Pharmacology V
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Yellow = Emphasized in lecture slides
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Name all the classes of small molecule inhibitors
BCL2, PI3K, IDH, CDK4/6, PARP, BRAF/MEK
What is the MOA of BCL2?
Anti-apoptotic protein
What inhibits BCL2?
BH3
Name the BCL2 inhibitor(s)
Venetoclax
What is the MOA of venetoclax?
Binds directly to BCL2 protein, leading to apoptosis
BCL2 Inhibitor
Indications: AML in 75+ OR w/ comorbidities that prevent intensive chemo, CLL
Dose reduction: Comcomitant use w/ moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, hepatic, hematologic
Metabolism: CYP3A4
Toxicities: tumor lysis syndrome, bone marrow suppression, infection, gastrointestinal (N/V/D/C)
Venetoclex
Select the risk factor for Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS)
All lymph nodes < 5 cm
AND
Absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) < 25 x 109
A. Low
B. Medium
C. High
Low
Select the risk factor for Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS)
Any lymph node 5 cm to < 10 cm
OR
ALC ≥ 25 x 109/L
A. Low
B. Medium
C. High
Medium
Select the risk factor for Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS)
Any lymph node ≥ 10 cm
OR
ALC ≥ 25 x 109/L AND any lymph node ≥ 5 cm
A. Low
B. Medium
C. High
High
Match the TLS risk category with the following management regimen:
Oral hydration + Allopurinol
A. Low
B. Medium
C. High
Low
Match the TLS risk category with the following management regimen:
Oral hydration (± IV hydration) + Allopurinol
A. Low
B. Medium
C. High
Medium
Match the TLS risk category with the following management regimen:
Oral hydration + IV hydration + allopurinol ± rasburicase (if baseline uric acid is elevated)
A. Low
B. Medium
C. High
High
What is the MOA of PI3K?
PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway is involved in cell growth and survival
What do class 1 PI3K inhibitors target?
one or more PI3K isoforms: ⍺, δ, and ɣ, as well as B-cell signaling pathways
What does inhibition of PI3k isoforms lead to?
Malignant B-cell apoptosis
Name the PI3k Inhibitor(s)
Idelalisib, Alpelisib
PI3K Inhibitor
Class: Selective PI3Kδ Inhibitor
Indication: CLL w/ rituxumab
Dose Adjustments: Hepatic, hematologic
Metabolism: CYP3A4, aldehyde oxidase
Toxicities: BBW: Hepatotoxicity, diarrhea/colitis, pneumonitis (limiting toxicity), infections and intestinal perforation
Idelalisib
PI3K Inhibitor
Class: Selective PI3K⍺ inhibitor
Indication: PIK3CA-mutated, HR (+), HER2 (-) metastatic breast cancer
Dose Adjustments: Hyperglycemia, dermatologic
Metabolism: Chemical/enzymatic hydrolysis to metabolite
Toxicities: Hyperglycemia: (baseline fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1C required), diarrhea, decreased appetite
Alpelisib
What is the MOA of Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK)?
Regulate cell cycle progression
What is the MOA of CDK inhibitors?
bind to CDK 4 and 6 —> blocks retinoblastoma (Rb) protein phosphorylation —> prevents cell cycle progression
Name the CDK 4/6 Inhibitor(s)
Ribociclib, Palbociclib, Abemaciclib
CDK 4/6 Inhibitor
Indications: HR (+), HER2 (-), advanced or metastatic breast cancer
Dose Adjustment: Renal, hepatic, hematologic
Metabolism: CYP3A4, oxidation
Toxicity: Neutropenia, QTc interval prolongation, N/V (MEC/HEC), alopecia, ILD
Ribociclib
CDK 4/6 Inhibitor
Indications: HR (+), HER2 (-), advanced or metastatic breast cancer
Dose Adjustment: Hepatic, hematologic
Metabolism: CYP3A4, oxidation, sulfonation
Toxicity: Neutropenia, alopecia, fatigue, infections, ILD
Palbociclib
CDK 4/6 Inhibitor
Indications: HR (+), HER2 (-), advanced or metastatic breast cancer
Dose Adjustment: Hepatic, hematologic
Metabolism: CYP3A4
Toxicity: Neutropenia, N/V/D (MEC/HEC), alopecia, hepatoxicity, VTE, ILD
Abemaciclib
What is the mechanism of PARP?
repair of single-strand breaks in DNA
What is the MOA of PARP Inhibitors?
bind to PARP and prevent the repair of single-strand DNA breaks, which can lead to double-strand DNA breaks
True/False:
BRCA-mutated cancers DO NOT have mechanisms (called homologous recombination, or HR) to repair double-strand DNA breaks, leading to disruption of cellular homeostasis and cell death
True
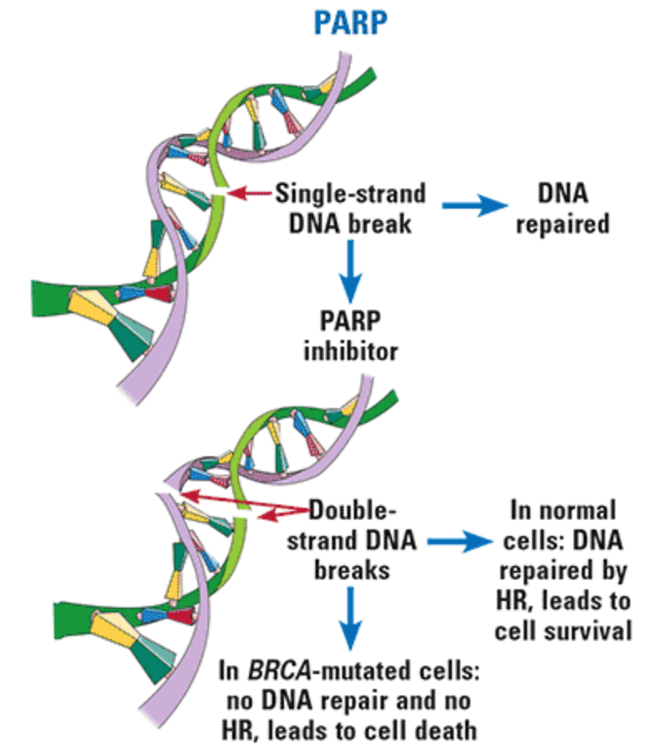
Name the PARP inhibitor(s)
Olaparib, Talazoparib
PARP Inhibitor
Indications: BRCA-mutated breast (early and metastatic), ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancers
Dose Adjustment: Renal
Metabolism: CYP3A4, oxidation, glucuronidation, sulfation
Toxicity: Secondary malignancies (MDS, AML), bone marrow suppression, pneumonitis, N/V
Olaparib
PARP Inhibitor
Indications: BRCA-mutated metastatic breast cancer
Dose Adjustment: Renal, hematologic
Metabolism: Glucuronidation and metabolic pathways
Toxicity: Secondary malignancies (MDS, AML), bone marrow suppression, N/V
Talazoparib
BRAF V600 mutations are found in ~45% of cutaneous melanoma.
A. V600M mutation is most common
B. V600E mutation is most common
C. V600Z mutation is most common
D. V600F mutation is most common
V600E mutation is most common
What is the mechanism of BRAF inhibitors?
inhibit mutated RAF protein, which prevents tumor cell growth
What is the mechanism of MEK inhibitors?
inhibit the downstream MEK protein, which allows for synergistic inhibition of the MAPK pathway and cancer cell death
Name the BRAF inhibitor(s)
Dabrafenib, Encorafenib, Vemurafenib
Name the MEK inhibitor(s)
Trametinib, Binimetinib, Cobimetinib
Correctly pair the BRAF inhibitor to the MEK inhibitor.
Binimetinib | Trametinib |
Vemurafenib | Encorafenib |
Dabrafenib | Cobimetinib |
Dabrafenib + Trametinib
Encorafenib + Binimetinib
Vemurafenib + Cobimetinib
Pharmacologic Category | BRAF Inhibitor | MEK Inhibitor |
Indications | BRAF V600E or V600K mutated melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, advanced solid tumors | |
Dosing | 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal | |
Dose reductions | Toxicity | |
Metabolism | CYP2C8, CYP3A4 | Deacetylation, glucuronidation |
Toxicities | N/A | |
Dabrafenib + Trametinib
Pharmacologic Category | BRAF Inhibitor | MEK Inhibitor |
Indications | BRAF V600E or V600K mutated melanoma, metastatic NSCLC | |
Dosing | Administer antiemetics to prevent N/V | |
Dose reductions | Hepatic, toxicity | Hepatic, toxicity |
Metabolism | CYP3A4 | UGT1A1 glucuronidation, CYP1A2, CYP2C19 |
Encorafenib + Binimetinib
Pharmacologic Category | BRAF Inhibitor | MEK Inhibitor |
Indications | BRAF V600E or V600K mutated melanoma | |
Dose reductions | Toxicity | Hepatic, toxicity |
Metabolism | CYP3A4 | CYP3A4 oxidation, UGT2B7 glucuronidation |
Vemurafenib + Cobimetinib
What are the most common toxicities of BRAF/MEK inhibitors?
Dermatologic (rash, skin cancers)
Pyrexia
Uveitis
Gastrointestinal
Joint pain
What is the mechanism of IDH (Isocitrate dehydrogenase)?
converts isocitrate to ⍺-ketoglutarate (⍺-KG)
What occurs when there are mutations in IDH enzymes?
⍺-KG converted to 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG)
metabolite that drives tumor progression
What is the mechanism of IDH inhibitors?
Binds to mutant IDH enzymes, which decreases 2-HG levels —> reduces leukemic blast counts + induced maturation of myeloid cells
IDH Inhibitor
Class: IDH1 inhibitor
Indication: IDH1 mutated AML
Metabolism: CYP3A4
Toxicities: Differentiation syndrome (BBW), QTc interval prolongation, leukocytosis
Ivosidenib
IDH Inhibitor
Class: IDH2 inhibitor
Indication: IDH2 mutated AML
Metabolism: Multiple CYP enzymes and UGTs
Toxicities: Differentiation syndrome (BBW), N/V (MEC), leukocytosis, hyperbilirubinemia
Enasidenib
Which IDH inhibitor inhibits IDH1?
Ivosidenib
Which IDH inhibitor inhibits IDH2?
Enasidenib