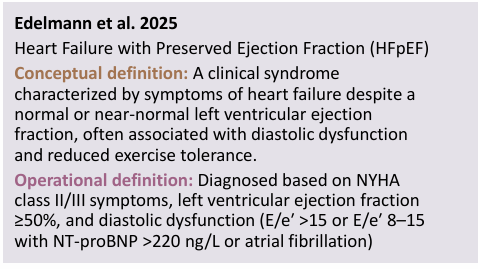
operational definition def
the operations (measurements) a researcher must perform to collect the desired info of a variable
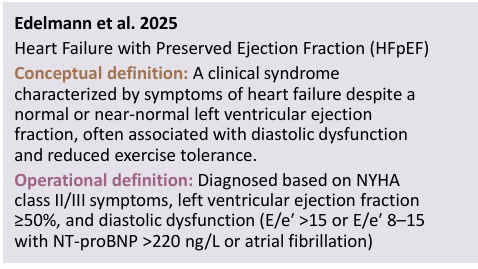

CONCEPTUAL VS OPERATIONAL DEFINITION (conti) what do they mean in diff studies
qual studies=conceptual definitions of key phenomena may be a major end product
quant studies=researchers must define concepts, conceptually and operationally, at the outset
researchers may conceptualize and operationalize a variable in diff ways

what are the major classes of quantitative research
experimental research
non-experimental research
experimental research def (what makes it experimental)
researchers actively introduce an intervention or tx (ex drug, a program), manipulate/control the IV
nursing/medical context: aka clinical trials, addressing therapy questions
what is the purpose of experimental research
test causal relationships – whether the intervention caused changes in the outcome
non-experimental research def
no intervention, rather data is collected without introducing an intervention/tx
nursing/medical context: aka observational studies, addressing etiology, prognosis, or diagnosis questions
what is the purpose of non-experimental research
explore potential causal relationships (but cannot definitely test causality)
examine non-causal relationships ex epidemiology research
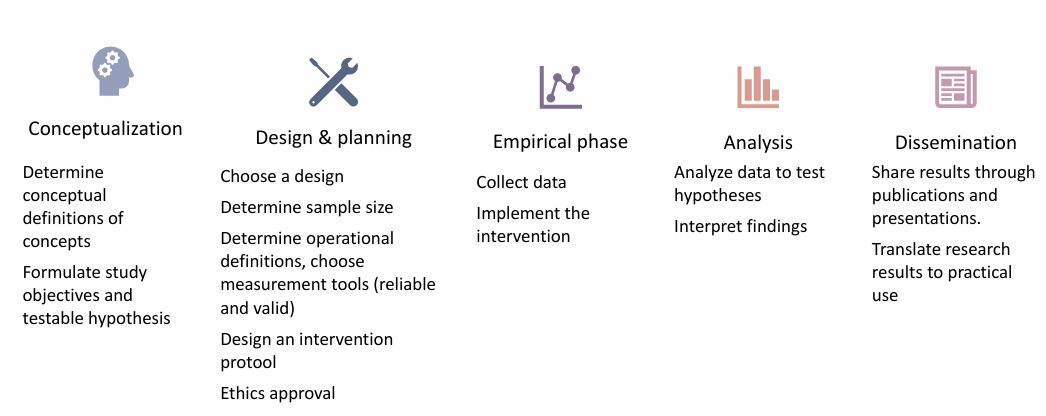
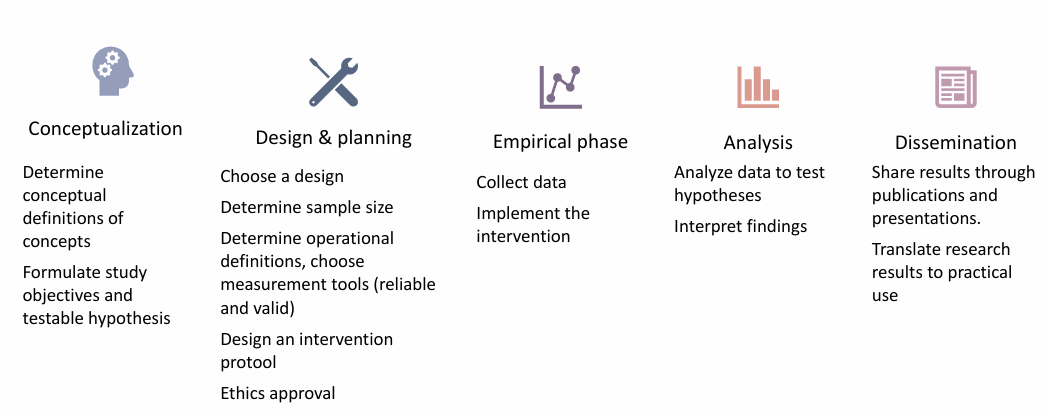
what are the phases of a quantitative study
linear progression of tasks:
conceptual phase = def of concepts, study goals
design & planning phase
empirical phase = collect data, do intervention
analytic phase = analyze/interpret data
dissemination phase
what are the major classes of qualitative research
Many qual nursing studies rooted in research traditions that originate in anthropology, psychology and sociology.
ethnography
phenomenology
grounded theory
ethnography def/characteristics
rooted in anthropology
focuses on the patterns and lifeways of a defined cultural/social group, ex shared beliefs, values, norms, and practices
extensive fieldwork (participating in culture)
learn from members of a cultural group with a goal of describing their customs and norms/understanding their worldview
what is the end outcome of ethnography
a rich, holistic description of a culture or social group
PHENOMENOLOGY def/characteristics
to understand the lived experience of individuals
focus on how people experience and make meaning of a phenomenon (essence of the experience)
what life experiences of people are like
what these life experiences mean
what is the outcome of phenomenology
a description of the essence or meaning of the phenomenon
grounded theory def
describe and understand key social psychological processes that characterize a particular event or episode
what is the outcome of grounded theory
a theory that is grounded in the data and explaining how something happens
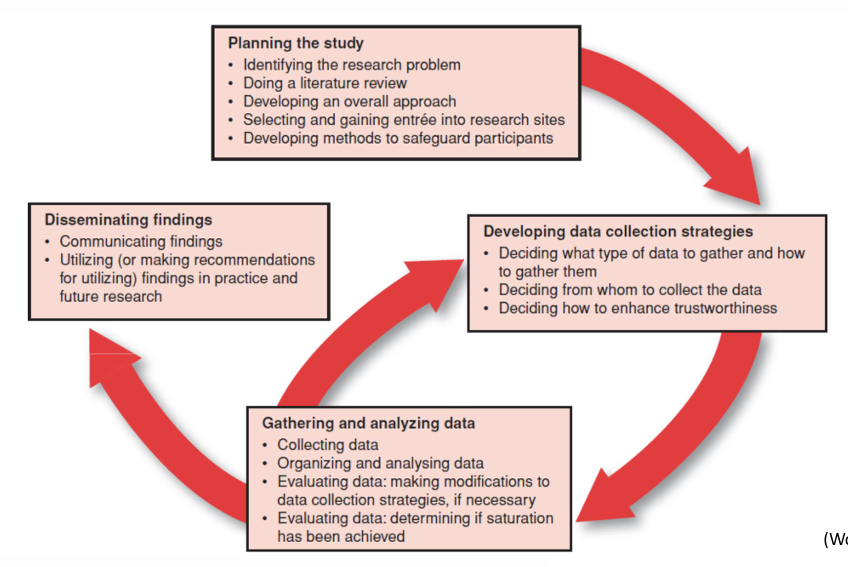
ACTIVITIES IN A QUAL STUDY: what does it look like
progression more like a circle (flexible)
continually examine and interpret data and make decisions about how to proceed based on what has been discovered
flow of activities may vary from one study to another
researchers themselves may not know in advance how the study will unfold
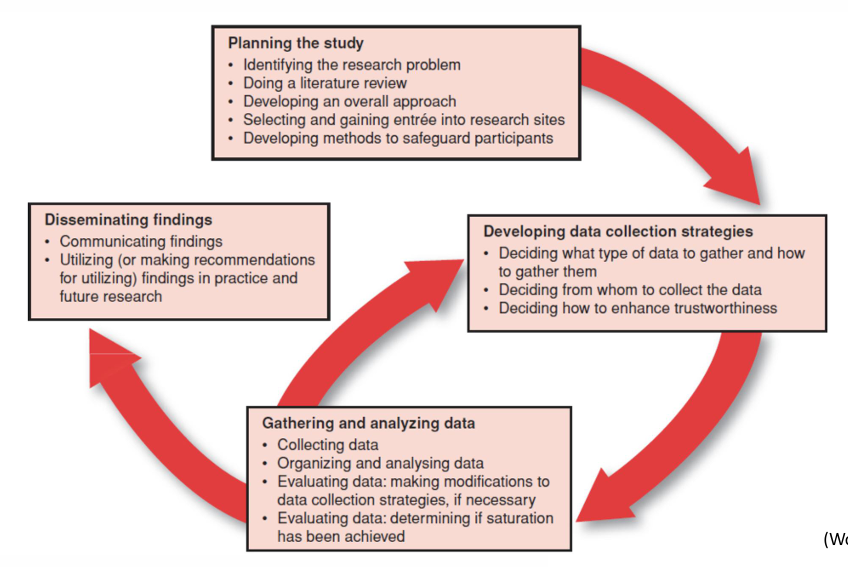
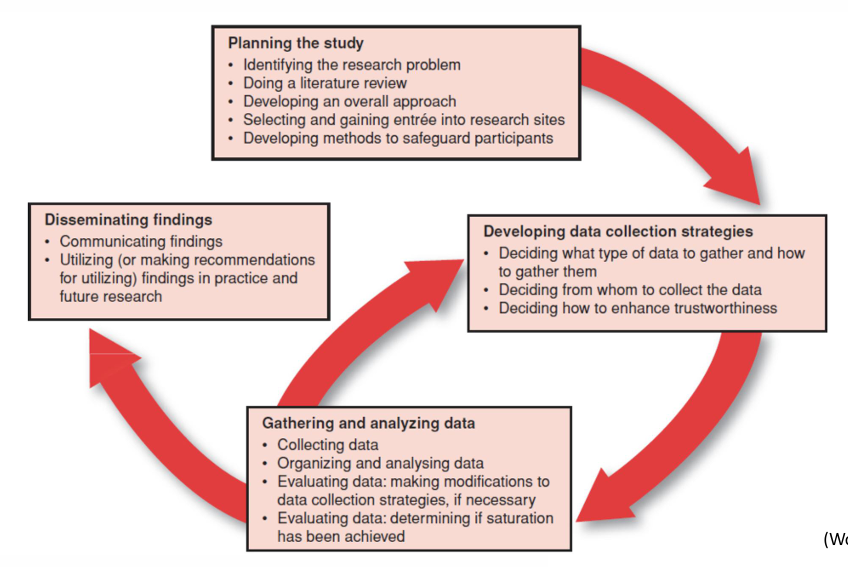
CONCEPTUALIZING AND PLANNING a qualitative study, what does it start like/include?
Typically begin with a broad topic – allows the focus to be sharpened and delineated more clearly.
Literature review may or may not occur.
Selecting and gaining entrée into research sites.
Negotiations with gatekeepers (e.g., administrators, program directors, president of an organization) who have the authority to permit entry into their world
Developing an overall approach (emergent design) – develops and evolves during data collection.
addressing ethical issues
special considerations given the more intimate and prolonged nature of relationships that typically develop between researchers and participants.
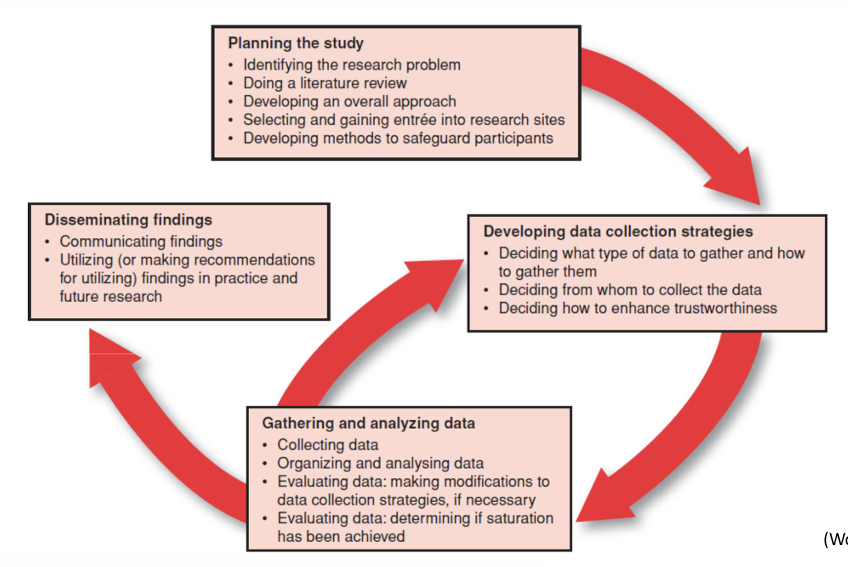
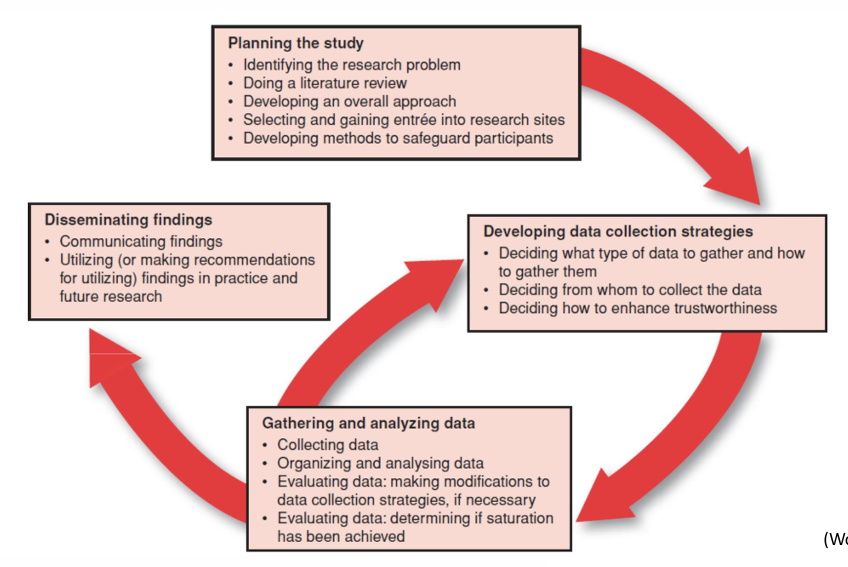
ACTIVITIES IN A QUAL STUDY (CONT.): CONDUCTING A QUALITATIVE STUDY
Begin with loosely structured discussions and observations, allowing participants to express a full range of beliefs, feelings, and behaviors.
Sampling decisions are guided by the data
Data collection: obtain data from participants and then analysis and interpretations are ongoing activities that guide “next steps”.
Data analysis: putting the data into a coherent picture
Through inductive reasoning, researchers identify themes and categories to build a rich description of theory of the phenomenon.
Data collection becomes increasingly purposeful – as understanding grows, researchers purposefully seek participants to confirm and enrich theoretical understandings or challenge them
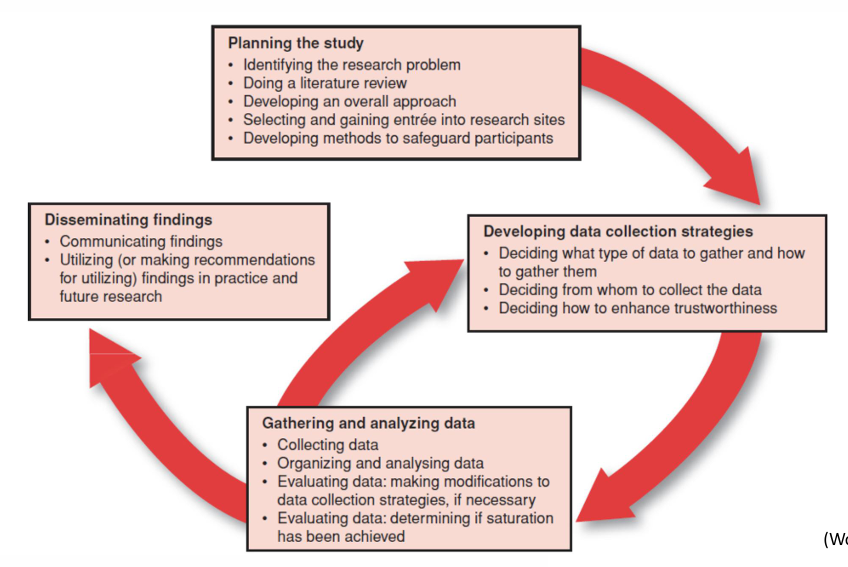
saturation def
same themes/categories are recurring, and additional data collection is not revealing new info