tertiary structure (domains)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
what is tertiary structure of the protein?
unique three-dimensional conformations that globular proteins assume as they fold into their native (biologically active) structures and prosthetic groups
what is Protein folding?
process in which an unorganized, nascent molecule acquires a highly organized structure, occurs as a consequence of the interactions between the molecule’s side chains
tertiary structure feutures?
1) polypeptides fold in such a fashion that amino acid residues distant [far] from each other in the primary structure come into close proximity
2)globular proteins are compact as water molecules are excluded from the interior making interactions between polar and non-polar possible
3)large globular proteins have domains (part of the tertiary structure that have specific function inside the chain)
THE CORE OF THE DOMAIN IS CALLED FOLD
4)a number of proteins are modular / mosiac proteins by which they contain duplicate or imperfect copies of one or more repeating domains linked in a series e.g: 1-fibronectine can bind to collagen and proteoglycans
2- immunoglobins
type and examples of domains:
Types :
Alpha domains : made only of alpha helices
Beta domains : made only of antiparallel beta strands
A/B domains : made up of a mix between the two
Examples
EF hand
Leucine zipper
B barrel
ATP binding domain of hexokinase
a/b zinc binding motif
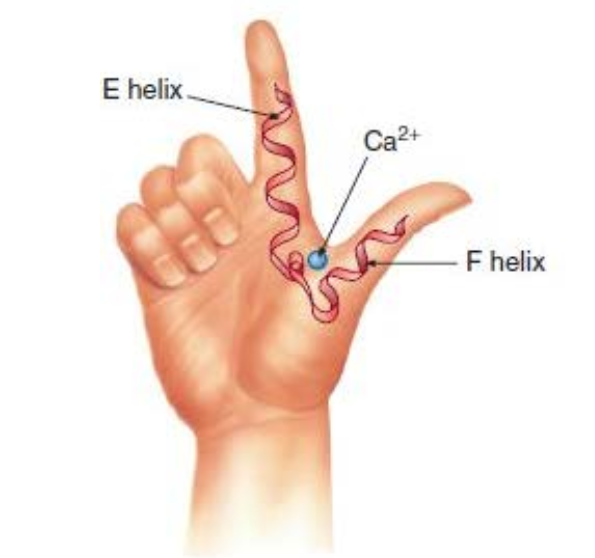
?
EF hand, a type of A-domains it is helix-loop-helix that binds specifically to Ca2+
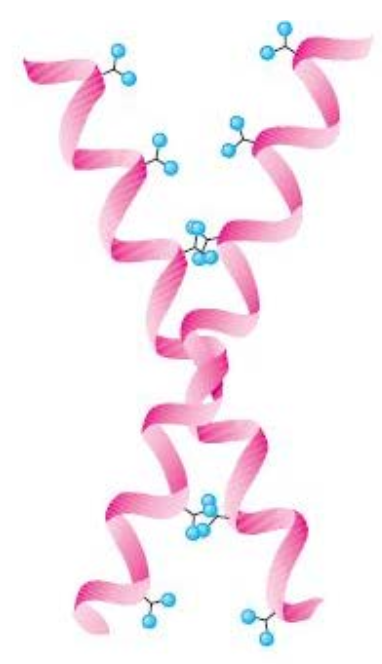
l?
leucine zipper
DNA binding domain are example of α-domains.
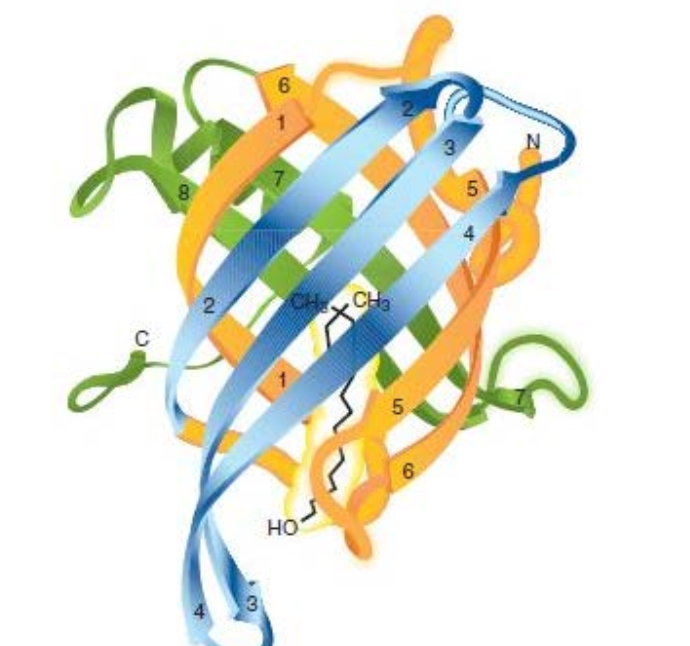
?
Human retinol-binding protein, a type of β-barrel domain
(retinol, a visual pigment molecule is shown in yellow
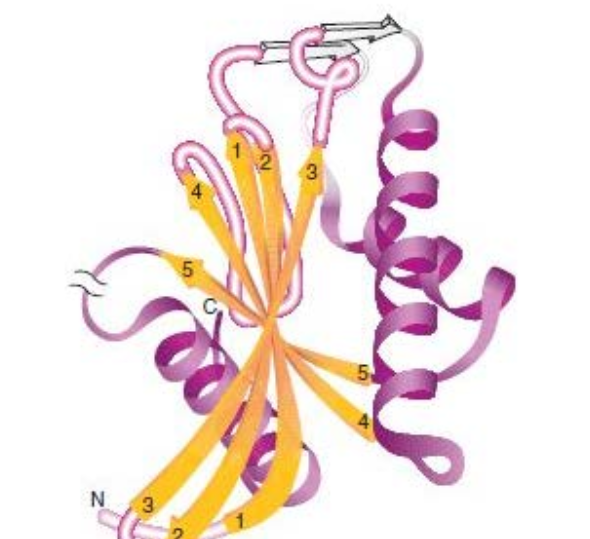
?
The ATP-binding domain of hexokinase, a type of α/β-domain.
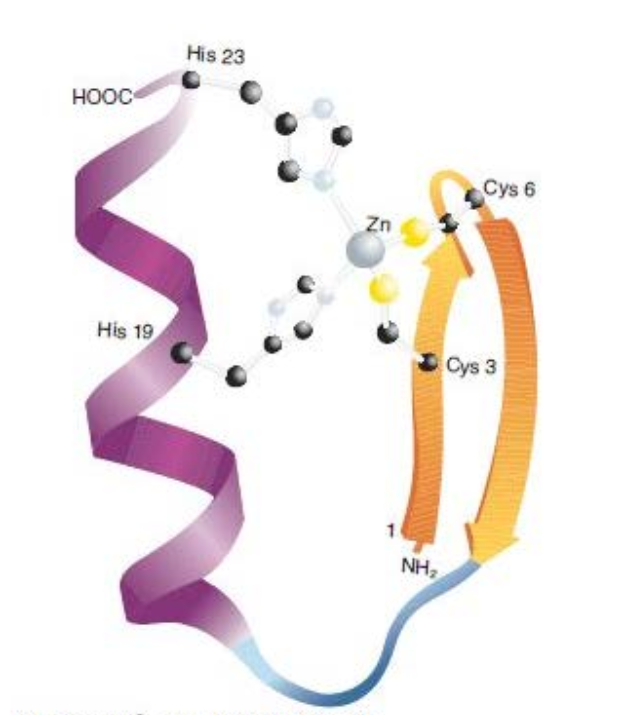
?
The α/β zinc-binding motif, a core feature of numerous DNA binding domains.
types of interactions stabilize tertiary structure
1- Hydrophobic interactions [non polar-non polar]
2-Electrostatic interactions. [salt-bridge , opposite charged ions , cavalent ] strongest type
3- Hydrogen bonds [between polar amino acids] 6
4- covalent bonds (disulfide bonds)
5- hydration water-bridge
![<p>1- Hydrophobic interactions [non polar-non polar]</p><p>2-Electrostatic interactions. [salt-bridge , opposite charged ions , cavalent ] strongest type</p><p>3- Hydrogen bonds [between polar amino acids] <mark data-color="yellow">6</mark></p><p>4- covalent bonds (disulfide bonds)</p><p>5- hydration water-bridge</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0925e351-2a04-4356-8024-26e1ebeb64c1.png)