Bacteria, Archaea, and Viruses
Domains
Eukaryotes
- Possibly multicelled
- Nucleus
- Branch off of archaea
- Membrane-bound organelles
Endosymbiosis theory
- Cyanobacteria
- chloroplasts
- Protobacteria
- mitochondria
- Phospholipid bi-layer
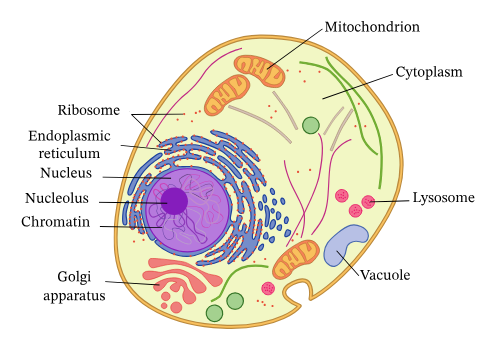
Protists
- Eukaryotes that are not plants, animals, or fungi
- Acquiring organelles
- Flexible cell surface that allows them to have infoldings
- These folds make cell compartments, these compartments have specialization
- Organelles are double membraned because when they entered the protist they took some of the cell wall with them.
- Mitochondria, used to detoxify O2
- cyanobacterium enters a cell, chloroplast has two membranes
- Eukaryote engulfs a green algae cell
- Green algae cell becomes a chloroplast, has three membranes
- Nuclear envelope - membrane infoldings
- Cytoskeleton - cytoplasmic microtubules
Prokaryotes
- Single celled
- DNA is in a ring
- Plasmids add DNA
- No mitosis
- Binary fission
- Cell wall, not cell membrane
- No nucleus
- No organelles
- Bacteria are prokaryotes
- Important decomposers
Nitrogen cycle
- Nitrogen fixers
- Convert atmospheric N2 to ammonia
- Air to ground
- Nitrifiers
- Ammonia to nitrate
- Soil to soil
- Nitrogen is now consumable by plants
- Denitrifiers
- Nitrate to N2
- Soil to air
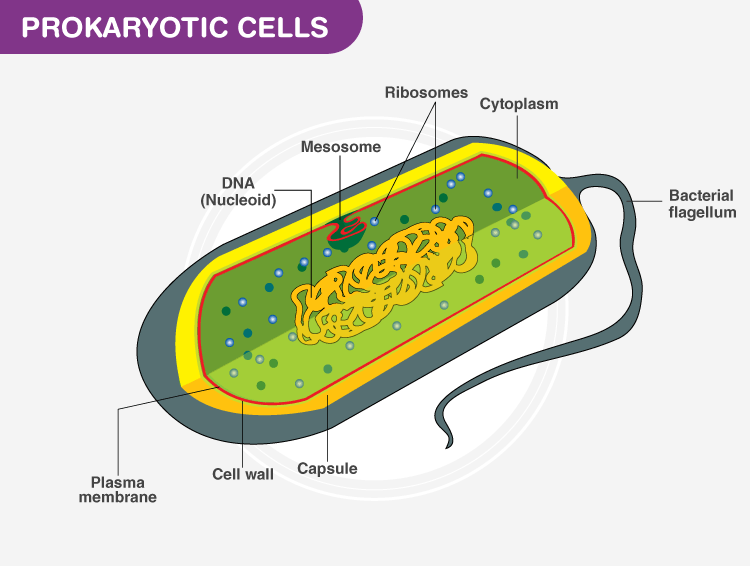
- Both
- Ribosomes
- Cell wall
- Metabolic pathways
- Respiration
- Photosynthesis
- ATP
Archaea
- Extremophiles
- rRNA allows you to differentiate between Archaea and Bacteria
- Common in soil or the ocean
- Prokaryotic
- No peptidoglycan
- Lipid monolayer
- Some are obligate anaerobes
Bacteria
Lateral Gene Transfer
- Bacteria transfer plasmids through “bridges” which donates genetic material to another bacteria
- Plasmids are the smallest stretch of DNA
- Have the ability to target the nucleus and alter DNA, GMO
- Bacteria from environment
- Common for antibiotic resistance
- Makes it difficult to interpret genome analysis
Bacterial Cell Wall
- Peptidoglycan
- Takes the place of cellulose
- Gram positive
- Thick outside layer of peptidoglycan
- Stains purple, blue stain bonds to PepGly
- Gram negative
- Cell envelope, thin peptidoglycan in a phospholipid bilayer sandwich
- Stains pink, stain does not bond
Shapes
- Coccus
- Sphere
- Cock and balls
- Bacillus
- Rod
- Back should be straight rod
- Spirillum
- Spiral
- Bacillus and Spirillum can form chains/clusters
- Chains form during division when cells fail to separate
- Branched filaments
- Produce spores in order to reproduce
Endospores
- Nutrients scarce? Simply pack your genetic material into a cell wall package and wait for that package to be rehydrated!
- Rest of the cell dies
- Food poisoning
Cyanobacteria
- Single-celled, form colonies
- Photosynthetic
- Fix nitrogen
- heterocyst
- Big oxygen producers
- Photosynthetic lamellae
- Those little indents in the cell wall that allow for photosynthesis to take place
- Works in place of a chloroplast
- Origin of chloroplasts in Eukaryotes
Spirochaeta
- Internal flagella that allows them to move around
- Syphilis, Lyme
- Chlamydia
- Obligate parasite
- STDs, pneumonia
Protobacteria
- Where the mitochondria was derived from
- Largest group of bacteria
- Nitrogen fixers
- Rhizobium, legumes
- Escherichai coli
Biofilms
- Sticky polysaccharide matrix
- Makes cells harder to kill, antibiotic resistance, environmental resistance
- Dental plaque
- Bacteria binds to a surface, a larger colony forms, the bacterial matrix forms
Quorum sensing
- Sending chemicals and establishing communication with other bacteria
- Attracts more bacteria to the biofilm area
Human Microbiomes
Endotoxins
- Lyse: bacterial puncture/death
Exotoxins
- Released by living bacteria, continual proliferation
- Highly toxic, often fatal
- Black plague
Extremophiles
- Prokaryotic
- Bacteria and archaea
- Thrive under extreme conditions
- Radiation, temperature, pH, salinity, heavy metals
- Thermostable proteins that prevent denaturing
- Not as abundant
- Obligate anaerobes
- Oxygen is poisonous
- Those homies that live inside termites
- Relic of prehistoric life
- Facultative anaerobes
- Both aerobic and anaerobic pathways
- Obligate aerobes
- Require oxygen
- Photoautotrophs
- Produce their energy from the sun, photosynthesise
- Use CO2
- Photoheterotrophs
- Use the sun for energy but have to consume organic material in order to get carbon
- Chemoautotrophs
- Get energy from inorganic compounds
- Use CO2 for carbon
- Chemoheterotrophs
- Get energy from organic compounds as well as their carbon
- Humans
Viruses
- Infectious particles
- Obligate parasites
- Need a host to survive
- DNA or RNA
- This is not typical
- Infect all forms of life
- Grouped based on genome structure
- Hard to classify based on physiological differences
What makes up a virus?
- Genetic material: RNA or DNA
- A viral capsid
- Protein around genetic material
- Some have a membrane envelope and spike proteins
- Similar to cell membrane
- Virus can leave cell and steal membrane
Negative-sense
- Has negative-sense RNA that is not ready to be translated
- Uses the host cell to create positive-sense RNA
- RNA polymerase helps it convert from negative to positive
Positive-sense
- RNA ready to be translated
- Doesn't need to bring its own RNA polymerase
- Host already has it
- Most abundant and diverse group
- Covid
- Mosaic viruses
- Just genetic material and capsid

