QUT: PYB102
1/191
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
Divisions of Nervous System
Central Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous System
Tracts
Bundle of axons in the CNS (white matter)
Nerves
Bundle of axons in the PNS (grey matter)
Nuclei
Groups of neuron cell bodies in the CNS (grey matter)
Ganglia
Groups of neuron cell bodies in PNS
Horizontal Plane
Sagittal Plane
Coronal Plane
Dorsal
Posterior
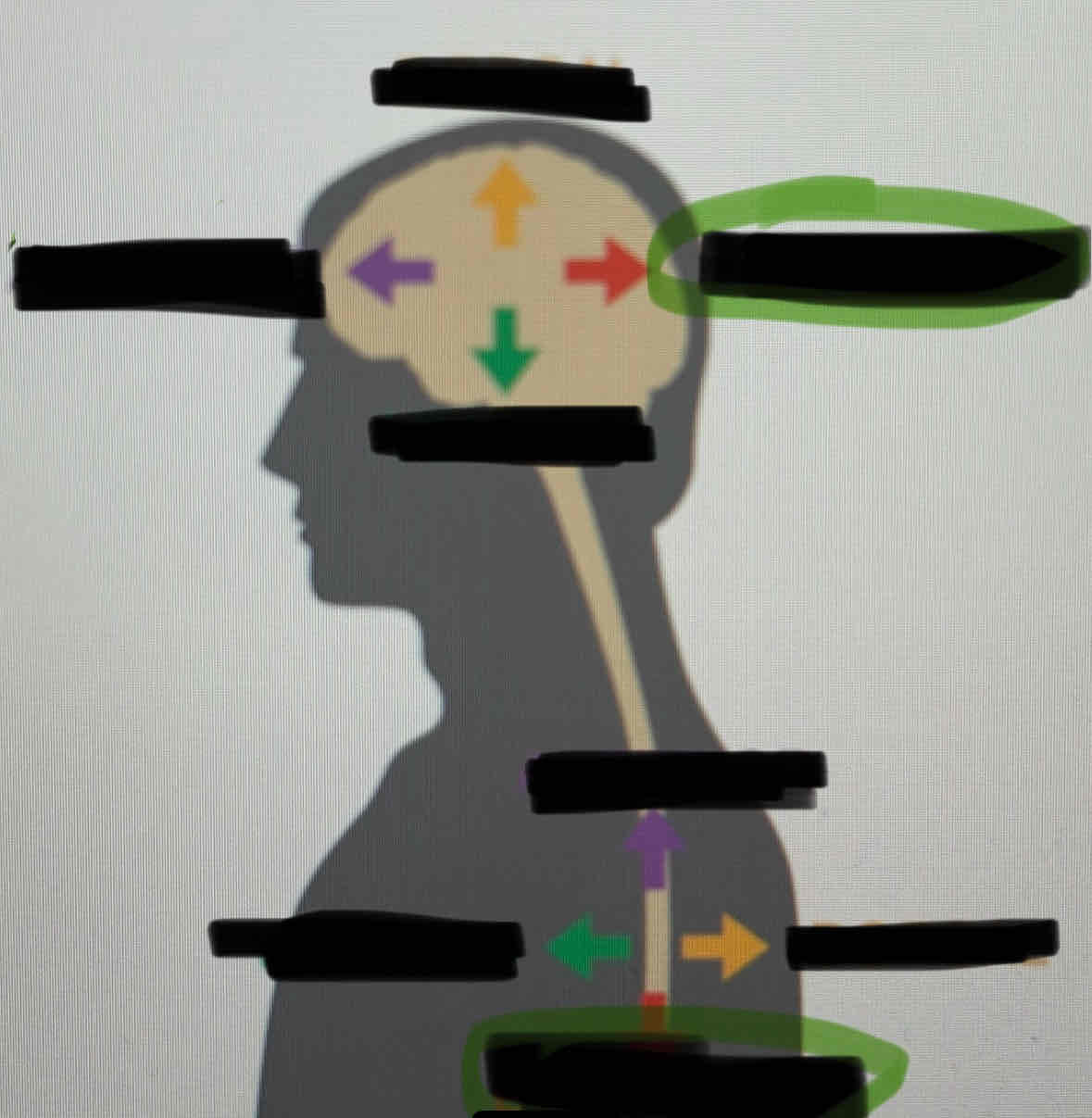
Ventral
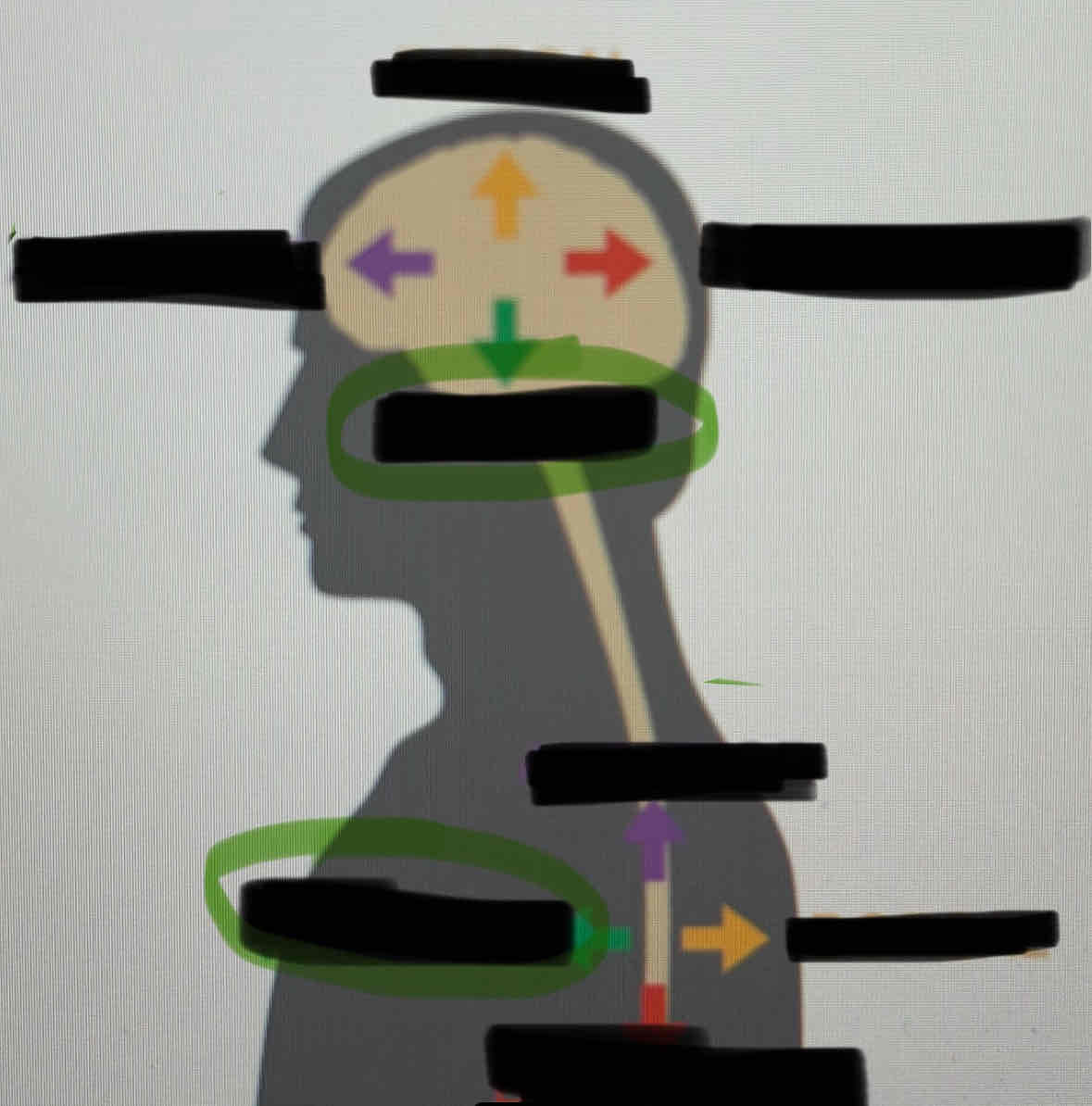
Anterior
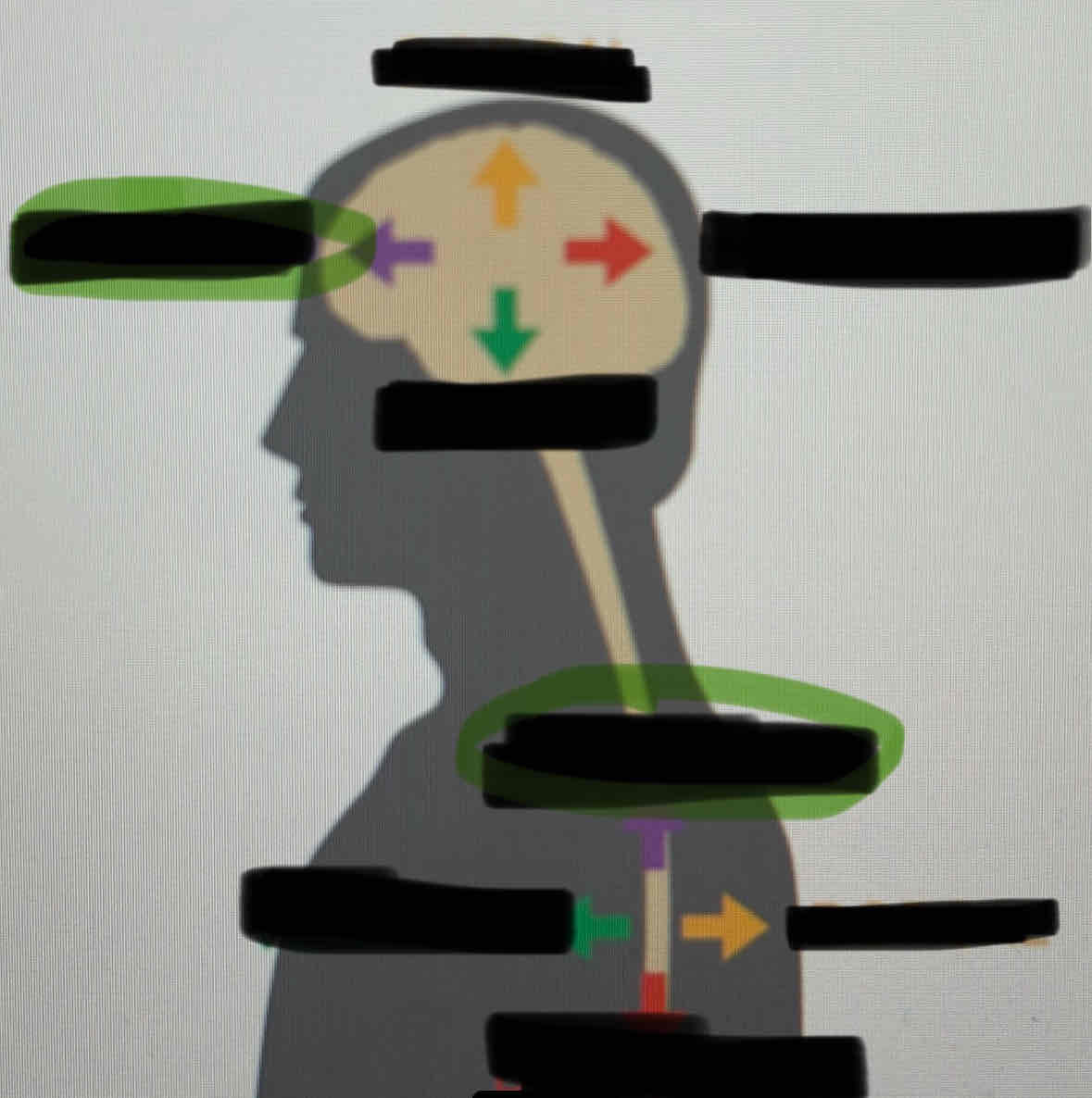
Medial
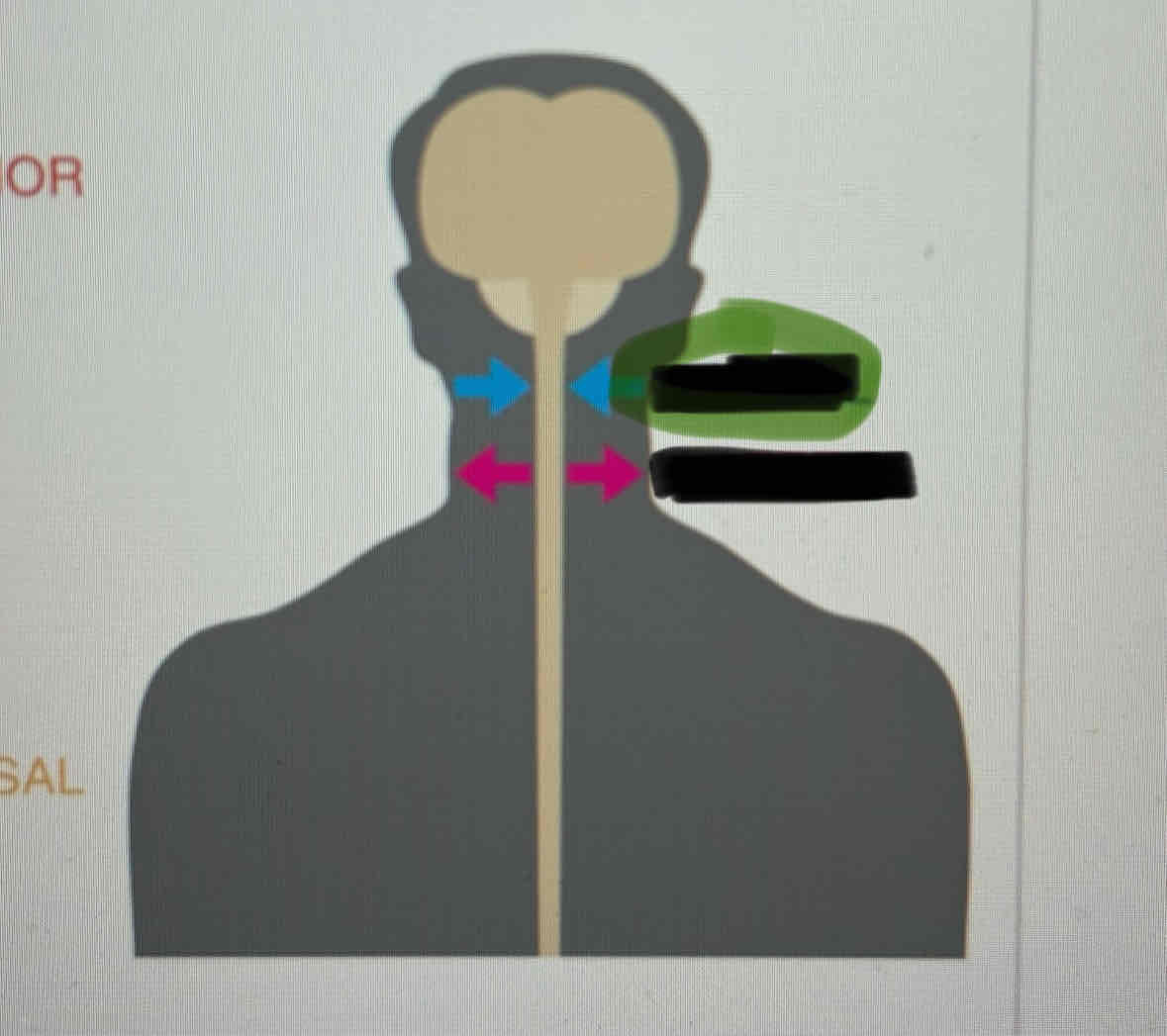
Lateral
Divisions of forebrain
Telencephalon and diencephalon
Telencephalon
Includes cerebral cortex, limb if system, basal ganglia
Diencephalon
Includes thalamus and hypothalamus
Midbrain
Includes the superior colliculi and inferior colliculi
Hindbrain
Includes medulla, pons, cerebellum, reticular formation
embryonic vesicles
Neural plate—> neural crest —> neural tube to form vesicles which develop major brain regions
Medulla
Contains circuits of neurons which control functions vital for survival like HR BP and respiration
Pons
bridge of fibres which connect brain stem with cerebellum
Several nuclei clusters
One cluster is reticular formation which influence consciousness and alertness
Cerebellum
critical for movement and balance
Superior (anterior) colliculi
relay visual info
Important for visual attention
Inferior (posterior) colliculi
Relay auditory info
important for auditory attention
Colliculi
appear as pair small bumps on dorsal surface of brain stem
Thalamus
relay station for all sensory info except smell
Filters and organises input
Two little avocados
Hypothalamus
major role regulating basic drives hunger and thirst
Controls automatic NS and Body temp
Controls pituitary gland
4 Fs (fighting fleeing feeding fucking)
Regulates through NS bad endocrine
Connected to pituitary gland
Limbic system
learning memory and emotional expression
Loosely connected structural network
Includes hippocampus and amygdala
Amygdala
important role processing emotional info and learning fear response
In front of hippocampus
Hippocampus
important role in memory, particularly consolidation
Cerebral cortex
outer layer cerebral hemispheres
Bumps on surface are gyrus/ gyri
Groove on surface are sulcus/ sulci
Occipital lobes
back of brain
Includes primary visual cortex
Vision
Parietal lobes
behind central sulcus (big mid one)
Perception of stimuli—> touch pressure temp pain
Body sensory info
Temporal lobes
below lateral fissure
Perception and recognition auditory and memory
Frontal lobes
Reasoning, planning, speech, movement, emotions, problem solving
Prefrontal cortex
cortical area
Problem solving, emotion, complex thought, higher order cognitive functions
Primary motor cortex
cortical area
Initiation of voluntary movement
Motor association cortex
cortical area
Coordination of complex movement
Primary somatosensory cortex
cortical area
Receives tactile information from body
Somatotopic organisation
Sensory association area
cortical area
Processing multisensory info
Visual cortex
cortical area
Detection of simple visual stimuli
Visual association cortex
Cortical area
complex processing of visual info
Auditory cortex
cortical area
Detection of sound quality—> tone and loudness
Auditory association area
cortical area
Complex processing of auditory information
Wernicke’s area
cortical area
Comprehension of language
Broca’s area
cortical area
Speech production
Association areas
primary area sends info to adjacent association cortex to analyse
If close to primary sensor, only info from one sensor, further means info from more sensors
Corpus callosum
important for communication between hemispheres, not only one but vital
Located between in middle
Lateralisation
localisation of function on one side of brain compared to other
Specialised side
Contralateral arrangement
motor cortex of each cerebral hemisphere mainly responsible movements on opposite side of body
Split Brain Experiment
epilepsy patients with severed corpus callosum
Found left hemisphere lateralised for speech
Right hemisphere could display what say through identifying and picking up object
Cerebral ventricles
chambers with CSF
Ventricular system
Lateral third and fourth ventricles
CSF ventricular circulation function
mechanical shock absorber, protect brain sudden movement
Medium for nutrient blood vessel and brain tissue exchange
Buoyancy to make brain lighter
Vascular system
brain depends on blood supply
Brain capillaries greater resistance than others
blood brain barrier
Blood brain barrier
protective mechanism to protect brain from infections/ blood borne toxins
Makes drug delivery to brain difficult
Meninges
protective sheaths around brain and spinal cord
Three layers: dura mater, arachnoid membrane, pia mater
Subarachnoid space
Between pia mater and arachnoid, gap filled with CSF
Spinal cord
motor signals to brain voluntary muscles
Collect sensory info from body, somatosensory info, take to brain to process
Protected by vertebral column and passes through hole in vertibrae
At lumbar region just mass of spinal nerves
Afferent Axons
arrive to spinal cord
Dorsal
Efferent axons
exit spinal cord
Ventral
Somatic Nervous System
carry motor info out and sensory in
Spinal and cranial nerves
Spinal nerves
each nerve consists fusion of two branches (roots)
Spinal nerves begin at junction dorsal/ventral roots spinal cord
Nerves leave vertebral column and travel to muscles or sensory receptors
Cranial nerves
twelve pairs of cranial nerves attached to ventral surface of brain
Most serve sensory and motor function head/ neck rroom
Tenth/vagus nerve regulates function of organs in thoracic and abdominal cavities
Autonomic nervous system
carries signals support basic life functions
Activated two sub divisions: sympathetic NS and parasympathetic NS
Sympathetic NS
involves activities associated with energy expenditure
Fight or flight
Dilated pupils, relaxed bronchi, accelerate and strengthen heartbeat, inhibits digestions, contracts vessels
Parasympathetic NS
associated with increased energy supply
Rest and digest
Contract pupils, constricts bronchi, slows heartbeat, stimulates digestive, dilated vessels
Neurons
basic NS functional units
Take info from other neurons (reception) integrate signals (conduction) and pass signals to others (transmission
Glial cells
nourish, protect, physically support neurons and though to be critical for brain development
Oligodenrocyte
glial cell
Covers axons of neurons with myelin—> substance critical to effective brain functioning
Dendrites
receive messages
Transmit info to soma
Soma (cell body)
contains mechanisms that control metabolism/ cell maintenance
Collate messages
Axon
carries messages away from soma to cells with which neuron communicates
messages called action potentials
Terminal buttons
located end of twigs that branch of axons
Secrete neurotransmitters which affect activity of other cells neuron communicating with
Myelin
insulated axons to promote efficient transmission of action potential
Increase speed of action potential propagation along axon
Neuron cell membrane
made of lipid bilayer: two layers of fatty molecules
Embedded protein molecules form pore/channel for material movement
Not transmitting? Pores closed
Neuron at rest
more sodium ions outside cell than inside
More potassium ions inside cell than outside
Resting potential neuron -70mV
Action potential
brief reversal resting neuron charge
When membrane sufficiently depolarised (resting potential moves towards 0)
Threshold -55mV, no reach no action potential
All or none
Action potential process
Sodium channels open, enter reversing membrane potential
Potassium channels open, leave restoring potential
Ion transporters pump both back to original locations
Action potential
Speed of action potential
determined by diameter of axon (bigger faster)
Presence/ absence myelin sheath (faster when there)
Myelin sheath properties
electrical insulator, prevents ion flow across
Ions only cross at breaks (nodes of ranvier)
Sodium concentrated at nodes, action potential only generated in gaps
Jumping from break to break increase speed
Synaptic transmission
when AP at peak release specialised chemicals (neurotransmitters) travel across cleft and received by dendrites
Sent is presynaptic receive is post synaptic
Release of neurotransmitters from terminal button stage 1
before AP arrive neurotransmitters stored in vesicles within terminal button
Release of neurotransmitters from terminal button stage 2
action potential triggers release of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft
Release of neurotransmitters from terminal button stage 3
neurotransmitters diffuse across synaptic cleft
Some attach to receptor molecules in postsynaptic membrane and activate them either inhibiting or enabling postsynaptic neuron to generate an AP
Otto Loewi Experiment
vagus nerve and cardiac muscle
Hearts in solution only one physical connected
Unconnected second heart also stimulated
this could only happen if vagus nerve happened through chemical/molecular process
Neurotransmitter
generic
If transmitter binds with receptor and depolarises then it is excitatory and increases likelihood of AP
If hyper-polarises membrane then inhibitory and makes AP less likely
Acetycholine (ACh)
Neurotransmitter
Activates motor neurons controlling skeletal muscles
Contributes to regulation of attention arousal and memory
Dopamine (DA)
Neurotransmitter
Contributes to control of voluntary movement
Important in reward motivation and pleasurable emotions
Serotonin (5-HT)
Neurotransmitter
Important in emotional states impulsiveness and dreaming
GABA
Neurotransmitter
Serves as widely distributed inhibitory transmitter
Endorphins
Neurotransmitter
Resemble opiate drugs in structure and effect
Contribute to pain relief and some pleasurable emotions
Basic memory processes
encoding
Storage
Retrieval
Encoding
transform sensory stimuli into form that can be placed in memory
Cherry 1953 cocktail party filter
Assumptions: stimuli processed in parallel, one stimulus allowed through while others buffered, prevents system overload
Storage
effectively retaining info for later use
Retrieval
locating the item and using it recall be recognition
Primacy effect: best for things learned first
Recency effect: good for things learned last
Context: memory better in context you learned
Role of attention
determines encoding quality
Maintenance rehearsal: role of repetition of info, without transformation into more meaningful code
Elaborate rehearsal: meaningful processing of info
Enrich encoding
visual imagery, concrete objects recalled better than abstract
Self referent encoding, applying info to own self
Sensory register
storage system that registers and briefly holds info from senses
Iconic memory
Echoic memory
Iconic memory
related to visual system
< ½ second duration
9-10 items (sperling 1960)